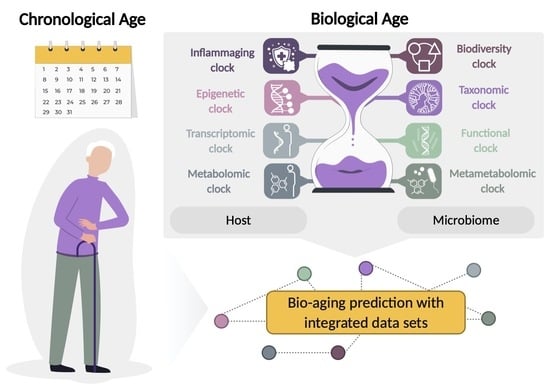
Utilization of Host and Microbiome Features in Determination of Biological Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Aging Clocks
2.1. Host-Based Aging Clocks
2.2. Microbiome-Based Diversity Clock
2.3. Microbiome-Based Taxonomic Clock
2.4. Microbiome-Based Functional Clock
2.5. Metametabolomic Clock
2.6. Integrated Data Sets in Predicting Biological Age
3. Perspectives, Opportunities, and Challenges in the Research of Microbiome Aging Clocks
3.1. Implication of Host and Microbiome Features in Determination of Age-Associated Diseases
3.2. Challenges in Microbiome Aging Research
3.3. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundu, P.; Blacher, E.; Elinav, E.; Pettersson, S. Our Gut Microbiome: The Evolving Inner Self. Cell 2017, 171, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bashiardes, S.; Abdeen, S.K.; Elinav, E. Personalized Nutrition: Are We There Yet? J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falony, G.; Joossens, M.; Vieira-silva, S.; Wang, J.; Darzi, Y.; Faust, K.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Valles-colomer, M.; Vandeputte, D.; et al. Population-Level Analysis of Gut Microbiome Variation. Science 2016, 352, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhernakova, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Schirmer, M.; Vatanen, T.; Mujagic, Z. Population-Based Metagenomics Analysis Reveals Markers for Gut Microbiome Composition and Diversity. Science 2016, 352, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McHugh, D.; Gil, J. Senescence and Aging: Causes, Consequences, and Therapeutic Avenues. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jagger, C.; Gillies, C.; Moscone, F.; Cambois, E.; van Oyen, H.; Nusselder, W.; Robine, J.-M. Inequalities in Healthy Life Years in the 25 Countries of the European Union in 2005: A Cross-National Meta-Regression Analysis. Lancet 2008, 372, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.Y.; Hendi, A.S. Recent Trends in Life Expectancy across High Income Countries: Retrospective Observational Study. BMJ 2018, 362, k2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afshin, A.; Sur, P.J.; Fay, K.A.; Cornaby, L.; Ferrara, G.; Salama, J.S.; Mullany, E.C.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Health Effects of Dietary Risks in 195 Countries, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crimmins, E.M. Recent Trends and Increasing Differences in Life Expectancy Present Opportunities for Multidisciplinary Research on Aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, A.; Wang, D.D.; Liu, X.; Dhana, K.; Franco, O.H.; Kaptoge, S.; di Angelantonio, E.; Stampfer, M.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Impact of Healthy Lifestyle Factors on Life Expectancies in the US Population. Circulation 2018, 138, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, G.B.; Kreiner, C.T.; Nielsen, T.H.; Serena, B.L. Understanding the Rise in Life Expectancy Inequality. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2021, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Cusack, S.; O’Sullivan, O.; Greene-Diniz, R.; de Weerd, H.; Flannery, E.; Marchesi, J.R.; Falush, D.; Dinan, T.; Fitzgerald, G.; et al. Composition, Variability, and Temporal Stability of the Intestinal Microbiota of the Elderly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeffery, I.B.; Lynch, D.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Composition and Temporal Stability of the Gut Microbiota in Older Persons. ISME J. 2016, 10, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thevaranjan, N.; Puchta, A.; Schulz, C.; Naidoo, A.; Szamosi, J.C.; Verschoor, C.P.; Loukov, D.; Schenck, L.P.; Jury, J.; Foley, K.P.; et al. Age-Associated Microbial Dysbiosis Promotes Intestinal Permeability, Systemic Inflammation, and Macrophage Dysfunction. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 455–466.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariat, D.; Firmesse, O.; Levenez, F.; Guimarǎes, V.D.; Sokol, H.; Doré, J.; Corthier, G.; Furet, J.P. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio of the Human Microbiota Changes with Age. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiihonen, K.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Rautonen, N. Human Intestinal Microbiota and Healthy Ageing. Ageing Res. Rev. 2010, 9, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; Beaumont, M.; Bell, J.T.; Clark, A.G.; Ley, R.E.; O’Toole, P.W.; Spector, T.D.; Steves, C.J. Signatures of Early Frailty in the Gut Microbiota. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Mejía, J.L.; Khakimov, B.; Krych, Ł.; Bülow, J.; Bechshøft, R.L.; Højfeldt, G.; Mertz, K.H.; Garne, E.S.; Schacht, S.R.; Ahmad, H.F.; et al. Physical Fitness in Community-dwelling Older Adults Is Linked to Dietary Intake, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolomic Signatures. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’sullivan, O.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Correlates with Diet and Health in the Elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Rampelli, S.; Turroni, S.; Quercia, S.; Candela, M.; Brigidi, P. The Gut Microbiota of Centenarians: Signatures of Longevity in the Gut Microbiota Profile. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 165, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Peña, C.; Álvarez-Cisneros, T.; Quiroz-Baez, R.; Friedland, R.P. Microbiota and Aging. A Review and Commentary. Arch. Med. Res. 2017, 48, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavella, T.; Rampelli, S.; Guidarelli, G.; Bazzocchi, A.; Gasperini, C.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Comte, B.; Barone, M.; Biagi, E.; Candela, M.; et al. Elevated Gut Microbiome Abundance of Christensenellaceae, Porphyromonadaceae and Rikenellaceae Is Associated with Reduced Visceral Adipose Tissue and Healthier Metabolic Profile in Italian Elderly. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1880221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidell, J.C.; Oosterlee, A.; Deurenberg, P.; Hautvast, J.G.; Ruijs, J.H. Abdominal Fat Depots Measured with Computed Tomography: Effects of Degree of Obesity, Sex, and Age. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 42, 805–815. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, M.; Martucci, M.; Sandri, M.; Franceschi, C.; Salvioli, S. The Dual Role of the Pervasive ‘Fattish’ Tissue Remodeling with Age. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinders, I.; Visser, M.; Schaap, L. Body Weight and Body Composition in Old Age and Their Relationship with Frailty. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, W.J.; Campbell, W.W. Sarcopenia and Age-Related Changes in Body Composition and Functional Capacity. J. Nutr. 1993, 123, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, J.-P.; Lemieux, I.; Bergeron, J.; Pibarot, P.; Mathieu, P.; Larose, E.; Rodés-Cabau, J.; Bertrand, O.F.; Poirier, P. Abdominal Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome: Contribution to Global Cardiometabolic Risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X. The Epidemiology of Central Fat Distribution in Relation to Disease. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, S120–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, R.A.; Irwin, R.; Quach, D.; Schaefer, L.; Zhang, J.; Lee, T.; Parameswaran, N.; McCabe, L.R.; Probiotic, L. Reuteri Treatment Prevents Bone Loss in a Menopausal Ovariectomized Mouse Model. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, A.G.; Sundh, D.; Bäckhed, F.; Lorentzon, M. Lactobacillus Reuteri Reduces Bone Loss in Older Women with Low Bone Mineral Density: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 284, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A New Immune–Metabolic Viewpoint for Age-Related Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; de Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; de Benedictis, G. Inflamm-Aging: An Evolutionary Perspective on Immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Franceschi, C.; Rampelli, S.; Severgnini, M.; Ostan, R.; Turroni, S.; Consolandi, C.; Quercia, S.; Scurti, M.; Monti, D.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Extreme Longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Zeng, T.; Zinellu, A.; Rubino, S.; Kelvin, D.J.; Carru, C. A Cross-Sectional Study of Compositional and Functional Profiles of Gut Microbiota in Sardinian Centenarians. mSystems 2019, 4, e00325-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bárcena, C.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Mayoral, P.; Garabaya, C.; Durand, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández-García, M.T.; Salazar, N.; Nogacka, A.M.; Garatachea, N.; et al. Healthspan and Lifespan Extension by Fecal Microbiota Transplantation into Progeroid Mice. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelli, S.; Soverini, M.; D’Amico, F.; Barone, M.; Tavella, T.; Monti, D.; Capri, M.; Astolfi, A.; Brigidi, P.; Biagi, E.; et al. Shotgun Metagenomics of Gut Microbiota in Humans with up to Extreme Longevity and the Increasing Role of Xenobiotic Degradation. mSystems 2020, 5, e00124-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Atarashi, K.; Plichta, D.R.; Arai, Y.; Sasajima, S.; Kearney, S.M.; Suda, W.; Takeshita, K.; Sasaki, T.