Environmental Exploration of Ultra-Dense Nanobubbles: Rethinking Sustainability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
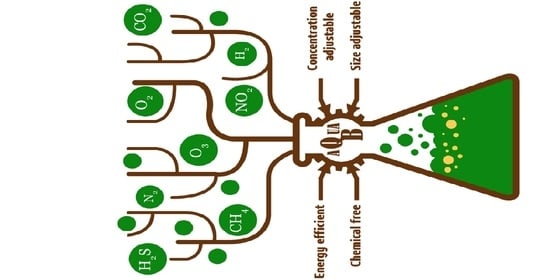
2. Microscopic Fundamentals
3. Techniques for Nanobubble Generation
- Device for generating nanobubbles by electric current supply [65]
- Water-containing oxygen nanobubbles and method for the production thereof [66]
- Method of forming nanobubbles [67]
- Method and apparatus for applying electrical charge through a liquid to enhance sanitizing properties [68]: this patent uses electrolysis with ionic sources.
4. Characterization of the Nano-Phase
5. The Context for Nanobubbles in Environmental Sustainability
6. A Wastewater and Ecosystem-Management Pathway
7. Case Study of Wastewater-Treatment
8. Agricultural Progress and Visions
9. Environmental and Sustainability Outlook
10. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seddon, J.R.T.; Lohse, D.; Ducker, W.A.; Craig, V.S.J. A deliberation on nanobubbles at surfaces and in bulk. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, D.; Zhang, X. Surface nanobubbles and nanodroplets. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alheshibri, M.; Qian, J.; Jehannin, M.; Craig, V.S.J. A history of nanobubbles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11086–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; An, H.; Alheshibri, M.; Liu, L.; Terpstra, P.M.; Liu, G.; Craig, V.S. Cleaning with bulk nanobubbles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11203–11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bhushan, B. Boundary slip and nanobubble study in micro/nanofluidics using atomic force microscopy. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 29–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchuk, N.; Ralston, J.; Fornasiero, D. Influence of very small bubbles on particle/bubble heterocoagulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 301, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, K.K.; Jana, A.; Ghosh, S.; Watson, R.; Pahan, K. A physically-modified saline suppresses neuronal apoptosis, attenuates tau phosphorylation and protects memory in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled Abdella Ahmed, A.; Sun, C.; Hua, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Marhaba, T.; Zhang, W. Colloidal Properties of Air, Oxygen, and Nitrogen Nanobubbles in Water: Effects of Ionic Strength, Natural Organic Matters, and Surfactants. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Kawagoe, Y.; Makino, Y.; Oshita, S. Effects of Nanobubbles on the Physicochemical Properties of Water: The Basis for Peculiar Properties of Water Containing Nanobubbles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 93, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demangeat, J.-L. Nanobulles et Superstructures Nanométriques Dans Les Hautes Dilutions Homéopathiques: Le Rôle Crucial de La Dynamisation et Hypothèse de Transfert de L’information. Rev. d’Homéopathie 2015, 6, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushikubo, F.Y.; Furukawa, T.; Nakagawa, R.; Enari, M.; Makino, Y.; Kawagoe, Y.; Shiina, T.; Oshita, S. Evidence of the Existence and the Stability of Nano-Bubbles in Water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 361, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Tao, D.; Honaker, R.; Luo, Z. Nanobubble Generation and Its Applications in Froth Flotation (Part IV): Mechanical Cells and Specially Designed Column Flotation of Coal. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 641–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Tao, D.; Honaker, R.; Luo, Z. Nanobubble Generation and Its Applications in Froth Flotation (Part III): Specially Designed Laboratory Scale Column Flotation of Phosphate. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhy, A.; Tao, D. Nanobubble Column Flotation of Fine Coal Particles and Associated Fundamentals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 124, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Tao, D.; Honaker, R.; Luo, Z. Nanobubble Generation and Its Applications in Froth Flotation (Part II): Fundamental Study and Theoretical Analysis. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Tao, D.; Honaker, R.; Luo, Z. Nanobubble Generation and Its Application in Froth Flotation (Part I): Nanobubble Generation and Its Effects on Properties of Microbubble and Millimeter Scale Bubble Solutions. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, D. Fundamental Studies of Nanobubble Generation and Applications in Flotation. In Separation Technologies for Minerals, Coal, and Earth Resources; Society for Mining, Metallurgy, and Exploration: Englewood, CO, USA, 2012; pp. 457–469. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, W.B.; Tesař, V.; Bandulasena, H.C.H. Towards Energy Efficient Nanobubble Generation with Fluidic Oscillation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, T.; Bui, T.T.; Han, M.; Kim, T.