Bacterial Populations in International Artisanal Kefirs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genetic Approaches for Identification of Bacteria in Kefir
2.1.1. Kefir Preparation
2.1.2. DNA Extraction
2.1.3. The16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.2. The 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Approaches for Identification of Bacteria in Kefir Samples
3.1.1. Bacterial Phyla and Genera Present in Artisanal Kefirs and Their Grains
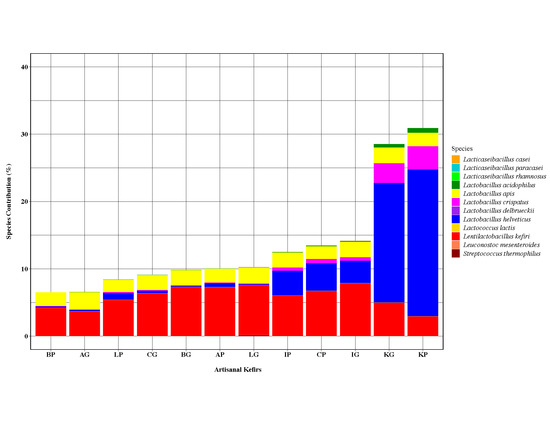
3.1.2. Bacterial Species Present in Artisanal Kefirs and Their Grains
3.1.3. Bacteriocinogenic and Beneficial Bacteria in Artisanal Kefirs
3.1.4. Correlation of Artisanal Kefir Products to Their Grains and Taxonomic Relationships Among International Artisanal Kefirs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nejati, F.; Junne, S.; Neubauer, P. A Big World in Small Grain: A Review of Natural Milk Kefir Starters. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalbantoglu, U.; Cakar, A.; Dogan, H.; Abaci, N.; Ustek, D.; Sayood, K.; Can, H. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community in kefir grains. Food Microbiol. 2014, 41, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.R.; Blandón, L.M.; Vandenberghe, L.P.; Rodrigues, C.; Castro, G.R.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Milk kefir: Composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourrie, B.C.; Willing, B.P.; Cotter, P.D. The Microbiota and Health Promoting Characteristics of the Fermented Beverage Kefir. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanirati, D.F.; Abatemarco, M., Jr.; Sandes, S.H.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nunes, Á.C.; Neumann, E. Selection of lactic acid bacteria from Brazilian kefir grains for potential use as starter or probiotic cultures. Anaerobe 2015, 32, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, B.; Gurakan, G.C.; Unlu, G. Kefir: A multifaceted fermented dairy product. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2014, 6, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfederico, L.; Hollmann, A.; Martínez, M.; Iglesias, N.G.; De Antoni, G.; Semorile, L. Molecular identification and typing of lactobacilli isolated from kefir grains. J. Dairy Res. 2006, 73, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neve, H.; Heller, K.J. The microflora of water kefir: A glance by scanning electron microscopy. Milchwirtschaftliche Forschungsberichte 2002, 54, 337–349. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, A.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.D.; Ross, P.; Hill, C. High-throughput sequence-based analysis of the bacterial composition of kefir and an associated kefir grain. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 320, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montville, T.J.; Matthews, K.R.; Kniel, K.E. Food Microbiology an Introduction, 3rd ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- da C. P. Miguel, M.G.; Cardoso, P.G.; Magalhães, K.T. Profile of microbial communities present in tibico (sugary kefir) grains from different Brazilian States. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Evaluation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Powder Milk and Live Lactic Acid Bacteria; FAO/WHO: Córdoba, Argentina, 2001; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Berni Canani, R.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamane, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Nakagaki, T.; Nakano, Y. Lactic Acid Bacteria from Kefir Increase Cytotoxicity of Natural Killer Cells to Tumor Cells. Foods 2018, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, Z.; Tang, W.; Geng, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the probiotic attributes of Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens XL10 isolated from Tibetan kefir grain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Pan, C.; Huang, Y. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus strains isolated from Tibetan kefir grains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slattery, C.; Cotter, P.D.; O’Toole, P.W. Analysis of Health Benefits Conferred by Lactobacillus Species from Kefir. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sindi, A.; Badsha, M.B.; Nielsen, B.; Ünlü, G. Antimicrobial Activity of Six International Artisanal Kefirs Against Bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Staphylococcus aureus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jeong, D.; Kim, H.; Kang, I.B.; Chon, J.W.; Song, K.Y.; Seo, K.H. Antimicrobial Activity of Kefir against Various Food Pathogens and Spoilage Bacteria. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balcázar, J.L.; de Blas, I.; Ruiz-Zarzuela, I.; Vendrell, D.; Gironés, O.; Muzquiz, J.L. Sequencing of variable regions of the 16S rRNA gene for identification of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the intestinal microbiota of healthy salmonids. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 30, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Ludwig, W.; Vogel, R.F. Comparative phylobiomic analysis of the bacterial community of water kefir by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing and ARDRA analysis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, A.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequence-based analysis of the microbial composition of water kefir from multiple sources. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 348, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Jia, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y. Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens, the sole dominant and stable bacterial species, exhibits distinct morphotypes upon colonization in Tibetan kefir grains. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Hsiao, P.J.; Hong, W.S.; Dai, T.Y.; Chen, M.J. Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1 isolated from milk kefir grains ameliorates experimental colitis in vitro and in vivo. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, W.-S.; Chen, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Chen, M.-J. Effects of kefir supernatant and lactic acid bacteria isolated from kefir grain on cytokine production by macrophage. Int. Dairy J. 2009, 19, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dertli, E.; Çon, A.H. Microbial diversity of traditional kefir grains and their role on kefir aroma. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvie, C.; Marie-Laure, G.; Laurence, M.; Catherine, G.; Christiane, B.; Dominique, C.; Chantal, B. Lactobacillus gigeriorum sp. nov., isolated from chicken crop. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kimoto, K.I.; Aizawa, T.; Urai, M.; Bao Ve, N.; Suzuki, K.I.; Nakajima, M.; Sunairi, M. Acidocella aluminiidurans sp. nov., an aluminium-tolerant bacterium isolated from Panicum repens grown in a highly acidic swamp in actual acid sulfate soil area of Vietnam. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60 Pt 4, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korsak, N.; Taminiau, B.; Leclercq, M.; Nezer, C.; Crevecoeur, S.; Ferauche, C.; Detry, E.; Delcenserie, V.; Daube, G. Short communication: Evaluation of the microbiota of kefir samples using metagenetic analysis targeting the 16S and 26S ribosomal DNA fragments. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3684–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özdemir, N.; Kök Taş, T.; Guzel-Seydim, Z. Effect of Gluconacetobacter spp. on Kefir Grains and Kefir Quality. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 99–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, C.; Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Aquilanti, L.; De Filippis, F.; Stellato, G.; Di Mauro, S.; Turchetti, B.; Buzzini, P.; Ercolini, D.; et al. Bacteria and yeast microbiota in milk kefir grains from different Italian regions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B.; Li, B.; Luo, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, T. Symbiosis between microorganisms from kombucha and kefir: Potential significance to the enhancement of kombucha function. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzler, S.R.; Clancy, S.M. Kefir improves lactose digestion and tolerance in adults with lactose maldigestion. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ts, L.; MaryPramela, P.; Iyer, P. Anti-microbial, anti-fungal and anti-carcinogenic properties of coconut milk kefir. Int. J. Home Sci. 2017, 3, 365–369. [Google Scholar]
- Güven, A.; Güven, A.; Gülmez, M. The effect of kefir on the activities of GSH-Px, GST, CAT, GSH and LPO levels in carbon tetrachloride-induced mice tissues. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2003, 50, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Mogensen, G.; Fondén, R.; Mättö, J.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Probiotic bacteria: Safety, functional and technological properties. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 84, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.-R.; Patra, J.K.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, S.-S. Antagonistic Activities and Probiotic Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria Derived From a Plant-Based Fermented Food. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.L.; Toh, M.; Liu, S.Q. Saccharomyces cerevisiae EC-1118 enhances the survivability of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 in an acidic environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6803–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.M.; Miguel, M.A.; Peixoto, R.S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Paschoalin, V.M.; Mayo, B.; Delgado, S. Probiotic potential of selected lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from Brazilian kefir grains. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3622–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabir, F.; Beyatli, Y.; Cokmus, C.; Onal-Darilmaz, D. Assessment of potential probiotic properties of Lactobacillus spp., Lactococcus spp., and Pediococcus spp. strains isolated from kefir. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, M568–M573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Sui, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, J. Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum Lp27 isolated from Tibetan kefir grains: A potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carasi, P.; Diaz, M.; Racedo, S.M.; De Antoni, G.; Urdaci, M.C.; Serradell Mde, L. Safety characterization and antimicrobial properties of kefir-isolated Lactobacillus kefiri. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 208974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosch, A.; Golowczyc, M.A.; Abraham, A.G.; Garrote, G.L.; De Antoni, G.L.; Yantorno, O. Rapid discrimination of lactobacilli isolated from kefir grains by FT-IR spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 111, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Chen, M.J. Microbiological study of lactic acid bacteria in kefir grains by culture-dependent and culture-independent methods. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Li, B. Chemical and microbiological characteristics of kefir grains and their fermented dairy products: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1272152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, J.L.; Caron, C.R.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Soccol, C.R. Bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria: Purification, properties and use as biopreservatives. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahrous, H.; Mohamed, A.; El-Mongy, M.A.; El-Batal, A.I.; Hamza, H.A. Study bacteriocin production and optimization using new isolates of Lactobacillus spp. isolated from some dairy products under different culture conditions. Food Nutr. Sci. 2013, 4, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suskovic, J.; Kos, B.; Beganovic, J.; Pavunc, A.L.; Habjanic, K.; Matosic, S. Antimicobial activity- the most important property of probiotic and starter lactic acid bacteria. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 296–307. [Google Scholar]
- Mokoena, M.P. Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Bacteriocins: Classification, Biosynthesis and Applications against Uropathogens: A Mini-Review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgasem, B.Y.; Hassan, Z.; Abdalsadiq, N.K.A.; Yusoff, W.M.W.; Musa, E.M.M.T.; Lani, M.N. Anti-adhesion activity of lactic acid bacteria supernatant against human pathogenic Candida species biofilm. Health Sci. J. 2015, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, C. Probiotics in obstetrics and gynaecology. Obst. Gynaecol. 2015, 55, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, Y.; Ono, H.; Kitagawa, H.; Ito, H.; Mu, F.; Sawa, N.; Zendo, T.; Sonomoto, K. Identification and characterization of leucocyclicin Q, a novel cyclic bacteriocin produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides TK41401. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8164–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simova, E.; Beshkova, D.; Dimitrov, Z. Characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional Bulgarian dairy products. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Dong, M. Analysis of the microflora in Tibetan kefir grains using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.F.; Fan, M.T.; Jin, D. Isolation of lactic acid bacteria from Tibetan kefir grains and study on its fermentation performance. J. Northwest. Sci. Technol. Univ. Agric. Forrest 2004, 32, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Simova, E.; Beshkova, D.; Angelov, A.; Hristozova, T.; Frengova, G.; Spasov, Z. Lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in kefir grains and kefir made from them. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barao, C.E.; Klososki, S.J.; Pinheiro, K.H.; Marcolino, V.; Valarini, J.O.; Cruz, A.G.; Da Silva, T.T.; Tatiana, P. Growth Kinetics of Kefir Biomass: Influence of the Incubation Temperature in Milk. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 75, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, O.; Mortas, M.; Atalar, I.; Dervisoglu, M.; Kahyaoglu, T. Manufacture and characterization of kefir made from cow and buffalo milk, using kefir grain and starter culture. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sindi, A.; Badsha, M.B.; Ünlü, G. Bacterial Populations in International Artisanal Kefirs. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091318
Sindi A, Badsha MB, Ünlü G. Bacterial Populations in International Artisanal Kefirs. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091318
Chicago/Turabian StyleSindi, Abrar, Md. Bahadur Badsha, and Gülhan Ünlü. 2020. "Bacterial Populations in International Artisanal Kefirs" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091318
APA StyleSindi, A., Badsha, M. B., & Ünlü, G. (2020). Bacterial Populations in International Artisanal Kefirs. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091318