Simulation Model and Method for Active Torsional Vibration Control of an HEV
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivations and Technical Challenges
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Original Contributions
2. Materials and Methods
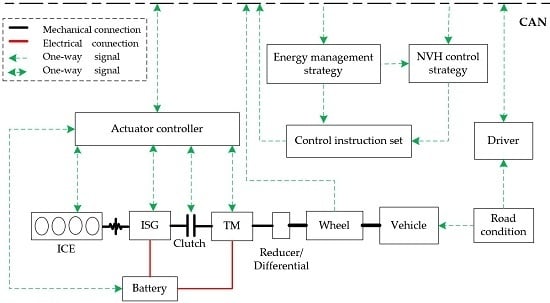
2.1. Structure and Working Principles of a Series-Parallel Hybrid System
2.1.1. Structure
2.1.2. Energy Management Strategy
2.1.3. Torsional Vibration Active Control System
2.2. Torsional Vibration Dynamics Model of Hybrid Powertrain System
2.2.1. Engine Dynamics Model
2.2.2. TM/ISG Dynamics Model
2.2.3. Other Components’ Dynamics Models
2.3. Dynamic Parameters Determination
2.3.1. Bench Testing System
2.3.2. Parameter Determination Method
2.3.3. Engine Moment of Inertia Determination
2.3.4. Engine Excitation Torque Parameter Correction
2.3.5. Motor Torque Response Time Identification
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Stopping from High Speed
4.2. Typical Urban Drive Cycles
4.3. Vibration Control Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




Appendix B
| Parameter | Value (kg·m2) | Parameter | Value (Nm/°) | Parameter | Value (Nm/(r/min)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.52 | Figure A5 | 0.6 | |||
| 2.14 | Figure A6 | 0.5 | |||
| 0.08 | 1500 | 0.1 | |||
| 2.22 | 900 | 150 | |||
| 18 | |||||
| 4950.45 |


