Sexual Dimorphism of the Neuroimmunoendocrine Response in the Spleen during a Helminth Infection: A New Role for an Old Player?
Abstract
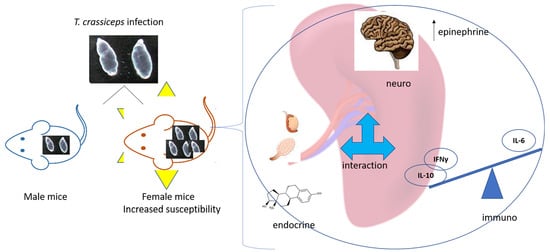
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Number of Parasites
2.2. Levels of Neurotransmitters in the Spleen
2.3. IL-2, IL-4, and IL-10 Spleen Expression
2.4. IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-6 Expression in the Spleen
2.5. Sex Steroids Levels in the Spleen
2.6. Expression of Sex Steroid Receptors in the Spleen
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Animals and Experimental Infections
4.3. Tissues Sample
4.4. Neurotransmitter Measurement
4.5. Cytokine Spleen Expression
4.6. Sex Steroids Levels in the Spleen
4.7. Expression of Steroids Receptors (ER, PR, and AR) in the Spleen by Western Blot
4.8. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larralde, C.; Sciutto, E.; Huerta, L.; Terrazas, I.; Fragoso, G.; Trueba, L.; Lemus, D.; Lomelí, C.; Tapia, G.; Montoya, R.M. Experimental cysticercosis by Taenia crassiceps in mice: Factors involved in susceptibility. Acta Leiden 1989, 57, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larralde, C.; Sotelo, J.; Montoya, R.M.; Palencia, G.; Padilla, A.; Govezensky, T.; Diaz, M.L.; Sciutto, E. Immunodiagnosis of human cysticercosis in cerebrospinal fluid. Antigens from murine Taenia crassiceps cysticerci effectively substitute those from porcine Taenia solium. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1990, 114, 926–928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rishi, A.K.; McManus, D.P. Molecular cloning of Taenia solium genomic DNA and characterization of taeniid cestodes by DNA analysis. Parasitology 1988, 97, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larralde, C.; Laclette, J.P.; Montoya, R.M.; Contreras, L.; Sandoval, M.; Bojalil, R.; Owen, C.S.; Arzate, J.; Goodsaid, F.; Diaz, M.L.; et al. Reliable Serology of Taenia solium Cysticercosis with Antigens from Cyst Vesicular Fluid: Elisa and Hemagglutination Tests. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1986, 35, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, A.; Fragoso, G.; Rosas, G.; Hernández, M.; Gevorkian, G.; López-Casillas, F.; Hernández, B.; Acero, G.; Huerta, M.; Larralde, C.; et al. Two Epitopes Shared by Taenia crassiceps and Taenia solium Confer Protection against Murine T. crassiceps Cysticercosis along with a Prominent T1 Response. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landa, A.; Navarro, L.; Ochoa-Sánchez, A.; Jiménez, L. Taenia solium and Taenia crassiceps: miRNomes of the larvae and effects of miR-10-5p and let-7-5p on murine peritoneal macrophages. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Manoutcharian, K.; Gevorkian, G.; Rosas-Salgado, G.; Hernández-Gonzalez, M.; Herrera-Estrella, L.R.; Cabrera-Ponce, J.L.; López-Casillas, F.; González-Bonilla, C.; et al. New Approaches to Improve a Peptide Vaccine Against Porcine Taenia solium Cysticercosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2002, 33, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Trueba, L.; Lemus, D.; Montoya, R.; Diaz, M.L.; Govezensky, T.; Lomeli, C.; Tapia, G.; Larralde, C. Cysticercosis vaccine: Cross protecting immunity with T. solium antigens against experimental murine T. crassiceps cysticercosis. Parasite Immunol. 1990, 12, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Velasco, T.; Tovar, V.; Fragoso, G.; Fleury, A.; Beltrán, C.; Villalobos, N.; Aluja, A.; Rodarte, L.; Sciutto, E.; et al. Castration and pregnancy of rural pigs significantly increase the prevalence of naturally acquired Taenia solium cysticercosis. Veter Parasitol. 2002, 108, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciutto, E.; Rosas, G.; Hernández, M.; Morales, J.; Cruz-Revilla, C.; Toledo, A.; Manoutcharian, K.; Gevorkian, G.; Blancas, A.; Acero, G.; et al. Improvement of the synthetic tri-peptide vaccine (S3Pvac) against porcine Taenia solium cysticercosis in search of a more effective, inexpensive and manageable vaccine. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Montor, J.; Chavarria, A.; De León-Nava, M.A.; Del Castillo, L.I.; Escobedo, E.G.; Sánchez, E.N.; Vargas, J.A.; Hernández-Flores, M.; Romo-González, T.; Larralde, C. Host gender in parasitic infections of mammals: An evaluation of the female host supremacy paradigm. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneses, G.; Berzunza, M.; Becker, I.; Bobes, R.J.; Rosas, G.; Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G. Taenia crassiceps cysticercosis: Variations in its parasite growth permissiveness that encounter with local immune features in BALB/c substrains. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 123, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larralde, C.; Morales, J.; Terrazas, I.; Govezensky, T.; Romano, M. Sex hormone changes induced by the parasite lead to feminization of the male host in murine Taenia crassiceps cysticercosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 52, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrazas, L.I.; Bojalil, R.; Govezensky, T.; Larralde, C. Shift from an early protective Th1-type immune response to a late permissive Th2-type response in murine cysticercosis (Taenia crassiceps). J. Parasitol. 1998, 84, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- I Terrazas, L.; Bojalil, R.; Govezensky, T.; Larralde, C. A role for 17-beta-estradiol in immunoendocrine regulation of murine cysticercosis (Taenia crassiceps). J. Parasitol. 1994, 80, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, L.; Terrazas, L.I.; Sciutto, E.; Larralde, C. Immunological Mediation of Gonadal Effects on Experimental Murine Cysticercosis Caused by Taenia crassiceps Metacestodes. J. Parasitol. 1992, 78, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLennan, D.A.; Brooks, D.R. Parasites and Sexual Selection: A Macroevolutionary Perspective. Q. Rev. Biol. 1991, 66, 255–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, G.; Meneses, G.; Sciutto, E.; Fleury, A.; Larralde, C. Preferential Growth of Taenia crassiceps Cysticerci in Female Mice Holds Across Several Laboratory Mice Strains and Parasite Lines. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Bello, R.; Nava-Castro, K.; Muniz-Hernandez, S.; Nava-Luna, P.; Trejo-Sánchez, I.; Tiempos-Guzman, N.; Mendoza-Rodriguez, Y.; Morales-Montor, J. Beyond the reproductive effect of sex steroids: Their role during immunity to helminth parasite infections. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, G.; Larralde, C.; Chavarria, A.; Cerbón, M.A.; Morales-Montor, J. Molecular mechanisms involved in the differential effects of sex steroids on the reproduction and infectivity of Taenia crassiceps. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, G.; Robert, C.W.; Carrero, J.C.; Morales-Montor, J. Parasite regulation by host hormones: An old mechanism of host exploitation? Trends Parasitol 2005, 21, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, L.C.; Artis, D. Beyond Host Defense: Emerging Functions of the Immune System in Regulating Complex Tissue Physiology. Cell 2018, 173, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, A.S.; Araujo, M.I.; Pearce, E.J. Immunology of Parasitic Helminth Infections. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davidson, R.A. Immunology of Parasitic Infections. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1985, 69, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Montor, J.; Larralde, C. The role of sex steroids in the complex physiology of the host-parasite relationship: The case of the larval cestode of Taenia crassiceps. Parasitology 2005, 131, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantzer, R. Neuroimmune Interactions: From the Brain to the Immune System and Vice Versa. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 477–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCorry, L.K. Physiology of the autonomic nervous system. Am. J. Pharm. Educ. 2007, 71, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulloa, L. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway meets microRNA. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1249–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, L. The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Selective Cholinergic Agonists. Shock 2011, 36, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arteaga, M.; Chavarría, A.; Montor, J.M. Immunoneuroendocrine communication network and homeostasis regulation: The use of hormones and neurohormones as immunotherapy. Rev. Investig. Clin. Organo Hosp. Enferm. Nutr. 2003, 54, 542–549. [Google Scholar]
