Herpesviruses and SARS-CoV-2: Viral Association with Oral Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
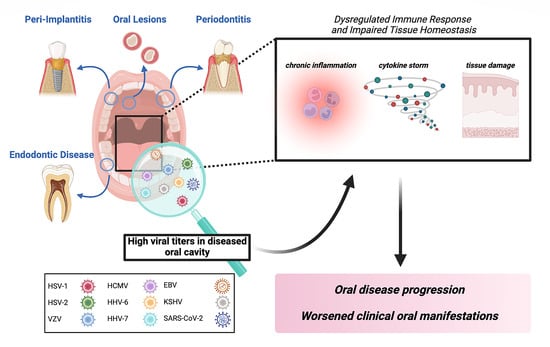
:1. Introduction
2. Human Herpesviruses and Oral Inflammatory Diseases
2.1. Human Herpesviruses and Periodontal Diseases
Human Herpesviruses and Bacterial Co-infection in Periodontal Diseases
2.2. Human Herpesviruses and Peri-Implantitis
Human Herpesviruses and Bacterial Co-Infection in Peri-Implantitis
2.3. Human Herpesviruses and Endodontic Diseases
2.3.1. Human Herpesviruses Activity and Endodontic Treatment Outcomes
2.3.2. Human Herpesviruses and Endodontic Diseases in Immunocompromised Patients
3. SARS-CoV-2 and Oral Inflammatory Diseases
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 and Periodontal Disease
3.1.1. Mechanistic Link between SARS-CoV-2 and Periodontal Disease
3.1.2. Peiodontital Tissue as a Target for SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.1.3. SARS-CoV-2 and Periodontopathic Bacteria
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 and Peri-Implantitis
3.3. SARS-CoV-2 and Endodontic Disease
4. Saliva as a Biological Fluid for Viral Diagnosis
4.1. Advantages of Saliva-Based Diagnostics
4.2. Saliva-Based Diagnostics and Self-Administered Testing
4.3. Advancements in Saliva-Based Diagnostics during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic
4.4. Accurate Alternatives to Saliva-Based Diagnostics
5. Discussion
6. Future Directions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregorczyk-Maga, I.; Fiema, M.; Kania, M.; Jachowicz-Matczak, E.; Romaniszyn, D.; Gerreth, K.; Klupa, T.; Wójkowska-Mach, J. Oral Microbiota—One Habitat or Diverse Niches? A Pilot Study of Sampling and Identification of Oral Bacterial and Fungal Biota in Patients with Type I Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Insulin Pump. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.L.; Bor, B.; Agnello, M.; Shi, W.; He, X. Ecology of the Oral Microbiome: Beyond Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghi, L.; DiMassa, V.; Harrington, A.; Lynch, S.V.; Kapila, Y.L. The Oral Microbiome: Role of Key Organisms and Complex Networks in Oral Health and Disease. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 87, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, P.; Banks, J.M.; Rahat, R.; Brandini, D.A.; Naqvi, A.R. Viruses of the Oral Cavity: Prevalence, Pathobiology and Association with Oral Diseases. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.R.; Shango, J.; Seal, A.; Shukla, D.; Nares, S. Herpesviruses and MicroRNAs: New Pathogenesis Factors in Oral Infection and Disease? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asai, D.; Nakashima, H. Pathogenic Viruses Commonly Present in the Oral Cavity and Relevant Antiviral Compounds Derived from Natural Products. Medicines 2018, 5, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomasini, R.L.; Pereira, F.S.M. Impact of Different Types of Herpesviral Infections in the Oral Cavity. WJS 2016, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatahzadeh, M.; Schwartz, R.A. Human Herpes Simplex Virus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Symptomatology, Diagnosis, and Management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 737–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimi, S.; Fiorillo, L.; Bianchi, A.; D’Amico, C.; Amoroso, G.; Gorassini, F.; Mastroieni, R.; Marino, S.; Scoglio, C.; Catalano, F.; et al. Herpes Virus, Oral Clinical Signs and QoL: Systematic Review of Recent Data. Viruses 2019, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, A.R.; Muddana, K. Viral Infections of Oral Cavity. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Morales, R.; Andreu, S.; López-Guerrero, J.A. The Role of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Infection in Demyelination of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Bielsa, A.; Gracia-Cazaña, T.; Aldea-Manrique, B.; Abadías-Granado, I.; Ballano, A.; Bernad, I.; Gilaberte, Y. COVID-19 Infection and Vaccines: Potential Triggers of Herpesviridae Reactivation. Anais Bras. Dermatol. 2023, 98, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atyeo, N.; Rodriguez, M.D.; Papp, B.; Toth, Z. Clinical Manifestations and Epigenetic Regulation of Oral Herpesvirus Infections. Viruses 2021, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phetsouphanh, C.; Darley, D.R.; Wilson, D.B.; Howe, A.; Munier, C.M.L.; Patel, S.K.; Juno, J.A.; Burrell, L.M.; Kent, S.J.; Dore, G.J.; et al. Immunological Dysfunction Persists for 8 Months Following Initial Mild-to-Moderate SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubchenko, S.; Kril, I.; Nadizhko, O.; Matsyura, O.; Chopyak, V. Herpesvirus Infections and Post-COVID-19 Manifestations: A Pilot Observational Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.A. Association between Human Herpes Virus and Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review. Saudi J. Dent. Res. 2017, 8, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, L.; Chacun, D.; Sy, K.; Grosgogeat, B.; Gritsch, K. Periodontal Diseases and COVID-19: A Scoping Review. Eur. J. Dent. 2021, 15, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia, J.C.; Guzzi, P.H.; Giorgi, F.M.; Khan, A.A. Predicting the Response of the Dental Pulp to SARS-CoV2 Infection: A Transcriptome-Wide Effect Cross-Analysis. Genes. Immun. 2020, 21, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafałowicz, B.; Wagner, L.; Rafałowicz, J. Long COVID Oral Cavity Symptoms Based on Selected Clinical Cases. Eur. J. Dent. 2022, 16, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Herpesviral–Bacterial Interactions in Periodontal Diseases: Herpesviral–Bacterial Interactions. Periodontol. 