Potential Use of Copper-Contaminated Soils for Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Growing Conditions
2.2. Chlorophyll Content
2.3. Determination of Nutrient Concentration
2.4. Determination of Malondialdehyde Content
2.5. Non-Protein Thiols Extraction and Determination
2.6. Extraction and Assay of OASTL Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plant Growth Rate, Chlorophyll Content and Nutritional Status
3.2. Malondialdehyde Content
3.3. Non-Protein Thiols Content and OASTL Activity Rate
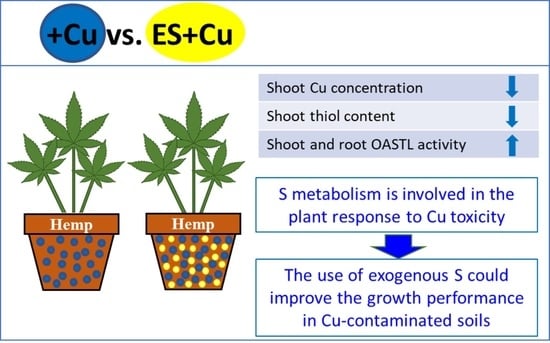
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Directive 2009/28/EC. Available online: https://www.buildup.eu/en/practices/publications/directive-200928ec-promotion-use-energy-renewable-sources-23-april-2009 (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Tilman, D.; Reich, P.B.; Knops, J.M.H. Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 2006, 441, 629–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffes, J.; Haniotis, T. Placing the 2006/08 Commodity Price Boom into Perspective; Policy Research Working Papers; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fagnano, M.; Boccia, L.; Pindozzi, S.; Infascelli, R.; Augno, S. Aree potenzialmente convertibili a colture energetiche: Caso studio della Regione Campania. In Proceedings of the XLI Convegno Società Italiana di Agronomia, Bari, Italy, 19–21 September 2012; pp. 464–466. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, G.; Montanarella, L.; Rusco, E. Threats to Soil Quality in Europe 2008; European Communities: Luxembourg, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Shafi, M.; Ma, J.; Zhong, B.; Guo, J.; Hu, X.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Effect of amendments on contaminated soil of multiple heavy metals and accumulation of heavy metals in plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28695–28704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschner, P. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Marschner, P., Ed.; Elselvier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto, G.; de Melo, G.W.B.; Terzano, R.; Del Buono, D.; Astolfi, S.; Tomasi, N.; Pii, Y.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S. Copper accumulation in vineyard soils: Rhizosphere processes and agronomic practices to limit its toxicity. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cesco, S.; Pii, Y.; Borruso, L.; Orzes, G.; Lugli, P.; Mazzetto, F.; Genova, G.; Signorini, M.; Brunetto, G.; Terzano, R.; et al. A Smart and Sustainable Future for Viticulture is Rooted in Soil: How to Face Cu Toxicity. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, M.; Čadková, E.; Chrastný, V.; Bordas, F.; Bollinger, J.C. Contamination of vineyard soils with fungicides: A review of environmental and toxicological aspects. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, Z.; Sardar, A.; Shabbir, A.; Abbas, G.; Shamshad, S.; Khalid, S.; Natasha; Murtaza, G.; Dumat, C.; Shahid, M. Copper uptake, essentiality, toxicity, detoxification and risk assessment in soil-plant environment. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, H.-P.; Brümmer, G.W.; Fleige, H.; Horn, R.; Kandeler, E.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Kretzschmar, R.; Stahr, K.; Wilke, B.-M. Scheffer/Schachtschabel Soil Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783642309410. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Saleem, M.H.; Bashir, S.; Ullah, S.; Peng, D. Copper environmental toxicology, recent advances, and future outlook: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18003–18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miotto, A.; Ceretta, C.A.; Brunetto, G.; Nicoloso, F.T.; Girotto, E.; Farias, J.G.; Tiecher, T.L.; De Conti, L.; Trentin, G. Copper uptake, accumulation and physiological changes in adult grapevines in response to excess copper in soil. Plant. Soil 2014, 374, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravet, K.; Pilon, M. Copper and Iron Homeostasis in Plants: The Challenges of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feil, S.B.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Tiziani, R.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S. Copper toxicity affects phosphorus uptake mechanisms at molecular and physiological levels in Cucumis sativus plants. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 157, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, E.; Miotto, A.; Ceretta, C.A.; Quartieri, M.; Sorrenti, G.; Brunetto, G.; Toselli, M. Soil-applied phosphorous is an effective tool to mitigate the toxicity of copper excess on grapevine grown in rhizobox. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 227, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Conti, L.; Cesco, S.; Mimmo, T.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Melo, G.W.B.; Ceretta, C.A.; Trentin, E.; Marques, A.C.; Brunetto, G. Iron fertilization to enhance tolerance mechanisms to copper toxicity of ryegrass plants used as cover crop in vineyards. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marastoni, L.; Sandri, M.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Brunetto, G.; Cesco, S.; Mimmo, T. Synergism and antagonisms between nutrients induced by copper toxicity in grapevine rootstocks: Monocropping vs. intercropping. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marastoni, L.; Tauber, P.