Influence of Temperature on Growth of Four Different Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Biofilms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Microbiological Analyses
2.4. Maximum Biofilm Yield Determination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biofilm Growth
3.2. Growth of P. aeruginosa, S. maltophilia, M. kansasii and A. fumigatus
3.3. Maximum Biofilm Yields
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Temperature on Opportunistic Pathogens
4.2. Impact on Possible Health Risk
4.3. Impact on Drinking Water Temperature Guidelines and Legislation
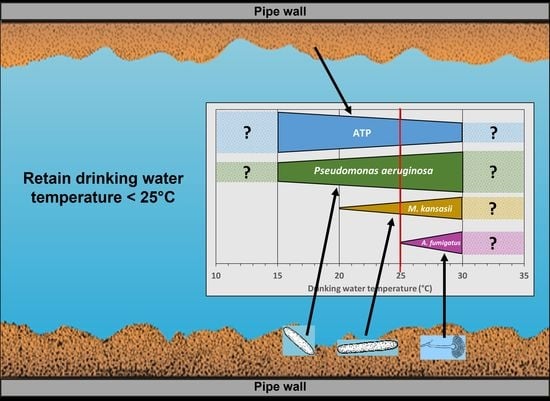
5. Conclusions
- The active biomass concentration in the drinking water biofilms decreases when temperatures increase from 15.0 to 30.0 °C.
- There is a realistic probability that the numbers of P. aeruginosa, M. kansasii and A. fumigatus will increase in drinking water distribution systems in temperate climates as drinking water temperatures rise due to climate change, posing an increased public health risk.
- Increasing the current drinking water temperature standard above the WHO guideline standard of 25 °C can result in higher P. aeruginosa and M. kansasii numbers and in the higher growth of A. fumigatus in drinking water systems than numbers occurring at temperatures below 25 °C. As a result, changing this guideline is not recommended.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Kooij, D.; van Lieverloo, J.H.M.; Shellart, J.; Hiemstra, P. Maintaining quality without a disinfectant residual. J. AWWA 1999, 91, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J. Environmental (saprozoic) pathogens of engineered water systems: Understanding their ecology for risk assessment and management. Pathogens 2015, 4, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engel, H.W.; Berwald, L.G.; Havelaar, A.H. The occurrence of Mycobacterium kansasii in tapwater. Tubercle 1980, 61, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Wielen, P.W.; van der Kooij, D. Nontuberculous mycobacteria, fungi, and opportunistic pathogens in unchlorinated drinking water in the Netherlands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Wielen, P.W.J.J.; Wullings, B.A. Genotype analyses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from drinking water reveal similar genotypes with patient strains. In Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Health Related Water Microbiology, Vienna, Austria, 15–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Verweij, P.E.; Meis, J.F.; Christmann, V.; Van der Bor, M.; Melchers, W.J.; Hilderink, B.G.; Voss, A. Nosocomial outbreak of colonization and infection with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in preterm infants associated with contaminated tap water. Epidemiol. Infect. 1998, 120, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasmacher, A.; Engelhart, S.; Exner, M. Infections from HPC organisms in drinking-water amongst the immunocompromised. In Heterotrophic Plate Counts and Drinking-Water Safety; Bartram, J., Cotruvo, J., Exner, M., Fricker, C., Glasmacher, A., Eds.; World Health Organization: Cornwall, UK, 2003; pp. 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Agudelo-Vera, C.; Avvedimento, S.; Boxall, J.; Creaco, E.; de Kater, H.; Di Nardo, A.; Djukic, A.; Douterelo, I.; Fish, E.K.; Iglesias Rey, L.P.; et al. Drinking water temperature around the globe: Understanding, policies, challenges and opportunities. Water 2020, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.; Tignor, M.M.B.; Miller, H.L. Climate Change 2007. The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- van der Wielen, P.W.J.J.; Italiaander, R.; Wullings, B.A.; Heijnen, L.; van der Kooij, D. Opportunistic pathogens in drinking water in the Netherlands. In Microbial Growth in Drinking-Water Supplies. Problems, Causes, Control and Research Needs; van der Kooij, D., van der Wielen, P.W.J.J., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 177–205. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 3rd ed.; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. A Global Overview of National Regulations and Standards for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooij, D.; Brouwer-Hanzens, A.H.; Veenendaal, H.R. Influence of the Water Temperature On Growth of Legionella pneumophila and Legionella anisa in Biofilms; KWR 09.056; KWR Watercycle Research Institute: Nieuwegein, The Netherlands, 2009. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooij, D.; Brouwer-Hanzens, A.J.; Veenendaal, H.R.; Wullings, B.A. Multiplication of Legionella pneumophila sequence types 1, 47, and 62 in buffered yeast extract broth and biofilms exposed to flowing tap water at temperatures of 38 °C to 42 °C. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6691–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhati, P.; Jain, S.; Shouche, S. Effect of temperatures on the growth of floral waste degrading fungi. Fungal Territ. 2019, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.D. Some general properties of a psychrophilic pseudomonad: The effects of temperature on some of these properties and the utilization of glucose by this organism and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 1957, 17, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrity, G.M. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2001–2011; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kozakiewicz, Z.; Smith, D. Physiology of Aspergillus. In Aspergillus; Smith, J.E., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1994; pp. 23–40. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, A.; Bemmakn, W.; Tröger, R. Das wachstum der thermophilen pilzstämme Aspergillus fumigatus und Mucor lusitanicus in n-alkan-medium. Zent. Bakteriol. Parasitenkd. Infekt. Hyg. Zweite Nat. Abt. Mikrobiol. Landwirtsch. Technol. Umw. 1981, 136, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Schünemann, W.; Fuß, J.; Kämpfer, P.; Lipski, A. Stenotrophomonas lactitubi sp. nov. and Stenotrophomonas indicatrix sp. nov., isolated from surfaces with food contact. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1830–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitler, R.; Seligmann, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa in drinking water. J. Appl. Bact. 1957, 20, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wullings, B.A. Genetypic Typing of Drinking Water Strains of Opportunistic Pathogens; KWR Water Research Institute: Nieuwegein, The Netherlands, 2017. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- van der Wielen, P.W.J.J.; Uytewaal-Aarts, M. Non-Tuberculous Mycobacteria in Drinking Water; KWR Water Research Institute: Nieuwegein, The Netherlands, 2013. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Van der Kooij, D.; Baggelaar, P.K.; Veenendaal, H.R.; Moulin, L.; Corfitzen, C.B.; Albrechtsen, H.J.; Holt, D.; Hambsch, B. Standardising the Biomass Production Potential Test Method for Determining the Enhancement of Microbial Growth by Construction Products in Contact with Drinking Water; KWR Water Research Institute: Nieuwegein, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Learbuch, K.L.G.; Lut, M.C.; Liu, G.; Smidt, H.; van der Wielen, P.W.J.J. Legionella growth potential of drinking water produced by a reverse osmosis pilot plant. Water Res. 2019, 157, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monod, J. Recherches sur la Croissance des Cultures Bactériennes; Hermann & cie: Paris, France, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Lipson, D.A. The complex relationship between microbial growth rate and yield and its implications for ecosystem processes. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farhat, N.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Bucs, S.S.; Staal, M. Effect of water temperature on biofouling development in reverse osmosis membrane systems. Water Res. 2016, 103, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Kooij, D.; Albrechtsen, H.-J.; Corfitzen, C.B.; Ashworth, J.; Parry, I.; Enkiri, F.; Hambsch, B.; Hametner, C.; Kloiber, R.; Veenendaal, H.R.; et al. Assessment of the Microbial Growth Support Potential of Products in Contact with Drinking Water (CPDW): Development of a Harmonised Test to Be Used in the European Acceptance Scheme Concerning CPDW; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, S.; Banin, E. Multi-species biofilms: Living with friendly neighbors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbing, M.E.; Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M.R.; Peterson, S.B. Bacterial competition: Surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anaissie, E.J.; Stratton, S.L.; Dignani, M.C.; Lee, C.K.; Summerbell, R.C.; Rex, J.H.; Monson, T.P.; Walsh, T.J. Pathogenic molds (including Aspergillus species) in hospital water distribution systems: A 3-year prospective study and clinical implications for patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood 2003, 101, 2542–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.K.; Wyles, S.; Dingley, M.; Hesse, F.; Kent, G.W. The isolation of high catalase Mycobacterium kansasii from tap water. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1970, 101, 430–431. [Google Scholar]
- Hageskal, G.; Knutsen, A.K.; Gaustad, P.; de Hoog, G.S.; Skaar, I. Diversity and significance of mold species in Norwegian drinking water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7586–7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrin, Y.; Bouchon, D.; Héchard, Y.; Moulin, L. Spatio-temporal survey of opportunistic premise plumbing pathogens in the Paris drinking water distribution system. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakhnini, E.; Weissmann, A.; Oren, I. Fulminant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia soft tissue infection in immunocompromised patients: An outbreak transmitted via tap water. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 323, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, R.; Tolson, C.; Huygens, F.; Hargreaves, M. Strain variation amongst clinical and potable water isolates of M. kansasii using automated repetitive unit PCR. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 304, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.K.; Brooks, R.B.; Glowicz, J.; Keckler, M.S.; Christensen, B.E.; Tsai, V.; Mitchell, C.S.; Wilson, L.E.; Laxton, R.; Moulton-Meissner, H.; et al. Outbreak investigation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. Am. J. Infect. Control 2019, 47, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anonymous. The Quality of the Drinking Water in the Netherlands 2015; Inspectie voor Leefomgeving en Transport: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2016. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The Quality of the Drinking Water in the Netherlands 2016; Inspectie voor Leefomgeving en Transport: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2017. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The Quality of the Drinking Water in the Netherlands 2017; Inspectie voor Leefomgeving en Transport: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2018. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The Quality of the Drinking Water in the Netherlands 2018; Inspectie voor Leefomgeving en Transport: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2019. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The Quality of the Drinking Water in the Netherlands 2019; Inspectie voor Leefomgeving en Transport: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2020. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Tison, D.L.; Pope, D.H.; Cherry, W.B.; Fliermans, C.B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1980, 39, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wadowsky, R.M.; Wolford, R.; McNamara, A.M.; Yee, R.B. Effect of temperature, pH, and oxygen level on the multiplication of naturally occurring Legionella pneumophila in potable water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yee, R.B.; Wadowsky, R.M. Multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in unsterilized tap water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valster, R.M.; Wullings, B.A.; van den Berg, R.; van der Kooij, D. Relationships between free-living protozoa, cultivable Legionella spp., and water quality characteristics in three drinking water supplies in the Caribbean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7321–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinweber, A.; Weigert, M.; Kümmerli, R. The bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa senses and gradually responds to interspecific competition for iron. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 2018, 72, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niggli, S.; Kümmerli, R. Strain background, species frequency, and environmental conditions are important in determining Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus population dynamics and species coexistence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00962-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheduzzaman, M.; Singh, R.; Haas, N.C.; Tolofari, D.; Yassaghi, H.; Hamilton, A.K.; Yang, Z.; Gurian, L.P. Reverse QMRA as a decision support tool: Setting acceptable concentration limits for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Naegleria fowleri. Water 2019, 11, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusin, P.A.; Rose, J.B.; Haas, C.N.; Gerba, C.P. Risk assessment of opportunistic bacterial pathogens in drinking water. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 152, 57–83. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Filho, L.V.; Tateno, A.F.; de Velloso, F.L.; Levi, J.E.; Fernandes, S.; Bento, C.N.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Ramos, S.R. Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia cepacia complex, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in respiratory samples from cystic fibrosis patients using multiplex PCR. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2004, 37, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challier, S.; Boyer, S.; Abachin, E.; Berche, P. Development of a serum-based Taqman real-time PCR assay for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 844–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Temperature (°C) | ATP (pg cm−2) | P. aeruginosa (gc cm−2) | M. kansasii (gc cm−2) | A. fumigatus (gc cm−2) |
| 15.0 | 2.4 ± 0.7 × 104 a | 3.6 ± 1.9 × 106 a | 1.5 ± 0.3 × 107 | 1.8 ± 0.4 × 107 a |
| 17.5 | 2.9 ± 0.4 × 104 a | 1.1 ± 0.3 × 107 b | 1.2 ± 0.7 × 107 a | 2.1 ± 0.5 × 107 a |
| 20.0 | 2.3 ± 0.6 × 104 | 7.1 ± 1.4 × 107 c | 2.1 ± 0.6 × 107 | 1.8 ± 1.0 × 107 a |
| 22.5 | 1.9 ± 0.5 × 104 | 5.9 ± 1.1 × 108 d | 4.0 ± 0.7 × 107 | 1.9 ± 0.4 × 107 a |
| 25.0 | 1.5 ± 0.5 × 104 | 8.2 ± 4.3 × 108 d | 1.2 ± 0.7 × 108 b | 8.6 ± 3.7 × 107 |
| 27.5 | 1.1 ± 0.3 × 104 b | 2.9 ± 0.7 × 109 e | 6.3 ± 5.5 × 107 | 1.0 ± 1.1 × 109 b |
| 30.0 | 1.1 ± 0.2 × 104 b | 1.1 ± 0.6 × 1010 f | 1.5 ± 1.7 × 108 | 2.2 ± 2.3 × 108 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van der Wielen, P.W.J.J.; Dignum, M.; Donocik, A.; Prest, E.I. Influence of Temperature on Growth of Four Different Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Biofilms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061574
van der Wielen PWJJ, Dignum M, Donocik A, Prest EI. Influence of Temperature on Growth of Four Different Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Biofilms. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061574
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan der Wielen, Paul W. J. J., Marco Dignum, Agata Donocik, and Emmanuelle I. Prest. 2023. "Influence of Temperature on Growth of Four Different Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Biofilms" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061574
APA Stylevan der Wielen, P. W. J. J., Dignum, M., Donocik, A., & Prest, E. I. (2023). Influence of Temperature on Growth of Four Different Opportunistic Pathogens in Drinking Water Biofilms. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061574