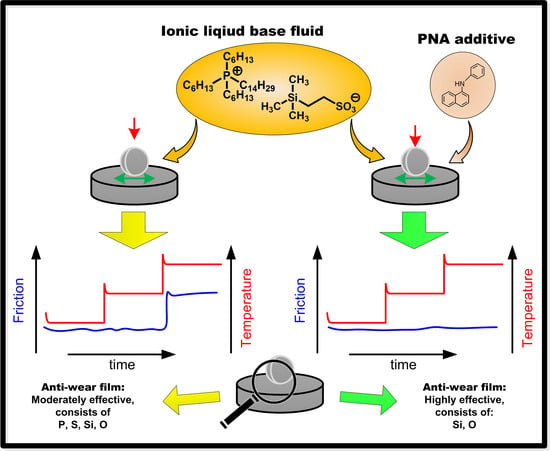
Formation of Boundary Film from Ionic Liquids Enhanced by Additives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lubricant Properties
2.2. Ball-on-Flat Reciprocating Tribotest
2.3. Surface Analysis
2.3.1. Quantification of Wear
2.3.2. SEM-EDS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stage 1: Limits of Operational Envelope of Neat P-SiSO
3.2. Stage 2: Effect of Additives in P-SiSO
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RTIL | room-temperature ionic liquid |
| PFPE | perfluoropolyether |
| PNA | N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine |
| BHT | 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol |
| OA | oleylamine |
| DMOP | 5,5-dimethyl-1,3,2-dioxaphosphorinan-2-one |
| OPP | ortho-phenylene phosphate |
| WSD | wear scar diameter |
| HzD | hertzian contact diameter |
| EP | extreme pressure |
| AW | anti-wear |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
References
- Rudnick, L.R. Lubricant Additives: Chemistry and Applications; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Spikes, H. The History and Mechanisms of ZDDP. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, E.S. Antiwear and extreme pressure additives for lubricants. Tribology 1970, 3, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Spikes, H. On the Mechanism of ZDDP Antiwear Film Formation. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosvami, N.N.; Bares, J.A.; Mangolini, F.; Konicek, A.R.; Yablon, D.G.; Carpick, R.W. Mechanisms of antiwear tribofilm growth revealed in situ by single-asperity sliding contacts. Science 2015, 348, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, E.S. The load-carrying action of organo-sulphur compounds—A review. Wear 1970, 15, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.M.; Gates, R.S. Boundary lubricating films: Formation and lubrication mechanism. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortier, R.M.; Fox, M.F.; Orszulik, S.T. Chemistry and Technology of Lubricants, 3rd ed.; Springer: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick, L.R.; Shubkin, R.L. Synthetic Lubricants and High-performance Functional Fluids, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 77. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, I.; Mori, S. Concept of molecular design towards additive technology for advanced lubricants. Lubr. Sci. 2007, 19, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Jiménez, A.E.; Sanes, J.; Carrión, F.J. Ionic liquids as advanced lubricant fluids. Molecules 2009, 14, 2888–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, I. Ionic liquids in tribology. Molecules 2009, 14, 2286–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somers, A.E.; Howlett, P.C.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. A Review of Ionic Liquid Lubricants. Lubricants 2013, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torimoto, T.; Tsuda, T.; Okazaki, K.; Kuwabata, S. New frontiers in materials science opened by ionic liquids. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1196–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L. Room-temperature ionic liquids: A novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2001, 21, 2244–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deetlefs, M.; Fanselow, M.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids: The view from Mount Improbable. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4280–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Chi, M.; Meyer, H.M.; Blau, P.J.; Dai, S.; Luo, H. Nanostructure and Composition of Tribo-Boundary Films Formed in Ionic Liquid Lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 43, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Inada, T.; Sasaki, R.; Nanao, H. Tribo-Chemistry of Phosphonium-Derived Ionic Liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2010, 40, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, H.; Chiba, T.; Watanabe, N.; Kubo, T.; Nanao, H.; Minami, I.; Mori, S. Effects of Carboxylic Acids on Friction and Wear Reducing Properties for Alkylmethylimidazolium Derived Ionic liquids. Tribol. Online 2006, 1, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura, H.; Kubo, T.; Minami, I.; Mori, S. Effect and mechanism of additives for ionic liquids as new lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Benzotriazole as the additive for ionic liquid lubricant: One pathway towards actual application of ionic liquids. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 23, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhou, F.; Pang, C.; Wang, B.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Tribological evaluation of α, ω-diimidazoliumalkylene hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid and benzotriazole as additive. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Watanabe, N.; Nanao, H.; Mori, S.; Fukumoto, K.; Ohno, H. Aspartic Acid-derived Wear-preventing and Friction-reducing Agents for Ionic Liquids. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 300–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, E.; Respatiningsih, C.Y.; Minami, I. Molecular design of advanced lubricant base fluids: Hydrocarbon-mimicking ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 6364–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, I.; Kikuta, S.; Okabe, H. Anti-wear and friction reducing additives composed of ortho-phenylene phosphate-amine salts for polyether type base stocks. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.J.; Zhu, D. Hertz Theory: Contact of Ellipsoidal Surfaces. In Encyclopedia of Tribology; Wang, Q.J., Chung, Y.-W., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1647–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Kalin, M.; Vižintin, J. Use of equations for wear volume determination in fretting experiments. Wear 2000, 237, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Uetz, H.; Föhl, J.; Khosrawi, M.A. The reaction layer formed on steel by additives based on sulphur and phosphorus compounds under conditions of boundary lubrication. Wear 1982, 77, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Song, H. Functionalized Ionic Liquids as Lubricants for Steel-Steel Contact. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 138, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Hu, L.; Feng, D. Crown-type ionic liquids as lubricants for steel-on-steel system. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Tribological performance of phosphonium based ionic liquids for an aluminum-on-steel system and opinions on lubrication mechanism. Wear 2006, 261, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.J.; Liu, X.Q.; Liang, Y.M.; Xue, Q.J. Effect of tetraalkylphosphonium based ionic liquids as lubricants on the tribological performance of a steel-on-steel system. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 26, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Effect of the functional groups in ionic liquid molecules on the friction and wear behavior of aluminum alloy in lubricated aluminum-on-steel contact. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Test Stage and Objective | Test Code |
|---|---|
| Stage 1: Determine limit of operational envelope of neat P-SiSO | V{100–300 N/25 °C/120 min} |
| V{150 N/40–100 °C/80 min} | |
| V{300 N/40–80 °C/60 min} | |
| Stage 2: Determine effect of additives in P-SiSO | C{150 N/25 °C/30 min} |
| V{300 N/40–80 °C/60 min} | |
| C{300 N/80 °C/30 min} |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nyberg, E.; Mouzon, J.; Grahn, M.; Minami, I. Formation of Boundary Film from Ionic Liquids Enhanced by Additives. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050433
Nyberg E, Mouzon J, Grahn M, Minami I. Formation of Boundary Film from Ionic Liquids Enhanced by Additives. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(5):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050433
Chicago/Turabian StyleNyberg, Erik, Johanne Mouzon, Mattias Grahn, and Ichiro Minami. 2017. "Formation of Boundary Film from Ionic Liquids Enhanced by Additives" Applied Sciences 7, no. 5: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050433
APA StyleNyberg, E., Mouzon, J., Grahn, M., & Minami, I. (2017). Formation of Boundary Film from Ionic Liquids Enhanced by Additives. Applied Sciences, 7(5), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7050433