Microwave Plasma Torch Generated in Argon for Small Berries Surface Treatment
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Plant Material and CAP Treatment
2.3. Sterilizing Effect of CAP Treatment
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of Methanolic Fruit Extracts
3. Results
3.1. Visual and Thermal Imaging
3.2. Optical Emission Spectroscopy
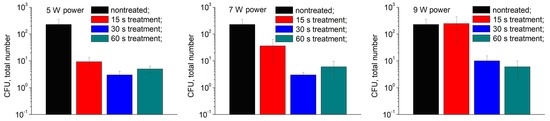
3.3. Plasma Inactivation of Microorganisms at Fruit Surface
3.4. Antioxidant Activity Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misra, N.N.; Tiwari, B.K.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Cullen, P.J. Nonthermal Plasma Inactivation of Food-Borne Pathogens. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fröhling, A.; Durek, J.; Schnabel, U.; Ehlbeck, J.; Bolling, J.; Schlüter, O. Indirect plasma treatment of fresh pork: Decontamination efficiency and effects on quality attributes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertwig, C.; Reineke, K.; Ehlbeck, J.; Erdoğdu, B.; Rauh, C.; Schlüter, O. Impact of remote plasma treatment on natural microbial load and quality parameters of selected herbs and spices. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167 Pt A, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlbeck, J.; Schnabel, U.; Andrasch, M.; Stachowiak, J.; Stolz, N.; Fröhling, A.; Schlüter, O.; Weltmann, K.-D. Plasma Treatment of Food. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2015, 55, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.; Wiacek, C.; Koethe, M.; Braun, P.G. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment of Salmonella Enteritidis inoculated eggshells. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 245, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, M.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Min, S.C. Mandarin preservation by microwave-powered cold plasma treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 39, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukeš, P.; Locke, B.R.; Brisset, J.L. Aqueous-phase chemistry of electrical discharge plasma in water and in gas–liquid environments. In Plasma Chemistry and Catalysis in Gases and Liquids; Parvulescu, V.I., Magureanu, M., Petr, L., Eds.; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 243–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, R.; Oda, T. Ozone production process in pulsed positive dielectric barrier discharge. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorzewski, F. Influence of Non-Thermal Plasma Species on the Structure and Functionality of Isolated and Plantbased 1,4-Benzopyrone Derivatives and Phenolic Acids. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität, Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Soloshenko, I.A.; Tsiolko, V.V.; Pogulay, S.S.; Kalyuzhnaya, A.G.; Bazhenov, V.Y.; Shchedrin, A.I. Effect of water adding on kinetics of barrier discharge in air. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 18, 045019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutchma, T. UV Light for Processing Foods. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2008, 30, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Bandla, S. Ultraviolet Pasteurization for Food Industry. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2012, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnin, E.A.; Stoffels, E.; Erofeev, M.V.; Kieft, I.E.; Kunts, S.E. The effects of UV irradiation and gas plasma treatment on living mammalian cells and bacteria: A comparative approach. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2004, 32, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K. Chapter 4—Atmospheric Pressure Nonthermal Plasma Sources. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture: Fundamentals and Applications; Misra, N.N., Schluter, O., Cullen, P.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 83–116. ISBN 978-0-12-801365-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.; Puligundla, P.; Mok, C. Corona Discharge Plasma Jet Inactivates Food-borne Pathogens Adsorbed onto Packaging Material Surfaces. Packag. Technol. Sci. Int. J. 2017, 30, 10681–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasena, D.; Kim, H.J.; Cheorun, J. Dielectric barrier discharge: Meat Treatment. In Encyclopedia of Plasma Technology, 1st ed.; Leon Shohet, J., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Lin, L.X.; Zhang, H. Understanding the multi-scale structure and functional properties of starch modulated by glow-plasma: A structure-functionality relationship. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, E.; Flikweert, A.J.; Stoffels, W.W.; Kroesen, G.M.W. Plasma needle: A non-destructive atmospheric plasma source for fine surface treatment of (bio)materials. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2002, 11, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Cullen, P.J.; Ostrikov, K. Chapter 6—Antimicrobial Mechanisms of Cold Plasma. In Cold Plasma in Food and Agriculture: Fundamentals and Applications; Misra, N.N., Schluter, O., Cullen, P.J., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-0-12-801365-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bermúdez-Aguirre, D.; Wemlinger, E.; Pedrow, P.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.; Garcia-Perez, M. Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma (APCP) on the inactivation of Escherichia coli in fresh produce. Food Control 2013, 34, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Noriega, E.; Thompson, A. Inactivation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium on fresh produce by cold atmospheric gas plasma technology. Food Microbiol. 