Molecular Diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in Asymptomatic School Children in Leganés, Madrid (Spain)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
2.2. Study Area and Stool Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction and Purification
2.4. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Giardia duodenalis
2.5. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. Isolates
2.6. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Blastocystis sp. Isolates
2.7. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Enterocytozoon bieneusi Isolates
2.8. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
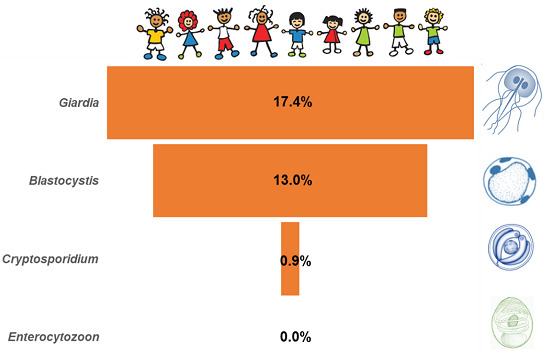
3.1. Occurrence of Enteric Parasites
3.2. Molecular Characterization of G. duodenalis Isolates
3.3. Molecular Characterization of Cryptosporidium spp. Isolates
3.4. Molecular Characterization of Blastocystis sp. Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torgerson, P.R.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Praet, N.; Speybroeck, N.; Willingham, A.L.; Kasuga, F.; Rokni, M.B.; Zhou, X.N.; Fèvre, E.M.; Sripa, B.; et al. World Health Organization estimates of the global and regional disease burden of 11 food-borne parasitic diseases, 2010: A data synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Feng, Y.; Santin, M. Host specificity of Enterocytozoon bieneusi and public health implications. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstratiou, A.; Ongerth, J.E.; Karanis, P. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: Review of worldwide outbreaks—An update 2011-2016. Water Res. 2017, 114, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, U.; Hijjawi, N.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Giardia: An under-reported foodborne parasite. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Certad, G.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabé, M.; Cacciò, S.M. Pathogenic mechanisms of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliez, M.C.M.; Buret, A.G. Extra-intestinal and long term consequences of Giardia duodenalis infections. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8974–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.S.; Cairncross, S.; Strina, A.; Barreto, M.L.; Oliveira-Assis, A.M.; Rego, S. Asymptomatic giardiasis and growth in young children; a longitudinal study in Salvador, Brazil. Parasitology 2005, 131, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lengerich, E.J.; Addiss, D.G.; Juranek, D.D. Severe giardiasis in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1994, 18, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcona-Gutiérrez, J.M.; de Lucio, A.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; García-García, C.; Soria-Blanco, L.M.; Morales, L.; Aguilera, M.; Fuentes, I.; Carmena, D. Molecular diversity and frequency of the diarrheagenic enteric protozoan Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. in a hospital setting in Northern Spain. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nourrisson, C.; Scanzi, J.; Pereira, B.; NkoudMongo, C.; Wawrzyniak, I.; Cian, A.; Viscogliosi, E.; Livrelli, V.; Delbac, F.; Dapoigny, M.; et al. Blastocystis is associated with decrease of fecal microbiota protective bacteria: Comparative analysis between patients with irritable bowel syndrome and control subjects. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casero, R.D.; Mongi, F.; Sánchez, A.; Ramírez, J.D. Blastocystis and urticaria: Examination of subtypes and morphotypes in an unusual clinical manifestation. Acta Trop. 2015, 148, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Fighting Disease Fostering Development; The World Health Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.; Rao, P.C.; Blacker, B.F.; Brown, A.; Brewer, T.G.; Colombara, D.V.; De Hostos, E.L.; Engmann, C.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Morbidity, mortality, and long-term consequences associated with diarrhoea from Cryptosporidium infection in children younger than 5 years: A meta-analyses study. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e758–e768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, L.O.; Stensvold, C.R. Blastocystis in health and disease: Are we moving from a clinical to a public health perspective? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lobo, M.L.; Xiao, L.; Antunes, F.; Matos, O. Microsporidia as emerging pathogens and the implication for public health: A 10-year study on HIV-positive and -negative patients. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.; Cacciò, S.M. Zoonotic potential of Giardia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, U.; Fayer, R.; Xiao, L. Cryptosporidium species in humans and animals: Current understanding and research needs. Parasitology 2014, 141, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Suresh, G.K.; Tan, K.S.W.; Thompson, R.C.A.; Traub, R.J.; Viscogliosi, E.; Yoshikawa, H.; Clark, C.G. Terminology for Blastocystis subtypes—A consensus. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, E.D.; Hudson-Wragg, M.; Mshar, P.; Cartter, M.L.; Hadler, J.L. Foodborne giardiasis in a corporate office setting. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 167, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, F.; Sulleiro, E.; Sánchez-Montalvá, A.; Alonso, C.; Santos, J.; Fuentes, I.; Molina, I. Epidemiological and clinical profile of adult patients with Blastocystis sp. infection in Barcelona, Spain. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubourg, A.; Xia, D.; Winpenny, J.P.; Al Naimi, S.; Bouzid, M.; Sexton, D.W.; Wastling, J.M.; Hunter, P.R.; Tyler, K.M. Giardia secretome highlights secreted tenascins as a key component of pathogenesis. Gigascience 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Roellig, D.M.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Comparative analysis reveals conservation in genome organization among intestinal Cryptosporidium species and sequence divergence in potential secreted pathogenesis determinants among major human-infecting species. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Márquez, M.V.; Guna, R.; Muñoz, C.; Gómez-Muñoz, M.T.; Borrás, R. High prevalence of subtype 4 among isolates of Blastocystis hominis from symptomatic patients of a health district of Valencia (Spain). Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmena, D.; Cardona, G.A.; Sánchez-Serrano, L.P. Current situation of Giardia infection in Spain: Implications for public health. World J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-i-Martinez, L.; del Águila, C.; Bornay-Llinares, F.J. Cryptosporidium: A genus in revision. The situation in Spain. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2011, 29, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulos, S.; Köster, P.C.; de Lucio, A.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; Cardona, G.A.; Fernández-Crespo, J.C.; Stensvold, C.R.; Carmena, D. Occurrence and subtype distribution of Blastocystis sp. in humans, dogs and cats sharing household in northern Spain and assessment of zoonotic transmission risk. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, G.A.; Carabin, H.; Goñi, P.; Arriola, L.; Robinson, G.; Fernández-Crespo, J.C.; Clavel, A.; Chalmers, R.M.; Carmena, D. Identification and molecular characterization of Cryptosporidium and Giardia in children and cattle populations from the province of Álava, North of Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412–413, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reh, L.; Muadica, A.S.; Köster, P.C.; Balasegaram, S.; Verlander, N.Q.; Chércoles, E.R.; Carmena, D. Substantial prevalence of enteroparasites Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia duodenalis and Blastocystis sp. in asymptomatic schoolchildren in Madrid, Spain, November 2017 to June 2018. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Schinkel, J.; Laeijendecker, D.; van Rooyen, M.A.; van Lieshout, L.; Polderman, A.M. Real-time PCR for the detection of Giardia lamblia. Mol. Cell. Probes 2003, 17, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, C.M.; Monis, P.T.; Thompson, R.C. Discrimination of all genotypes of Giardia duodenalis at the glutamate dehydrogenase locus using PCR-RFLP. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2004, 4, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalle, M.; Pozio, E.; Capelli, G.; Bruschi, F.; Crotti, D.; Cacciò, S.M. Genetic heterogeneity at the beta-giardin locus among human and animal isolates of Giardia duodenalis and identification of potentially zoonotic subgenotypes. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, I.M.; Fayer, R.; Bern, C.; Gilman, R.H.; Trout, J.M.; Schantz, P.M.; Das, P.; Lal, A.A.; Xiao, L. Triose phosphate isomerase gene characterization and potential zoonotic transmission of Giardia duodenalis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiangtip, R.; Jongwutiwes, S. Molecular analysis of Cryptosporidium species isolated from HIV-infected patients in Thailand. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2002, 7, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feltus, D.C.; Giddings, C.W.; Schneck, B.L.; Monson, T.; Warshauer, D.; McEvoy, J.M. Evidence supporting zoonotic transmission of Cryptosporidium spp. in Wisconsin. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4303–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scicluna, S.M.; Tawari, B.; Clark, C.G. DNA barcoding of Blastocystis. Protist 2006, 157, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckholt, M.A.; Lee, J.H.; Tzipori, S. Prevalence of Enterocytozoon bieneusi in swine: An 18-month survey at a slaughterhouse in Massachusetts. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2595–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lucio, A.; Martínez-Ruiz, R.; Merino, F.J.; Bailo, B.; Aguilera, M.; Fuentes, I.; Carmena, D. Molecular genotyping of Giardia duodenalis isolates from symptomatic individuals attending two major public hospitals in Madrid, Spain. PLoS ONE. 2015, 10, e0143981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slapeta, J. Cryptosporidium species found in cattle: A proposal for a new species. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.; Mateo, M.; Montoya, A.; Bailo, B.; Saugar, J.M.; Aguilera, M.; Fuentes, I.; Carmena, D. Detection and molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis in children attending day care centers in Majadahonda, Madrid, Central Spain. Medicine 2014, 93, e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucio, A.; Bailo, B.; Aguilera, M.; Cardona, G.A.; Fernández-Crespo, J.C.; Carmena, D. No molecular epidemiological evidence supporting household transmission of zoonotic Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium spp. from pet dogs and cats in the province of Álava, Northern Spain. Acta Trop. 2017, 170, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Moreno, O.; Roellig, D.M.; Oliver, L.; Huguet, J.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Epidemiological distribution of genotypes of Giardia duodenalis in humans in Spain. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabín-García, L.B.; Bartolomé, C.; Abal-Fabeiro, J.L.; Méndez, S.; Llovo, J.; Maside, X. Strong genetic structure revealed by multilocus patterns of variation in Giardia duodenalis isolates of patients from Galicia (NW-Iberian Peninsula). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 48, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Canut-Blasco, A.; Martín-Sánchez, A.M. Seasonal prevalences of Cryptosporidium and Giardia infections in children attending day care centres in Salamanca (Spain) studied for a period of 15 months. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 12, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, R.; Prim, N.; Montemayor, M.; Valls, M.E.; Muñoz, C. Predominant virulent IbA10G2 subtype of Cryptosporidium hominis in human isolates in Barcelona: A five-year study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abal-Fabeiro, J.L.; Maside, X.; Llovo, J.; Bartolomé, C. Aetiology and epidemiology of human cryptosporidiosis cases in Galicia (NW Spain), 2000–2008. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 3022–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lucio, A.; Merino, F.J.; Martínez-Ruiz, R.; Bailo, B.; Aguilera, M.; Fuentes, I.; Carmena, D. Molecular genotyping and sub-genotyping of Cryptosporidium spp. isolates from symptomatic individuals attending two major public hospitals in Madrid, Spain. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 37, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, S.A.; Ryan, U. Cryptosporidium and Giardia in Africa: Current and future challenges. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casadevall, A.; Fang, F.C.; Pirofski, L.A. Microbial virulence as an emergent property: Consequences and opportunities. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerf-Bensussan, N.; Gaboriau-Routhiau, V. The immune system and the gut microbiota: Friends or foes? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Chen, G.Y.; Inohara, N.; Núñez, G. Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sánchez, A.M.; Canut-Blasco, A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, J.; Montes-Martínez, I.; García-Rodríguez, J.A. Epidemiology and clinical significance of Blastocystis hominis in different population groups in Salamanca (Spain). Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 8, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Moreno, O.; Domingo, L.; Teixidor, J.; Gracenea, M. Prevalence and associated factors of intestinal parasitisation: A cross-sectional study among outpatients with gastrointestinal symptoms in Catalonia, Spain. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 108, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Aguila, C.; Navajas, R.; Gurbindo, D.; Ramos, J.T.; Mellado, M.J.; Fenoy, S.; Muñoz Fernandez, M.A.; Subirats, M.; Ruiz, J.; Pieniazek, N.J. Microsporidiosis in HIV-positive children in Madrid (Spain). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1997, 44, 84S–85S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfellani, M.A.; Stensvold, C.R.; Vidal-Lapiedra, A.; Onuoha, E.S.; Fagbenro-Beyioku, A.F.; Clark, C.G. Variable geographic distribution of Blastocystis subtypes and its potential implications. Acta Trop. 2013, 126, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Christiansen, D.B.; Olsen, K.E.; Nielsen, H.V. Blastocystis sp. subtype 4 is common in Danish Blastocystis-positive patients presenting with acute diarrhea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattiucci, S.; Crisafi, B.; Gabrielli, S.; Paoletti, M.; Cancrini, G. Molecular epidemiology and genetic diversity of Blastocystis infection in humans in Italy. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, P.C.; Pérez-Ayala, A.; Molina, A.; Trelis, M.; Ruiz, G.; García-Hortelano, M.; Mellado, M.J.; Azcona Gutiérrez, J.M.; Martín, O.; Paulos, S.; et al. Variabilidad genética de Blastocystis sp. en pacientes atendidos en hospitales públicos españoles. In Proceedings of the XI Congress of the Spanish Society of Tropical Medicine and International Health, Ávila, Spain, 27–30 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Stensvold, C.R. Thinking Blastocystis out of the box. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, D.; Sanciu, G.; Poirier, P.; El Alaoui, H.; Chabé, M.; Delhaes, L.; Dei-Cas, E.; Delbac, F.; Luigi Fiori, P.; Di Cave, D.; et al. Molecular subtyping of Blastocystis sp. isolates from symptomatic patients in Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 109, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyer, A.; Karasartova, D.; Ruh, E.; Güreser, A.S.; Turgal, E.; Imir, T.; Taylan-Ozkan, A. Epidemiology and prevalence of Blastocystis spp. in North Cyprus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouad, S.A.; Basyoni, M.M.; Fahmy, R.A.; Kobaisi, M.H. The pathogenic role of different Blastocystis hominis genotypes isolated from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 12, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.C.; Suresh, K.G.; Smith, H.V. Phenotypic and genotypic characterisation of Blastocystis hominis isolates implicates subtype 3 as a subtype with pathogenic potential. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 104, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Arbex, A.P.; David, É.B.; Tenório, M.D.S.; Cicchi, P.J.P.; Patti, M.; Coradi, S.T.; Lucheis, S.B.; Jim, J.; Guimarães, S. Diversity of Blastocystis subtypes in wild mammals from a zoo and two conservation units in southeastern Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 78, 104053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valença-Barbosa, C.; do Bomfim, T.C.B.; Teixeira, B.R.; Gentile, R.; Neto, S.F.D.C.; Magalhães, B.S.N.; Balthazar, D.A.; da Silva, F.A.; Biot, R.; d’Avila Levy, C.M.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Blastocystis isolated from animals in the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villanueva-Garcia, C.; Gordillo-Chavez, E.J.; Lopez-Escamilla, E.; Rendon-Franco, E.; Muñoz-Garcia, C.I.; Gama, L.; Martinez-Flores, W.A.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, N.; Romero-Valdovinos, M.; Diaz-Lopez, H.; et al. Clarifying the cryptic host specificity of Blastocystis spp. isolates from Alouatta palliata and A. pigra howler monkeys. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenbrook, W.D.; Shields, W.M.; Whipps, C.M. Characterization of Blastocystis species infection in humans and mantled howler monkeys, Alouatta palliata aequatorialis, living in close proximity to one another. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Alfellani, M.A.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, S.; Prip, K.; Victory, E.L.; Maddox, C.; Nielsen, H.V.; Clark, C.G. Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolates from synanthropic and zoo animals and identification of a new subtype. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sak, B.; Brady, D.; Pelikánová, M.; Květoňová, D.; Rost, M.; Kostka, M.; Tolarová, V.; Hůzová, Z.; Kváč, M. Unapparent microsporidial infection among immunocompetent humans in the Czech Republic. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Aguila, C.; López-Velez, R.; Fenoy, S.; Turrientes, C.; Cobo, J.; Navajas, R.; Visvesvara, G.S.; Croppo, G.P.; Da Silva, A.J.; Pieniazek, N.J. Identification of Enterocytozoon bieneusi spores in respiratory samples from an AIDS patient with a 2-year history of intestinal microsporidiosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galván, A.L.; Sánchez, A.M.; Valentín, M.A.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Izquierdo, F.; Fenoy, S.; del Aguila, C. First cases of microsporidiosis in transplant recipients in Spain and review of the literature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Vélez, R.; Turrientes, M.C.; Garrón, C.; Montilla, P.; Navajas, R.; Fenoy, S.; del Aguila, C. Microsporidiosis in travelers with diarrhea from the tropics. J. Travel Med. 1999, 6, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lores, B.; López-Miragaya, I.; Arias, C.; Fenoy, S.; Torres, J.; del Aguila, C. Intestinal microsporidiosis due to Enterocytozoon bieneusi in elderly human immunodeficiency virus–negative patients from Vigo, Spain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abreu-Acosta, N.; Lorenzo-Morales, J.; Leal-Guio, Y.; Coronado-Álvarez, N.; Foronda, P.; Alcoba-Florez, J.; Izquierdo, F.; Batista-Díaz, N.; Del Aguila, C.; Valladares, B. Enterocytozoon bieneusi (Microsporidia) in clinical samples from immunocompetent individuals in Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| School | n | Giardia duodenalis | Cryptosporidium spp. | Blastocystis sp. | Enterocytozoon bieneusi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global | 1512 | 17.4 (15.5–19.4) | 0.9 (0.5–1.5) | 13.0 (11.4–14.8) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 1 | 233 | 25.8 (20.3–31.9) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 17.6 (12.9–23.1) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 2 | 134 | 26.1 (18.9–34.4) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 11.9 (7.0–18.7) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 3 | 124 | 20.2 (13.5–28.3) | 0.8 (0.0–4.4) | 9.7 (5.1–16.3) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 4 | 54 | 7.4 (2.1–17.9) | 1.9 (0.0–9.9) | 3.7 (0.5–12.7) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 5 | 65 | 1.5 (0.0–8.3) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 13.8 (6.5–24.7) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 6 | 144 | 9.0 (4.9–14.9) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 13.2 (8.1–19.8) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 7 | 214 | 11.2 (7.3–16.2) | 3.7 (1.6–7.2) | 14.5 (10.1–19.9) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 8 | 73 | 11.0 (4.9–20.5) | 1.4 (0.0–7.4) | 15.1 (7.8–25.4) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 9 | 142 | 9.9 (5.5–16.0) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 12.0 (7.1–18.5) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 10 | 136 | 30.9 (23.2–39.4) | 1.5 (0.2–5.2) | 11.8 (6.9–18.4) | 0.0 (NA |
| 11 | 128 | 19.5 (13.1–27.5) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 10.2 (5.5–16.7) | 0.0 (NA) |
| 12 | 65 | 18.5 (9.9–30.0) | 1.5 (0.0–8.3) | 15.4 (7.6–26.5) | 0.0 (NA) |
| Sample ID | gdh | bg | tpi | Assigned Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 125 | Negative | Negative | BIV | BIV |
| 384 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 507 | AII | AII | AII | AII |
| 554 | BIV | B | BIV | BIV |
| 566 | BIV | Negative | BIV | BIV |
| 579 | BIV | Negative | BIV | BIV |
| 737 | AII | AII | AII | AII |
