Orthology-Based Estimate of the Contribution of Horizontal Gene Transfer from Distantly Related Bacteria to the Intraspecific Diversity and Differentiation of Xylella fastidiosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Orthology Assertion
2.2. Analysis of the Core Genome
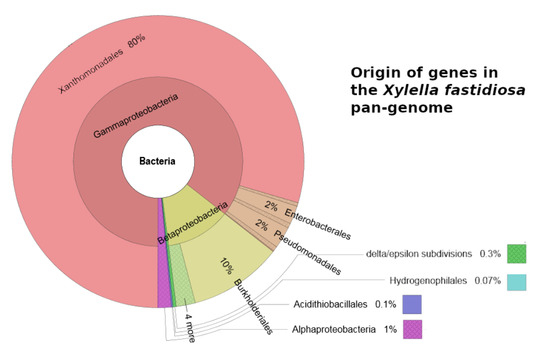
2.3. Analysis of the Pan-Genome
2.4. Genomic Profiling of Pathway Activity for Xylella fastidiosa
2.5. Evidence of Recent HGT in Xylella fastidiosa Genomes
3. Discussion
3.1. BUSCO Analysis Confirmed the Reduction of Xylella fastidiosa Genome
3.2. Distantly Related Bacteria Contributed to the Shape of the Xylella fastidiosa Accessory Genome
3.3. Xylella fastidiosa Gained Different Functions from Various Clades
3.4. Xylella fastidiosa and the Xylem Sap Microbiome
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Obtaining the Pan-Genomes
4.2. Classification of Gene According to Orthology and Homology Searches
4.3. Functional Assignments and Other Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeger, M.; Caffier, D.; Candresse, T.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Gilioli, G.; Grégoire, J.C.; Jaques Miret, J.A.; MacLeod, A.; Navajas Navarro, M.; et al. Updated pest categorisation of Xylella fastidiosa. EFSA J. 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janse, J.D.; Obradovic, A. Xylella fastidiosa: Its biology, diagnosis, control and risks. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, S35–S48. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Lindow, S. Living in two worlds: The plant and insect lifestyles of Xylella fastidiosa. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2008, 46, 243–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, D.L.; Purcell, A.H. Xylella fastidiosa: Cause of Pierce’s disease of grapevine and other emergent diseases. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunney, L.; Vickerman, D.B.; Bromley, R.E.; Russell, S.A.; Hartman, J.R.; Morano, L.D.; Stouthamer, R. Recent evolutionary radiation and host plant specialization in the Xylella fastidiosa subspecies native to the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Jarret, R.L.; Qin, X.; Hartung, J.S.; Banks, D.; Chang, C.J.; Hopkins, D.L. 16S rDNA sequence analysis of Xylella fastidiosa strains. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 23, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Grajales, A.; Arrieta-Ortiz, M.L.; Salazar, C.; Restrepo, S.; Bernal, A. Genomes-based phylogeny of the genus Xanthomonas. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, C.-C.; Deng, W.-L.; Jan, F.-J.; Chang, C.-J.; Huang, H.; Shih, H.-T.; Chen, J. Xylella taiwanensis sp. nov., causing pear leaf scorch disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4766–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaad, N.W.; Postnikova, E.; Lacy, G.; Fatmi, M.; Chang, C.-J. Xylella fastidiosa subspecies: X. fastidiosa subsp. [correction] fastidiosa [correction] subsp. nov., X. fastidiosa subsp. multiplex subsp. nov., and X. fastidiosa subsp. pauca subsp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelletti, S.; Scortichini, M. Genome-wide comparison and taxonomic relatedness of multiple Xylella fastidiosa strains reveal the occurrence of three subspecies and a new Xylella species. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denancé, N.; Briand, M.; Gaborieau, R.; Gaillard, S.; Jacques, M.-A. Identification of genetic relationships and subspecies signatures in Xylella fastidiosa. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scally, M.; Schuenzel, E.L.; Stouthamer, R.; Nunney, L. Multilocus sequence type system for the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa and relative contributions of recombination and point mutation to clonal diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8491–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunney, L.; Hopkins, D.L.; Morano, L.D.; Russell, S.E.; Stouthamer, R. Intersubspecific recombination in Xylella fastidiosa strains native to the United States: Infection of novel hosts associated with an unsuccessful invasion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunney, L.; Ortiz, B.; Russell, S.A.; Ruiz Sánchez, R.; Stouthamer, R. The complex biogeography of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa: Genetic evidence of introductions and subspecific introgression in Central America. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coletta-Filho, H.D.; Francisco, C.S.; Lopes, J.R.S.; Muller, C.; Almeida, R.P.P. Homologous recombination and Xylella fastidiosa host-pathogen associations in South America. Phytopathology 2017, 107, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potnis, N.; Kandel, P.P.; Merfa, M.V.; Retchless, A.C.; Parker, J.K.; Stenger, D.C.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Bergsma-Vlami, M.; Westenberg, M.; Cobine, P.A.; et al. Patterns of inter-and intrasubspecific homologous recombination inform eco-evolutionary dynamics of Xylella fastidiosa. