A Soft Master-Slave Robot Mimicking Octopus Arm Structure Using Thin Artificial Muscles and Wire Encoders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
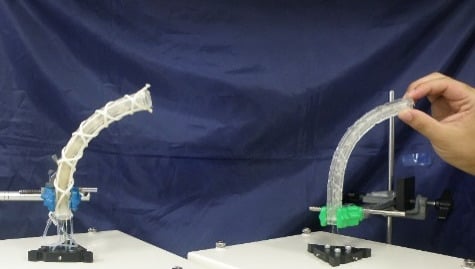
2. Structure of the Soft Robot Arm
2.1. Thin McKibben Artificial Muscle
2.2. Soft Robot Arm Structure
3. Master-Slave Control of the Soft Robot Arm
3.1. Configuration of the Sensing Part
3.2. Master-Slave Control
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzumori, K.; Ikuta, S.; Tanaka, H. Development of Flexible Microactuator and Its Applications to Robotic Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Sacramento, CA, USA, 9–11 April 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Folladora, M.; Dario, P. Soft Robot Arm Inspired by the Octopus. Adv. Rob. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; McMahan, W.; Walker, I. Design and Analysis of a Novel Pneumatic Manipulator. Int. Fed. Acc. Mechatron. Syst. 2004, 37, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.K.; Patkar, U.S.; Majumdar, S. Micro gripper for micromanipulation using IPMCs (ionic polymer metal composites). J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2009, 68, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J.; Culha, U.; Giardina, F.; Guenther, F.; Rosendo, A.; Iida, F. Soft Manipulators and Grippers: A Review. Front. Rob. AI 2016, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, H.F. The Characteristics of the McKibben Artificial Muscle. In The Application of External Power in Prosthetics and Orthotics; National Academy of Science-National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; pp. 94–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.P.; Hannaford, B. Measurement and modeling of McKibben pneumatic artificial muscles. IEEE Trans. Rob. Autom. 1996, 12, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tondu, B. Robust and Accurate Closed-Loop Control of McKibben Artificial Muscle Contraction with a Linear Single Integral Action. Actuators 2014, 3, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Ibadi, A.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Davis, S. Efficient Structure-Based Models for the McKibben Contraction Pneumatic Muscle Actuator: The Full Description of the Behaviour of the Contraction PMA. Actuators 2017, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothera, C.S.; Jangid, M.; Sirohi, J.; Wereley, N.M. Experimental Characterization and Static Modeling of McKibben Actuators. J. Mech. Des. 2009, 131, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felt, W.; Chin, K.Y.; Remy, C.D. Smart Braid Feedback for the Closed-Loop Control of Soft Robotic Systems. Soft Rob. 2017, 4, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakimoto, S.; Misumi, J.; Suzurmoi, K. New concept and fundamental experiments of a smart pneumatic artificial muscle with a conductive fiber. Sens. Actuators A 2016, 250, 15–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Saitoh, H.; Kawakami, T.; Yamanishi, S.; Ikemoto, S.; Hosoda, K. Development of an embedded sensor system for pneumatic artificial muscle proprioceptors. Artif. Life Rob. 2016, 21, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noritsugu, T.; Sasaki, D.; Kameda, M.; Fukunaga, A.; Takaiwa, M. Wearable Power Assist Device for Standing Up Motion Using Pneumatic Rubber Artificial Muscles. J. Rob. Mechatron. 2007, 19, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.J.; Wu, M.J.; Lu, T.J.; Wu, F.K.; Hyang, C.R. Control of McKibben pneumatic muscles for a power-assist, lower-limb orthosis. Mechatronics 2010, 20, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Aida, T.; Hashimoto, T. Muscle suit development and factory application. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 2009, 3, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurumaya, S.; Suzumori, K.; Nabae, H.; Wakimoto, S. Musculoskeletal lower-limb robot driven by multifilament muscles. Robomech J. 2016, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takuma, T.; Hosoda, K. Controlling the Walking Period of a Pneumatic Muscle Walker. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2006, 25, 9–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faudzi, A.A.M.; Endo, G.; Kurumaya, S.; Suzumori, K. Long-Legged Hexapod Giacometti Robot Using Thin Soft McKibben Actuator. IEEE Rob. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, P.; Valle, L.; King, J.; Low, K.; Yi, J.; Atkeson, C.G.; Park, Y.L. Design of a Lightweight Soft Robotic Arm Using Pneumatic Artificial Muscles and Inflatable Sleeves. Soft Rob. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Abeach, L.A.T.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Davis, S. Design of a Variable Stiffness Soft Dexterous Gripper. Soft Rob. 2017, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, W.; Chitrakaran, V.; Csencsite, M.; Dawson, C.; Walker, I.D.; Jones, B.A.; Pritts, M.; Dienno, D.; Grissom, M.; Rahn, C.D. Field Trials and Testing of the OctArm Continuum Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, K.; Suzumori, K.; Wakimoto, S. Development of contraction and extension artificial muscles with different braid angles and their application to stiffness changeable bending rubber mechanism by their combination. J. Rob. Mechatron. 2011, 23, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S.; Sudani, M.; Deng, M.; Noge, Y.; Wakimoto, S. Modeling and system integration for a thin pneumatic rubber 3-DOF actuator. Actuators 2019, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, T.; Wakimoto, S.; Suzumori, K.; Mori, K. Proposal of Flexible robotic arm with thin McKibben actuators mimicking octopus arm structure. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aliff, M.; Dohta, S.; Akagi, T.; Li, H. Development of a Simple-Structured Pneumatic Robot Arm and its Control using Low-Cost Embedded Controller. Procedia Eng. 2012, 41, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Rahn, D.R.; Kier, W.M.; Walker, I.D. Soft robotics: Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, D.; Noritsugu, T.; Takaiwa, M. Wearable master-slave training device for lower limb constructed with pneumatic rubber artificial muscles. In Proceedings of the JFPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, Toyama, Japan, 15–18 September 2008. [Google Scholar]

















© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furukawa, S.; Wakimoto, S.; Kanda, T.; Hagihara, H. A Soft Master-Slave Robot Mimicking Octopus Arm Structure Using Thin Artificial Muscles and Wire Encoders. Actuators 2019, 8, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020040
Furukawa S, Wakimoto S, Kanda T, Hagihara H. A Soft Master-Slave Robot Mimicking Octopus Arm Structure Using Thin Artificial Muscles and Wire Encoders. Actuators. 2019; 8(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurukawa, Shota, Shuichi Wakimoto, Takefumi Kanda, and Hiroki Hagihara. 2019. "A Soft Master-Slave Robot Mimicking Octopus Arm Structure Using Thin Artificial Muscles and Wire Encoders" Actuators 8, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020040
APA StyleFurukawa, S., Wakimoto, S., Kanda, T., & Hagihara, H. (2019). A Soft Master-Slave Robot Mimicking Octopus Arm Structure Using Thin Artificial Muscles and Wire Encoders. Actuators, 8(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/act8020040