Influence of Ammonia Stripping Parameters on the Efficiency and Mass Transfer Rate of Ammonia Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Considerations
2.1. Ammonia–Water System
2.2. Ammonia Stripping
2.3. Mass Transfer of Ammonia
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation
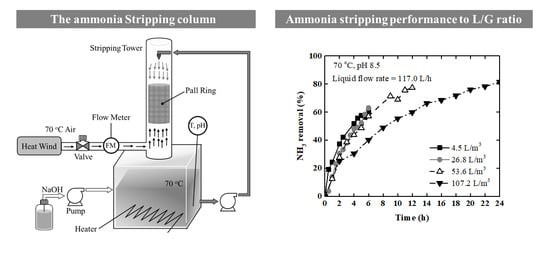
3.2. Stripping Column
3.3. Packed Tower
3.4. Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Air Stripping without Liquid Circulation
4.2. Packed Tower Air Stripping with Liquid Circulation
4.3. The Comparison of Results with Literature
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bousek, J.; Scroccaro, D.; Sima, J.; Weissenbacher, N.; Fuchs, W. Influence of the gas composition on the efficiency of ammonia stripping. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Ambrose, R.F.; Ullman, J.L.; Winfrey, B.K.; Wang, J.; Gong, J. Treatment of rich ammonia nitrogen wastewater with polyvinyl alcohol immobilized nitrifier biofortified constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, Q. Research on the transformation of nitrogen during hydrothermal carbonization of sludge. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 175, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panequea, M.; Rosa, D.L.J.M.; Kern, J.; Reza, M.T.; Knicker, H. Hydrothermal carbonization and pyrolysis of sewage sludges: What happen to carbon and nitrogen? J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 128, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vecino, X.; Reig, M.; Bhushan, B.; Gibert, O.; Valderrama, C.; Cortina, J.L. Liquid fertilizer production by ammonia recovery from treated ammonia-rich regenerated streams using liquid-liquid membrane contactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatí, A.; Flotats, X. Air stripping of ammonia from pig slurry: Characterisation and feasibility as a pre- or post-treatment to mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddella, V.K.; Ndegwa, P.M.; Ullman, J.L.; Jiang, A. Mass transfer coefficients of ammonia for liquid dairy manure. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 66, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Lua, W.; Zhang, Y. Research on mechanism of air stripping enabled ammonia removal from Industrial wastewater and Its application. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 62, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Mangan, C.; Li, X. Ammonia recovery from anaerobically digested cattle manure by steam stripping. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinidi, L.; Tan, I.A.W.; Wahab, N.B.A.; Tamrin, K.F.B.; Hipolito, C.N.; Salleh, S.F. Recent Development in ammonia stripping process for industrial wastewater treatment. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viotti, P.; Gavasci, R. Scaling of ammonia stripping towers in the treatment of groundwater polluted by municipal solid waste landfill leachate: Study of the causes of scaling and its effects on stripping performance. Rev. Ambiente Agua 2015, 10, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, F.M.; Povinelli, J.; Vieira, E.M. Ammonia removal from landfill leachate by air stripping and absorption. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guštin, S.; Marinšek-Logar, R. Effect of pH, temperature and air flow rate on the continuous ammonia stripping of the anaerobic digestion effluent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2011, 89, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Giannis, A.; Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.C.; Wang, J.Y. Air stripping process for ammonia recovery from source-separated urine: Modeling and optimization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dong, D.M.; Hua, X.Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Z.Y. Ammonia nitrogen removal and recovery from acetylene purification wastewater by air stripping. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2538–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.W.; Lu, J.H. Nitrogen removal using air stripping tower in urban wastewater treatment plant. China Water Wastewater 2006, 22, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Q.B.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Frear, C.S. Evaluation of an integrated ammonia stripping, recovery, and biogas scrubbing system for use with anaerobically digested dairy manure. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 119, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escala, M.; Zumbuhl, T.; Koller, C.H.; Junge, R.; Krebs, R. Hydrothermal Carbonization as an Energy-Efficient Alternative to Established Drying Technologies for Sewage Sludge: A Feasibility Study on a Laboratory Scale. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.F.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. Influence of temperature on nitrogen fate during hydrothermal carbonization of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, U.; Matthias, B. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 7th ed.; Willey VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Matter-Müller, C.; Gujer, W.; Giger, W. Transfer of volatile substances from water to the atmosphere. Water Res. 1981, 15, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, T.; Xiang, J. Air stripping of ammonia in a water-sparged aerocyclone reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnieszka, U.; Małgorzata, K.K.; Mateusz, W.; Przemysław, S.; Marcin, B.; Halina, P.K.; Monika, S.T.; Krystian, K.; Lukasz, N. Treatment of liquid by-products of hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of agricultural digestate using membrane separation. Energies 2020, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degermenci, N.; Ata, O.N.; Yildız, E. Ammonia removal by air stripping in a semi-batch jet loop reactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Temperature (°C) | pH (-) | Initial NH3 Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 8.9 | 2900 |
| 9.4 | 1500–2900 | |
| 10.2 | 2900 | |
| 10.8 | 2900 |
| Design Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tower diameter | 0.2 | m |
| Tower height | 1.5 | m |
| Packed layer height | 0.48 | m |
| Packed materials | PP pall ring | - |
| Liquid tank volume | 147 | L |
| Initial NH3 Conc. (mg/L) | Liquid Flow Rate (L/h) | Gas Flow Rate (L/h) | Liquid-Gas Ratio, L/G (L-Liquid/m3-Gas) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1100–3700 | 117.0 | 26,200 | 4.5 |
| 1100 | 117.0 | 4367 | 26.8 |
| 1100 | 117.0 | 2183 | 53.6 |
| 1100 | 117.0 | 1092 | 107.2 |
| Equipment | T (°C) | pH | Time (h) | Air Supplied (L-Air/L-Liquid) | L/G a (L-Liquid/m3-Air) | (%) | (/h) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stripping column without circulation | 20 | 8.9 | 0.260 | 2.5 | 2250 | - | 13.9 | 0.219 | This work |
| 9.4 | 0.527 | 38.0 | 0.340 | ||||||
| 10.2 | 0.875 | 62.4 | 0.462 | ||||||
| 10.8 | 0.965 | 72.6 | 0.574 | ||||||
| 25 | 10 | 0.864 | 3 | 1125 | - | 24.8 | 0.084 | [15] | |
| 12 | 0.998 | 1125 | 55.4 | 0.24 | |||||
| 12 | 0.998 | 2250 | 76.1 | 0.44 | |||||
| Packed tower with circulation | 70 | 8.5 | 0.761 | 6 | 1572 | 4.5 | 57.1 | 0.194 | This work |
| 6 | 262 | 26.8 | 63.0 | 0.222 | |||||
| 12 | 262 | 53.6 | 77.3 | 0.174 | |||||
| 24 | 262 | 107.2 | 81.5 | 0.099 | |||||
| 50 | 10 | 0.970 | 12 | 720 | - | 63.6 | 0.086 | [14] | |
| 1440 | 83.4 | 0.166 | |||||||
| 2880 | 98.7 | 0.368 | |||||||
| 25 | 11 | 0.985 | 24 | 4500 | 6.67 | 99 | 0.18 | [12] | |
| 15 | 10.8 b | 0.937 b | 3.5 | 3000 | 0.332 | 75 | 0.42 | [16] | |
| Jet loop reactor | 20 | 11 | 0.978 | 7.8 | 930 | 2500 | 45.6 | 0.081 | [24] |
| 7.8 | 1400 | 1667 | 87.2 | 0.299 | |||||
| 6.8 | 2030 | 1000 | 96.3 | 0.629 | |||||
| Water-sparged aerocyclone | 25 | 11.5 b | 0.995 | 3.5 | 1540 | 0.0032 | 98.9 | 0.78 | [22] |
| 2660 | 0.0018 | 93.7 | 1.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, E. Influence of Ammonia Stripping Parameters on the Efficiency and Mass Transfer Rate of Ammonia Removal. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010441
Kim EJ, Kim H, Lee E. Influence of Ammonia Stripping Parameters on the Efficiency and Mass Transfer Rate of Ammonia Removal. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(1):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010441
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun Ju, Ho Kim, and Eunsil Lee. 2021. "Influence of Ammonia Stripping Parameters on the Efficiency and Mass Transfer Rate of Ammonia Removal" Applied Sciences 11, no. 1: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010441
APA StyleKim, E. J., Kim, H., & Lee, E. (2021). Influence of Ammonia Stripping Parameters on the Efficiency and Mass Transfer Rate of Ammonia Removal. Applied Sciences, 11(1), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010441