Deep Learning Applied to Chest Radiograph Classification—A COVID-19 Pneumonia Experience
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
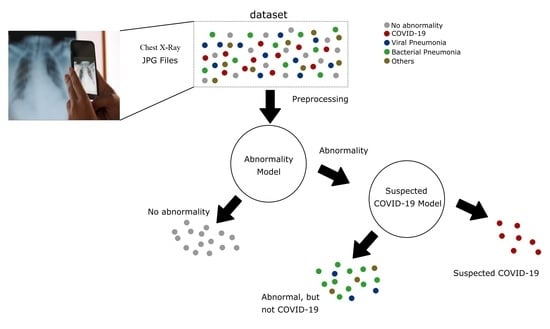
- The proposal of a new DL system based on the Inception V3 architecture, one that supports the identification of normal and abnormal CXR examinations and the diagnosis of COVID-19.
- The preparation and publication of an annotated CXR dataset with 1158 images. It is an external validation dataset suitable not only for this but also for future works.
- The evaluation of the classification metrics of our algorithm in an external validation dataset and a comparison of the performance with a state-of-art algorithm.
- The guarantee of reproducibility.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Pre-Processing
2.2. External Validation Dataset
2.3. Benchmark Algorithm
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Algorithm Evaluation
3.2. External Validation
3.3. Explainability of the AI Models
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ai, T.; Yang, Z.; Hou, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, C.; Lv, W.; Tao, Q.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L. Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases. Radiology 2020, 296, E32–E40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Sirajuddin, A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Teng, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lu, M. The role of imaging in 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4874–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hui, K.P.Y.; Ho, J.C.W.; Cheung, M.-C.; Ng, K.-C.; Ching, R.H.H.; Lai, K.-L.; Kam, T.T.; Gu, H.; Sit, K.-Y.; Hsin, M.K.Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo. Nature 2022, 603, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontone, G.; Scafuri, S.; Mancini, M.E.; Agalbato, C.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Fusini, L.; Andreini, D.; Mushtaq, S.; et al. Role of computed tomography in COVID-19. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2020, 15, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, E.A.; Blažić, I.; Yaacoub, S.; Frija, G.; Chou, R.; Appiah, J.A.; Fatehi, M.; Flor, N.; Hitti, E.; Jafri, H.; et al. Use of Chest Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19: A WHO Rapid Advice Guide. Radiology 2021, 298, E63–E69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, G.D.; Ryerson, C.J.; Haramati, L.B.; Sverzellati, N.; Kanne, J.; Raoof, S.; Schluger, N.W.; Volpi, A.; Yim, J.-J.; Martin, I.B.K.; et al. The Role of Chest Imaging in Patient Management during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multinational Consensus Statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020, 296, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, S.; Kay, F.U.; Abbara, S.; Bhalla, S.; Chung, J.H.; Chung, M.; Henry, T.S.; Kanne, J.P.; Kligerman, S.; Ko, J.P.; et al. Radiological Society of North America Expert Consensus Statement on Reporting Chest CT Findings Related to COVID-19. Endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA—Secondary Publication. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Sarker, S.; Al Miraj, A.; Nihal, R.A.; Haque, A.K.M.N.; Al Noman, A. Deep Learning–Driven Automated Detection of COVID-19 from Radiography Images: A Comparative Analysis. Cogn. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelaira, M.D.C.; Abelaira, F.C.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Fernández-Villar, A. Use of Conventional Chest Imaging and Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Infection. A Review of the Literature. Open Respir. Arch. 2021, 3, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, C.; Aryal, S. New bag of deep visual words based features to classify chest x-ray images for COVID-19 diagnosis. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2021, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, C.; Shahi, T.B.; Aryal, S.; Marzbanrad, F. Fusion of multi-scale bag of deep visual words features of chest X-ray images to detect COVID-19 infection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, C.; Hossain, M.B. Attention-based VGG-16 model for COVID-19 chest X-ray image classification. Appl. Intell. 2020, 51, 2850–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Covnet, A.; Driggs, D.; Thorpe, M.; Gilbey, J.; Yeung, M.; Ursprung, S.; Aviles-Rivero, A.I.; Etmann, C.; McCague, C.; et al. Common pitfalls and recommendations for using machine learning to detect and prognosticate for COVID-19 using chest radiographs and CT scans. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2021, 3, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Beymer, D.; Rajan, D.; Coy, A.; Mukherjee, V.V.; Manica, M.; Prasanna, P.; Ballah, D.; Guindy, M.; Shaham, D.; et al. On the role of artificial intelligence in medical imaging of COVID-19. Patterns 2021, 2, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cabrera, J.D.; Orozco-Morales, R.; Portal-Diaz, J.A.; Lovelle-Enríquez, O.; Pérez-Díaz, M. Current limitations to identify COVID-19 using artificial intelligence with chest X-ray imaging. Health Technol. 2021, 11, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. A deep-learning pipeline for the diagnosis and discrimination of viral, non-viral and COVID-19 pneumonia from chest X-ray images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbe, R.M.; Sheng, J.; Dutta, S.; Chai, S.; Dravid, A.; Barutcu, S.; Wu, Y.; Cantrell, D.R.; Xiao, N.; Allen, B.D.; et al. DeepCOVID-XR: An Artificial Intelligence Algorithm to Detect COVID-19 on Chest Radiographs Trained and Tested on a Large U.S. Clinical Data Set. Radiology 2021, 299, E167–E176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Choi, J.W.; Halsey, K.; Tran, T.M.L.; Hsieh, B.; Wang, D.; Eweje, F.; Wang, R.; Chang, K.; Wu, J.; et al. Prognostication of patients with COVID-19 using artificial intelligence based on chest x-rays and clinical data: A retrospective study. Lancet Digit. Health 2021, 3, e286–e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AAnaya-Isaza, A.; Mera-Jiménez, L.; Zequera-Diaz, M. An overview of deep learning in medical imaging. Informatics Med. Unlocked 2021, 26, 100723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RSNA Pneumonia Detection Challenge. 2018. Available online: https://www.rsna.org/education/ai-resources-and-training/ai-image-challenge/RSNA-Pneumonia-Detection-Challenge-2018 (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Bustos, A.; Pertusa, A.; Salinas, J.-M.; de la Iglesia-Vayá, M. PadChest: A large chest x-ray image dataset with multi-label annotated reports. Med Image Anal. 2020, 66, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Iglesia Vayá, M.; Saborit, J.M.; Montell, J.A.; Pertusa, A.; Bustos, A.; Cazorla, M.; Galant, J.; Barber, X.; Orozco-Beltrán, D.; García-García, F.; et al. BIMCV COVID-19+: A Large Annotated Dataset of RX and CT Images from COVID-19 Patients. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.01174v3 (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Cohen, J.P.; Morrison, P.; Dao, L.; Roth, K.; Duong, T.Q.; Ghassemi, M. COVID-19 Image Data Collection: Prospective Predictions Are the Future. Available online: https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset (accessed on 20 February 2022).
- LeCun, Y.A.; Bottou, L.; Orr, G.B.; Müller, K.R. Efficient BackProp. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Montavon, G., Orr, G.B., Müller, K.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabottke, C.F.; Spieler, B.M. The Effect of Image Resolution on Deep Learning in Radiography. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2020, 2, e190015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cimatec_XCOV19 Git Page. Available online: https://github.com/CRIA-CIMATEC/covid-19 (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Delong, E.R.; Delong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the Areas under Two or More Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves: A Nonparametric Approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaître, G.; Nogueira, F.; Aridas, C.K. Imbalanced-learn: A Python Toolbox to Tackle the Curse of Imbalanced Datasets in Machine Learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2017, 18, 1–5. Available online: http://jmlr.org/papers/v18/16-365.html (accessed on 28 August 2021).
- Winston, J.; Jackson, D.; Wozniak, D.; Zeisler, J.; Farish, S.; Thoma, P. Quality Control recommendations for diagnostic radiography volume 3 radiographic or fluoroscopic. In Radiographic or Fluoroscopic Machines; CRCPD Publication: Frankfort, KY, USA, 2001; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Jing, B.; Wang, Z.; Xin, H.; Tong, H. SODA: Detecting COVID-19 in Chest X-rays with Semi-supervised Open Set Domain Adaptation. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Joshi, A.; Pareek, A.; Ng, A.Y.; Lungren, M.P. CheXternal: Generalization of deep learning models for chest X-ray interpretation to photos of chest X-rays and external clinical settings. In Proceedings of the Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning, Virtual, 8–9 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Ref. | Objective | Base Model | Training Dataset (# of CXR) | External Validation Dataset (# of CXR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | Detect common thoracic disease | DenseNet-121 | 120,702 | 24,500 |
| [19] | Diagnose COVID-19 and multiclass classification | DenseNet-121 | 27,825/1571 1 | China 1899/98 1 China 1034 Ecuador 650/132 1 |
