Removal of Crotamiton from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by a TiO2/Zeolite Composite Sheet
Abstract
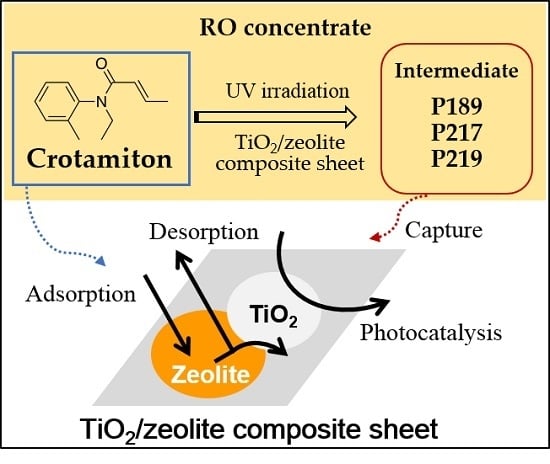
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Quantitative Analyses
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption of Crotamiton by the HSZ-385/P25 Composite Sheet
3.2. Photocatalytic Degradation of Crotamiton by the F9/P25 Composite Sheet
3.3. Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Crotamiton by the HSZ-385/P25 Composite Sheet
3.4. Behavior of the Degradation Intermediates during Photocatalysis
3.5. Cyclic Use of the HSZ-385/P25 Composite Sheet
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joo, S.H.; Tansel, B. Novel technologies for reverse osmosis concentrate treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 150, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L. Recent advancements in the treatment of municipal wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate—An overview. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 193–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L. Comparison of coagulation efficiency of aluminium and ferric-based coagulants as pre-treatment for UVC/H2O2 treatment of wastewater RO concentrate. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L. Assessing the potential of a UV-based AOP for treating high-salinity municipal wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 1994–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerhoff, P.; Moon, H.; Minakata, D.; Crittenden, J. Oxidation of organics in retentates from reverse osmosis wastewater reuse facilities. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3992–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Ricart, M.; Köck-Schulmeyer, M.; Guasch, H.; Bonnineau, C.; Proia, L.; de Alda, M.L.; Sabater, S.; Barceló, D. Pharmaceuticals and pesticides in reclaimed water: Efficiency assessment of a microfiltration-reverse osmosis (MF-RO) pilot plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Hu, H.Y.; Wu, Q.Y.; Tang, X.; Sun, Y.X.; Shi, X.L.; Huang, J.J. Effects of chemical agent injections on genotoxicity of wastewater in a microfiltration-reverse osmosis membrane process for wastewater reuse. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, A.; Jacangelo, J.G. Treatment technologies for reverse osmosis concentrate volume minimization: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E.; Tsang, Y.F. Occurrences and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in drinking water and water/sewage treatment plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596–597, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, M.N.; Jin, B.; Chow, C.W.K.; Saint, C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2997–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Wang, J.M.; Pal, A. Nano silver impregnation on commercial TiO2 and a comparative photocatalytic account to degrade malachite green. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 89, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaeh, S.; Perisic, D.J.; Biosic, M.; Kusic, H.; Babic, S.; Stangar, U.L.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Bozic, A.L. Diclofenac removal by simulated solar assisted photocatalysis using TiO2-based zeolite catalyst; mechanisms, pathways and environmental aspects. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, V.N.; Ward, J.E.; Russell, B.J.; Agrios, A.G. Photocatalytic effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on aquatic organisms—Current knowledge and suggestions for future research. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 185, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Fujiwara, T.; Fukahori, S.; Ishigaki, T. Factors affecting the adsorptive removal of bisphenol A in landfill leachate by high silica Y-type zeolite. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2788–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.T. Adsorbents: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 0471297410. [Google Scholar]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Fu, J.; Lazaridis, N.K.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Matis, K.A. New approaches on the removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewaters with adsorbent materials. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 209, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hameed, B.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Omirou, M. A review on waste-derived adsorbents from sugar industry for pollutant removal in water and wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Nanoadsorbents for pollutants removal: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 203, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Chen, Z. Guidelines for rational design of high-performance absorbents: A case study of zeolite adsorbents for emerging pollutants in water. Green Energy Environ. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Funamizu, N.; Matsukawa, K.; Ito, R. Adsorptive removal of sulfonamide antibiotics in livestock urine using the high-silica zeolite HSZ-385. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wu, X.-L.; Wang, Z.-M.; Aoki, H.; Kutsuna, S.; Jimura, K.; Hayashi, S. Anchoring titanium dioxide on carbon spheres for high-performance visible light photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, P.-S.; Cheah, Y.-L.; Srinivasan, M.; Lim, T.-T. Bimodal N-doped P25-TiO2/AC composite: Preparation, characterization, physical stability, and synergistic adsorptive-solar photocatalytic removal of sulfamethazine. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 427–428, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T. Modeling of sulfonamide antibiotic removal by TiO2/high-silica zeolite HSZ-385 composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 272, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lu, B.; Ke, Q.F.; Guo, Y.J.; Guo, Y.P. Synergetic effect between adsorption and photodegradation on nanostructured TiO2/activated carbon fiber felt porous composites for toluene removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukahori, S.; Ichiura, H.; Kitaoka, T.; Tanaka, H. Photocatalytic decomposition of bisphenol A in water using composite TiO2-zeolite sheets prepared by a papermaking technique. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukahori, S.; Ichiura, H.; Kitaoka, T.; Tanaka, H. Capturing of bisphenol A photodecomposition intermediates by composite TiO2–zeolite sheets. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Tanishima, T.; Shinohara, H.; Kiri, K.; Takada, H. Pharmaceutical chemicals and endocrine disrupters in municipal wastewater in Tokyo and their removal during activated sludge treatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, N.; Yasojima, M.; Okayasu, Y.; Komori, K.; Suzuki, Y. Mass balance analysis of triclosan, diethyltoluamide, crotamiton and carbamazepine in sewage treatment plants. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, I.; Yasuda, Y.; Kagota, K.; Yoneda, S.; Nakada, N. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety contribution of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) to whole toxicity of water samples collected in effluent-dominated urban streams. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. Pulps-Preparation of Laboratory Sheets for Physical Testing-Conventional Sheet-Former Method, JIS P8222: 2015. Available online: http://www.jisc.go.jp/app/jis/general/GnrJISSearch.html (accessed on 26 July 2017).
- Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. Photocatalytic decomposition of crotamiton over aqueous TiO2 suspensions: Determination of intermediates and the reaction pathway. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, T.X.; Choi, H. Influence of ionic strength, anions, cations, and natural organic matter on the adsorption of pharmaceuticals to silica. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L. Effect of coagulation on treatment of municipal wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate by UVC/H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 266, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Ito, R.; Funamizu, N. pH-Dependent adsorption of sulfa drugs on high silica zeolite: Modeling and kinetic study. Desalination 2011, 275, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, T. UV-absorption—The primary process in photocatalysis and some practical consequences. Molecules 2014, 19, 18192–18214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsydenova, O.; Batoev, V.; Batoeva, A. Solar-enhanced advanced oxidation processes for water treatment: Simultaneous removal of pathogens and chemical pollutants. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9542–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokumura, M.; Sugawara, A.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Masunaga, S. Comprehensive study on effects of water matrices on removal of pharmaceuticals by three different kinds of advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudlek, E.; Dudziak, M.; Bohdziewicz, J. Influence of inorganic ions and organic substances on the degradation of pharmaceutical compound in water matrix. Water 2016, 8, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lim, T.T.; Chin, S.S.; Fane, A.G. Treatment of organics in reverse osmosis concentrate from a municipal wastewater reclamation plant: Feasibility test of advanced oxidation processes with/without pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.A.; Crittenden, J.C.; Hand, D.W.; Selzer, V.H.; Sutter, L.L.; Salman, S.R. Effect of inorganic ions in heterogeneous photocatalysis of TCE. J. Environ. Eng. 1999, 125, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioja, N.; Benguria, P.; Peñas, F.J.; Zorita, S. Competitive removal of pharmaceuticals from environmental waters by adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11168–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Zhu, B.; Gray, S.; Duke, M.; Muthukumaran, S. Hybrid processes combining photocatalysis and ceramic membrane filtration for degradation of humic acids in saline water. Membranes 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Fukahori, S.; Fujiwara, T. Adsorptive removal and photocatalytic decomposition of sulfamethazine in secondary effluent using TiO2-zeolite composites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-S.; Lin, C.