Hypomethylation and Over-Expression of the Beta Isoform of BLIMP1 is Induced by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of B Cells; Potential Implications for the Pathogenesis of EBV-Associated Lymphomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Induction of BLIMP1β Expression Following EBV Infection of Primary Human B cells

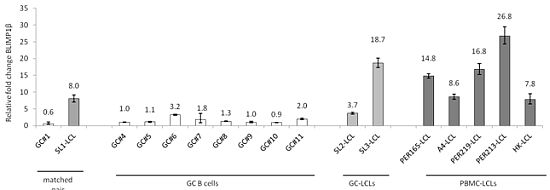
2.2. The BLIMP1β-specific Promoter is Hypomethylated in EBV-infected Human Germinal Center B cells

2.3. Hypomethylation and Increased Expression of BLIMP1β in Hodgkin’s Lymphoma

2.4. Discussion of Results
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cells
3.2. Reverse-Transcriptase-PCR
3.3. Quantitative PCR
3.4. Bisulphite Modification and Pyrosequencing
3.5. Methylation-Specific PCR (MSP)
3.6. Methylation Analysis of Micro-dissected HRS Cells by Nested-MSP
3.7. Immunoblotting
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Györy, I.; Fejér, G.; Ghosh, N.; Seto, E.; Wright, K.L. Identification of a functionally impaired positive regulatory domain I binding factor 1 transcription repressor in myeloma cell lines. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro-Shelef, M.; Lin, K.I.; McHeyzer-Williams, L.J.; Liao, J.; McHeyzer-Williams, M.G.; Calame, K. Blimp-1 is required for the formation of immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and pre-plasma memory B cells. Immunity 2003, 19, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calame, K.L.; Lin, K.I.; Tunyaplin, C. Regulatory mechanisms that determine the development and function of plasma cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, K. Leukemogenesis of the EVI1/MEL1 Gene Family. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 85, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. The retinoblastoma protein-interacting zinc finger gene RIZ in 1p36-linked cancers. Front Biosci. 1999, 4, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, R.B.; Jiang, G.L.; Bennington, G.A.; Yuan, B.; Johnson, C.K.; Stevens, M.W.; Niemann, T.H.; Peltomaki, P.; Huang, S.; de la Chapelle, A. Candidate tumor suppressor RIZ is frequently involved in colorectal carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Perkins, G.; Fang, W.; Yang, X.H.; Van Gele, M.; Carling, T.; Gu, J.; Buyse, I.M.; Fletcher, J.A.; Liu, J.; Bronson, R.; Chadwick, R.B.; de la Chapelle, A.; Zhang, X.; Speleman, F.; Huang, S. Tumor formation and inactivation of RIZ1, an Rb-binding member of a nuclear proteinmethyltransferase superfamily. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 2250–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, O.; Meguro, K.; Tohmiya, Y.; Funato, T.; Shibahara, S.; Sasaki, T. Altered expression of retinoblastoma protein-interacting zinc finger gene, RIZ, in human leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 119, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yu, J.X.; Liu, L.; Buyse, I.M.; Wang, M.S.; Yang, Q.C.; Nakagawara, A.; Brodeur, G.M.; Shi, Y.E.; Huang, S. RIZ1, but not the alternative RIZ2 product of the same gene, is underexpressed in breast cancer, and forced RIZ1 expression causes G2-M cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4238–4244. [Google Scholar]
- Cuenco, G.M.; Nucifora, G.; Ren, R. Human AML1/MDS1/EVI1 fusion protein induces an acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) in mice: A model for human AML. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderholm, J.; Kobayashi, H.; Mathieu, C.; Rowley, J.D.; Nucifora, G. The leukemia-associated gene MDS1/EVI1 is a new type of GATA-binding transactivator. Leukemia 1997, 11, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa, M.; Mitani, K.; Imai, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Yazaki, Y.; Hirai, H. The t(3;21) fusion product, AML1/Evi-1, interacts with Smad3 and blocks transforming growth factor-beta-mediated growth inhibition of myeloid cells. Blood 1998, 92, 4003–4012. [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa, M.; Mitani, K.; Irie, K.; Matsuyama, T.; Takahashi, T.; Chiba, S.; Yazaki, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Hirai, H. The oncoprotein Evi-1 represses TGF-beta signalling by inhibiting Smad3. Nature 1998, 394, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucifora, G. The EVI1 gene in myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1997, 11, 2022–2031. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, R.; Talwar-Trikha, A.; Chakrabarti, S.R.; Nucifora, G. MDS1/EVI1 enhances TGF-beta1 signaling and strengthens its growth-inhibitory effect but the leukemia-associated fusion protein AML1/MDS1/EVI1, product of the t(3;21), abrogates growth inhibition in response to TGF-betal. Leukemia 1999, 13, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjesteh van Waalwijk van Doorn-Khosrovani, S.; Erpelinck, C.; van Putten, W.L.; Valk, P.J.; van der Poel-van de Luytgaarde, S.; Hack, R.; Slater, R.; Smit, E.M.; Beverloo, H.B.; Verhoef, G.; Verdonck, L.F.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Sonneveld, P.; de Greef, G.E.; Löwenberg, B.; Delwel, R. High EVI1 expression predicted poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia: A study of 319 de novo AML patients. Blood 2003, 101, 837–845. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, N.; Shimizu, S.; Nagasawa, T.; Tanaka, H.; Taniwaki, M.; Yokota, J.; Morishita, K. A novel gene, MEL1, mapped to 1p36.3 is highly homologous to the MDS1/EVI1 gene and is transcriptionally activated in t(1;3)(p36;q21)-positive leukemia cells. Blood 2000, 96, 3209–3214. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, W.; Gomez, M.; Chadburn, A.; Lee, J.W.; Chan, W.C.; Knowles, D.M. Mutational analysis of PRDM1 indicates a tumor-suppressor role in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2006, 107, 4090–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Compagno, M.; Houldsworth, J.; Monti, S.; Grunn, A.; Nandula, S.V.; Aster, J.C.; Murty, V.V.; Shipp, M.A.; Dalla-Favera, R. Inactivation of the PRDM1/BLIMP1 gene in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocana, E.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Mora-Lopez, F.; Brieva, J.A.; Campos-Caro, A. The expression of PRDI-BF1 beta isoform in multiple myeloma plasma cells. Haematologica 2006, 91, 1579–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, L.; Leboeuf, C.; Zhang, Y.W.; Ma, J.; Garcia, J.F.; Song, Y.P.; Li, J.M.; Shen, Z.X.; Chen, Z.; Janin, A.; Chen, S.J. PRDM1 is involved in chemoresistance of T-cell lymphoma and down-regulated by the proteasome inhibitor. Blood 2008, 111, 3867–3871. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Leboeuf, C.; Shi, J.Y.; Li, J.M.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Garcia, J.F.; Shen, Z.X.; Chen, Z.; Janin, A.; Chen, S.J.; Zhao, W.L. Rituximab plus CHOP (R-CHOP) overcomes PRDM1-associated resistance to chemotherapy in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, H.Q.; Chen, Y.; Jiao, B.; Shen, Z.X.; Chen, S.J.; Zhao, W.L. Loss of promoter methylation contributes to the expression of functionally impaired PRDM1β isoform in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2010, 92, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumforth, K.R.N.; Flavell, J.R.; Davies, G.; Reynolds, G.M.; Pettit, T.; Wei, W.; Kishi, Y.; Arai, H.; Morgan, S.; Stankovic, T.; Nowakova, M.; Pratt, G.; Aoki, J.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Young, L.S.; Murray, P.G. Induction of autotaxin by Epstein-Barr virus promotes the growth and survival of Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells. Blood 2005, 106, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Asano, N.; Oshiro, A.; Suzuki, R.; Kagami, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Izumo, T.; Mori, S.; Ohshima, K.; Suzumiya, J.; Nakamura, N.; Abe, M.; Ichimura, K.; Sato, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Naoe, T.; Shimoyama, Y.; Kamiya, Y.; Kinoshita, T. Age-related EBV-associated B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders constitute a distinct clinicopathologic group: A study of 96 patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5124–5132. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Vaeth, S.; Cuomo, L.; Boccellato, F.; Vincenti, S.; Cirone, M.; Presutti, C.; Junker, S.; Winberg, G.; Frati, L.; Wade, P.A.; Faggioni, A.; Trivedi, P. Epstein-Barr virus infection leads to partial phenotypic reversion of terminally differentiated malignant B cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 284, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzalikova, K.; Vockerodt, M.; Leonard, S.; Bell, A.; Wei, W.; Schrader, A.; Wright, K.L.; Kube, D.; Rowe, M.; Woodman, C.B.; Murray, P.G. Down-regulation of BLIMP1α by the EBV oncogene LMP1 disrupts the plasma cell differentiation program and prevents viral replication in B cells: Implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-associated B cell lymphomas. Blood 2011, 117, 5907–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, S.; Wei, W.; Anderton, J.; Vockerodt, M.; Rowe, M.; Murray, P.G.; Woodman, C.B.J. An investigation of the epigenetic and transcriptional changes which follow Epstein-Barr virus infection of germinal centre B cells and their relevance to the pathogenesis of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9568–9577. [Google Scholar]
- Shimshon, L.; Michaeli, A.; Hadar, R.; Nutt, S.L.; David, Y.; Navon, A.; Waisman, A.; Tirosh, B. SUMOylation of Blimp-1 promotes its proteasomal degradation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2405–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.Y.; Su, S.T.; Hsu, P.H.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, I.Y.; Tseng, Y.H.; Tsai, M.D.; Shih, H.M.; Lin, K.I. SUMOylation of Blimp-1 is critical for plasma cell differentiation. EMBO Rep. 2012. (Epub ahead of print). [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, D.; Nayak, A.; Schumann, J.E.; Schimpl, A.; Berberich, I.; Berberich-Siebelt, F. Blimp-1Deltaexon7: A naturally occurring Blimp-1 deletion mutant with auto-regulatory potential. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 3614–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Maurin, M.; Cho, H.I.; Becknell, B.; Freud, A.G.; Yu, J.; Wei, S.; Djeu, J.; Celis, E.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Wright, K.L. PRDM1/Blimp-1 controls effector cytokine production in human NK cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6058–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbondanza, C.; De Rosa, C.; D'Arcangelo, A.; Pacifico, M.; Spizuoco, C.; Piluso, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Gazzerro, P.; Medici, N.; Moncharmont, B.; Puca, GA. Identification of a functional estrogen-responsive enhancer element in the promoter 2 of PRDM2 gene in breast cancer cell lines. J. Cell Physiol. 2012, 227, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunyaplin, C.; Shapiro, M.A.; Calame, K.L. Characterization of the B lymphocyte induced maturation protein-1 (Blimp-1) gene, mRNA isoforms and basal promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4846–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, M.; Greiner, A.; Avramidou, A.; Jäck, H.M.; Niedobitek, G. Evidence of abortive plasma cell differentiation in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2005, 23, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoretti, G.; Angelin-Duclos, C.; Shaknovich, R.; Zhou, H.; Wang, D.; Alobeid, B. PRDM1/Blimp-1 is expressed in human B-lymphocytes committed to the plasma cell lineage. J. Pathol. 2005, 206, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.F.; Roncador, G.; García, J.F.; Sánz, A.I.; Maestre, L.; Lucas, E.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Fernandez Victoria, R.; Martinez-Torrecuadrara, J.L.; Marafioti, T.; Mason, D.Y.; Piris, M.A. PRDM1/BLIMP-1 expression in multiple B and T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2006, 91, 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Natkunam, Y.; Hsi, E.D.; Aoun, P.; Zhao, S.; Elson, P.; Pohlman, B.; Naushad, H.; Bast, M.; Levy, R.; Lossos, I.S. Expression of the human germinal center-associated lymphoma (HGAL) protein identifies a subset of classic Hodgkin lymphoma of germinal center derivation and improved survival. Blood 2007, 109, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamesaki, H.; Fukuhara, S.; Tatsumi, E.; Uchino, H.; Yamabe, H.; Miwa, H.; Shirakawa, S.; Hatanaka, M.; Honjo, T. Cytochemical, immunologic, chromosomal, and molecular genetic analysis of a novel cell line derived from Hodgkin's disease. Blood 1986, 68, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Schaadt, M.; Diehl, V.; Stein, H.; Fonatsch, C.; Kirchner, H.H. Two neoplastic cell lines with unique features derived from Hodgkin's disease. Int. J. Cancer 1980, 26, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, H.G.; Gignac, S.M.