-I.; Park, H. Micro and Nanobubble Technologies as a New Horizon for Water-Treatment Techniques: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 246, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, K.; Cen, C.; Wu, X.; Mao, R.; Zheng, Y. Role of bulk nanobubbles in removing organic pollutants in wastewater treatment. AMB Express 2021, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Xia, Z. Application of Ozone Micro-Nano-Bubbles to Groundwater Remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, O.; Urban, A.S.; Day, J.; Lal, S.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Solar Vapor Generation Enabled by Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imaizumi, K.; Tinwongger, S.; Kondo, H.; Hirono, I. Disinfection of an EMS/AHPND Strain of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Using Ozone Nanobubbles. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, B. The Effect of Ultrasonic Waves on the Nucleation of Pure Water and Degassed Water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, K.E.; Caudell, D.N.; Sutton, J.T.; Klegerman, M.E.; Vela, D.; Pyne-Geithman, G.J.; Abruzzo, T.; Cyr, P.E.P.; Geng, Y.-J.; McPherson, D.D.; et al. Ultrasound-Enhanced Delivery of Targeted Echogenic Liposomes in a Novel Ex Vivo Mouse Aorta Model. J. Control. Release 2010, 144, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenk, H.J.; Steppe, K.; Jansen, S. Nanobubbles: A New Paradigm for Air-Seeding in Xylem. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Gupta, B.S.; Sahu, J.N. Application of Colloidal Gas Aphrons for Pollution Remediation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, L.; Song, D.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Subsurface Transport Behaviour of Micro-Nano Bubbles and Potential Applications for Groundwater Remediation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 11, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, L.; Ding, Y.; Liu, B.; Zeng, H.; Zhong, L.; Li, X. Foam, a Promising Vehicle to Deliver Nanoparticles for Vadose Zone Remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, L.R.; Banyard, D.A.; Ziegler, M.E.; Obagi, Z.; Prussak, J.; Klopfer, M.J.; Evans, G.R.; Widgerow, A.D. Topical Oxygen Therapy by Micro/nanobubbles: A New Modality for Tissue Oxygen Delivery. Int. Wound J. 2018, 15, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argenziano, M.; Banche, G.; Luganini, A.; Finesso, N.; Allizond, V.; Gulino, G.R.; Khadjavi, A.; Spagnolo, R.; Tullio, V.; Giribaldi, G.; et al. Vancomycin-Loaded Nanobubbles: A New Platform for Controlled Antibiotic Delivery against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nedělka, J.; Nedělka, T. 17th International Congress of the International Society for Medical Schockwave Treatment 27–29 Června 2014, Milán. Bolest 2014, 17, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuge, H. Micro- and Nanobubbles: Fundamentals and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sette, D.; Wanderlingh, F. Nucleation by Cosmic Rays in Ultrasonic Cavitation. Phys. Rev. 1962, 125, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Shkirin, A.V.; Suyazov, N.V.; Babenko, V.A.; Sychev, A.A.; Penkov, N.V.; Belosludtsev, K.N.; Gudkov, S.V. Formation and Dynamics of Ion-Stabilised Gas Nanobubble Phase in the Bulk of Aqueous NaCl Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetovoy, V.B.; Sanders, R.G.P.; Elwenspoek, M.C. Transient Nanobubbles in Short-Time Electrolysis. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 184002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Saitoh, Y.; Miwa, N. Electrolytically Generated Hydrogen Warm Water Cleanses the Keratin-Plug-Clogged Hair-Pores and Promotes the Capillary Blood-Streams, More Markedly than Normal Warm Water Does. Med. Gas Res. 2018, 8, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren, S.; Eriksson, J.C. The Lifetime of a Colloid-Sized Gas Bubble in Water and the Cause of the Hydrophobic Attraction. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 129, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usanov, A.D.; Ulyanov, S.S.; Ilyukhina, N.S.; Usanov, D.A. Monitoring of Changes in Cluster Structures in Water under AC Magnetic Field. Opt. Spectrosc. 2016, 120, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunkin, N.F.; Ninham, B.W.; Ignatiev, P.S.; Kozlov, V.A.; Shkirin, A.V.; Starosvetskij, A.V. Long-Living Nanobubbles of Dissolved Gas in Aqueous Solutions of Salts and Erythrocyte Suspensions. J. Biophotonics 2011, 4, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Tuziuti, T.; Kanematsu, W. Mysteries of Bulk Nanobubbles (Ultrafine Bubbles); Stability and Radical Formation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 48, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Dong, Y. Understanding the Stability of Surface Nanobubbles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2013, 25, 184007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijs, J.H.; Lohse, D. Why Surface Nanobubbles Live for Hours. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 54501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weijs, J.H.; Seddon, J.R.T.; Lohse, D. Diffusive Shielding Stabilises Bulk Nanobubble Clusters. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epstein, P.S.; Plesset, M.S. On the stability of gas bubbles in liquid-gas solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1950, 18, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, B.H.; An, H.; Ohl, C.-D. Stability of surface and bulk nanobubbles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 53, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.J.; Barigou, M. Bulk nanobubbles or not nanobubbles: That is the question. Langmuir 2020, 36, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alheshibri, M.; Craig, V.S. Armoured nanobubbles; ultrasound contrast agents under pressure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 537, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, D.-W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L. Effects of Micro-Nano Bubbles on the Nucleation and Crystal Growth of Sucrose and Maltodextrin Solutions during Ultrasound-Assisted Freezing Process. LWT 2018, 92, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K. Recent Patents on Micro- and Nano-Bubble Applications and Potential Application of a Swirl-Type Generator. Recent Patents Mech. Eng. 2011, 4, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.F.; Yu, X. Pico-Nano Bubble Column Flotation Using Static Mixer-Venturi Tube for Pittsburgh No. 8 Coal Seam. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Saiki, Y.; Kubo, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Yang, J. Influence of High-Power Ultrasonic Irradiation on Primary Nucleation Process during Solidification. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 4939–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fales, A.M.; Vogt, W.C.; Wear, K.A.; Pfefer, J.; Ilev, I.K. Size-Dependent Thresholds for Melting and Nanobubble Generation Using Pulsed-Laser Irradiated Gold Nanoparticles. In Progress in Biomedical Optics and Imaging—Proceedings of SPIE; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018; p. 105090C. [Google Scholar]
- Znak, Z.O.; Sukhatskiy, Y.V.; Zin, O.I.; Khomyak, S.V.; Mnykh, R.V.; Lysenko, A.V. The Decomposition of the Benzene in Cavitation Fields. Vopr. Khimii Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii 2018, 1, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, X.; Alheshibri, M. The effect of ultrasound on bulk and surface nanobubbles: A review of the current status. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Peng, F. Optimisation of Cavitation Venturi Tube Design for Pico and Nano Bubbles Generation. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2015, 25, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Y. Progresses in Research and Application of Micro-Nano Bubble Generating Device. Shiyou Huagong/Petrochem. Technol. 2014, 43, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar]
- German, S.R.; Luo, L.; White, H.S.; Mega, T.L. Controlling Nanobubble And Nanoparticle Dynamics In Conical Nanopores. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, R.; English, N.J.; Marracino, P.; Liberti, M.; Apollonio, F. Dipolar response and hydrogen-bond kinetics in liquid water in square-wave time-varying electric fields. Molec. Phys. 2014, 112, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futera, Z.; English, N.J. Electric-Field Effects on Adsorbed-Water Structural and Dynamical Properties at Rutile- and Anatase-TiO2 Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 19603–19612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futera, Z.; English, N.J. Communication: Influence of external static and alternating electric fields on water from long-time non-equilibrium ab initio molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 031102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghaani, M.R.; Kusalik, P.G.; English, N.J. Massive Generation of Metastable Bulk Nano-bubbles in Water by External Electric Fields. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz0094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tetsuroh, O.; Koichiro, S. Device for Generating Nanobubbles by Electric Current Supply, PCT ref. WO2014148397A1, 18 March 2013. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2014148397A1/en (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Kaneo, C.; Masayoshi, T. Water Containing Oxygen Nano Bubbles and Method for Production Thereof. Ref. WO2005084786A1. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2005084786A1/en (accessed on 5 March 2004).