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Astolfi, S.; Simoni, A.; Brunetto, G.; Cesco, S.; Mimmo, T. The potential of two different Avena sativa L. cultivars to alleviate Cu toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monni, S.; Salemaa, M.; White, C.; Tuittila, E.; Huopalainen, M. Copper resistance of Calluna vulgaris originating from the pollution gradient of a Cu–Ni smelter, in southwest Finland. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 109, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauser, W.E. Structure and function of metal chelators produced by plants. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 31, 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheay, H.T.; Omondi, E.C.; Brewer, C.E. Potential of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) for paired phytoremediation and bioenergy production. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Tehsin, Z.; Malik, S.T.; Asad, S.A.; Shahzad, M.; Bilal, M.; Shah, M.M.; Khan, S.A. Phytoremediation Potential of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Identification and Characterization of Heavy Metals Responsive Genes. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2015, 44, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meers, E.; Ruttens, A.; Hopgood, M.; Lesage, E.; Tack, F.M.G. Potential of Brassic rapa, Cannabis sativa, Helianthus annuus and Zea mays for phytoextraction of heavy metals from calcareous dredged sediment derived soils. Chemosphere 2006, 61, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celletti, S.; Paolacci, A.R.; Mimmo, T.; Pii, Y.; Cesco, S.; Ciaffi, M.; Astolfi, S. The effect of excess sulfate supply on iron accumulation in three graminaceous plants at the early vegetative phase. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 128, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celletti, S.; Astolfi, S.; Guglielmo, N.; Colla, G.; Cesco, S.; Mimmo, T. Evaluation of a Legume-Derived Protein Hydrolysate to Mitigate Iron Deficiency in Plants. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal Bashir, M.; Silvestri, C.; Coppa, E.; Brunori, E.; Cristofori, V.; Rugini, E.; Ahmad, T.; Hafiz, I.A.; Abbasi, N.A.; Shah, M.K.N.; et al. Response of Olive Shoots to Salinity Stress Suggests the Involvement of Sulfur Metabolism. Plants 2021, 10, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celletti, S.; Pii, Y.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S.; Astolfi, S. The characterization of the adaptive responses of durum wheat to different Fe availability highlights an optimum Fe requirement threshold. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 109, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, J.A. Handbook of Energy Crops 1983; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Chanet, G.; Morin-Crini, N. Applications of hemp in textiles, paper industry, insulation and building materials, horticulture, animal nutrition, food and beverages, nutraceuticals, cosmetics and hygiene, medicine, agrochemistry, energy production and environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 1451–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, S.; Celletti, S.; Vigani, G.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S. Interaction Between Sulfur and Iron in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.T.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, B. Nutrition Influence on Copper Accumulation by Brassica pekinensis Rupr. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2002, 53, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, S.; Pii, Y.; Terzano, R.; Mimmo, T.; Celletti, S.; Allegretta, I.; Lafiandra, D.; Cesco, S. Does Fe accumulation in durum wheat seeds benefit from improved whole-plant sulfur nutrition? J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, S.; Ortolani, M.R.; Catarcione, G.; Paolacci, A.R.; Cesco, S.; Pinton, R.; Ciaffi, M. Cadmium exposure affects iron acquisition in barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesco, S.; Nikolic, M.; Römheld, V.; Varanini, Z.; Pinton, R. Uptake of 59Fe from soluble 59Fe-humate complexes by cucumber and barley plants. Plant. Soil 2002, 241, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasser, O.; Köhl, K.; Römheld, V. Overestimation of apoplastic Fe in roots of soil grown plants. Plant. Soil 1999, 210, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, B.M.; McInturf, S.A.; Stein, R.J. Rosette iron deficiency transcript and microRNA profiling reveals links between copper and iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5903–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, H.; Wang-Müller, Q.; Witt, T.; Malaisse, F.; Küpper, H. Differences in copper accumulation and copper stress between eight populations of Haumaniastrum katangense. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 79, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesco, S.; Tolotti, A.; Nadalini, S.; Rizzi, S.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Mimmo, T.; Porfido, C.; Allegretta, I.; Giovannini, O.; Perazzolli, M.; et al. Plasmopara viticola infection affects mineral elements allocation and distribution in Vitis vinifera leaves. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Sun, C.-X.; Ye, X.-Z.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. The effect of biochar and crop straws on heavy metal bioavailability and plant accumulation in a Cd and Pb polluted soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 132, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancenón, V.; Puig, S.; Mira, H.; Thiele, D.J.; Peñarrubia, L. Identification of a copper transporter family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2003, 51, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wintz, H.; Fox, T.