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Leber, B.F.; Norton, J.; Lok, M.S.; Minowada, J. Characterization of Hodgkin's disease derived cell line HDLM-2. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1989, 117, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargou, R.C.; Mapara, M.Y.; Zugck, C.; Daniel, P.T.; Pawlita, M.; Döhner, H.; Dörken, B. Characterization of a novel Hodgkin cell line, HD-MyZ, with myelomonocytic features mimicking Hodgkin's disease in severe combined immunodeficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Kapp, U.; Bohlen, H.; Kornacker, M.; Schoch, C.; Stahl, B.; Mucke, S.; von Kalle, C.; Fonatsch, C.; Schaefer, H.E.; Hansmann, M.L.; Diehl, V. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells of a patient with advanced Hodgkin's lymphoma give rise to permanently growing Hodgkin-Reed Sternberg cells. Blood 1996, 87, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar]
- Drexler, H.G.; Leber, B.F.; Norton, J.; Yaxley, J.; Tatsumi, E.; Hoffbrand, A.V.; Minowada, J. Genotypes and immunophenotypes of Hodgkin's disease-derived cell lines. Leukemia 1988, 2, 371–376. [Google Scholar]
- Diehl, V.; Kirchner, H.H.; Burrichter, H.; Stein, H.; Fonatsch, C.; Gerdes, J.; Schaadt, M.; Heit, W.; Uchanska-Ziegler, B.; Ziegler, A.; Heintz, F.; Sueno, K. Characteristics of Hodgkin's disease-derived cell lines. Canc. Treat. Rep. 1982, 66, 615–632. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.H.; Revillard, J.P.; Magaud, J.P.; Lenoir, G.; Vuillaume, M.; Manel, A.M.; Vincent, C.; Bryon, P.A. B-cell maturation stages of Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines according to Epstein-Barr virus status and type of chromosome translocation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1987, 78, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Magrath, I.T.; Freeman, C.B.; Pizzo, P.; Gadek, J.; Jaffe, E.; Santaella, M.; Hammer, C.; Frank, M.; Reaman, G.; Novikovs, L. Characterization of lymphoma-derived cell lines: Comparison of cell lines positive and negative for Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. II. Surface markers. J. Natl.Cancer Inst. 1980, 64, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, G.; Lindahl, T.; Jondal, M.; Leibold, W.; Menezes, J.; Nilsson, K.; Sundstrom, C. Continuous lymphoid cell lines with characteristics of B cells, lacking the EBV genome and derived from three human lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3283–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Dombos, L.; Gothosokar, B. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) producer and non-producer human lymphoblastoid cell lines to superinfection of with EB-virus. Int. J. Cancer 1972, 10, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, Y.M.; Barr, Y.; Zajac, B.; Henle, G.; Henle, W. Morphological and virological investigations on cultured Burkitt tumor lymphoblasts (strain Raji). J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1966, 37, 547–559. [Google Scholar]
- King, W.; Thomas-Poweil, A.L.; Raab-Traub, N.; Hawke, M.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA. V. Viral RNA in a restringently infected, growth-transformed cell line. J. Virol. 1980, 36, 506–518. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, G.; Dombos, L. Relationship between the sensitivity of EBV-carrying lymphoblastoid lines to superinfection and the inducibility of the resident viral genome. Int. J. Cancer 1973, 11, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweeddale, M.E.; Lim, B.; Jamal, N.; Robinson, J.; Zalcberg, J.; Lockwood, G.; Minden, M.D.; Messner, H.A. The presence of clonogenic cells in high-grade malignant lymphoma: A prognostic factor. Blood 1987, 69, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, K.; Bennich, H.; Johansson, S.G.; Pontén, J. Established immunoglobulin producing myeloma (IgE) and lymphoblastoid (IgG) cell lines from an IgE myeloma patient. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1970, 7, 477–489. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, A.I.; Groves, K.; Kelly, G.L.; Croom-Carter, D.; Hui, E.; Chan, A.T.; Rickinson, A.B. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in endemic Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumour cells by using quantitative real-time PCR assays. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2885–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.G.; Qiu, G.H.; Fu, L.; Waites, E.R.; Srivastava, G.; Heys, D.; Agathanggelou, A.; Latif, F.; Grundy, R.G.; Mann, J.R.; Starczynski, J.; Crocker, J.; Parkes, S.E.; Ambinder, R.F.; Young, L.S.; Tao, Q. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the RASSF1A tumor suppressor gene in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Oncogene 2004, 23, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, P.G.; Fan, Y.; Davies, G.; Ying, J.; Geng, H.; Ng, K.M.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.; Kapatai, G.; Bose, S.; Anderton, J.A.; Reynolds, G.M.; Ito, A.; Woodman, C.B.J.; Marafioti, T.; Ambinder, R.F.; Tao, Q. Epigenetic silenncing of a proapoptotic cell adhesion molecule-the immunoglobulin superfamily member IGSF4 by promoter CpG methylation protects Hodgkin’s lymphoma cells from apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar]

| Gene name | Applied Biosystem Gene expression assay |
|---|---|
| BLIMP1 (PRDM1) α isoform | Hs01068508_m1 |
| GAPDH | 4310886E |
| β2m | 4310884E |
| primer | sequence |
|---|---|
| PCR forward biotinylated primer (region 1) | TAGGTTTGGTTAGTGA |
| PCR reverse non biotinylated primer (region 1) | CACTTTTATCTTTCCA |
| Sequencing primer (region 1) | TTTTATCAATTTTTCC |
| PCR forward non biotinylated primer (region 2) | GGTGGAGGATAGTTGA |
| PCR reverse biotinylated primer (region 2) | AAATAAACCAAATTCC |
| Sequencing primer (region 2) | TGTATAGTTGTTTGGG |
| LCM case No. | Original MD HRS case No. | EBV status | BLIMP1βmethylation |
|---|---|---|---|
| LCM1 | 4/054 | − | U |
| LCM2 | 4/133 | − | M |
| LCM3 | 05/452 | − | W |
| LCM4 | 05/363 | + | W |
| LCM5 | 05/009 | − | W |
| LCM6 | 05/092 | + | U |
| LCM7 | 05/494 | − | U |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vrzalikova, K.; Leonard, S.; Fan, Y.; Bell, A.; Vockerodt, M.; Flodr, P.; Wright, K.L.; Rowe, M.; Tao, Q.; Murray, P.G. Hypomethylation and Over-Expression of the Beta Isoform of BLIMP1 is Induced by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of B Cells; Potential Implications for the Pathogenesis of EBV-Associated Lymphomas. Pathogens 2012, 1, 83-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1020083
Vrzalikova K, Leonard S, Fan Y, Bell A, Vockerodt M, Flodr P, Wright KL, Rowe M, Tao Q, Murray PG. Hypomethylation and Over-Expression of the Beta Isoform of BLIMP1 is Induced by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of B Cells; Potential Implications for the Pathogenesis of EBV-Associated Lymphomas. Pathogens. 2012; 1(2):83-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1020083
Chicago/Turabian StyleVrzalikova, Katerina, Sarah Leonard, Yichao Fan, Andrew Bell, Martina Vockerodt, Patrik Flodr, Kenneth L. Wright, Martin Rowe, Qian Tao, and Paul G. Murray. 2012. "Hypomethylation and Over-Expression of the Beta Isoform of BLIMP1 is Induced by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of B Cells; Potential Implications for the Pathogenesis of EBV-Associated Lymphomas" Pathogens 1, no. 2: 83-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1020083
APA StyleVrzalikova, K., Leonard, S., Fan, Y., Bell, A., Vockerodt, M., Flodr, P., Wright, K. L., Rowe, M., Tao, Q., & Murray, P. G. (2012). Hypomethylation and Over-Expression of the Beta Isoform of BLIMP1 is Induced by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of B Cells; Potential Implications for the Pathogenesis of EBV-Associated Lymphomas. Pathogens, 1(2), 83-101. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens1020083