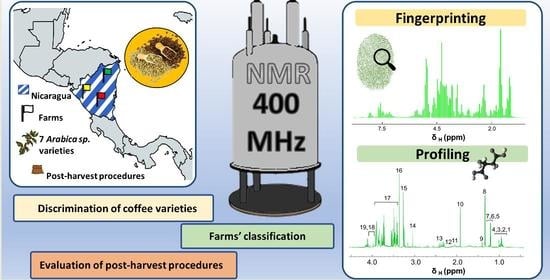
Phenotyping Green and Roasted Beans of Nicaraguan Coffea Arabica Varieties Processed with Different Post-Harvest Practices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coffee Beans
2.2. NMR Samples
2.3. NMR Spectroscopic Analysis and Data ProcessingNMR Data Analysis
2.4. NMR Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Unsupervised Analysis of 1H NMR Coffee Beans Spectra
3.2. Coffee Varieties
3.3. Coffee Farms
3.4. Evaluation of the Fermentation and Drying Effects on Coffee Metabolomic Profile
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vegro, C.L.R.; de Almeida, L.F. Chapter 1—Global Coffee Market: Socio-Economic and Cultural Dynamics. In Coffee Consumption and Industry Strategies in Brazil; De Almeida, L.F., Spers, E.E., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Consumer Sci & Strat Market; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 3–19. ISBN 978-0-12-814721-4. [Google Scholar]
- Samoggia, A.; Riedel, B. Consumers’ Perceptions of Coffee Health Benefits and Motives for Coffee Consumption and Purchasing. Nutrients 2019, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hameed, A.; Hussain, S.A.; Ijaz, M.U.; Ullah, S.; Pasha, I.; Suleria, H.A.R. Farm to Consumer: Factors Affecting the Organoleptic Characteristics of Coffee. II: Postharvest Processing Factors. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1184–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worku, M.; de Meulenaer, B.; Duchateau, L.; Boeckx, P. Effect of Altitude on Biochemical Composition and Quality of Green Arabica Coffee Beans Can Be Affected by Shade and Postharvest Processing Method. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, F.; Zhang, S.J.; Pothakos, V.; Torres, J.; Lambot, C.; Moroni, A.V.; Callanan, M.; Sybesma, W.; Weckx, S.; De Vuyst, L. Exploring the Impacts of Postharvest Processing on the Microbiota and Metabolite Profiles during Green Coffee Bean Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02398-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guizellini, F.C.; Marcheafave, G.G.; Rakocevic, M.; Bruns, R.E.; Scarminio, I.S.; Soares, P.K. PARAFAC HPLC-DAD Metabolomic Fingerprint Investigation of Reference and Crossed Coffees. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.-J.; Jeong, H.-J.; Moon, H.; Kim, H.-N.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, J.-E.; Hong, K.S.; Hong, Y.-S. Assessment of Green Coffee Bean Metabolites Dependent on Coffee Quality Using a 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Approach. Food Res. Int. 2015, 67, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, A.; Ghini, V.; Meoni, G.; Licari, C.; Takis, P.G.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Luchinat, C. High-Throughput Metabolomics by 1D NMR. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 968–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R.; Cogliati, C. NMR Based Geographical Characterization of Roasted Coffee. Talanta 2012, 88, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Furihata, K.; Hu, F.; Miyakawa, T.; Tanokura, M. Complex Mixture Analysis of Organic Compounds in Green Coffee Bean Extract by Two-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2010, 48, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Furihata, K.; Koda, M.; Hu, F.; Kato, R.; Miyakawa, T.; Tanokura, M. 13C NMR-Based Metabolomics for the Classification of Green Coffee Beans According to Variety and Origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10118–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Furihata, K.; Koda, M.; Hu, F.; Miyakawa, T.; Tanokura, M. Roasting Process of Coffee Beans as Studied by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: Time Course of Changes in Composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Ruge, W.; Kuballa, T.; Ilse, M.; Winkelmann, O.; Diehl, B.; Thomas, F.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Rapid Approach to Identify the Presence of Arabica and Robusta Species in Coffee Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicho, N.C.; Leitão, A.E.; Ramalho, J.C.; de Alvarenga, N.B.; Lidon, F.C. Impact of Roasting Time on the Sensory Profile of Arabica and Robusta Coffee. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2013, 52, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Coffee Research. Available online: https://worldcoffeeresearch.org/ (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Mengistu, M.W.; Workie, M.A.; Mohammed, A.S. Biochemical Compounds of Arabica Coffee (Coffea arabica L.) Varieties Grown in Northwestern Highlands of Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1741319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Hong, D.; Bai, X.; Guo, T.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Qiu, M. Chemical Ingredients Characterization Basing on 1H NMR and SHS-GC/MS in Twelve Cultivars of Coffea Arabica Roasted Beans. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenori, L.; Santucci, C.; Meoni, G.; Morrocchi, V.; Matteucci, G.; Luchinat, C. NMR Metabolomic Fingerprinting Distinguishes Milk from Different Farms. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelio, N.; Fontanive, L.; Uggeri, F.; Suggi-Liverani, F.; Navarini, L. NMR Reinvestigation of the Caffeine–Chlorogenate Complex in Aqueous Solution and in Coffee Brews. Food Biophys. 2009, 4, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal Component Analysis. WIREs Comp. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Posthoc.Kruskal.Dunn.Test: Pairwise Test for Multiple Comparisons of Mean Rank Sums (Dunn’s-Test). Available online: https://www.rdocumentation.org/packages/PMCMR/versions/4.3/topics/posthoc.kruskal.dunn.test (accessed on 27 November 2021).