- Kaneo, C.; Masayoshi, T. Method of Forming Nanobubbles. U.S. Patent Application 10/591,977, 16 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Field, B.F. Method and Apparatus for Applying Electrical Charge through A Liquid to Enhance Sanitizing Properties. U.S. Patent Application 12/639,622, 17 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, F.; Alheshibri, M.; Swenson, J. Differentiating bulk nanobubbles from nanodroplets and nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 53, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.J.; Tu, W.-C.; Levers, O.; Bröhl, A.; Hallett, J.P. Green and Sustainable Solvents in Chemical Processes. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 747–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Z. Ionic liquids: Green and tailor-made solvents in drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Policy Department for External Relations, The Use of Pesticides in Developing Countries and Their Impact on Health and the Right to Food, Directorate General for External Policies of the European Union, PE 653.622—January 2021. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/STUD/2021/653622/EXPO_STU(2021)653622_EN.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Agrawal, S.; Dev, P.; English, N.J.; Thampi, K.R.; MacElroy, J.M.D. A TD-DFT study of the effects of structural variations on the photochemistry of polyene dyes. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomley, M.J.; Cooke, J.C.; Unger, E.C.; Monaghan, M.J.; Cosgrove, D.O. Microbubble contrast agents: A new era in ultrasound. BMJ 2001, 322, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kurata, K. Application of microbubbles to hydroponics solution promotes lettuce growth. HortTechnology 2009, 19, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregi, P.; Varley, J. Colloidal gas aphrons: Potential applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, C.J.; English, N.J. Free-energy calculations of the intercage hopping barriers of hydrogen molecules in clathrate hydrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 16561–16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futera, Z.; English, N.J. Exploring Rutile (110) and Anatase (101) TiO2 Water Interfaces by Reactive Force-Field Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 6701–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, N.; Bentvelzen, A.; English, N.J.; Yarovsky, I. Electromagnetic-field effects on structure and dynamics of amyloidogenic peptides. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 085101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- English, N.J.; Clarke, E.T. Molecular dynamics study of CO2 hydrate dissociation: Fluctuation-dissipation and non-equilibrium analysis. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 094701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaani, M.R.; English, N.J. Developments of Cutting-Edge Techniques for Facile Gas/liquid Nano-Bubble/droplet Formation for Greatly-Enhanced Gas Storage in Liquids for Months (Several-Fold above Equilibrium Solubility), and Facile de-Gassing, British Patent Office, Oct. 2018. Ref. # 1816766.2019, 8, and Three Ensuing PCT Filings Now at National-Examination Stage in EU, Japan, USA, Canada, S. Korea, Saudi Arabia, China, Australia, New Zealand. These Three PCT Details are as Follows: (i) A System, Method and Generator for Generating Nanobubbles or Nanodroplets PCT/EP2019/078003 (Oct 2019); (ii) A System and Method for the Treatment of Biogas and Wastewater PCT/EP/2019/078017 (Oct 2019); (iii) A System, Method and Generator for Generating Nanobubbles or Nanodroplets at Ambient Conditions PCT/EP2020/061107 (Apr 2020). Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2021073780 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Yang, X.; Nie, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Adachi, M.K.Y.; Shimizu, K.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced hydrolysis of waste activated sludge for methane production via anaerobic digestion under N2-nanobubble water addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchepare, R.; Oliveira, H.; Azevedo, A.; Rubio, J. Separation of emulsified crude oil in saline water by dissolved air flotation with micro and nanobubbles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieszuk, P.; Strzyżewska, A.; Ulatowski, K. Investigation of the possibility of culturing aerobic yeast with oxygen nanobubble addition and evaluation of the results of batch and semi-batch cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2021, 159, 108247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelSontro, T.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Downing, J.A. Greenhouse gas emissions from lakes and impoundments: Upscaling in the face of global change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 3, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, N.