- Valentin, A.P.; Kevin, J.T. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Brain Behav. Immun. 2005, 19, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Bottasso, O.; Morales-Montor, J. Neuroimmunomodulation during Infectious Diseases: Mechanisms, Causes and Consequences for the Host. Neuroimmunomodulation 2009, 16, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, A.R.; Bottasso, O.; Savino, W. The Impact of Infectious Diseases upon Neuroendocrine Circuits. Neuroimmunomodulation 2009, 16, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chess, L. Chapter 2 How the Immune System Achieves Self–Nonself Discrimination During Adaptive Immunity. Adv. Immunol. 2009, 102, 95–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia-Mendoza, M.; Morales-Montor, J. Immune Tumor Microenvironment in Breast Cancer and the Participation of Estrogen and Its Receptors in Cancer Physiopathology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerage, D.; Sloan, E.K.; Mattarollo, S.R.; McCombe, P.A. Interaction of neurotransmitters and neurochemicals with lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 332, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arreola, R.; Villanueva, L.E.B.; Cruz-Fuentes, C.; Velasco-Velazquez, M.A.; Garcés-Alvarez, M.E.; Hurtado-Alvarado, G.; Quintero-Fabian, S.; Pavón, L. Immunomodulatory Effects Mediated by Serotonin. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 354957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Russell, R.M.; Pifer, R.; Menezes-Garcia, Z.; Cuesta, S.; Narayanan, S.; MacMillan, J.B.; Sperandio, V. The Serotonin Neurotransmitter Modulates Virulence of Enteric Pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 41–53.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Trujillo, J.; Rivera-Montoya, I.; Rodriguez-Sosa, M.; Terrazas, L.I. Nitric oxide contributes to host resistance against experimental Taenia crassiceps cysticercosis. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 100, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, B.A.; Campbell, K.S.; Munson, A.E. Norepinephrine and serotonin content of the murine spleen: Its relationship to lymphocyte beta-adrenergic receptor density and the humoral immune response in vivo and in vitro. Cell. Immunol. 1988, 117, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grailer, J.; Haggadone, M.; Ward, P. Catecholamines promote an M2 macrophage activation phenotype (P1299). J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 63.7. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, K.; Godinez, D.R.; Brust-Mascher, I.; Miller, E.N.; Gareau, M.G.; Reardon, C. Neuroanatomy of the spleen: Mapping the relationship between sympathetic neurons and lymphocytes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herr, N.; Bode, C.; Duerschmied, D. The Effects of Serotonin in Immune Cells. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, N.; Goyal, P.K.; Mahida, Y.R.; Li, K.F.; Wakelin, D. Early cytokine responses during intestinal parasitic infections. Immunology 1998, 93, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitson, J.P.; Grainger, J.R.; Maizels, R.M. Helminth immunoregulation: The role of parasite secreted proteins in modulating host immunity. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Saucedo, D.; Ruiz-Rosado, J.D.D.; Terrazas, C.; Callejas, B.E.; Satoskar, A.R.; Partida-Sánchez, S.; Terrazas, L.I. Taenia crassiceps-Excreted/Secreted Products Induce a Defined MicroRNA Profile that Modulates Inflammatory Properties of Macrophages. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Kreider, T.; Urban, J.F.; Gause, W.C. Characterisation of effector mechanisms at the host:parasite interface during the immune response to tissue-dwelling intestinal nematode parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, E.K.; Inclan-Rico, J.M.; Siracusa, M.C. Type 2 Cytokine Responses: Regulating Immunity to Helminth Parasites and Allergic Inflammation. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 3, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Maizels, R.M. IL-6 controls susceptibility to helminth infection by impeding Th2 responsiveness and altering the Treg phenotype in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, C.W.; Walker, W.; Alexander, J. Sex-Associated Hormones and Immunity to Protozoan Parasites. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, S.L. Hormonal and immunological mechanisms mediating sex differences in parasite infection. Parasite Immunol. 2004, 26, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.M.D.; Smith, N.C.; Ikin, R.J.; Boulter, N.R.; Dalton, J.P.; Donnelly, S. Immunological Interactions between 2 Common Pathogens, Th1-Inducing Protozoan Toxoplasma gondii and the Th2-Inducing Helminth Fasciola hepatica. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearce, E.J.; Kane, C.M.; Sun, J.; Taylor, J.J.; McKee, A.S.; Cervi, L. Th2 response polarization during infection with the helminth parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 201, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, E.; Chauvin, A. Immunity against Helminths: Interactions with the Host and the Intercurrent Infections. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Che, Q.; Liu, B.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T. Activation of a positive feedback loop involving Il 6 and aromatase promotes intratumoral 17Ò estradiol biosynthesis in endometrial carcinoma microenvironment. Cancer Cell Biol. 2014, 135, 282–294. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Montor, J.; Baig, S.; Hallal-Calleros, C.; Damian, R. Taenia crassiceps: Androgen reconstitution of the host leads to protection during cysticercosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2002, 100, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Montor, J.; Baig, S.; Mitchell, R.; Deway, K.; Hallal-Calleros, C.; Damian, R.T. Immunoendocrine interactions during chronic cysticercosis determine male mouse feminization: Role of IL-6. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4527–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bechir, M.; Schelling, E.; Hamit, M.A.; Tanner, M.; Zinsstag, J. Parasitic Infections, Anemia and Malnutrition Among Rural Settled and Mobile Pastoralist Mothers and Their Children in Chad. EcoHealth 2011, 9, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpio, A.; Romo, M.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Short, B.; Dua, T. Parasitic diseases of the central nervous system: Lessons for clinicians and policy makers. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2016, 16, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorais, F.J.; Esch, G.W. Growth rate of two Taenia crassiceps strains. Exp. Parasitol. 1969, 25, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nava-Castro, K.E.; Pavón, L.; Becerril-Villanueva, L.E.; Ponce-Regalado, M.D.; Aguilar-Díaz, H.; Segovia-Mendoza, M.; Morales-Montor, J. Sexual Dimorphism of the Neuroimmunoendocrine Response in the Spleen during a Helminth Infection: A New Role for an Old Player? Pathogens 2022, 11, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030308
Nava-Castro KE, Pavón L, Becerril-Villanueva LE, Ponce-Regalado MD, Aguilar-Díaz H, Segovia-Mendoza M, Morales-Montor J. Sexual Dimorphism of the Neuroimmunoendocrine Response in the Spleen during a Helminth Infection: A New Role for an Old Player? Pathogens. 2022; 11(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleNava-Castro, Karen Elizabeth, Lenin Pavón, Luis Enrique Becerril-Villanueva, María Dolores Ponce-Regalado, Hugo Aguilar-Díaz, Mariana Segovia-Mendoza, and Jorge Morales-Montor. 2022. "Sexual Dimorphism of the Neuroimmunoendocrine Response in the Spleen during a Helminth Infection: A New Role for an Old Player?" Pathogens 11, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030308
APA StyleNava-Castro, K. E., Pavón, L., Becerril-Villanueva, L. E., Ponce-Regalado, M. D., Aguilar-Díaz, H., Segovia-Mendoza, M., & Morales-Montor, J. (2022). Sexual Dimorphism of the Neuroimmunoendocrine Response in the Spleen during a Helminth Infection: A New Role for an Old Player? Pathogens, 11(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030308