2000 2010, 52, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomo, S.; Miyahara, G.I.; Simonato, L.E. Oral Mucositis in a SARS-CoV-2-infected Patient: Secondary or Truly Associated Condition? Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paces, J.; Strizova, Z.; Smrz, D.; Cerny, J. COVID-19 and the Immune System. Physiol. Res. 2020, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindell, E. Studies on the Possible Presence of a Virus in Subacute and Chronic Periapical Granulomas. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1962, 15, 1382–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustigian, R.; Smulow, J.B.; Tye, M.; Gibson, W.A.; Shindell, E. Studies on Latent Infection of Skin and Oral Mucosa in Individuals with Recurrent Herpes Simplex**From the Departments of Microbiology, Periodontology and Dermatology, Tufts University School of Medicine and Dental Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1966, 47, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, B.; Slots, J. Detection of Human Viruses in Periodontal Pockets Using Polymerase Chain Reaction. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 11, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilichodmath, S.; Mangalekar, S.B.; Sharma, D.C.G.; Prabhakar, A.K.; Reddy, S.B.; Kalburgi, N.B.; Patil, S.R.; Bhat, K. Herpesviruses in Chronic and Aggressive Periodontitis Patients in an Indian Population. J. Oral Sci. 2009, 51, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankson, P.; Blankson, H.N.A.; Obeng-Nkrumah, N.; Turkson, A.A.; Tormeti, D.; Adamafio, M.; Awuah-Mensah, G.; Asmah, R.H. Detection of Herpes Viruses in Ghanaian Patients with Periodontitis. J. Invest. Clin. Dent. 2019, 10, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Krithiga, G.S.P.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Detection of Human Herpes Viruses in Patients with Chronic and Aggressive Periodontitis and Relationship between Viruses and Clinical Parameters. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2012, 16, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.R.; Brambila, M.F.; Martínez, G.; Chapa, G.; Nares, S. Dysregulation of Human miRNAs and Increased Prevalence of HHV miRNAs in Obese Periodontitis Subjects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puletic, M.; Popovic, B.; Jankovic, S.; Brajovic, G. Detection Rates of Periodontal Bacteria and Herpesviruses in Different Forms of Periodontal Disease. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 64, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotola, A.; Cassai, E.; Farina, R.; Caselli, E.; Gentili, V.; Lazzarotto, T.; Trombelli, L. Human Herpesvirus 7, Epstein–Barr Virus and Human Cytomegalovirus in Periodontal Tissues of Periodontally Diseased and Healthy Subjects. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agut, H.; Bonnafous, P.; Gautheret-Dejean, A. Laboratory and Clinical Aspects of Human Herpesvirus 6 Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, T.M.; Ferreira, D.C.; Carmo, F.L.; Pinheiro, R.; Leite, D.C.A.; Cavalcante, F.S.; Belinho, R.A.; Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, A.S.; dos Santos, K.R.N.; et al. Herpesvirus in the Oral Cavity of Children with Leukaemia and Its Impact on the Oral Bacterial Community Profile. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, A.J.; Rogers, R.S. Oral Manifestations of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Clin. Dermatol. 2004, 22, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatahzadeh, M. Oral Manifestations of Viral Infections. Atlas Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. 2017, 25, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairston, B.R.; Bruce, A.J.; Rogers, R.S. Viral Diseases of the Oral Mucosa. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovska-Stojanoska, M.; Popovska, M.; Anastasovska, V.; Kocova, M.; Zendeli-Bedzeti, L.; Dimova, C.; Taseva, A. Detection of Virus Herpes Simplex Type 1 in Patients with Chronic Periodontal Disease. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navidad, J.; Pfotenhauer, B.; Leigh, N.; Maas, E.; Gradus, S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Clinical Evaluation and Cost Analysis of a Trioplex Real-Time PCR Assay for the Detection and Differentiation of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 in Cutaneous and Mucocutaneous Lesions. J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Xia, D.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, W.; Xu, S.; Yin, Y. An Evaluation of a Multiplex PCR Assay for the Detection of Treponema Pallidum, HSV-1, and HSV-2. Diagn Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 106, 115958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-J.; Baek, Y.-H.; Park, M.-Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Sung, N.; Sohn, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.-E.; Yang, Y.-J. Performance Analysis of Self-Collected Nasal and Oral Swabs for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, A.D.; Gargiulo, C.I.; Malcangi, G.; Ciocia, A.M.; Patano, A.; Azzollini, D.; Piras, F.; Barile, G.; Settanni, V.; Mancini, A.; et al. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 during the Pandemic by Multiplex RT-rPCR hCoV Test: Future Perspectives. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S.M.; Filioreanu, A.M.; Stelea, C.G.; Grigoras, S.I.; Sufaru, I.G.; Maftei, G.A.; Martu, S.; Scutariu, M.M.; Popa, C. The Assessment of the Association between Herpesviruses and Subgingival Bacterial Plaque by Real-Time PCR Analysis. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Periodontal Herpesviruses: Prevalence, Pathogenicity, Systemic Risk. Periodontol. 