-F.; Hong, P.-K.A. Photocatalytic degradation of methamphetamine by UV/TiO2-Kinetics, intermediates, and products. Water Res. 2015, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.; Ahn, C.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Joo, J. Enhanced removal of trichloroethylene in water using nano-ZnO/polybutadiene rubber composites. Catalysts 2016, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.S.; Lin, C.F.; Hong, P.K.A. Photocatalytic mineralization of codeine by UV-A/TiO2-Kinetics, intermediates, and pathways. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 301, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khraisheh, M.; Kim, J.; Campos, L.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Al-Hawari, A.; Al Ghouti, M.; Walker, G.M. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) pollutants from water by novel TiO2-coconut shell powder (TCNSP) composite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Shainy, F.; Christa, J. Synthesis and characterization of polyacrylic acid-grafted-carboxylic graphene/titanium nanotube composite for the effective removal of enrofloxacin from aqueous solutions: Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, L.; Zeng, J.; He, C.; Tan, X.; He, Z. Combined adsorption and catalytic ozonation for removal of endocrine disrupting compounds over MWCNTs/Fe3O4 composites. Catal. Today 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, M.; Motlagh, H.R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Mostoufi, A.; Saeedi, R.; Barzegar, G.; Jorfi, S. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and real pharmaceutical wastewater using MWCNT/TiO2 nano-composite. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 186, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, P.-S.; Lim, T.-T. Solar regeneration of powdered activated carbon impregnated with visible-light responsive photocatalyst: Factors affecting performances and predictive model. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3054–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Li, J.; Dai, J.; Xia, L.; Barrow, C.J.; Wang, H.; Jegatheesan, J.; Yang, M. Bisphenol A removal on TiO2 -MoS2-reduced graphene oxide composite by adsorption and photocatalysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.-Y.; Zhou, K.; Chen, B.-Y.; Chang, C.-T. Graphene/TiO2/ZSM-5 composites synthesized by mixture design were used for photocatalytic degradation of oxytetracycline under visible light: Mechanism and biotoxicity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 362, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Parameter | Value | Ion | mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.8 | Na+ | 223 |
| Conductivity (mS/m) | 170 | NH4+ | 25.7 |
| K+ | 26.4 | ||
| TOC (mgC/L) a | 10.1 | Mg2+ | 22.2 |
| Ca2+ | 45.5 | ||
| CODcr (mg/L) b | 22 | Cl− | 316 |
| UV absorbance (λ = 365 nm) (1/cm) c | 0.049 | NO2− | 15.6 |
| NO3− | 46.8 | ||
| Alkalinity (mgCaCO3/L) | 158 | SO42− | 87.5 |
| Composite | Target Pollutant | Water Matrix | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2–coconut shell powder composite | Carbamazepine, clofibric acid, and triclosan | Ultrapure water | [47] |
| Polyacrylic acid-grafted-carboxylic graphene/titanium nanotube composite | Enrofloxacin | Distilled water and simulated poultry farm effluent | [48] |
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Fe3O4 composites | Bisphenol A | Doubly-distilled deionized water | [49] |
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/TiO2 nanocomposite | Tetracycline | Pharmaceutical wastewater | [50] |
| Nitrogen-doped-TiO2/activated carbon composite | Bisphenol-A, sulfamethazine, and clofibric acid | Ultrapure water | [51] |
| TiO2-MoS2-reduced graphene oxide composite | Bisphenol A | Not mentioned | [52] |
| Graphene/TiO2/ZSM-5 composites | Oxytetracycline | Deionized water | [53] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, Q.; Fukahori, S.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H.; Fujiwara, T. Removal of Crotamiton from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by a TiO2/Zeolite Composite Sheet. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080778
Xiang Q, Fukahori S, Yamashita N, Tanaka H, Fujiwara T. Removal of Crotamiton from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by a TiO2/Zeolite Composite Sheet. Applied Sciences. 2017; 7(8):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080778
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Qun, Shuji Fukahori, Naoyuki Yamashita, Hiroaki Tanaka, and Taku Fujiwara. 2017. "Removal of Crotamiton from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by a TiO2/Zeolite Composite Sheet" Applied Sciences 7, no. 8: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080778
APA StyleXiang, Q., Fukahori, S., Yamashita, N., Tanaka, H., & Fujiwara, T. (2017). Removal of Crotamiton from Reverse Osmosis Concentrate by a TiO2/Zeolite Composite Sheet. Applied Sciences, 7(8), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080778