| 764 | Negative | B | Negative | B |
| 823 | BIV | Negative | BIV | BIV |
| 980 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 991 | BIV | Negative | BIV | BIV |
| 1030 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 1435 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 1459 | BIV | B | Negative | BIV |
| 1662 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 1721 | BIV | B | BIV | BIV |
| 1777 | Negative | Negative | BIV | BIV |
| 1784 | BIV | B | Negative | BIV |
| 1821 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 1904 | BIV | Negative | Negative | BIV |
| 1991 | AII | AII | AII | AII |
| 1997 | AII | Negative | Negative | AII |
| 2041 | BIV | B | BIV | BIV |
| 2172 | BIII/BIV | Negative | Negative | BIII/BIV |
| Locus | Assemblage | Sub-Assemblage | Isolates | Reference Sequence | Stretch | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms | GenBank ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gdh | A | AII | 3 | L40510 | 64–496 | None | MN844134 |
| 1 | 76–491 | T269Y1 | MN844135 | ||||
| B | BIV | 6 | L40508 | 76–491 | None | MN844136 | |
| 1 | 76–496 | C102Y, C105Y, C432Y, C435Y | MN844137 | ||||
| 1 | 78–485 | C126Y | MN844138 | ||||
| 5 | 76–441 | T183C, T387C, C396T, C423T | MN844139 | ||||
| 2 | 76–482 | T183Y, T387Y, C396Y, C423Y | MN844140 | ||||
| 1 | 76–496 | T183Y, T387Y, C423Y | MN844141 | ||||
| BIII/BIV | 1 | 76–496 | C85Y2, T135Y, T183Y, G186R, C255Y, C273Y, C345Y, T366Y, C372Y, T387Y, A438R, G453R | MN844142 | |||
| bg | A | AII | 3 | AY072723 | 96–604 | None | MN844143 |
| B | B | 3 | AY072727 | 93–593 | G159A, C165T, C309T, C324T, C393T, T471C | MN844144 | |
| 1 | 102–590 | G159A, C165T, A265R3, C309T, C324T, C393T, T471C | MN844145 | ||||
| 1 | 93–604 | G159A, C165T, C309T, C324T, C352T4, C393T, T471C | – | ||||
| 1 | 102–604 | G159A, C165T, C309T, C324T, C372T, C393T, T471C | MN844146 | ||||
| tpi | A | AII | 2 | U57897 | 282–751 | None | MN844147 |
| 1 | 276–805 | C287G, A291W5 | MN844148 | ||||
| B | BIV | 7 | AF069560 | 1–479 | None | MN844149 | |
| 1 | 1–479 | A201R6 | MN844150 | ||||
| 1 | 1–479 | G305A, G425A, G426A7 | MN844151 |
| Species | No. of Isolates | Reference Sequence | Stretch | Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms | GenBank ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. hominis | 5 | AF108865 | 572–994 | None | MN836820 |
| 2 | 606–938 | C607T, C620T | MN836821 | ||
| 1 | 589–985 | C607T, C620T, 697insT1, G862T | MN836822 | ||
| 1 | 536–949 | 695_697delTTT2, T795C | MN836823 | ||
| 1 | 687–952 | A855G | MN836824 | ||
| C. parvum | 2 | AF112571 | 603–877 | Unknown3 | – |
| 1 | 535–1025 | A646G, T648C, T649G, 686-689delTAAT2, A691T, T910C | MN836825 | ||
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 1 | – | – | – | – |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muadica, A.S.; Köster, P.C.; Dashti, A.; Bailo, B.; Hernández-de-Mingo, M.; Reh, L.; Balasegaram, S.; Verlander, N.Q.; Ruiz Chércoles, E.; Carmena, D. Molecular Diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in Asymptomatic School Children in Leganés, Madrid (Spain). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040466
Muadica AS, Köster PC, Dashti A, Bailo B, Hernández-de-Mingo M, Reh L, Balasegaram S, Verlander NQ, Ruiz Chércoles E, Carmena D. Molecular Diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in Asymptomatic School Children in Leganés, Madrid (Spain). Microorganisms. 2020; 8(4):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040466
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuadica, Aly Salimo, Pamela Carolina Köster, Alejandro Dashti, Begoña Bailo, Marta Hernández-de-Mingo, Lucia Reh, Sooria Balasegaram, Neville Q Verlander, Esther Ruiz Chércoles, and David Carmena. 2020. "Molecular Diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in Asymptomatic School Children in Leganés, Madrid (Spain)" Microorganisms 8, no. 4: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040466
APA StyleMuadica, A. S., Köster, P. C., Dashti, A., Bailo, B., Hernández-de-Mingo, M., Reh, L., Balasegaram, S., Verlander, N. Q., Ruiz Chércoles, E., & Carmena, D. (2020). Molecular Diversity of Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp. and Blastocystis sp. in Asymptomatic School Children in Leganés, Madrid (Spain). Microorganisms, 8(4), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040466