2000 2015, 69, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, G.; Santonocito, S.; Lupi, S.M.; Polizzi, A.; Sclafani, R.; Patini, R.; Marchetti, E. Periodontal Health and Disease in the Context of Systemic Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 9720947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, E.Q.M.; da Rocha, T.E.; Toro, L.F.; Guiati, I.Z.; Freire, J.d.O.A.; Ervolino, E.; Brandini, D.A.; Garcia, V.G.; Theodoro, L.H. Adjuvant Effects of Curcumin as a Photoantimicrobial or Irrigant in the Non-Surgical Treatment of Periodontitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 34, 102265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras, A.; Slots, J. Mammalian Viruses in Human Periodontitis. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 11, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, A.; Mardirossian, A.; Slots, J. Herpesviruses in HIV-Periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2001, 28, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, A.; Umeda, M.; Chen, C.; Bakker, I.; Morrison, J.L.; Slots, J. Relationship Between Herpesviruses and Adult Periodontitis and Periodontopathic Bacteria. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, S.R.; Imbronito, A.V.; Okuda, O.S.; Pannuti, C.M.; Nunes, F.D.; Lima, L.A. Relationship Between Herpesviruses and Periodontopathogens in Patients With HIV and Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emecen-Huja, P.; Danaher, R.J.; Dawson, D.R., 3rd; Wang, C.; Kryscio, R.J.; Ebersole, J.L.; Miller, C.S. Relationship between Herpesviruses and Periodontal Disease Progression. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Consensus Report of Workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S286–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turri, A.; Rossetti, P.; Canullo, L.; Grusovin, M.; Dahlin, C. Prevalence of Peri-Implantitis in Medically Compromised Patients and Smokers: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-Implant Mucositis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S237–S245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, S.; Aleksic, Z.; Dimitrijevic, B.; Lekovic, V.; Milinkovic, I.; Kenney, B. Correlation between Different Genotypes of Human Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus and Peri-Implant Tissue Status: Viruses and Peri-Implant Tissue Status. Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Pesce, P.; Botticelli, D.; Covani, U.; Jankovic, S.; Jovanovic, T.; Rakic, M. What Is the Impact of Epstein-Barr Virus in Peri-Implant Infection? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthiban, S.; Ahmed, N.; Ramakrishnan, T.; Balakumar, V.; Raja, M.; Shekhar, H. Herpes Simplex 1 and Periopathogen Role in Peri-Implantitis. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahama, A.; de Lima, H.G.; Ito, F.A.; Ribeiro-Silva, A.; León, J.E. Epstein-Barr Virus–Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer Mimicking Peri-Implantitis in a Patient With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Filho, J.S.; Gobara, J.; da Silva Salomao, G.V.; Sumita, L.M.; Shibli, J.A.; Viana, R.G.; Schwartz Filho, H.O.; Pannuti, C.S.; Braz-Silva, P.H.; Pallos, D. Cytokine Levels and Human Herpesviruses in Saliva from Clinical Periodontal Healthy Subjects with Peri-Implantitis: A Case-Control Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandini, D.A.; Takamiya, A.S.; Thakkar, P.; Schaller, S.; Rahat, R.; Naqvi, A.R. Covid-19 and Oral Diseases: Crosstalk, Synergy or Association? Rev. Med. Virol. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus Report of Workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Classification and Case Definitions for Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, M.; Simon, J.H.; Slots, J. Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus Are Associated with Symptomatic Periapical Pathosis: Herpesviruses in Periapical Lesions. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 18, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slots, J.; Nowzari, H.; Sabeti, M. Cytomegalovirus Infection in Symptomatic Periapical Pathosis. Int. Endod. J. 2004, 37, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabeti, M.; Daneshmand, A.; Simon, J.H.; Slots, J. Cytomegalovirus-Infected Inflammatory Cells in Dental Periapical Lesions. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 24, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherme, B.P.S.; Ferreira, D.C.; Rôças, I.N.; Provenzano, J.C.; Santos, K.R.N.; Siqueira, J.F. Herpesvirus Carriage in Saliva and Posttreatment Apical Periodontitis: Searching for Association. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2011, 112, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, V.; Chen, Y.; Baumgartner, J.C.; Machida, C.A. Herpesviruses in Endodontic Pathoses: Association of Epstein-Barr Virus with Irreversible Pulpitis and Apical Periodontitis. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernádi, K.; Gyöngyösi, E.; Mészáros, B.; Szakács, L.; Szalmás, A.; Csoma, E.; Mogyorósi, R.; Czompa, L.; Veress, G.; Varga, I.; et al. Elevated Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Expression in Periapical Lesions Infected by Epstein-Barr Virus. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovljevic, A.; Knezevic, A.; Nikolic, N.; Soldatovic, I.; Jovanovic, T.; Milasin, J.; Andric, M. Herpesviruses Viral Loads and Levels of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Apical Periodontitis. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdugo, F.; Castillo, A.; Simonian, K.; Castillo, F.; Farez-Vidal, E.; D’Addona, A. Periodontopathogen and Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Periapical Periodontitis May Be the Source of Retrograde Infectious Peri-Implantitis: EBV-Associated Periapical Periodontitis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Takeichi, O.; Hatori, K.; Imai, K.; Ochiai, K.; Ogiso, B. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Chronically Inflamed Periapical Granulomas. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Periodontitis: Facts, Fallacies and the Future. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 75, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboia-Dantas, C.J.; Coutrin de Toledo, L.F.; Sampaio-Filho, H.R.; Siqueira, J.F. Herpesviruses in Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis Lesions: An Immunohistochemical Approach. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 22, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovljevic, A.; Andric, M. Human Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr Virus in Etiopathogenesis of Apical Periodontitis: A Systematic Review. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D. The Role of the Oral Cavity in SARS-CoV-2- and Other Viral Infections. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, S.M.; Peter, T.K.; Withanage, M.H.H.; Boksa, F.; Zeng, E.; Martinez, A.; Dabdoub, S.M.; Dhingra, K.; Hernandez-Kapila, Y. COVID-19 Associated Oral and Oropharyngeal Microbiome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Periodontol. 2000 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, N.; Granwehr, B.P.; Hanna, E.Y.; Chambers, M.S. Salivary Detection of SARS-CoV -2 ( COVID -19) and Implications for Oral Health-care Providers. Head Neck 2020, 42, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.M.; Ashwaq, O.; Sarief, A.; Azad John Mohamed, A.K. A Comprehensive Review about SARS-CoV-2. Future Virol. 2020, 15, 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Mohindra, R.; Chauhan, P.K.; Singla, V.; Goyal, K.; Sahni, V.; Gaur, R.; Verma, D.K.; Ghosh, A.; Soni, R.K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Gingival Crevicular Fluid. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim dos Santos, J.; Normando, A.G.C.; Carvalho da Silva, R.L.; De Paula, R.M.; Cembranel, A.C.; Santos-Silva, A.R.; Guerra, E.N.S. Oral Mucosal Lesions in a COVID-19 Patient: New Signs or Secondary Manifestations? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 97, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, T.B.; Gueiros, L.A.; Melo, T.S.; Prado-Ribeiro, A.C.; Nesrallah, A.C.F.A.; Prado, G.V.B.; Santos-Silva, A.R.; Migliorati, C.A. Oral Lesions in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Could the Oral Cavity Be a Target Organ? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2021, 131, e45–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Rodríguez, M.; Jimenez Romera, A.; Villarroel, M. Oral Manifestations Associated with COVID-19. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 960–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavina, A.; Biočina-Lukenda, D.; Mravak-Stipetić, M.; Markeljević, J. Oral Symptoms and Lesions in SARS-CoV-2-positive Patient. Oral Dis 2022, 28, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Cauhe, J.; Ortega-Quijano, D.; de Perosanz-Lobo, D.; Burgos-Blasco, P.; Vañó-Galván, S.; Fernandez-Guarino, M.; Fernandez-Nieto, D. Enanthem in Patients With COVID-19 and Skin Rash. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marouf, N.; Cai, W.; Said, K.N.; Daas, H.; Diab, H.; Chinta, V.R.; Hssain, A.A.; Nicolau, B.; Sanz, M.; Tamimi, F. Association between Periodontitis and Severity of COVID-19 Infection: A Case–Control Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín Carreras-Presas, C.; Amaro Sánchez, J.; López-Sánchez, A.F.; Jané-Salas, E.; Somacarrera Pérez, M.L. Oral Vesiculobullous Lesions Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Woolley, J. Necrotizing Periodontal Disease: Oral Manifestation of COVID-19. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 768–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riad, A.; Klugar, M.; Krsek, M. COVID-19-Related Oral Manifestations: Early Disease Features? Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapia-Orihuela, R.K.A. Hypertension and Coronavirus Disease 2019 Mortality. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1197–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradowska-Stolarz, A. Oral Manifestations of COVID-19: Brief Review. Dent. Med. Probl. 2021, 58, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, G.; Bizzoca, M.E.; Lo Muzio, L. COVID-19 and Periodontitis: Reflecting on a Possible Association. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larvin, H.; Wilmott, S.; Wu, J.; Kang, J. The Impact of Periodontal Disease on Hospital Admission and Mortality During COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 604980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, Z.; Gaudin, A.; Struillou, X.; Amador, G.; Soueidan, A. Periodontal Pockets: A Potential Reservoir for SARS-CoV-2? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, C.; Çelen, K.; Dede, F.Ö.; Gökmenoğlu, C.; Kara, N.B. Is Periodontal Disease a Risk Factor for Developing Severe Covid-19 Infection? The Potential Role of Galectin-3. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, V.; Gupta, S. COVID-19 & Periodontitis: The Cytokine Connection. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 109908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Kamio, N.; Kobayashi, R.; Iinuma, T.; Imai, K. Aspiration of Periodontopathic Bacteria Due to Poor Oral Hygiene Potentially Contributes to the Aggravation of COVID-19. J. Oral Sci. 2021, 63, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, K.; Tadepalli, A. Nexus between COVID-19 and Periodontal Disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 3000605211002695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G. Interconnection of Periodontal Disease and Comorbidities: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Implications. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 89, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martu, M.A.; Maftei, G.A.; Sufaru, I.G.; Jelihovschi, I.; Luchian, I.; Hurjui, L.; Martu, I.; Pasarin, L. COVID-19 and Periodontal Disease—Ethiopathogenic and Clinical Implications. Rom. J. Oral. Rehabil. 2020, 12, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, Y.; Hayakawa, A.; Sano, R.; Fukuda, H.; Harada, M.; Kubo, R.; Okawa, T.; Kominato, Y. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Suppress ACE2 and ABO Simultaneously, Suggesting a Preventive Potential against COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.F.; Morandini, A.C.; Dionísio, T.J.; Faria, F.A.; Lima, M.C.; Figueiredo, C.M.; Colombini-Ishikiriama, B.L.; Sipert, C.R.; Maciel, R.P.; Akashi, A.P.; et al. Functional Local Renin-Angiotensin System in Human and Rat Periodontal Tissue. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Lian, J.-Q.; Du, P.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.-X.; Gong, L.; et al. CD147-Spike Protein Is a Novel Route for SARS-CoV-2 Infection to Host Cells. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, M.; La, V.D.; Lombardo Bedran, T.B.; Palomari Spolidorio, D.M.; Grenier, D. Porphyromonas Gingivalis-Mediated Shedding of Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer (EMMPRIN) by Oral Epithelial Cells: A Potential Role in Inflammatory Periodontal Disease. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes Matuck, B.; Dolhnikoff, M.; Maia, G.V.A.; Isaac Sendyk, D.; Zarpellon, A.; Costa Gomes, S.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Rebello Pinho, J.R.; Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Sousa, S.C.O.M.; et al. Periodontal Tissues Are Targets for Sars-Cov-2: A Post-Mortem Study. J. Oral Microbiol. 2021, 13, 1848135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.S.; Jadhav, P.; Kamath, K.P.; Kumar, S.R.; Vijayalaxmi, S.; Anil, S. A Case-control Study on the Association between Periodontitis and Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). J. Periodontol. 2021, 93, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, L.; Ma, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, J.; Yang, D.; et al. Corrigendum to: Genomic Diversity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus 2 in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, ciab900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kawanami, T.; Yatera, K.; Fukuda, K.; Noguchi, S.; Nagata, S.; Nishida, C.; Kido, T.; Ishimoto, H.; Taniguchi, H.; et al. Significance of Anaerobes and Oral Bacteria in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestle, D.; Heindl, M.R.; Limburg, H.; Van Lam van, T.; Pilgram, O.; Moulton, H.; Stein, D.A.; Hardes, K.; Eickmann, M.; Dolnik, O.; et al. TMPRSS2 and Furin Are Both Essential for Proteolytic Activation of SARS-CoV-2 in Human Airway Cells. Life Sci. Alliance 2020, 3, e202000786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-S.; Sun, L.-W.; Brickner, H.; Sun, P.-Q. Downregulating Galectin-3 Inhibits Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells via RNA Interference. Cell Immunol. 2015, 294, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.; ISERC-Team; Reis, A.; Miranda, A.; Martins, C.; Serre-Miranda, C.; Nobrega, C.; Silva, C.S.; Sarmento, H.; Cotter, J.; et al. Increased Gal-3BP Plasma Levels in Hospitalized Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 23, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-H.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, M.R.; Urbina, A.N.; Assavalapsakul, W.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Chen, Y.-H.; Liu, F.-T.; Wang, S.-F. The Role of Galectins in Virus Infection - A Systemic Literature Review. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S. Metagenome of SARS-CoV2 Patients in Shenzhen with Travel to Wuhan Shows a Wide Range of Species—Lautropia, Cutibacterium, Haemophilus Being Most Abundant—And Campylobacter Explaining Diarrhea. 2020. Available online: https://osf.io/preprints/osf/jegwq (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Nardelli, C.; Gentile, I.; Setaro, M.; Di Domenico, C.; Pinchera, B.; Buonomo, A.R.; Zappulo, E.; Scotto, R.; Scaglione, G.L.; Castaldo, G.; et al. Nasopharyngeal Microbiome Signature in COVID-19 Positive Patients: Can We Definitively Get a Role to Fusobacterium Periodonticum? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Retamal-Valdes, B.; Alonso, B.; Feres, M. Acute Periodontal Lesions (Periodontal Abscesses and Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases) and Endo-Periodontal Lesions: Dd56II Joint EFP-AAP Workshop. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S85–S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Sampson, V. The Role of Oral Bacteria in COVID-19. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcuac, O.; Berglundh, T. Composition of Human Peri-Implantitis and Periodontitis Lesions. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N. Microbiological and Immuno-Pathological Aspects of Peri-Implant Diseases. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Tan, J. The Impact of the COVID-19 Epidemic on the Utilization of Emergency Dental Services. J. Dent. Sci. 2020, 15, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, D.; Haapasalo, M.; Shen, Y. Characteristics of Endodontic Emergencies during Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak in Wuhan. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosme-Silva, L.; Dal-Fabbro, R.; Cintra, L.T.A.; dos Santos, V.R.; Duque, C.; Ervolino, E.; Mogami Bomfim, S.; Gomes-Filho, J.E. Systemic Administration of Probiotics Reduces the Severity of Apical Periodontitis. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.G.; Lira Junior, R.; Retamal-Valdes, B.; Figueiredo, L.C.d.; Malheiros, Z.; Stewart, B.; Feres, M. Periodontal Disease and Its Impact on General Health in Latin America. Section V: Treatment of Periodontitis. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34, e026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, V.; Kamona, N.; Sampson, A. Could There Be a Link between Oral Hygiene and the Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infections? Br. Dent. J. 2020, 228, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.-A.; Kwon, J.-S.; Kim, S.-M.; Jeon, N.Y.; Kim, M.-C.; Chong, Y.P.; Lee, S.-O.; Choi, S.-H.; et al. Diagnostic Usefulness of Varicella-Zoster Virus Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis of DNA in Saliva and Plasma Specimens From Patients With Herpes Zoster. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 217, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohra, P.; Belkhode, V.; Nimonkar, S.; Potdar, S.; Bhanot, R.; Izna; Tiwari, R.V.C. Evaluation and Diagnostic Usefulness of Saliva for Detection of HIV Antibodies: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa Sierra, C.B.; Kourí Cardellá, V.; Pérez Santos, L.; Silverio, C.E.; Hondal, N.; Florin, J. Herpesviruses Excretion in Saliva of Pediatric Transplant Recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmento, D.J.d.S.; Caliento, R.; Souza, A.O.d.; Tozetto-Mendoza, T.R.; Palmieri, M.; Martins, V.A.d.O.; Braz-Silva, P.H.; Gallottini, M. Salivary Shedding of Herpesviruses in Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.; Yapar, M.; Kubar, A. Detection and Quantification of Herpesviruses in Kostmann Syndrome Periodontitis Using Real-time Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Case Report. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 21, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.K.; Nelman-Gonzalez, M.; Tyring, S.K.; Tong, Y.; Beitman, A.; Crucian, B.E.; Renner, A.N.; Pierson, D.L. Localization of VZV in Saliva of Zoster Patients. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1686–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, J.; Jeon, N.Y.; Kim, M.; Chong, Y.P.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Woo, J.H.; et al. Relationships of Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV)-specific Cell-mediated Immunity and Persistence of VZV DNA in Saliva and the Development of Postherpetic Neuralgia in Patients with Herpes Zoster. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Selva, A.; Negreiros, R.M.; Bezerra, D.T.; Rosa, E.P.; Pavesi, V.C.S.; Navarro, R.S.; Bello-Silva, M.S.; Ramalho, K.M.; Aranha, A.C.C.; Braz-Silva, P.H.; et al. Treatment of Herpes Labialis by Photodynamic Therapy: Study Protocol Clinical Trial (SPIRIT Compliant). Medicine 2020, 99, e19500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, K.M.; Cunha, S.R.; Gonçalves, F.; Escudeiro, G.S.; Steiner-Oliveira, C.; Horliana, A.C.R.T.; Eduardo, C.d.P. Photodynamic Therapy and Acyclovir in the Treatment of Recurrent Herpes Labialis: A Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 33, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farisyi, M.A.; Sufiawati, I. Detection of Epstein–Barr Virus DNA in Saliva of HIV-1-infected Individuals with Oral Hairy Leukoplakia. Oral Dis. 2020, 26, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, M.M.; Dunn, D.T.; Speakman, A.; McCabe, L.; Ward, D.; Witzel, T.C.; Harbottle, J.; Collins, S.; Gafos, M.; Burns, F.M.; et al. Protocol, Rationale and Design of SELPHI: A Randomised Controlled Trial Assessing Whether Offering Free HIV Self-Testing Kits via the Internet Increases the Rate of HIV Diagnosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzel, T.C.; Bourne, A.; Burns, F.M.; Rodger, A.J.; McCabe, L.; Gabriel, M.M.; Gafos, M.; Ward, D.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Dunn, D.T.; et al. HIV Self-Testing Intervention Experiences and Kit Usability: Results from a Qualitative Study among Men Who Have Sex with Men in the SELPHI (Self-Testing Public Health Intervention) Randomized Controlled Trial in England and Wales. HIV Med. 2020, 21, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shaibari, K.S.A.; Mousa, H.A.-L.; Alqumber, M.A.A.; Alqfail, K.A.; Mohammed, A.; Bzeizi, K. The Diagnostic Performance of Various Clinical Specimens for the Detection of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of RT-PCR Studies. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lübke, N.; Repges, K.; Menne, C.; Walker, A.; Jensen, B.-E.O.; Freise, N.F.; Gliga, S.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Bosse, H.M.; Adams, O.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Different Respiratory Specimens on Two Automated Test Systems for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 105, 115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Wan, R.; Zhang, Q. Application of Reverse Transcription-PCR and Real-Time PCR in Nanotoxicity Research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 926, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, H. The Oral Cavity Potentially Serving as a Reservoir for SARS-CoV-2 but Not Necessarily Facilitating the Spread of COVID-19 in Dental Practice. Eur. J. Dent. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.C.; Rôças, I.N.; Paiva, S.S.M.; Carmo, F.L.; Cavalcante, F.S.; Rosado, A.S.; Santos, K.R.N.; Siqueira, J.F. Viral-Bacterial Associations in Acute Apical Abscesses. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2011, 112, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabeti, M.; Slots, J. Herpesviral-Bacterial Coinfection in Periapical Pathosis. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero, J.E.; Parra, B.; Jaramillo, A.; Contreras, A. Subgingival Human Cytomegalovirus Correlates with Increased Clinical Periodontal Parameters and Bacterial Coinfection in Periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slots, J. Herpesviruses in Periodontal Diseases. Periodontol. 2000 2005, 38, 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhong, M.-M.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Zhao, J.; Dusenge, M.A.; Feng, Y.; Ye, Q.; Hu, J.; et al. Potential Interaction between the Oral Microbiota and COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis and Bioinformatics Prediction. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1193340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, E.; Israelow, B.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Lu, P.; Wyllie, A.L.; Tokuyama, M.; Venkataraman, A.; Brackney, D.E.; Ott, I.M.; Petrone, M.E.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by Multiplex RT-qPCR. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Conley, B.M.; Shin, M.; Choi, J.-H.; Bektas, C.K.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, K.-B. Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of Mutated Viral RNAs with Single-Nucleotide Resolution Using a Nanoporous Electrode Array (NPEA). ACS Nano 2022, 16, 5764–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, S.K.; Bullotta, A.; Husain, S.; Rinaldo, C.R. Clinical Evaluation of Multiplex Real-Time PCR Panels for Rapid Detection of Respiratory Viral Infections. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourout, M.; Fisher, C.; Purkayastha, A.; Tibbetts, C.; Winkelman, V.; Williamson, P.; Nakhasi, H.L.; Duncan, R. Multiplex Detection and Identification of Viral, Bacterial, and Protozoan Pathogens in Human Blood and Plasma Using a High-Density Resequencing Pathogen Microarray Platform. Transfusion 2016, 56, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Simultaneous Detection of Five Notifiable Viral Diseases of Cattle by Single-Tube Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 217, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Single-Tube Multiplexed Molecular Detection of Endemic Porcine Viruses in Combination with Background Screening for Transboundary Diseases. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Human Herpesviruses (Linear, Double-Stranded DNA, Enveloped Vírus) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Herpes Simplex Virus-1 (HSV-1) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Persistent mucocutaneous and oral lesions; recurrent herpetiform ulcerations (sold Sores) | Severe generalized pain in oral cavity, difficulty eating and opening mouth | Oral necrotizing disease | Valacyclovir (anti-viral); immunosuppressive and myeloablative agents (busulfan IV, fludarabine, fludarabine, keratinocyte growth factor), antibiotics (amoxicillin/clavulanate) (pre-transplant); superficial cleanings, chlorhexidine (post-transplant) |
| Infection of the gums | Tissue destruction, loss of connective tissues that support teeth | Aggressive periodontitis | Deep cleaning (scaling, root planing) |
| Oral nodular lesions; oral hairy leukoplakia | Recurrent oral ulcers, lip ulceration, painful nodular lesions on tongue, gums, and palate, fevers, rigors, inflammation | Immune Reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) | High-dose cotrimoxazole and oral therapy, tenofovir/emtricitabine and efavirenz (antiretroviral), antituberculosis therapy, acyclovir |
| Neonatal gingival infection | Decreased eating/drinking, lethargy, vomiting, hypoxia in neonates; Fever, muscle and joint pain, lesions in oropharynx, along vermillion border | Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis (PHGS) | Valacyclovir for mother; acyclovir, ampicillin, gentamicin for neonate |
| Herpes Simplex Virus-2 (HSV-2) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Painful infection of gingival and hard palate | Low fever, malaise, cervical lymphadenopathy, severely painful oral lesions, marginal alveolar bone loss | Acute herpetic gingivostomatitis (AHGS)/primary herpetic gingivostomatitis (PHGS) | Acyclovir (antiviral), betadine mouthwash, oral analgesics |
| Varicella-Zoster Virus (VSV) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Infection of maxillary and mandibular branches of trigeminal nerve, oral vesicles | Mucosal vesicles and erosion, jaw osteonecrosis, teeth exfoliation, pulp calcification and necrosis, periapical lesions, lichen planus in oral cavity (gingival erythema and leukoplakia), severe pain | Herpes zoster infection (HZI); severe periodontitis; internal root resorption | Root canal |
| Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Periodontal infection | Persistent and severe inflammation of the gums due to immune response, alveolar bone resorption and loss of tooth attachment | Periodontitis (in Kostmann syndrome)/aggressive periodontitis | Scaling, deep cleaning, trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (antibiotics) |
| Endodontic infection | Endodontic tissue swelling | Apical periodontitis | Antibiotics, root canal |
| Endodontic lesions | Slow-healing oral lesions, endodontic abscesses | Pulp necrosis | Root canal, coronal restoration |
| Subgingival infection | Probing depths ≥ 6 mm, recurrent gum inflammation, no response to conventional treatment | Severe periodontitis | Valacyclovir (Valtrex®, antiviral) |