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Y.; Sun, L.; Gao, H.; Pu, Z.; Yang, W. Environment-friendly surface cleaning using micro-nano bubbles. Particuology 2022, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Hu, J. Defouling and cleaning using nanobubbles on stainless steel. J. Bioadhesion Biofilm Res. 2009, 25, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, R.; English, N.J.; Marracino, P.; Liberti, M.; Apollonio, F. Translational and Rotational Diffusive Motion in Liquid Water in Square-Wave Time-Varying Electric Fields. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 582, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human Development Report 2006. In UNDP, 2006, Coping with Water Scarcity. Challenge of the Twenty-First Century; United Nations Water Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- United Nations; Department of Economic and Social Affairs; Population Division. World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision, Methodology of the United Nations Population Estimates and Projections; ESA/P/WP.242; UN Population Office: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Cao, H.; English, N.J.; MacElroy, J.M.D. Diffusive hydrogen inter-cage migration in hydrogen and hydrogen-tetrahydrofuran clathrate hydrates. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 094507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Future Markets Technology Report. The Market for Nanobubbles/Ultrafine Bubbles: Applications, Markets and Companies, Jan. 2016. 2021. Available online: https://www.futuremarketsinc.com/nanobubbles-ultrafine-bubbles-applications-markets-and-companies/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Ahmed, A.K.A.; Shi, X.; Hua, L.; Manzueta, L.; Qing, W.; Marhaba, T.; Zhang, W. Influences of Air, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Carbon Dioxide Nanobubbles on Seed Germination and Plant Growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5117–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Dai, H.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, W.; Hu, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W. Nanobubbles promote nutrient utilization and plant growth in rice by upregulating nutrient uptake genes and stimulating growth hormone production. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Oshita, S.; Kawabata, S.; Makino, Y.; Yoshimoto, T. Identification of ROS Produced by Nanobubbles and Their Positive and Negative Effects on Vegetable Seed Germination. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11295–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Hirao, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Kawato, Y.; Kaneshiro, S.; Morimoto, T.; Koizumi, K.; Yoshikawa, H. Oxygen and air nanobubble water solution promote the growth of plants, fishes, and mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohnari, H.; Ohnari, H.; Nakayama, T.; Nakata, A.; Yamamoto, T. Generating mechanism of microbubble and its physiological characteristics. Vis. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 23, 105–106. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.; Agblevor, F.A. Microbubble fermentation of Trichoderma reesei for cellulase production. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, H.; Ohta, T.; Shundo, A.; Fukunaga, Y.; Tanaka, K. Simple surface treatment of cell-culture scaffolds with ultrafine bubble water. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15238–15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo Vega-Vásquez, N.S. Mosier and Joseph Irudayaraj, Nanoscale Drug Delivery Systems: From Medicine to Agriculture. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, C.; Gulati, S.; Fioravanti, G.; Stewart, P.; Exner, A. On the Fate of Mesh-Stabilised Lipid Nanobubbles after Destruction with Ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.; Soster, M.; Argenziano, M. Nanobubbles: A Promising Efficienft Tool for Therapeutic Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 117–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Competitive Performance Indicator | Value |
|---|---|
| Bubble lifetime: exponential-decay half-life | Minutes to months, depending on gas/solvent type |
| Energy cost of Aqua-B NB generators | kW/kg O2 transferred/h |
| Aeration efficiency (AE) | kg O2/kWh |
| “Bubbles per buck”—energy cost per kg gas in NBs | W/mg/L |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
English, N.J. Environmental Exploration of Ultra-Dense Nanobubbles: Rethinking Sustainability. Environments 2022, 9, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9030033
English NJ. Environmental Exploration of Ultra-Dense Nanobubbles: Rethinking Sustainability. Environments. 2022; 9(3):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnglish, Niall J. 2022. "Environmental Exploration of Ultra-Dense Nanobubbles: Rethinking Sustainability" Environments 9, no. 3: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9030033
APA StyleEnglish, N. J. (2022). Environmental Exploration of Ultra-Dense Nanobubbles: Rethinking Sustainability. Environments, 9(3), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments9030033