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2319–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, A.I.; Chacón-Díaz, C.; Rodríguez-Murillo, N.; Coletta-Filho, H.D.; Almeida, R.P.P. Impacts of local population history and ecology on the evolution of a globally dispersed pathogen. BMC Genom. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, I.; Pesic, A.; Petras, D.; Royer, M.; Suessmuth, R.D.; Cociancich, S. What makes Xanthomonas albilineans unique amongst xanthomonads? Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez-Quintero, A.L.; Ortiz-Castro, M.; Lang, J.M.; Rieux, A.; Wu, G.; Liu, S.; Chapman, T.A.; Chang, C.; Ziegle, J.; Peng, Z.; et al. Genomic acquisitions in emerging populations of Xanthomonas vasicola pv. vasculorum infecting corn in the united states and argentina. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, I.; Royer, M.; Barbe, V.; Carrere, S.; Koebnik, R.; Cociancich, S.; Couloux, A.; Darrasse, A.; Gouzy, J.; Jacques, M.-A.; et al. The complete genome sequence of Xanthomonas albilineans provides new insights into the reductive genome evolution of the xylem-limited Xanthomonadaceae. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altenhoff, A.M.; Glover, N.M.; Train, C.-M.; Kaleb, K.; Warwick Vesztrocy, A.; Dylus, D.; de Farias, T.M.; Zile, K.; Stevenson, C.; Long, J.; et al. The OMA orthology database in 2018: Retrieving evolutionary relationships among all domains of life through richer web and programmatic interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D477–D485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleb, K.; Vesztrocy, A.W.; Altenhoff, A.; Dessimoz, C. Expanding the Orthologous Matrix (OMA) programmatic interfaces: REST API and the OmaDB packages for R and Python. F1000Research 2019, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medini, D.; Crabtree, J.; Mora, M.; Peterson, J.; Tettelin, H.; Angiuoli, S.; Ros, I.; Ward, N.; Donati, C.; Scarselli, M.; et al. Genome analysis of multiple pathogenic isolates of Streptococcus agalactiae: Implications for the microbial “pan-genome”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13950–13955. [Google Scholar]
- De Carvalho, M.O.; Loreto, E.L.S. Methods for detection of horizontal transfer of transposable elements in complete genomes. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 35, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, J.G.; Ochman, H. Amelioration of bacterial genomes: Rates of change and exchange. J. Mol. Evol. 1997, 44, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenbeck, J.; Cohan, F.M. Origins of bacterial diversity through horizontal genetic transfer and adaptation to new ecological niches. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 957–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandroemme, J.; Cottyn, B.; Baeyen, S.; de Vos, P.; Maes, M. Draft genome sequence of Xanthomonas fragariae reveals reductive evolution and distinct virulence-related gene content. BMC Genom. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shvetsov, A.V.; Lebedev, D.V.; Chervyakova, D.B.; Bakhlanova, I.V.; Yung, I.A.; Radulescu, A.; Kuklin, A.I.; Baitin, D.M.; Isaev-Ivanov, V.V. Structure of RecX protein complex with the presynaptic RecA filament: Molecular dynamics simulations and small angle neutron scattering. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirz, R.T.; Chin, J.K.; Andes, D.R.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Craig, W.A.; Romesberg, F.E. Inhibition of mutation and combating the evolution of antibiotic resistance. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaber, J.W.; Hochhut, B.; Waldor, M.K. SOS response promotes horizontal dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Nature 2004, 427, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studholme, D.J.; Kemen, E.; MacLean, D.; Schornack, S.; Aritua, V.; Thwaites, R.; Grant, M.; Smith, J.; Jones, J.D.G. Genome-wide sequencing data reveals virulence factors implicated in banana Xanthomonas wilt. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 310, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birch, R.G. Xanthomonas albilineans and the antipathogenesis approach to disease control. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2001, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-J.; Jung, B.; Lee, J.; Han, S.-W. Functional characterization of a putative DNA methyltransferase, EadM, in Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. glycines by proteomic and phenotypic analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajeshwari, R.; Jha, G.; Sonti, R.V. Role of an in planta-expressed xylanase of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in promoting virulence on rice. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wessel, M.; Klüsener, S.; Gödeke, J.; Fritz, C.; Hacker, S.; Narberhaus, F. Virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens requires phosphatidylcholine in the bacterial membrane. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farberg, A.M.; Hart, W.K.; Johnson, R.J. The unusual substrate specificity of a virulence associated serine hydrolase from the highly toxic bacterium, Francisella tularensis. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 7, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kulasakara, H.; Lee, V.; Brencic, A.; Liberati, N.; Urbach, J.; Miyata, S.; Lee, D.G.; Neely, A.N.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; et al. Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa diguanylate cyclases and phosphodiesterases reveals a role for bis-(3′-5′)-cyclic-GMP in virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2839–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akita, H.; Kimura, Z.I.; Hoshino, T. Pseudomonas humi sp. nov., isolated from leaf soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Müller, D.B.; Srinivas, G.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Potthoff, E.; Rott, M.; Dombrowski, N.; Münch, P.C.; Spaepen, S.; Remus-Emsermann, M.; et al. Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, F. Toxins-antitoxins: Plasmid maintenance, programmed cell death, and cell cycle arrest. Science 2003, 301, 1496–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.W.; Tan, C.C.; Rogers, E.E.; Stenger, D.C. Toxin-antitoxin systems mqsR/ygiT and dinJ/relE of Xylella fastidiosa. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 87, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Sato, S.; Asamizu, E.; Kato, T.; Sasamoto, S.; Watanabe, A.; Idesawa, K.; Ishikawa, A.; Kawashima, K.; et al. Complete genome structure of the nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Mesorhizobium loti. DNA Res. 2000, 7, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, J.D.; Reddy, S.L.; Hopkins, D.L.; Gabriel, D.W. TolC is required for pathogenicity of Xylella fastidiosa in Vitis vinifera grapevines. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guilhabert, M.R.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Identification of Xylella fastidiosa antivirulence genes: Hemagglutinin adhesins contribute a biofilm maturation to X. fastidiosa and colonization and attenuate virulence. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Sluys, M.A.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Monteiro-Vitorello, C.B.; Miyaki, C.Y.; Furlan, L.R.; Camargo, L.E.A.; da Silva, A.C.R.; Moon, D.H.; Takita, M.A.; Lemos, E.G.M.; et al. Comparative analyses of the complete genome sequences of Pierce’s disease and citrus variegated chlorosis strains of Xylella fastidiosa. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roper, M.C.; Greve, L.C.; Warren, J.G.; Labavitch, J.M.; Kirkpatrick, B.C. Xylella fastidiosa requires polygalacturonase for colonization and pathogenicity in Vitis vinifera grapevines. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purcell, A.H.; Hopkins, D.L. Fastidious xylem-limited bacterial plant pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1996, 34, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achari, G.A.; Ramesh, R. Diversity, biocontrol, and plant growth promoting abilities of xylem residing bacteria from solanaceous crops. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, E.K.; Gyaneshwar, P.; Mathan, N.; Barraquio, W.L.; Reddy, P.M.; Iannetta, P.P.M.; Olivares, F.L.; Ladha, J.K. Infection and colonization of rice seedlings by the plant growth-promoting bacterium Herbaspirillum seropedicae Z67. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2002, 15, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Compant, S.; Reiter, B.; Sessitsch, A.; Nowak, J.; Clément, C.; Barka, E.A. Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by plant growth-promoting bacterium Burkholderia sp. strain PsJN. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Compant, S.; Kaplan, H.; Sessitsch, A.; Nowak, J.; Ait Barka, E.; Clément, C. Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by Burkholderia phytofirmans strain PsJN: From the rhizosphere to inflorescence tissues. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 63, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacava, P.T.; Azevedo, J.L.; Miller, T.A.; Hartung, J.S. Interactions of Xylella fastidiosa and endophytic bacteria in citrus: A review. Tree For. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 3, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Deyett, E.; Rolshausen, P.E. Temporal dynamics of the sap microbiome of grapevine under high Pierce’s disease pressure. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, S.H.; Retchless, A.C.; Kwan, J.Y.; Almeida, R.P.P. Effects of DNA size on transformation and recombination efficiencies in Xylella fastidiosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanhove, M.; Retchless, A.C.; Sicard, A.; Rieux, A.; Coletta-Filho, H.D.; de La Fuente, L.; Stenger, D.C.; Almeida, R.P.P. Genomic diversity and recombination among Xylella fastidiosa subspecies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02972-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wasukira, A.; Tayebwa, J.; Thwaites, R.