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Feng, V.; Chen, W.; Chang, H.-S.; Zhu, T.; Vulpe, C. Expression Profiles of Arabidopsis thaliana in Mineral Deficiencies Reveal Novel Transporters Involved in Metal Homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47644–47653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korshunova, Y.O.; Eide, D.; Clark, W.G.; Guerinot, M.L.; Pakrasi, H.B. The IRT1 protein from Arabidopsis thaliana is a metal transporter with a broad substrate range. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1999, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Tewari, R.K.; Sharma, P.N. Modulation of copper toxicity-induced oxidative damage by excess supply of iron in maize plants. Plant. Cell Rep. 2008, 27, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lock, K.; Criel, P.; De Schamphelaere, K.A.C.; Van Eeckhout, H.; Janssen, C.R. Influence of calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium and pH on copper toxicity to barley (Hordeum vulgare). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2007, 68, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-C.; Ho, P.-C.; Juang, K.-W. Alleviation effects of magnesium on copper toxicity and accumulation in grapevine roots evaluated with biotic ligand models. Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinraide, T.B.; Pedler, J.F.; Parker, D.R. Relative effectiveness of calcium and magnesium in the alleviation of rhizotoxicity in wheat induced by copper, zinc, aluminum, sodium, and low pH. Plant. Soil 2004, 259, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lan, P. The Understanding of the Plant Iron Deficiency Responses in Strategy I Plants and the Role of Ethylene in This Process by Omic Approaches. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuchi, S.; Watanabe, M.; Hubberten, H.-M.; Bromke, M.; Osorio, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Celletti, S.; Paolacci, A.R.; Catarcione, G.; Ciaffi, M.; et al. The interplay between sulfur and iron nutrition in tomato. Plant. Physiol. 2015, 169, 2624–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noriega, G.; Caggiano, E.; Lecube, M.L.; Cruz, D.S.; Batlle, A.; Tomaro, M.; Balestrasse, K.B. The role of salicylic acid in the prevention of oxidative stress elicited by cadmium in soybean plants. BioMetals 2012, 25, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid Peroxidation: Production, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Umeno, A.; Shichiri, M. Lipid peroxidation biomarkers for evaluating oxidative stress and assessing antioxidant capacity in vivo. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2013, 52, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.S.; Dietz, K.-J. The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant. Sci. 2009, 14, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, K.; Jakob, U. The role of thiols in antioxidant systems. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 140, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E. Plant Physiology, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003; ISBN 0-87893-823-0. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, J.R.; Parmar, S.; Jones, J.; Shepherd, C.E.; Corol, D.-I.; Galster, A.M.; Hawkins, N.D.; Miller, S.J.; Baker, J.M.; Verrier, P.J.; et al. Co-ordinated expression of amino acid metabolism in response to N and S deficiency during wheat grain filling. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidian, J.-C.; Kopriva, S. Regulation of Sulfate Uptake and Assimilation—The Same or Not the Same? Mol. Plant. 2010, 3, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappartient, A.G.; Touraine, B. Demand-Driven Control of Root ATP Sulfurylase Activity and SO42-Uptake in Intact Canola (The Role of Phloem-Translocated Glutathione). Plant. Physiol. 1996, 111, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Plasma Power (kW) | 1.4 |
| Pump Speed (Rpm) | 30 |
| Coolant Flow (L min−1) | 14 |
| Auxiliary Flow (L min−1) | 0.8 |
| Nebulizer Flow (L min−1) | 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quagliata, G.; Celletti, S.; Coppa, E.; Mimmo, T.; Cesco, S.; Astolfi, S. Potential Use of Copper-Contaminated Soils for Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivation. Environments 2021, 8, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110111
Quagliata G, Celletti S, Coppa E, Mimmo T, Cesco S, Astolfi S. Potential Use of Copper-Contaminated Soils for Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivation. Environments. 2021; 8(11):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110111
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuagliata, Giulia, Silvia Celletti, Eleonora Coppa, Tanja Mimmo, Stefano Cesco, and Stefania Astolfi. 2021. "Potential Use of Copper-Contaminated Soils for Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivation" Environments 8, no. 11: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110111
APA StyleQuagliata, G., Celletti, S., Coppa, E., Mimmo, T., Cesco, S., & Astolfi, S. (2021). Potential Use of Copper-Contaminated Soils for Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Cultivation. Environments, 8(11), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110111