| Recurrent ulcers in oral mucosa | Sores due to ulcers in oral mucosa, lip and facial swelling | Lymphoproliferative disorder (can be mistaken for aggressive lymphoma) | Antibiotics (not successful) |
| Oral epithelial cell infection; lymphatic B cell infection | Sore throat, decreased appetite, fatigue, myalgia, cough, runny and stuffy nose | Infectious mononucleosis (kissing disease) | Corticosteroids (to open airways), valacyclovir |
| Oral mucosa infection | Oral mucosa lesion, soft and white, asymptomatic lesion, hairy surface usually on lateral aspect of tongue (lesions have been reported in oropharynx, soft palate, buccal mucosa, and mouth floor) | Oral hairy leukoplakia (OHL) | Valacyclovir, acyclovir, and desciclovir (antivirals) |
| Mediates nasopharyngeal carcinogenesis | Tumor growth, metastasis | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) | Surgical removal (nasopharyngectomy), chemotherapy, immunotherapy (immune checkpoint inhibitor) |
| Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Infection of the gums | Destruction of oral connective tissues, inflammation, tissue loss | Periodontitis (in Kostmann syndrome) | Scaling, deep cleaning, chlorhexidine rinse, trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (antibiotics) |
| Endodontic infection | Endodontic tissue swelling | Apical periodontitis | Root canal |
| Endodontic lesions | Slow-healing oral lesions, endodontic abscesses | Pulp necrosis | Root canal, coronal restoration |
| Oral ulcers following organ transplant | Oral lesions following renal transplant (lesions in buccal mucosa, hard and soft palate, tongue, and mouth floor) | Cytomegalovirus disease | Prednisone, Tacrolimus, Cyclosporin A, Azathioprine, Mycophenolate Mofetil (immunosuppressants), Ganciclovir (antiviral) |
| Human Herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Endodontic infection | Endodontic tissue swelling | Apical periodontitis | Root canal |
| Endodontic lesions | Slow-healing oral lesions, endodontic abscesses | Pulp necrosis | Root canal, coronal restoration |
| Human Herpesvirus-7 (HHV-7) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Periodontium infection | Elevated viral expression as measured by PCR in gingival and periodontal tissue, tissue acting as a viral reservoir/infection site | None | None |
| Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) | |||
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Endodontic infection | Endodontic tissue swelling | Apical periodontitis | Root canal |
| Endodontic lesions | Slow-healing oral lesions, endodontic abscesses | Pulp necrosis | Root canal, coronal restoration |
| SARS-CoV-2 (Linear, Single-Stranded RNA, Enveloped Vírus) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Manifestations | Signs and Symptoms | Disease Association | Treatment |
| Necrotizing gingivitis | Necrotic interdental papillae, bleeding in gingival sulcus and halitosis, erythematous and oedematous gingivae | Oral necrotizing disease | Debridement, deep cleaning (scaling, root planning), metronidazole or ampicillin, chlorhexidine mouthwash |
| Dark pigmentation | Dark brown pigmentation in the palate and gingiva | Oral melanotic macule, oral lichen planus, oral cancer | Ibuprofen |
| Xerostomia | Dry feeling in the mouth, frequent thirst, difficulty swallowing dry foods, diminished or altered taste | Periodontitis, caries, COVID-19 | Artificial saliva substitutes |
| Dysgeusia | Altered taste perception (frequent metallic or bitter taste) | Periodontitis, COVID-19 | Addressing cause of dysgeusia (e.g., vitamin supplements for vitamin deficiency, switching medications if dysgeusia is a side effect of medication) |
| Mucositis | Red pigmentation and swelling on affected mucous membranes, ulcers and sores | Gingivitis, periodontitis, COVID-19 | Benzydamine, artificial saliva substitutes, low-level laser therapy |
| Periodontal infection | Persistent and severe inflammation of the gums due to immune response, alveolar bone resorption and loss of tooth attachment | Periodontitis (in COVID-19) | Scaling, deep cleaning, trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (antibiotics) |
| Erythematous bullae on palate | Erythema (redness), fluid-filled blisters, pain or tenderness on palate | Pemphigus vulgaris, HSV infection, COVID-19 | Corticosteroids, acyclovir or valacyclovir, saline rinse |
| Tongue depapillation | Flat or glossy tongue surface, xerostomia, halitosis | Candida infection, COVID-19 | Nystatin oral suspension or fluconazole |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banks, J.M.; Capistrano, K.J.; Brandini, D.A.; Zaidi, F.; Thakkar, P.; Rahat, R.; Schwartz, J.; Naqvi, A.R. Herpesviruses and SARS-CoV-2: Viral Association with Oral Inflammatory Diseases. Pathogens 2024, 13, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010058
Banks JM, Capistrano KJ, Brandini DA, Zaidi F, Thakkar P, Rahat R, Schwartz J, Naqvi AR. Herpesviruses and SARS-CoV-2: Viral Association with Oral Inflammatory Diseases. Pathogens. 2024; 13(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanks, Jonathan M., Kristelle J. Capistrano, Daniela A. Brandini, Filza Zaidi, Pari Thakkar, Rani Rahat, Joel Schwartz, and Afsar R. Naqvi. 2024. "Herpesviruses and SARS-CoV-2: Viral Association with Oral Inflammatory Diseases" Pathogens 13, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010058
APA StyleBanks, J. M., Capistrano, K. J., Brandini, D. A., Zaidi, F., Thakkar, P., Rahat, R., Schwartz, J., & Naqvi, A. R. (2024). Herpesviruses and SARS-CoV-2: Viral Association with Oral Inflammatory Diseases. Pathogens, 13(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13010058