2013, 33, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, Y.J. Inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus on the beef jerky by radio-frequency atmospheric pressure plasma discharge treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 22, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzina, D.; Patil, S.; Cullen, P.J.; Keener, K.M.; Bourke, P. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium and Listeria monocytogenes inoculated on fresh produce. Food Microbiol. 2014, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Kushner, M.J.; Locke, B.R.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Graham, W.G.; Graves, D.B.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Maric, D.; Reid, J.P.; Ceriani, E.; et al. Plasma-liquid interactions: A review and roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbin-Figlewicz, N.; Jarmoluk, A.; Marycz, K. Antimicrobial activity of low-pressure plasma treatment against selected foodborne bacteria and meat microbiota. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, N.; Patil, S.; Moiseev, T.; Bourke, P.; Mosnier, J.; Keener, K.; Cullen, P. In-package atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment of strawberries. J. Food Eng. 2014, 125, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, N.; Moiseev, T.; Patil, S.; Pankaj, S.; Bourke, P.; Mosnier, J.; Keener, K.; Cullen, P. Cold plasma in modified atmospheres for post-harvest treatment of strawberries. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3045–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, A.; Niemira, B.A.; Gurtler, J.B.; Fan, X.; Sites, J.; Boyd, G.; Chen, H. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of aerobic microorganisms on blueberries and effects on quality attributes. Food Microbial. 2015, 46, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smet, C.; Baka, M.; Steen, L.; Fraeye, I.; Walsh, J.; Valdramidis, V.; Van Impe, J. Combined effect of cold atmospheric plasma, intrinsic and extrinsic factors on the microbial behavior in/on (food) model systems during storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benova, E.; Atanasova, M.; Bogdanov, T.; Marinova, P.; Krčma, F.; Mazánková, V.; Dostál, L. Microwave Plasma Torch at a Water Surface. Plama Med. 2016, 6, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.; Vašina, P.; Hnilica, J.; Foest, R.; Kudrle, V.; Weltmann, K.-D. Visualization of Revolving Modes in RF and MW Nonthermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jets. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 39, 12341543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krčma, F.; Tsonev, I.; Smejkalová, K.; Truchlá, D.; Kozáková, Z.; Zhekova, M.; Marinova, P.; Bogdanov, T.; Benova, E. Microwave micro torch generated in argon based mixtures for biomedical applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free-Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. Food Sci. Technol. LWT 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisan, M.; Zakrzewski, Z. Plasma sources based on the propagation of electromagnetic surface waves. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1991, 24, 1025–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, M. The use of the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) for estimating antioxidant. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2004, 26, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Sharrer, M.J.; Summerfelt, S.T.; Bullock, G.L.; Gleason, L.E.; Taeuber, J. Inactivation of bacteria using ultraviolet irradiation in a recirculating salmonid culture system. Aquac. Eng. 2005, 33, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, M.; Shama, G.; Deng, X.T.; Greenacre, E.; Brocklehurst, T.; Kong, M.G. Atmospheric plasma inactivation of biofilm-forming bacteria for food safety control. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2005, 33, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukeš, P.; Člupek, M.; Babický, V.; Janda, V.; Šunka, P. Generation of ozone by pulsed corona discharge over water surface in hybrid gas–liquid electrical discharge reactor. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogdanov, T.; Tsonev, I.; Marinova, P.; Benova, E.; Rusanov, K.; Rusanova, M.; Atanassov, I.; Kozáková, Z.; Krčma, F. Microwave Plasma Torch Generated in Argon for Small Berries Surface Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101870
Bogdanov T, Tsonev I, Marinova P, Benova E, Rusanov K, Rusanova M, Atanassov I, Kozáková Z, Krčma F. Microwave Plasma Torch Generated in Argon for Small Berries Surface Treatment. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(10):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101870
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogdanov, Todor, Ivan Tsonev, Plamena Marinova, Evgenia Benova, Krasimir Rusanov, Mila Rusanova, Ivan Atanassov, Zdenka Kozáková, and František Krčma. 2018. "Microwave Plasma Torch Generated in Argon for Small Berries Surface Treatment" Applied Sciences 8, no. 10: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101870
APA StyleBogdanov, T., Tsonev, I., Marinova, P., Benova, E., Rusanov, K., Rusanova, M., Atanassov, I., Kozáková, Z., & Krčma, F. (2018). Microwave Plasma Torch Generated in Argon for Small Berries Surface Treatment. Applied Sciences, 8(10), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101870