Characterization of the Micro-Arc Coatings Containing β-Tricalcium Phosphate Particles on Mg-0.8Ca Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Evaluation of the Corrosion Behavior of the CaP Coated and Uncoated Mg Alloy
2.4. Electrochemical Studies
3. Results and Discussion
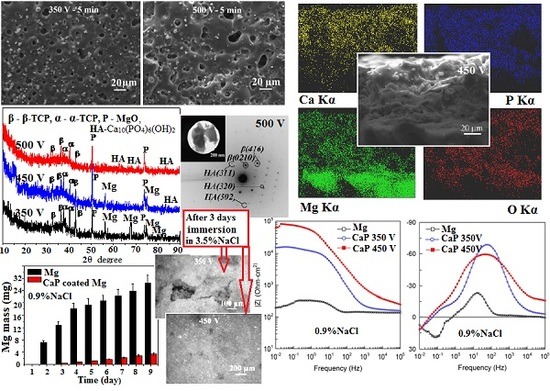
3.1. Regularities of Formation of the CaP Coatings on the Mg Alloy
3.2. Morphology of the CaP Coatings on the Mg Alloy
3.3. Structured–Phase and Elemental Compositions of the CaP Coatings on the Mg Alloy
3.4. Corrosion Behavior Comparison of the CaP Coated and Uncoated Mg Alloys
3.5. Electrochemical Properties of the CaP Coated and Uncoated Mg Alloy
4. Conclusions
- With increasing of the MAO voltage from 350 to 500 V the intensity of micro-arc discharges increases, so the thickness and surface roughness (Ra) of CaP coatings on Mg alloy increase linearly from 6 to 150 µm and from 2.0 to 8.0 µm, respectively.
- The maximal Ca and P concentrations and, as consequently, maximal Ca/P ratio are detected in the surface regions with accumulation of isometric β-TCP particles for the coatings deposited at 350 V. With increase in the voltage to 500 V, the Ca/P ratio in these regions decreases from 1.7 to 1.0 and the Ca/P ratio in the coating surface area without β-TCP particles increases from 0.7 to 0.9. It is associated with partial dissolution and transformation of β-TCP particles in the powerful high temperature micro-arc discharges fields under the high voltages.
- The coatings deposited at 350 V have homogeneous porous morphology and structure with micro-pores close in size (1.5–3.0 µm). The formation of large pores occurred at higher voltages of 450–500 V at the expense of the smaller ones.
- The β-Ca3(PO4)2, α-Ca3(PO4)2 and MgO crystalline phases are formed in the coatings deposited at the MAO voltages of 350–400 V. β-TCP is partially transformed into a high-temperature α-TCP phase during the MAO process. The increase of the voltage to 450–500 V leads to the partial dissolution of α-TCP with formation of HA phase in the coatings.
- The biodegradation rate of the CaP coated Mg alloy is almost 10 times less than uncoated alloy.
- The potentiodynamic polarization data have shown the reduction of the corrosion current of CaP coated Mg alloy in comparison to the uncoated alloy. This reduction for the coatings deposited at 350 and 450 V was 2 and 10 times, correspondingly. This is due to the change of the phase composition and the growth of the coating thickness.
- The levels of barrier properties of the studied samples estimated by the electrochemical measurements are directly related to the thicknesses and the phase composition of the deposited layers, the thicker coatings containing hydroxyapatite provide the higher protection.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, P.; Liu, X. Surface modification of biodegradable magnesium and its alloys for biomedical applications. Regener. Biomater. 2015, 2, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Lan, G.; Xia, H.; Yin, Q. The beneficial influence of microarc oxidation-coated magnesium alloy on the adhesion, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillekens, W.H. Magnesium-based biodegradable implants. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2013, 2, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F.; Hort, N.; Vogt, C.; Cohen, S.; Kainer, K.U.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Degradable biomaterials based on magnesium corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2008, 12, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Pröfrock, D.; Hort, N.; Willumeit, R.; Feyerabend, F. Reprint of: Improved cytotoxicity testing of magnesium materials. Mater. Sci. Eng 2013, 176, 1773–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Seng, R.C.; Liu, C.L.; Gao, J.C. Comparison of calcium phosphate coatings on Mg-Al and Mg-Ca alloys and their corrosion behavior in Hank’s solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 201, 3636–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Tan, L.; Wan, P.; Yu, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, K. Effect of preparation parameters on the properties of hydroxyapatite containing micro-arc oxidation coating on biodegradable ZK60 magnesium alloy. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 10043–10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Ni, J.; Zhao, C.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X. Doping inorganic ions to regulate bioactivity of Ca-P coating on bioabsorbable high purity magnesium. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2014, 24, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, M.P.; Pietak, A.M.; Huadmai, J.; Dias, G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadanbaz, S.; Dias, G.J. Calcium phosphate coatings on magnesium alloys for biomedical applications: A review. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.K.; Chen, C.Z.; Wang, D.G.; Lin, Z.Q. Preparation and bioactivity of micro-arc oxidized calcium phosphate coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 141, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H.; Dubé, D.; Mantovani, D. Developments in metallic biodegradable stents. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbel, R.; Mario, C.D.; Bartunek, J.; Bonnier, J.; Bruyne, B.; Eberli, F.R.; Erne, P.P.; Haude, P.M.; Heublein, B.; Horrigan, M.; et al. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: A prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 2007, 369, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.N.; Zheng, Y.F. A review on magnesium alloys as biodegradable materials. Front. Mater. Sci. China 2010, 4, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal-hay, A.; Dewidar, M.; Lim, J.K. Biocorrosion behavior and cell viability of adhesive polymer coated magnesium based alloys for medical implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, X.; Mao, L.; Niu, J.; Ding, W. Comparison of biodegradable behaviors of AZ31 and Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloys in Hank’s physiological solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, T.S.N.S.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H. Strategies to improve the corrosion resistance of microarc oxidation (MAO) coated magnesium alloys for degradable implants: Prospects and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 60, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Zeng, R.C.; Chen, R.S.; Liu, C.L.; Gao, J.C. Preparation of calcium phosphate coatings on Mg-1.0Ca alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, M.; Guo, Y. Biodegradable orthopedic magnesium-calcium (MgCa) alloys, process, and corrosion performance. Materials 2012, 5, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velikokhatnyi, O.I.; Kumta, P.N. First-principles studies on alloying and simplified thermodynamic aqueous chemical stability of calcium-, zinc-, aluminum-, yttrium- and iron-doped magnesium alloys. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, Z. Adjustment of the ratio of Ca/P in the ceramic coating on Mg alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6724–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.L.; Han, X.; Bai, J.; Xue, F.; Chu, P.K. Surface modification of biomedical magnesium alloy wires by micro-arc oxidation. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.; Shi, Z.; Dargusch, M.S.; Atrens, A. Influence of surface condition on the corrosion of ultra-high-purity Mg alloy wire. Corros. Sci. 2016, 108, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Hu, J.; Ding, Z.K.; Wang, C. Formation mechanism of calcium phosphate coating on micro-arc oxidized magnesium. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Qin, L.; Lai, Y. Corrosion and biocompatibility improvement of magnesium-based alloys as bone implant materials: A review. Regener. Biomater. 2017, 4, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Hu, J. Self-adjustment of calcium phosphate coating on micro-arc oxidized magnesium and its influence on the corrosion behaviour in simulated body fluids. Corros. Sci. 2014, 79, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Hu, J.; Ding, Z.K.; Wang, C. Bioactive calcium phosphate coating formed on micro-arc oxidized magnesium by chemical deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.F.; Gu, Y. Advances in microarc oxidation coated AZ31 Mg alloys for biomedical applications. Corros. Sci. 2015, 91, 7–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Dong, Q.; Dou, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, C. Structure and in vitro bioactivity of ceramic coatings on magnesium alloys by microarc oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 388, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cai, S.; Xu, G.; Shen, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, X. Corrosion behavior of mesoporous bioglass-ceramic coated magnesium alloy under applied forces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 56, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosemann, P.; Schmidt, J.; Heyn, A. Short and long term degradation behaviour of Mg–1Ca magnesium alloys and protective coatings based on plasma-chemical oxidation and biodegradable polymercoating in synthetic body fluid. Mater. Corros. 2013, 64, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legostaeva, E.V.; Kulyashova, K.S.; Komarova, E.G.; Epple, M.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Khlusov, I.A. Physical, chemical and biological properties of micro-arc deposited calcium phosphate coatings on titanium and zirconium-niobium alloy. Mat.-Wiss. Werkstofftech. 2013, 44, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikova, M.B.