- Ribeiro, B.B.; de Carvalho, A.M.; Cirillo, M.Â.; Câmara, F.M.d.M.; Montanari, F.F. Sensory Profile of Coffees of Different Cultivars, Plant Exposure and Post-Harvest. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 14, 1111–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casal, S.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Alves, M.R.; Ferreira, M.A. Discriminate Analysis of Roasted Coffee Varieties for Trigonelline, Nicotinic Acid, and Caffeine Content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3420–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.A.; El-Kersh, D.M.; Ehrlich, A.; Choucry, M.A.; El-Seedi, H.; Frolov, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Variation in Ceratonia Siliqua Pod Metabolome in Context of Its Different Geographical Origin, Ripening Stage and Roasting Process. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, C.; Ballester, J.F.; Doulbeau, S.; Dussert, S.; Hamon, S.; Noirot, M. Trigonelline and Sucrose Diversity in Wild Coffea Species. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Tanokura, M. Chapter 10—Chemical Changes in the Components of Coffee Beans during Roasting. In Coffee in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 83–91. ISBN 978-0-12-409517-5. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Salces, R.M.; Serra, F.; Reniero, F.; HÉberger, K. Botanical and Geographical Characterization of Green Coffee (Coffea Arabica and Coffea Canephora): Chemometric Evaluation of Phenolic and Methylxanthine Contents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4224–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, M.N.; Kazi, T. The Influence of Coffee Bean Maturity on the Content of Chlorogenic Acids, Caffeine and Trigonelline. Food Chem. 1987, 26, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehari, B.; Redi-Abshiro, M.; Chandravanshi, B.S.; Atlabachew, M.; Combrinck, S.; McCrindle, R. Simultaneous Determination of Alkaloids in Green Coffee Beans from Ethiopia: Chemometric Evaluation of Geographical Origin. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Frankowski, R.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Comparison of Methylxantines, Trigonelline, Nicotinic Acid and Nicotinamide Contents in Brews of Green and Processed Arabica and Robusta Coffee Beans—Influence of Steaming, Decaffeination and Roasting Processes on Coffee Beans. LWT 2020, 125, 109344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Ma, C.; Ren, X.; Xia, T.; Li, X. LC–MS/MS-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Caffeine-Degrading Fungus Aspergillus Sydowii during Tea Fermentation. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Farm | Variety | Fermentation Time (h) | Drying | Municipality | Batch Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CR | 12 | Us | Dipilto | 346 |
| 1 | CR | 12 | Ds | Dipilto | 347 |
| 1 | CR | 24 | Us | Dipilto | 348 |
| 1 | CR | 24 | Ds | Dipilto | 349 |
| 1 | MC | 12 | Us | Dipilto | 352 |
| 1 | MC | 12 | Ds | Dipilto | 353 |
| 1 | MC | 24 | Us | Dipilto | 350 |
| 1 | MC | 24 | Ds | Dipilto | 351 |
| 1 | BO | 12 | Us | Dipilto | 356 |
| 1 | BO | 12 | Ds | Dipilto | 357 |
| 1 | BO | 24 | Us | Dipilto | 354 |
| 1 | BO | 24 | Ds | Dipilto | 355 |
| 2 | CA | 12 | Us | Dipilto | 337 |
| 2 | CA | 12 | Ds | Dipilto | 336 |
| 2 | CA | 24 | Us | Dipilto | 335 |
| 2 | CA | 24 | Ds | Dipilto | 334 |
| 2 | PA | 12 | Us | Dipilto | 341 |
| 2 | PA | 12 | Ds | Dipilto | 340 |
| 2 | PA | 24 | Us | Dipilto | 339 |
| 2 | PA | 24 | Ds | Dipilto | 338 |
| 2 | BO | 12 | Us | Dipilto | 345 |
| 2 | BO | 12 | Ds | Dipilto | 344 |
| 2 | BO | 24 | Us | Dipilto | 343 |
| 2 | BO | 24 | Ds | Dipilto | 342 |
| 3 | CR | 12 | Us | Mozonte | 362 |
| 3 | CR | 12 | Ds | Mozonte | 363 |
| 3 | CR | 24 | Us | Mozonte | 364 |
| 3 | CR | 24 | Ds | Mozonte | 365 |
| 3 | TE | 12 | Us | Mozonte | 366 |
| 3 | TE | 12 | Ds | Mozonte | 367 |
| 3 | TE | 24 | Us | Mozonte | 368 |
| 3 | TE | 24 | Ds | Mozonte | 369 |
| 3 | BR | 12 | Us | Mozonte | 358 |
| 3 | BR | 12 | Ds | Mozonte | 359 |
| 3 | BR | 24 | Us | Mozonte | 360 |
| 3 | BR | 24 | Ds | Mozonte | 361 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meoni, G.; Luchinat, C.; Gotti, E.; Cadena, A.; Tenori, L. Phenotyping Green and Roasted Beans of Nicaraguan Coffea Arabica Varieties Processed with Different Post-Harvest Practices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11779. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411779
Meoni G, Luchinat C, Gotti E, Cadena A, Tenori L. Phenotyping Green and Roasted Beans of Nicaraguan Coffea Arabica Varieties Processed with Different Post-Harvest Practices. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(24):11779. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411779
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeoni, Gaia, Claudio Luchinat, Enrico Gotti, Alejandro Cadena, and Leonardo Tenori. 2021. "Phenotyping Green and Roasted Beans of Nicaraguan Coffea Arabica Varieties Processed with Different Post-Harvest Practices" Applied Sciences 11, no. 24: 11779. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411779
APA StyleMeoni, G., Luchinat, C., Gotti, E., Cadena, A., & Tenori, L. (2021). Phenotyping Green and Roasted Beans of Nicaraguan Coffea Arabica Varieties Processed with Different Post-Harvest Practices. Applied Sciences, 11(24), 11779. https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411779