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Novel Bile Acid Biosynthetic Pathways Are Enriched in the Microbiome of Centenarians. Nature 2021, 599, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Ostan, R.; Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; Capri, M.; Franceschi, C. Gut Microbiota Changes in the Extreme Decades of Human Life: A Focus on Centenarians. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Hazelton, W.D.; Luebeck, G.E.; Grady, W.M. Epigenetic Aging: More Than Just a Clock When It Comes to Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Yin, S.; Zhu, X.; Ren, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Z.; Niu, Y.-N.; Huang, X.; Li, J. Linking Inter-Individual Variability in Functional Brain Connectivity to Cognitive Ability in Elderly Individuals. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lowsky, D.J.; Olshansky, S.J.; Bhattacharya, J.; Goldman, D.P. Heterogeneity in Healthy Aging. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitnitski, A.; Rockwood, K. Aging as a Process of Deficit Accumulation: Its Utility and Origin. In Aging and Health—A Systems Biology Perspective; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 40, pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Galkin, F.; Mamoshina, P.; Aliper, A.; de Magalhães, J.P.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Zhavoronkov, A. Biohorology and Biomarkers of Aging: Current State-of-the-Art, Challenges and Opportunities. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 60, 101050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, N.; Huang, Y.; Nguyen, K.; Krejciova-Rajaniemi, Z.; Grawe, A.P.; Gao, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Alpert, A.; Cui, L.; et al. An Inflammatory Aging Clock (IAge) Based on Deep Learning Tracks Multimorbidity, Immunosenescence, Frailty and Cardiovascular Aging. Nat. Aging 2021, 1, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S.; Raj, K. DNA Methylation-Based Biomarkers and the Epigenetic Clock Theory of Ageing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoshina, P.; Volosnikova, M.; Ozerov, I.V.; Putin, E.; Skibina, E.; Cortese, F.; Zhavoronkov, A. Machine Learning on Human Muscle Transcriptomic Data for Biomarker Discovery and Tissue-Specific Drug Target Identification. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopu, V.; Cai, Y.; Krishnan, S.; Rajagopal, S.; Camacho, F.R.; Toma, R.; Torres, P.J.; Vuyisich, M.; Perlina, A.; Banavar, G.; et al. An Accurate Aging Clock Developed from the Largest Dataset of Microbial and Human Gene Expression Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Aging. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.H.; Schumacher, B. BiT Age: A Transcriptome-Based Aging Clock near the Theoretical Limit of Accuracy. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.A.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Lehallier, B. Systematic Review and Analysis of Human Proteomics Aging Studies Unveils a Novel Proteomic Aging Clock and Identifies Key Processes That Change with Age. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 60, 101070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehallier, B.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Johnson, A.A. Data Mining of Human Plasma Proteins Generates a Multitude of Highly Predictive Aging Clocks That Reflect Different Aspects of Aging. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehallier, B.; Gate, D.; Schaum, N.; Nanasi, T.; Lee, S.E.; Yousef, H.; Moran Losada, P.; Berdnik, D.; Keller, A.; Verghese, J.; et al. Undulating Changes in Human Plasma Proteome Profiles across the Lifespan. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Akker, E.B.; Trompet, S.; Wolf, J.J.H.B.; Beekman, M.; Suchiman, H.E.D.; Deelen, J.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Boersma, E.; Cats, D.; Elders, P.M.; et al. Predicting Biological Age Based on the BBMRI-NL 1H-NMR Metabolomics Repository. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertel, J.; Friedrich, N.; Wittfeld, K.; Pietzner, M.; Budde, K.; van der Auwera, S.; Lohmann, T.; Teumer, A.; Völzke, H.; Nauck, M.; et al. Measuring Biological Age via Metabonomics: The Metabolic Age Score. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, M.A.; Eden, G.; Ryan, F.J.; Bensalem, J.; Wang, X.; Blake, S.J.; Choo, J.M.; Chern, Y.T.; Sribnaia, A.; James, J.; et al. The Composition of the Gut Microbiota Following Early-Life Antibiotic Exposure Affects Host Health and Longevity in Later Life. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, A.T.; Reimer, R.A. Obesity, Early Life Gut Microbiota, and Antibiotics. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubaud-Baudron, C.; Ruiz, V.E.; Swan, A.M.; Vallance, B.A.; Ozkul, C.; Pei, Z.; Li, J.; Battaglia, T.W.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Blaser, M.J. Long-Term Effects of Early-Life Antibiotic Exposure on Resistance to Subsequent Bacterial Infection. mBio 2019, 10, e02820-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, G.B.; Papanicolas, L.E.; Wesselingh, S.L. Antibiotic Stewardship in Aged Care Facilities. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1061–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Rampelli, S.; Jeffery, I.B.; Santoro, A.; Neto, M.; Capri, M.; Giampieri, E.; Jennings, A.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Intervention Alters the Gut Microbiome in Older People Reducing Frailty and Improving Health Status: The NU-AGE 1-Year Dietary Intervention across Five European Countries. Gut 2020, 69, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannum, G.; Guinney, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Hughes, G.; Sadda, S.; Klotzle, B.; Bibikova, M.; Fan, J.-B.; Gao, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Methylation Profiles Reveal Quantitative Views of Human Aging Rates. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horvath, S. DNA Methylation Age of Human Tissues and Cell Types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, O.; Chadeau Hyam, M.; Karaman, I.; Climaco Pinto, R.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Handakas, E.; Fiorito, G.; Gao, H.; Heard, A.; Jarvelin, M.; et al. Determinants of Accelerated Metabolomic and Epigenetic Aging in a UK Cohort. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jylhävä, J.; Pedersen, N.L.; Hägg, S. Biological Age Predictors. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.H.; Marioni, R.E.; Colicino, E.; Peters, M.J.; Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Tsai, P.-C.; Roetker, N.S.; Just, A.C.; Demerath, E.W.; Guan, W.; et al. DNA Methylation-Based Measures of Biological Age: Meta-Analysis Predicting Time to Death. Aging 2016, 8, 1844–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marioni, R.E.; Shah, S.; McRae, A.F.; Chen, B.H.; Colicino, E.; Harris, S.E.; Gibson, J.; Henders, A.K.; Redmond, P.; Cox, S.R.; et al. DNA Methylation Age of Blood Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Later Life. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perna, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mons, U.; Holleczek, B.; Saum, K.-U.; Brenner, H. Epigenetic Age Acceleration Predicts Cancer, Cardiovascular, and All-Cause Mortality in a German Case Cohort. Clin. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horvath, S.; Gurven, M.; Levine, M.E.; Trumble, B.C.; Kaplan, H.; Allayee, H.; Ritz, B.R.; Chen, B.; Lu, A.T.; Rickabaugh, T.M.; et al. An Epigenetic Clock Analysis of Race/Ethnicity, Sex, and Coronary Heart Disease. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, S.; Kimura, R.; Otsuka, I.; Funabiki, Y.; Murai, T.; Hishimoto, A. Epigenetic Clock Analysis and Increased Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marioni, R.E.; Shah, S.; McRae, A.F.; Ritchie, S.J.; Muniz-Terrera, G.; Harris, S.E.; Gibson, J.; Redmond, P.; Cox, S.R.; Pattie, A.; et al. The Epigenetic Clock Is Correlated with Physical and Cognitive Fitness in the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotas, M.E.; Medzhitov, R. Homeostasis, Inflammation, and Disease Susceptibility. Cell 2015, 160, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, E.L.; Dixit, V.D. Drivers of Age-Related Inflammation and Strategies for Healthspan Extension. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 265, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, A.; Pickman, Y.; Leipold, M.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; Ji, X.; Gaujoux, R.; Rabani, H.; Starosvetsky, E.; Kveler, K.; Schaffert, S.; et al. A Clinically Meaningful Metric of Immune Age Derived from High-Dimensional Longitudinal Monitoring. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, J.; Peng, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, B.; Suh, Y.; Tu, Z. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Difference between ‘Healthy’ and ‘Common’ Aging and Their Connection with Age-related Diseases. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shokhirev, M.N.; Johnson, A.A. Modeling the Human Aging Transcriptome across Tissues, Health Status, and Sex. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Lunetta, K.L.; Zhao, Q.; Mandaviya, P.R.; Rong, J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Joehanes, R.; Levy, D.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Larson, M.G.; et al. Whole Blood Gene Expression Associated with Clinical Biological Age. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2019, 74, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Toole, P.W.; Jeffery, I.B. Gut Microbiota and Aging. Science 2015, 350, 1214–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Hua, Y.; Zeng, B.; Ning, R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Gut Microbiota Signatures of Longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R832–R833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maffei, V.; Kim, S.; Blanchard, E.; Luo, M.; Jazwinski, M.S.; Taykor, C.M.; Welsh, D.A. Biological Aging and the Human Gut Microbiota. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 72, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sala, C.; Giampieri, E.; Vitali, S.; Garagnani, P.; Remondini, D.; Bazzani, A.; Franceschi, C.; Castellani, G.C. Gut Microbiota Ecology: Biodiversity Estimated from Hybrid Neutral-Niche Model Increases with Health Status and Aging. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Wilms, E.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Smidt, H.; Zoetendal, E.G.; Jonkers, D. Age-Dependent Changes in GI Physiology and Microbiota: Time to Reconsider? Gut 2018, 67, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, E.; Nylund, L.; Candela, M.; Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Pini, E.; Nikkïla, J.; Monti, D.; Satokari, R.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Through Ageing, and beyond: Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Status in Seniors and Centenarians. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.Y.; Hejndorf, S.; Tharmabalan, R.T.; Poppema, S.; Pettersson, S. Regional Diets Targeting Gut Microbial Dynamics to Support Prolonged Healthspan. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 659465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmanski, T.; Diener, C.; Rappaport, N.; Patwardhan, S.; Wiedrick, J.; Lapidus, J.; Earls, J.C.; Zimmer, A.; Glusman, G.; Robinson, M.; et al. Gut Microbiome Pattern Reflects Healthy Ageing and Predicts Survival in Humans. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Haiminen, N.; Carrieri, A.-P.; Hu, R.; Jiang, L.; Parida, L.; Russell, B.; Allaband, C.; Zarrinpar, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; et al. Human Skin, Oral, and Gut Microbiomes Predict Chronological Age. mSystems 2020, 5, e00630-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poretsky, R.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Luo, C.; Tsementzi, D.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Strengths and Limitations of 16S RRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing in Revealing Temporal Microbial Community Dynamics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galkin, F.; Mamoshina, P.; Aliper, A.; Putin, E.; Moskalev, V.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Zhavoronkov, A. Human Gut Microbiome Aging Clock Based on Taxonomic Profiling and Deep Learning. iScience 2020, 23, e00630-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, J.P.; McCormick, B.A. Aging, Frailty, and the Microbiome—How Dysbiosis Influences Human Aging and Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongsisay, V. The Immunobiology of Campylobacter Jejuni: Innate Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D. The Gut Microbiome and Its Role in Obesity. Nutr. Today 2016, 51, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Hardy, T.; Huang, Y.; Hui, Q.; Crusto, C.A.; Wright, M.L.; Taylor, J.Y.; Sun, Y.V. Association of Obesity with DNA Methylation Age Acceleration in African American Mothers from the InterGEN Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, H.; Li, P.; Mcdonald, D.; Sheng, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Ji, G.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Regional Variation Limits Applications of Healthy Gut Microbiome Reference Ranges and Disease Models. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Saunier, K.; Hanisch, C.; Norin, E.; Alm, L.; Midtvedt, T.; Cresci, A.; Silvi, S.; Orpianesi, C.; Verdenelli, M.C.; et al. Differences in Fecal Microbiota in Different European Study Populations in Relation to Age, Gender, and Country: A Cross-Sectional Study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louca, S.; Jacques, S.M.S.; Pires, A.P.F.; Leal, J.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Farjalla, V.F.; Doebeli, M. High Taxonomic Variability despite Stable Functional Structure across Microbial Communities. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Kriete, A.; Rosen, G.L. Selecting Age-Related Functional Characteristics in the Human Gut Microbiome. Microbiome 2013, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.C.; Parker, K.; Aguirre, B.F.; Nemkov, T.G.; D’Alessandro, A.; Johnson, S.A.; Seals, D.R.; Martens, C.R. The Plasma Metabolome as a Predictor of Biological Aging in Humans. GeroScience 2019, 41, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, M.J.; Roth, A.; Frommherz, L.; Weinert, C.H.; Krüger, R.; Merz, B.; Bunzel, D.; Mack, C.; Egert, B.; Bub, A.; et al. Metabolite Patterns Predicting Sex and Age in Participants of the Karlsruhe Metabolomics and Nutrition (KarMeN) Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-Gut Microbiota Metabolic Interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonowal, R.; Swimm, A.; Sahoo, A.; Luo, L.; Matsunaga, Y.; Wu, Z.; Bhingarde, J.A.; Ejzak, E.A.; Ranawade, A.; Qadota, H.; et al. Indoles from Commensal Bacteria Extend Healthspan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7506–E7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minois, N.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Madeo, F. Polyamines in Aging and Disease. Aging 2011, 3, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jun, S.R.; Cheema, A.; Bose, C.; Boerma, M.; Palade, P.T.; Carvalho, E.; Awasthi, S.; Singh, S.P. Multi-Omic Analysis Reveals Different Effects of Sulforaphane on the Microbiome and Metabolome in Old Compared to Young Mice. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.R.; Spagou, K.; Lewis, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Glei, D.A.; Seeman, T.E.; Coe, C.L.; Goldman, N.; Ryff, C.D.; Weinstein, M.; et al. Microbial-Mammalian Cometabolites Dominate the Age-Associated Urinary Metabolic Phenotype in Taiwanese and American Populations. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3166–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psihogios, N.G.; Gazi, I.F.; Elisaf, M.S.; Seferiadis, K.I.; Bairaktari, E.T. Gender-Related and Age-Related Urinalysis of Healthy Subjects by NMR-Based Metabonomics. NMR Biomed. 2008, 21, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collino, S.; Montoliu, I.; Martin, F.P.J.; Scherer, M.; Mari, D.; Salvioli, S.; Bucci, L.; Ostan, R.; Monti, D.; Biagi, E.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Extreme Longevity in Northern Italian Centenarians Reveal a Complex Remodeling of Lipids, Amino Acids, and Gut Microbiota Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, F.M.; Porrelli, A.; Vacca, M.; Comte, B.; Nimptsch, K.; Pinart, M.; Pischon, T.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; de Angelis, M. Metaproteomics Approach and Pathway Modulation in Obesity and Diabetes: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.; Wu, T.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, J.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Human Gut Microbiome Aging Clocks Based on Taxonomic and Functional Signatures through Multi-View Learning. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2025016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.E. Modeling the Rate of Senescence: Can Estimated Biological Age Predict Mortality More Accurately Than Chronological Age? J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belsky, D.W.; Caspi, A.; Houts, R.; Cohen, H.J.; Corcoran, D.L.; Danese, A.; Harrington, H.; Israel, S.; Levine, M.E.; Schaefer, J.D.; et al. Quantification of Biological Aging in Young Adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4104–E4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belsky, D.W.; Caspi, A.; Arseneault, L.; Baccarelli, A.; Corcoran, D.; Gao, X.; Hannon, E.; Harrington, H.L.; Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Houts, R.; et al. Quantification of the Pace of Biological Aging in Humans through a Blood Test, the DunedinPoAm DNA Methylation Algorithm. eLife 2020, 9, e54870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, P.; Thyagarajan, B.; Sun, F.; Schupf, N.; Newman, A.B.; Montano, M.; Perls, T.T. Biomarker Signatures of Aging. Aging Cell 2017, 16, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, D.W.; Moffitt, T.E.; Cohen, A.A.; Corcoran, D.L.; Levine, M.E.; Prinz, J.A.; Schaefer, J.; Sugden, K.; Williams, B.; Poulton, R.; et al. Eleven Telomere, Epigenetic Clock, and Biomarker-Composite Quantifications of Biological Aging: Do They Measure the Same Thing? Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 187, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoshina, P.; Kochetov, K.; Putin, E.; Cortese, F.; Aliper, A.; Lee, W.-S.; Ahn, S.-M.; Uhn, L.; Skjodt, N.; Kovalchuk, O.; et al. Population Specific Biomarkers of Human Aging: A Big Data Study Using South Korean, Canadian, and Eastern European Patient Populations. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2018, 73, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, M.; Bird, A. The Impact of Diet and Lifestyle on Gut Microbiota and Human Health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Zhang, S.; Poleksic, A.; Xie, L. Heterogeneous Multi-Layered Network Model for Omics Data Integration and Analysis. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, U.; Cohen, Y.; Valdes-Mas, R.; Kviatcovsky, D.; Elinav, E.; Avron, H. Dimensionality Reduction of Longitudinal ’Omics Data Using Modern Tensor Factorization. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.14159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Walter, S.; Abugessaisa, I.; Miñambres-Herraiz, R.; Palomares, L.B.; Butcher, L.; Erusalimsky, J.D.; Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Carnicero, J.; Hardman, T.C.; et al. A Robust Machine Learning Framework to Identify Signatures for Frailty: A Nested Case-Control Study in Four Aging European Cohorts. GeroScience 2021, 43, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roetker, N.S.; Pankow, J.S.; Bressler, J.; Morrison, A.C.; Boerwinkle, E. Prospective Study of Epigenetic Age Acceleration and Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes in the ARIC Study (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities). Circ. Genom. Precis. Med. 2018, 11, e001937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsden, A.J.; Riley, D.R.J.; Birkett, S.; Rodriguez-Barucg, Q.; Guinn, B.; Carroll, S.; Ingle, L.; Sathyapalan, T.; Beltran-Alvarez, P. Love Is in the Hair: Arginine Methylation of Human Hair Proteins as Novel Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Amino Acids 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.D.; Jafari, N.; Hou, L.; Li, Y.; Stewart, J.D.; Zhang, G.; Lamichhane, A.; Manson, J.E.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Whitsel, E.A.; et al. A Longitudinal Study of DNA Methylation as a Potential Mediator of Age-Related Diabetes Risk. GeroScience 2017, 39, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacos, K.; Gillberg, L.; Volkov, P.; Olsson, A.H.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Gjesing, A.P.; Eiberg, H.; Tuomi, T.; Almgren, P.; et al. Blood-Based Biomarkers of Age-Associated Epigenetic Changes in Human Islets Associate with Insulin Secretion and Diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwangbo, N.; Zhang, X.; Raftery, D.; Gu, H.; Hu, S.-C.; Montine, T.J.; Quinn, J.F.; Chung, K.A.; Hiller, A.L.; Wang, D.; et al. An Aging Clock Using Metabolomic CSF. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.E.; Hosgood, H.D.; Chen, B.; Absher, D.; Assimes, T.; Horvath, S. DNA Methylation Age of Blood Predicts Future Onset of Lung Cancer in the Women’s Health Initiative. Aging 2015, 7, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Joyce, B.T.; Colicino, E.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Dai, Q.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Kibbe, W.A.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Blood Epigenetic Age May Predict Cancer Incidence and Mortality. EBioMedicine 2016, 5, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Adams, D.H.; Fava, F.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Hold, G.; Quraishi, M.N.; Kinross, J.; Smidt, H.; Tuohy, K.M.; et al. The Gut Microbiota and Host Health: A New Clinical Frontier. Gut 2016, 65, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and Disease Markers Correlate with Gut Microbiome Composition across Thousands of People. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Siles, M.; Duncan, S.H.; Garcia-Gil, L.J.; Martinez-Medina, M. Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii: From Microbiology to Diagnostics and Prognostics. ISME J. 2017, 11, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiman, D.; Metwally, A.A.; Sun, J.; Dai, Y. PopPhy-CNN: A Phylogenetic Tree Embedded Architecture for Convolutional Neural Networks to Predict Host Phenotype From Metagenomic Data. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Dellière, S.; Rodriguez, C.; Birgand, G.; Lescure, F.-X.; Fourati, S.; Ruppé, E. Machine Learning in the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory: Has the Time Come for Routine Practice? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Zambrano, L.J.; Karaduzovic-Hadziabdic, K.; Loncar Turukalo, T.; Przymus, P.; Trajkovik, V.; Aasmets, O.; Berland, M.; Gruca, A.; Hasic, J.; Hron, K.; et al. Applications of Machine Learning in Human Microbiome Studies: A Review on Feature Selection, Biomarker Identification, Disease Prediction and Treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 634511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, G.D.; Kopylova, E.; Zhu, Q.; Carpenter, C.; Fraraccio, S.; Wandro, S.; Kosciolek, T.; Janssen, S.; Metcalf, J.; Song, S.J.; et al. Microbiome Analyses of Blood and Tissues Suggest Cancer Diagnostic Approach. Nature 2020, 579, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitmeier, S.; Kiessling, S.; Clavel, T.; List, M.; Almeida, E.L.; Ghosh, T.S.; Neuhaus, K.; Grallert, H.; Linseisen, J.; Skurk, T.; et al. Arrhythmic Gut Microbiome Signatures Predict Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 258–272.