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Aritua, V.; Kubiriba, J.; Smith, J.; Grant, M.; Studholme, D.J. Genome-wide sequencing reveals two major sub-lineages in the genetically monomorphic pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pathovar musacearum. Genes 2012, 3, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maglott, D.; Ostell, J.; Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T. Entrez gene: Gene-centered information at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D52–D57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenhoff, A.M.; Gil, M.; Gonnet, G.H.; Dessimoz, C. Inferring hierarchical orthologous groups from orthologous gene pairs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deorowicz, S.; Debudaj-Grabysz, A.; Gudys, A. FAMSA: Fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment of huge protein families. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Serra, F.; Bork, P. ETE 3: Reconstruction, analysis, and visualization of phylogenomic data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teeling, H.; Waldmann, J.; Lombardot, T.; Bauer, M.; Glöckner, F.O. TETRA: A web-service and a stand-alone program for the analysis and comparison of tetranucleotide usage patterns in DNA sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Xylella fastidiosa | Xanthomonas vasicola | Xanthomonas albilineans | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| POG0909014H | POG0909014H | POG0909014H | UDP-N-acetylmuramoylalanine-d-glutamate ligase |
| POG090901AA | POG090901AA | POG090901AA | Small ribosomal subunit biogenesis GTPase RsgA |
| POG090901YD | POG090901YD | POG090901YD | membrane protein |
| POG09090233 | POG09090233 | POG09090233 | apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase |
| POG090902S9 | POG090902S9 | POG090902S9 | threonylcarbamoyl-AMP synthase |
| POG090903DC | POG090903DC | POG090903DC | argininosuccinate lyase |
| POG0909029O | POG0909029O | Thymidylate kinase | |
| POG090901QT | peptide chain release factor 1 | ||
| POG090900DY | tRNA N6-adenosine threonylcarbamoyltransferase | ||
| POG090900A4 | tRNA modification GTPase MnmE | ||
| POG090900LM | Bifunctional uridylyltransferase/uridylyl-removing enzyme | ||
| POG0909004H | Bifunctional glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase/adenylyl-removing enzyme | ||
| POG090901JJ | d-aminoacyl-tRNA deacylase | ||
| POG090901Q3 | RNA-binding protein | ||
| POG09090284 | tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase B | ||
| POG090902SD | membrane protein | ||
| POG090903LW | Regulatory protein RecX |
| Xanthomonas vasicola | Xanthomonas albilineans | Xylella fastidiosa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.9 | 3.7 | 2.5 | Average genome size (Mbp) |
| 3888 | 2919 | 2176 | Average number of predicted proteins |
| Core genome: | |||
| 1828 | 2386 | 1045 | Genes searched for orthology and homology |
| 1828 (100%) | 2371 (99.4%) | 1038 (99.3%) | Genes that have orthologs or close paralogs in the Xanthomonadales |
| 0 (0%) | 15 (0.6%) | 7 (0.7%) | Genes that have orthologs in taxa not belonging to Xanthomonadales |
| Pan-genome: | |||
| 5296 | 3536 | 3673 | Protein encoding genes in pan-genome |
| 5155 | 3369 | 3049 | Genes searched for orthology and homology |
| 5085 (98.6%) | 3198 (94.9%) | 2395 (78.6%) | Genes that have orthologs or close paralogs in the Xanthomonadales |
| 70 (1.4%) | 171 (5.1%) | 654 (21.4%) | Genes that have orthologs in taxa not belonging to Xanthomonadales (Figure 1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Firrao, G.; Scortichini, M.; Pagliari, L. Orthology-Based Estimate of the Contribution of Horizontal Gene Transfer from Distantly Related Bacteria to the Intraspecific Diversity and Differentiation of Xylella fastidiosa. Pathogens 2021, 10, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010046
Firrao G, Scortichini M, Pagliari L. Orthology-Based Estimate of the Contribution of Horizontal Gene Transfer from Distantly Related Bacteria to the Intraspecific Diversity and Differentiation of Xylella fastidiosa. Pathogens. 2021; 10(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleFirrao, Giuseppe, Marco Scortichini, and Laura Pagliari. 2021. "Orthology-Based Estimate of the Contribution of Horizontal Gene Transfer from Distantly Related Bacteria to the Intraspecific Diversity and Differentiation of Xylella fastidiosa" Pathogens 10, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010046
APA StyleFirrao, G., Scortichini, M., & Pagliari, L. (2021). Orthology-Based Estimate of the Contribution of Horizontal Gene Transfer from Distantly Related Bacteria to the Intraspecific Diversity and Differentiation of Xylella fastidiosa. Pathogens, 10(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10010046