Fast Sound Source Localization Based on SRP-PHAT Using Density Peaks Clustering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sound Signal Preprocessing
3. SRP-PHAT Algorithm
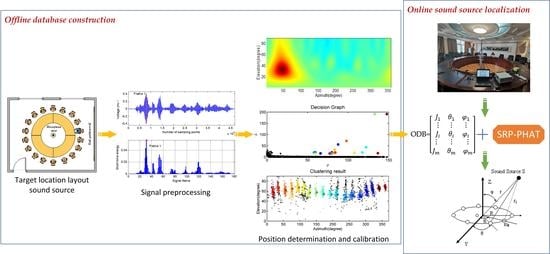
4. ODB-SRP-PHAT
4.1. Offline Database Construction
| Algorithm 1 The Flow of DPC. |
|
Step 1. Calculating the distance between any two sample points Step 2. Calculating the local density of any sample point according to the cutoff distance Step 3. Computing for any sample point Step 4. Plotting the decision graph of versus Step 5. In the decision graph, designating the points with big values of both and as the centers of clusters, and the points with big and small as noise Step 6. Allocating the remaining points, with each of them being assigned to the closest cluster in which the points have a larger local density |
4.2. Online Sound Source Localization
5. Simulations
5.1. Offline Database Construction
5.2. Comparison of Sound Source Localization
5.3. Computational Load Analysis
6. Real Environment Test
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.Q.; Gao, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Dai, Y.J.; Wang, J.W.; Zhang, L.R.; Ma, J.L. Locating and tracking sound sources on a horizontal axis wind turbine using a compact microphone array based on beamforming. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 146, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.H.; Amezquita-Semprun, K.; Chen, P.C.Y.; Zheng, Z. Design and Evaluation of a Prototype System for Real-Time Monitoring of Vehicle Honking. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Too, Y.M.; Chitre, M.; Barbastathis, G.; Pallayil, V. Localizing Snapping Shrimp Noise Using a Small-Aperture Array. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 44, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Behler, G.; Vorlaender, M. A Synthesis Model for a Moving Sound Source Based on Beamforming. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2018, 104, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padois, T. Acoustic source localization based on the generalized cross-correlation and the generalized mean with few microphones. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, EL393–EL398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Han, X.; Yang, J. Performance comparison of UCA and UCCA based real-time sound source localization systems using circular harmonics SRP method. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 164, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandstein, M.S.; Silverman, H.F. A practical methodology for speech source localization with microphone arrays. Comput. Speech Lang. 1997, 11, 91–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knapp, C.; Carter, G. The generalized correlation method for estimation of time delay. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1976, 24, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Yin, F. A microphone position calibration method based on combination of acoustic energy decay model and TDOA for distributed microphone array. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 95, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Yuen, C.; Rahardja, S. Indoor Sound Source Localization with Probabilistic Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6403–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBiase, J.H. A High-Accuracy, Low-Latency Technique for Talker Localization in Reverberant Environments Using Microphone Arrays. Ph.D. Thesis, Brown University, Providence, RI, USA, May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.; Yook, D.; Chang, S.; Kim, H. Sound source localization for robot auditory systems. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2009, 55, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yook, D.; Lee, T.; Cho, Y. Fast Sound Source Localization Using Two-Level Search Space Clustering. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 46, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Tang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Z. Accelerated steered response power method for sound source localization via clustering search. Sci. China Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron. 2013, 56, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z. Accelerated steered response power method for sound source localization using orthogonal linear array. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wu, Z. Improved steered response power method for sound source localization based on principal eigenvector. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wu, Z. Sound source localization based on discrimination of cross-correlation functions. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, B. Real-time sound source localization using hybrid framework. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badía, J.M.; Belloch, J.A.; Cobos, M.; Igual, F.D.; Quintana-Ortí, E.S. Accelerating the SRP-PHAT algorithm on multi- and many-core platforms using OpenCL. J. Supercomput. 2018, 75, 1284–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.O.; Martins, W.A.; Lima, M.V.; Biscainho, L.W.; Goncalves, F.M.; Said, A.; Lee, B. A Steered-Response Power Algorithm Employing Hierarchical Search for Acoustic Source Localization Using Microphone Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 5171–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.; Laio, A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science 2014, 344, 1492–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A Density-Based Algorithm for Discovering Clusters in Large Spatial Databases with Noise. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining KDD-96, Portland, OR, USA, 2–4 August 1996; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Garofolo, J.; Lamel, L.; Fisher, W.M.; Fiscus, J.G. TIMIT Acoustic-Phonetic Continuous Speech Corpus. Linguistic Data Consortium. 1993. Available online: https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC93S1 (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Allen, J.B.; Berkley, D.A. Image method for efficiently simulating small-room acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 65, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Node | 5 db | 10 db | 15 db | 20 db | 25 db | 30 db | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | |
| 45 | 37 | 45 | 37 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | |
| 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 56 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | |
| 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | |
| 75 | 56 | 75 | 57 | 75 | 57 | 75 | 57 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | |
| 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | |
| 105 | 55 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | |
| 134 | 37 | 135 | 37 | 135 | 37 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | |
| 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 58 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | |
| Node | 20 ms | 300 ms | 500 ms | 700 ms | 900 ms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | |
| 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 37 | 45 | 37 | |
| 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 56 | 45 | 59 | |
| 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 74 | 38 | 74 | 38 | |
| 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | |
| 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 106 | 38 | |
| 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 57 | 105 | 57 | |
| 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 37 | 135 | 37 | |
| 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 58 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 58 | |
| Node | 10 Frames | 20 Frames | 30 Frames | 50 Frames | 100 Frames | 150 Frames | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | θ | φ | |
| 45 | 39 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | 45 | 38 | |
| 45 | 55 | 45 | 53 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | 45 | 57 | |
| 75 | 39 | 75 | 39 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | 75 | 38 | |
| 76 | 55 | 74 | 54 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | 75 | 56 | |
| 105 | 39 | 105 | 39 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | 105 | 38 | |
| 105 | 56 | 105 | 54 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | 105 | 56 | |
| 135 | 39 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | 135 | 38 | |
| 135 | 55 | 135 | 55 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | 135 | 57 | |
| Number | θ | φ | Number | θ | φ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 319 | 52 | 126 | 54 | ||
| 301 | 50 | 111 | 63 | ||
| 281 | 41 | 93 | 66 | ||
| 256 | 44 | 73 | 64 | ||
| 235 | 41 | 53 | 62 | ||
| 209 | 47 | 32 | 67 | ||
| 191 | 48 | 17 | 59 | ||
| 168 | 50 | 357 | 56 | ||
| 147 | 54 | 339 | 55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuo, D.-B.; Cao, H. Fast Sound Source Localization Based on SRP-PHAT Using Density Peaks Clustering. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010445
Zhuo D-B, Cao H. Fast Sound Source Localization Based on SRP-PHAT Using Density Peaks Clustering. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(1):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010445
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuo, De-Bing, and Hui Cao. 2021. "Fast Sound Source Localization Based on SRP-PHAT Using Density Peaks Clustering" Applied Sciences 11, no. 1: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010445
APA StyleZhuo, D. -B., & Cao, H. (2021). Fast Sound Source Localization Based on SRP-PHAT Using Density Peaks Clustering. Applied Sciences, 11(1), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11010445