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, F.; Hertel, J.; Sandt, E.; Thinnes, C.C.; Neuberger-Castillo, L.; Pavelka, L.; Betsou, F.; Krüger, R.; Thiele, I.; Aguayo, G.; et al. Parkinson’s Disease-Associated Alterations of the Gut Microbiome Predict Disease-Relevant Changes in Metabolic Functions. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.S.; Das, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Adjusting for Age Improves Identification of Gut Microbiome Alterations in Multiple Diseases. eLife 2020, 9, e50240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Dong, T.S.; Krause-Sorio, B.; Siddarth, P.; Milillo, M.M.; Lagishetty, V.; Datta, T.; Aguilar-Faustino, Y.; Jacobs, J.P.; Lavretsky, H. The Intestinal Microbiota as a Predictor for Antidepressant Treatment Outcome in Geriatric Depression: A Prospective Pilot Study. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2021, 34, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajca, S.; Grondin, V.; Louis, E.; Vernier-Massouille, G.; Grimaud, J.-C.; Bouhnik, Y.; Laharie, D.; Dupas, J.-L.; Pillant, H.; Picon, L.; et al. Alterations in the Intestinal Microbiome (Dysbiosis) as a Predictor of Relapse after Infliximab Withdrawal in Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human Gut Microbiome Viewed across Age and Geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschasaux, M.; Bouter, K.E.; Prodan, A.; Levin, E.; Groen, A.K.; Herrema, H.; Tremaroli, V.; Bakker, G.J.; Attaye, I.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J.; et al. Depicting the Composition of Gut Microbiota in a Population with Varied Ethnic Origins but Shared Geography. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Z.; Sun, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, C.; Wang, T.; Tan, D.; Qi, S.; Jun, C.; et al. Metagenomics Study Reveals Changes in Gut Microbiota in Centenarians: A Cohort Study of Hainan Centenarians. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Sasaki, R. Geographical Epidemiologic Studies on Factors Associated with Centenarians in Japan. Jpn. J. Geriatr. 1995, 32, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robine, J.-M.; Cubaynes, S. Worldwide Demography of Centenarians. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 165, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugane, S. Why Has Japan Become the World’s Most Long-Lived Country: Insights from a Food and Nutrition Perspective. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, W.C.; Scherbov, S. Measuring the Speed of Aging across Population Subgroups. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Tomás, J.M.; Calatayud, P. Contributions of Psychosocial Factors and Physical Activity to Successful Aging. Span. J. Psychol. 2018, 21, E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadecka, A.; Bielak-Zmijewska, A. Slowing Down Ageing: The Role of Nutrients and Microbiota in Modulation of the Epigenome. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quigley, E.M.M. Gut Microbiome as a Clinical Tool in Gastrointestinal Disease Management: Are We There Yet? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, W.K.; Chehadeh, F.; Husband, S. Recent Advances in Understanding the Structure and Function of the Human Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 825338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ratiner, K.; Abdeen, S.K.; Goldenberg, K.; Elinav, E. Utilization of Host and Microbiome Features in Determination of Biological Aging. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030668
Ratiner K, Abdeen SK, Goldenberg K, Elinav E. Utilization of Host and Microbiome Features in Determination of Biological Aging. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030668
Chicago/Turabian StyleRatiner, Karina, Suhaib K. Abdeen, Kim Goldenberg, and Eran Elinav. 2022. "Utilization of Host and Microbiome Features in Determination of Biological Aging" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030668
APA StyleRatiner, K., Abdeen, S. K., Goldenberg, K., & Elinav, E. (2022). Utilization of Host and Microbiome Features in Determination of Biological Aging. Microorganisms, 10(3), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030668