| [20] | Detect COVID-19 pneumonia | Ensemble of CNN: Densenet-121, Resnet-50, Inception, Inception-Resnet, Xcepton, EfficientNet-B2 | Pre-training: NIH-CXR14 dataset >100,000 Fine-tunning: 14,788/4253 1 | 2214 images/1192 1 |
| [21] | Predict COVID-19 severity and progression | VGG-11 and EfficientNet-B0 | 1834 all COVID-19 patients | 475 |
| [22] | Detect COVID-19 cases | COVID-Net CNN | 13,975/358 1 | 300/100 1 |
| [23] | Detect COVID-19 (3 binary classifiers) | ResNet-50 | 7406/3411 | N/A 2 |
| [24] | Detect COVID-19 and Multiclass Classification | DarkNet-19 | 1125/125 1 | N/A 2 |
| This work | Detect COVID-19 | Inception-V3 | 44,031/2917 1 | 1158/13 1 |
| Dataset | Description | # of CXR |
|---|---|---|
| RSNA Pneumonia Detection Challenge [27] | Images labeled by the Society for Thoracic Radiology and MD.ai for pneumonia cases found in the chest radiograph database made public by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). | 25,497 |
| BIMCV PadChest [28] | Digital Medical Image Bank of the Valencian Community. Images were interpreted and reported by radiologists at Hospital San Juan (Spain) from 2009 to 2017. | 14,252 |
| BIMCV COVID-19 [29] | Digital Medical Image Bank of the Valencian Community related to COVID-19 cases. | 1762 |
| HM Hospitales | CXR images from patients from the HM Hospitales group in different cities in Spain. Private Dataset. | 1277 |
| COVID-19 Image Data Collection [30] | Data was collected from public sources, as well as through indirect collection from hospitals and doctors organized by a researcher from the University of Montreal. | 613 |
| HC USP Competition | Images obtained from patients from the HC hospital in São Paulo used for a competition. Private Dataset. | 593 |
| Hospital Santa Izabel | Images interpreted and reported by radiologists at Hospital Santa Izabel, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Private Dataset. | 37 |
| Parameter | Number of Examinations | Age(y) | Sex | Positive RT-PCR Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Patients | 1158 | 72.56 ± 10.02 | 830 female | 30 |
| Radiologists’ Diagnosis Breakdown | ||||
| Lack of Consensus (agreement < 75%) | 17 | 74.35 ± 9.38 | 10 female | 3 |
| Normal | 1108 | 72.32 ± 9.94 | 802 female | 12 |
| Mild Viral Infection | 1 | 71 | 1 male | 1 |
| Moderate Viral Infection | 3 | 78.67 ± 10.01 | 2 female | 3 |
| Severe Viral Infection | 10 | 81 ± 6.55 | 5 female | 10 |
| Mild Bacterial Infection | 9 | 78.11 ± 11.86 | 6 female | 1 |
| Moderate Bacterial Infection | 7 | 78.43 ± 9.81 | 4 male | 0 |
| Severe Bacterial Infection | 3 | 85.67 ± 16.44 | 2 female | 0 |
| Ref. | Name | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | ROC | PRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | Wang et al. | N/A 1 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.97 | N/A |
| [20] | DeepCOVID-XR | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.83 | N/A |
| [22] | COVID-Net | 0.93 | 0.91 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| [23] | Narin etal (Resnet50) | 1 | 1 | 1 | N/A | N/A |
| [24] | DarkCovidNet | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.91 | N/A | N/A |
| This work | Cimatec_XCOV19 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.96 |
| Metrics for “ Suggestive of COVID-19 Infection” | Cimatec_XCOV19 Performance on the External Validation Dataset | Cimatec_XCOV19 Previous Performance | DeepCOVID-XR Performance on the External Validation Dataset | DeepCOVID-XR Previous Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.75 |
| Specificity | 0.82 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.93 |
| Accuracy | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.83 |
| AUC ROC | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.90 |
| AUC PRC | 0.48 | 0.96 | 0.7 | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furtado, A.; Andrade, L.; Frias, D.; Maia, T.; Badaró, R.; Nascimento, E.G.S. Deep Learning Applied to Chest Radiograph Classification—A COVID-19 Pneumonia Experience. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083712
Furtado A, Andrade L, Frias D, Maia T, Badaró R, Nascimento EGS. Deep Learning Applied to Chest Radiograph Classification—A COVID-19 Pneumonia Experience. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(8):3712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083712
Chicago/Turabian StyleFurtado, Adhvan, Leandro Andrade, Diego Frias, Thiago Maia, Roberto Badaró, and Erick G. Sperandio Nascimento. 2022. "Deep Learning Applied to Chest Radiograph Classification—A COVID-19 Pneumonia Experience" Applied Sciences 12, no. 8: 3712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083712
APA StyleFurtado, A., Andrade, L., Frias, D., Maia, T., Badaró, R., & Nascimento, E. G. S. (2022). Deep Learning Applied to Chest Radiograph Classification—A COVID-19 Pneumonia Experience. Applied Sciences, 12(8), 3712. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12083712