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Komarova, E.G.; Khlusov, I.A.; Chebodaeva, V.V. Structure and properties of the wollastonite–calcium phosphate coatings deposited on titanium and titanium–niobium alloy by the micro-arc oxidation method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkeev, Y.; Komarova, E.; Sedelnikova, M.; Sun, Z.M.; Zhu, Q.F.; Zhang, J.; Tolkacheva, T.; Uvarkin, P. Structure and properties of micro-arc calcium phosphate coatings on pure titanium and Ti-40Nb alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhurinskiy, D.; Gao, Y.; Yeung, W.K.; Strumban, E.; Leshchinsky, V.; Chu, P.J.; Matthews, A.; Yerokhin, A.; Maev, R.G. Characterization and corrosion evaluation of TiO2: N-HA coatings on titanium alloy formed by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 269, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Krok-Borkowicz, M.; Pamuła, E.; Simka, W. Electrochemical and biological characterization of coatings formed on Ti–15Mo alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Dercz, G.; Suchanek, K.; Kalemba–Rec, I.; Piotrovski, J.; Simka, W. Biofunctionalization of Ti–13Nb–13Zr alloy surface by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Part I. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Piedade, C.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Montemor, M.F.; Carmezim, M.J. Parallel nano-assembling of a multifunctional GO/HapNP coating on ultrahigh-purity magnesium for biodegradable implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, D.; Rameshbabu, N. Development and characterization of MgO/hydroxyapatite composite coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation coupled with electrophoretic deposition. Mater. Lett. 2012, 68, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, F.R.; Hort, N.; Salgado-Ordorica, M.A.; Kainer, K.U. Magnesium permanent mold castings optimization. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 690, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM G59–97. Standard Test Method for Conducting Potentiodynamic Polarization Resistance Measurements; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, M.; Atrens, A. Measurement of the corrosion rate of magnesium alloys using Tafel extrapolation. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Atrens, A. An innovative specimen configuration for the study of Mg corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Shi, Z.; Hofstetter, J.; Uggowitzed, P.J.; Song, G.; Liu, M.; Atrens, A. Corrosion of ultra-high-purity Mg in 3.5% NaCl solution saturated with Mg(OH)2. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ning, C.; Zhang, J. Residual stresses in microarc oxidation ceramic coatings on biocompatible AZ31 magnesium alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.W.; Shan, D.Y.; Han, E.H. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy for biomaterial application. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3276–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Calcium orthophosphates (CaPO4): Occurrence and properties. Prog. Biomater. 2016, 5, 9–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnedenkov, S.V.; Khrisanfova, O.A.; Zavidnaya, A.G.; Sinebryukhov, S.L.; Egorkin, V.S.; Nistratova, M.V.; Yerokhin, A.; Matthews, A. PEO coatings obtained on an Mg-Mn type alloy under unipolar and bipolar modes in silicate-containing electrolytes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2316–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | EC, V (Ag/AgCl) | jC, A cm−2 | Rp, Ω cm2 | |Z|f→0 Hz, Ω cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1.35 | 7.0 × 10−6 | 4.3 × 103 | 2.0 × 102 |
| 2 | −1.58 | 1.8 × 10−6 | 2.0 × 104 | 1.5 × 104 |
| 3 | −1.65 | 7.2 × 10−7 | 4.6 × 104 | 6.1 × 104 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sedelnikova, M.B.; Komarova, E.G.; Sharkeev, Y.P.; Tolkacheva, T.V.; Sheikin, V.V.; Egorkin, V.S.; Mashtalyar, D.V.; Kazakbaeva, A.A.; Schmidt, J. Characterization of the Micro-Arc Coatings Containing β-Tricalcium Phosphate Particles on Mg-0.8Ca Alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040238
Sedelnikova MB, Komarova EG, Sharkeev YP, Tolkacheva TV, Sheikin VV, Egorkin VS, Mashtalyar DV, Kazakbaeva AA, Schmidt J. Characterization of the Micro-Arc Coatings Containing β-Tricalcium Phosphate Particles on Mg-0.8Ca Alloy. Metals. 2018; 8(4):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040238
Chicago/Turabian StyleSedelnikova, Mariya B., Ekaterina G. Komarova, Yurii P. Sharkeev, Tatiana V. Tolkacheva, Vladimir V. Sheikin, Vladimir S. Egorkin, Dmitry V. Mashtalyar, Aigerim A. Kazakbaeva, and Juergen Schmidt. 2018. "Characterization of the Micro-Arc Coatings Containing β-Tricalcium Phosphate Particles on Mg-0.8Ca Alloy" Metals 8, no. 4: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040238
APA StyleSedelnikova, M. B., Komarova, E. G., Sharkeev, Y. P., Tolkacheva, T. V., Sheikin, V. V., Egorkin, V. S., Mashtalyar, D. V., Kazakbaeva, A. A., & Schmidt, J. (2018). Characterization of the Micro-Arc Coatings Containing β-Tricalcium Phosphate Particles on Mg-0.8Ca Alloy. Metals, 8(4), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040238