Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys—Substrate Effect on Wear and Corrosion Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate Materials and Coating Formation
2.2. PEO Process Characterisation
2.3. Coating Characterisation
2.4. Wear and Corrosion Resistance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrical Process Data
3.2. Coating Morphology and Composition
3.3. Coating Hardness
3.4. Visual Coating Appearance
3.5. Wear Behaviour
3.6. Corrosion Behaviour
4. Conclusions
- (i)
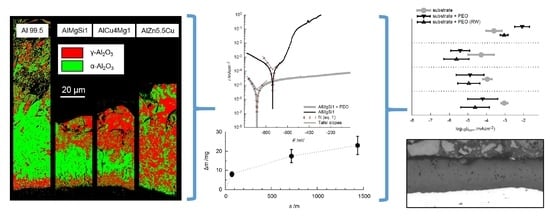
- The aluminum oxide modifications formed by PEO on Al 99.5 are more sensitive to chemical dissolution by the electrolyte used. This consideration is supported by the fact that the layer formation was just possible after the elevation of the silicate content of the electrolyte and the withdrawal of the additional hydroxide compounds improved its passivation and lowered the chemical dissolution of aluminum oxide respectively. Furthermore, the results of the EBSD measurements (Figure 9) showed that the presence and consequently also the absence of certain alloying elements within the substrate material can significantly affect the oxide formation and transformation processes.
- (ii)
- The shifted electrolyte composition leads to initiation of cathodic discharges during the PEO process which is suggested by the time axis symmetric course of the anodic and cathodic process voltage envelopes (Figure 2e). Therefore, the channels within the PEO layer could undergo discharge phenomena during both the cathodic and anodic half cycle. This could hinder the solidification of dense oxide zones.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rakoch, A.G.; Bardin, I.V.; Kovalev, V.L.; Avanesyan, T.G. Microarc oxidation of light constructional alloys: Part 1. Main notions on the microarc oxidation of light constructional alloys. Rus. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2013, 54, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A.; Dowey, S.J. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Alisch, G.; Lampke, T.; Nickel, D. Anodizing—A key surface treatment for aluminium. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 384, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoch, A.G.; Gladkova, A.A.; Ovalev, V.L.; Seferyan, A.G. The mechanism of formation of composite microarc coatings on aluminum alloys. Prot. Met. 2013, 384, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, G.; Krishna, L.R. Mechanisms underlying the formation of thick alumina coatings through the mao coating technology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 167, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapkiv, M. Simulation of synthesis of oxide-ceramic coatings in discharge channels of a metal-electrolyte system. Mater. Sci. 1999, 35, 279–283, UDC 533.9:541.115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, J.A.; Kalkanci, H.; Magurova, Y.; Clyne, T.W. Mullite-rich plasma electrolytic oxide coatings for thermal barrier applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 8683–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, V.; Liu, X.Y.; Luan, B.L.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Rohani, S. Phase transformation in plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on 6061 aluminum alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 251, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkanci, H.; Kurnaz, S.C. The effect of process parameters on mullite-based plasma electrolytic oxide coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 203, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Mun, J.I.; Kim, J.H. Effects of alloying elements on microstructure and protective properties of Al2O3 coatings formed on aluminum alloy substrates by plasma electrolysis. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillous, K.; Toll-Duchanoy, T.; Bauer-Grosse, E.; Hericher, L.; Geandier, G. Microstructure and phase composition of microarc oxidation surface layers formed on aluminium and its alloys 2214-t6 and 7050-t7. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 2969–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Meletis, E.I.; Jian, J.C.; Leyland, A.; Yerokhin, A.L.; Matthews, A. Abrasive wear/corrosion properties and tem analysis of Al2O3 coatings fabricated using plasma electrolysis. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 149, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerik, D.A.; Ayday, A.; Kumruoglu, L.C.; Kurnaz, S.C.; Oezel, A. The effects of Na2SiO3 concentration on the properties of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on 6060 aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudareva, N.Y.; Abramova, M.M. The structure of plasma-electrolytic coating formed on Al-Si alloys by the micro-arc oxidation method. Prot. Met. 2016, 52, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Cai, D.; Guo, G.; Liu, P. Evolution of residual stresses in micro-arc oxidation ceramic coatings on 6061 Al alloy. CJME 2013, 26, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, L.R.; Purnima, A.S.; Sundararajan, G. A comparative study of tribological behavior of microarc oxidation and hard-anodized coatings. Wear 2006, 261, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, M.; Mehner, T.; Dietrich, D.; Alisch, G.; Nickel, D.; Meyer, D.; Scharf, I.; Lampke, T. Wear-resistant coatings on aluminium produced by plasma anodising-a correlation of wear properties, microstructure, phase composition and distribution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 240, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanyu, S.; Wang, Y. Influence of electrolyte parameters on the properties of the ceramic coatings deposited on aluminum alloy by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2015, 54, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatkina, E.I.; Rakoch, A.G.; Belov, N.A.; Avanesyan, T.G. Corrosion resistance of boron-bearing aluminum alloys and its increase after plasma electrolytic oxidation. Prot. Met. 2014, 50, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, N.; Song, R.G.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Mao, Q.Z.; Xiong, Y. Study on microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behavior of peo coatings formed on aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 5022–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleinik, S.V.; Rudnev, V.S.; Kuzenkov, A.Y.; Yarovaya, T.P.; Trubetskaya, L.F.; Nedozorov, P.M. Modification of plasma electrolytic coatings on aluminum alloys with corrosion inhibitors. Prot. Met. 2013, 49, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleinik, S.V.; Rudnev, V.S.; Kuzenkov, A.Y.; Yarovaya, T.P.; Trubetskaya, L.F.; Nedozorov, P.M. Corrosion inhibitors in peo-coatings on aluminum alloys. Prot. Met. 2014, 50, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Lei, M. Effect of shot peening and plasma electrolytic oxidation on the intergranular corrosion behavior of 7a85 aluminum alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 27, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchen, F.; Sieber, M.; Lampke, T. Electrolyte influence on ignition of plasma electrolytic oxidation processes on light metals. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 315, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Jeong, Y. Generation mechanism of microdischarges during plasma electrolytic oxidation of Al in aqueous solutions. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1506–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wank, A.; Schwenk, A.; Wielage, B.; Pokhmurska, H. Behavior of thermally sprayed wear protective coatings exposed to different abrasive wear conditions in comparison to hard chromium platings. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Thermal Spray Conference and Exposition, Beijing, China, 14–16 May 2007; pp. 1011–1016. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |















| Element | Al 99.5 | AlCu4Mg1 | AlMgSi1 | AlZn5.5MgCu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | ≤0.25 | ≤0.5 | 0.7–1.3 | ≤0.4 |
| Fe | ≤0.4 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.5 |
| Cu | ≤0.05 | 3.8–4.9 | ≤0.1 | 1.2–2.0 |
| Mn | ≤0.05 | 0.3–0.9 | 0.4–1.0 | ≤0.3 |
| Mg | ≤0.05 | 1.2–1.8 | 0.6–1.2 | 2.1–2.9 |
| Cr | ≤0.1 | ≤0.25 | 0.18–0.28 | |
| Zn | ≤0.05 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.2 | 5.1–6.1 |
| Ti | ≤0.03 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.2 |
| others | ≤0.05 | ≤0.15 |
| Substance | NaSiO·5 HO | KOH | NaHPO |
|---|---|---|---|
| c / g·L | |||
| electrolyte 1 | 5 | 5 | 1 |
| electrolyte 2 | 10 | 1 | |
| Colour Coordinates | Al 99.5 | AlMgSi1 | AlCu4Mg1 | AlZn5.5MgCu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 89.59 ± 0.4 | 67.6 ± 0.3 | 49.2 ± 1.1 | 56.9 ± 1.4 |
| a | −0.579 ± 0.05 | 2.81 ± 0.12 | 0.94 ± 0.16 | 0.24 ± 0.21 |
| b | 0.949 ± 0.26 | 8.31 ± 0.21 | 3.21 ± 0.24 | −0.8 ± 0.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sieber, M.; Simchen, F.; Morgenstern, R.; Scharf, I.; Lampke, T. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys—Substrate Effect on Wear and Corrosion Performance. Metals 2018, 8, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050356
Sieber M, Simchen F, Morgenstern R, Scharf I, Lampke T. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys—Substrate Effect on Wear and Corrosion Performance. Metals. 2018; 8(5):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050356
Chicago/Turabian StyleSieber, Maximilian, Frank Simchen, Roy Morgenstern, Ingolf Scharf, and Thomas Lampke. 2018. "Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys—Substrate Effect on Wear and Corrosion Performance" Metals 8, no. 5: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050356
APA StyleSieber, M., Simchen, F., Morgenstern, R., Scharf, I., & Lampke, T. (2018). Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys—Substrate Effect on Wear and Corrosion Performance. Metals, 8(5), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8050356