References
- Zhang, B.Z. A Study on Energy Management Control Strategy for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicle. Ph.D. Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D. Research on Energy Optimal Management Control Strategy for ISG Hybrid Electric Vehicle. Ph.D. Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, L.P.; Song, J. Correctional DP-based energy management strategy of plug-in hybrid electric bus for city-bus route. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 2792–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.H.; Yang, N.N.; Wang, J.N.; Song, D.F.; Zhang, N.; Shang, M.L.; Liu, J.X. Predictive-model-based dynamic coordination control strategy for power-split hybrid electric bus. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 60–61, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudzadeh, A.A.; Pesiridis, A.; Karvountzis, K.A.; Esfahanian, V. Hybrid electric vehicle performance with organic Rankine cycle waste heat recovery system. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Sun, S.X.; Walker, P.; Zhang, N. Off-Line optimization based active control of torsional oscillation for electric vehicle drivetrain. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, W.M.; Xu, K.; Zahid, T.; Qin, F.Y.; Li, C.M. Energy management strategy for a hybrid electric vehicle based on deep reinforcement learning. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.X.; Liu, B.S.; Shen, J.W.; Guo, N.Y.; Yan, W.S.; Chen, Z. Comparisons of energy management methods for a parallel plug-in hybrid electric vehicle between the convex optimization and dynamic programming. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadallah, M.; Tawadros, P.; Walker, P.; Zhang, N. Dynamic modelling and simulation of a manual transmission based mild hybrid vehicle. Mech. Mach. Theory 2017, 112, 218–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.C.; Yang, F.Y.; Yu, P. Torsional vibration response and parameter influence analysis for the entire drive line of a hybrid electric bus. Eng. Mech. 2014, 31, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, B.Q.; Hou, Z.C.; Liu, R.X. PID control on the torsional vibration of an auxiliary power unit during starting. Automot. Eng. 2018, 2, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.L.; Yang, W.; Hu, X.S.; Zhang, D.J. A novel simplified model for torsional vibration analysis of a series-parallel hybrid electric vehicle. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.Q.; Marco, J.; Greenwood, D.; Harper, L.; Corrochano, D. Powertrain modelling for engine stop–start dynamics and control of micro/mild hybrid construction machines. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K 2017, 231, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, C.Q.; Yan, F.W.; Yan, Y.B.; Yang, P.L. Methods of engine torque estimation for control algorithms. Trans. CSICE 2008, 26, 446–451. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.B. Study on the Dynamic Control in Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.T. Architecture Design, Analysis and Mode Transition Research of a Multi-Mode Hybrid Powertrain Using a Single Electric Machine. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, H.R.; Xu, Z.F.; Zeng, F.Q.; Zi, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.F. Start-up performance simulation of military hybrid vehicle engine based on ISG. J. Mil. Transp. Univ. 2017, 19, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Tian, Z.L.; Yang, Z.J.; Ding, K. Analysis and improvement of the torsional vibration of car powertrain under acceleration condition. Automot. Eng. 2018, 40, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, M.; Gulec, M. Reduction of cogging torque in double-rotor axial-flux permanent-magnet disk motors: A review of cost-effective magnet-skewing techniques with experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2014, 61, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.G.; Wu, S.L.; Wu, X.D.; Shen, J.; Lin, F. Analytical model and optimization of torque of an axial flux permanent magnet synchronous motor. Trans. China Electr. Soc. 2016, 31, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Yu, P.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y. Active control of the electrical machines fluctuating torque based on current harmonics optimization. Mechatronics 2016, 22, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, D.P.; Fang, Z.D. Robust control of integrated motor-transmission powertrain system over controller area network for automotive applications. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 58–59, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, F.U.; Kuang, M.L.; Hao, Y. Active damping wheel-torque control system to reduce driveline oscillations in a power-split hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 4769–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.S.; Weslati, F. Development of a Hybrid Powertrain Active Damping Control System via Sliding Mode Control Scheme; SAE Technical Paper 2013-01-0486; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.T.; Zhao, Q.; Adel, B. Dynamic torque control strategy of engine clutch in hybrid electric vehicle. J. Mech. Eng. 2013, 49, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.D.; Zhang, N. Active damping of transient vibration in dual clutch transmission equipped powertrains: A comparison of conventional and hybrid electric vehicles. Mech. Mach. Theory 2014, 77, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadamalu, R.S.; Beidl, C. MPC for active torsional vibration reduction of hybrid electric powertrains. IFAC-PapersOnline 2016, 49, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.L. Hardware-in-the-Loop simulation of robust mode transition control for a series–parallel hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Song, J.; Li, L.; Li, S.B.; Cao, D.P. Economical launching and accelerating control strategy for a single-shaft parallel hybrid electric bus. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 76–77, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbanks, J.; Michael, J.L. Two-Scale command shaping for reducing powertrain vibration during engine restart. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2017, 112, 218–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.G. Torsional Vibration Analysis and Control for the Driveline of a Hybrid Electric Bus. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Hou, Z.C. Measurement and curve fitting of the friction torque of rolling bearings subjected to radial loads. J. Tsinghua Univ. 2014, 54, 744–749. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.M.; Lei, Z.D.; Li, D.Y.; Ren, L.S.; Huang, Y.M. An experimental study on the effects of grease on the friction torque of hub bearing and the fuel consumption of vehicle. Automot. Eng. 2017, 39, 588–592. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Yang, F.Y.; Yang, Y.P.; Ouyang, M.G. Development of CNG-fueled series hybrid electric city bus. Automot. Eng. 2008, 3, 202–210. [Google Scholar]






















| Part Name | Type | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICE | Natural gas engine | Power (kW) | 155 |
| Peak torque (Nm) | 710 | ||
| ISG motor | PMSM (Pole pairs: 8) | Power (kW) | 100 |
| Peak torque (Nm) | 850 | ||
| TM motor | PMSM (Pole pairs: 8) | Power (kW) | 135 |
| Peak torque (Nm) | 2100 | ||
| Clutch | Two-stage torsion spring | Stiffness (Nm/°) | ≤±1.5°: 66.7 >±1.5°: 457 |
| Torsional damper | Three-stage torsion spring | Stiffness (Nm/°) | ≤±3°: 60 ±3°–±8°: 190 >±8°: 650 |
| Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 1.52 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, B.; Deng, B.; Zhao, H. Simulation Model and Method for Active Torsional Vibration Control of an HEV. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010034
Zhong B, Deng B, Zhao H. Simulation Model and Method for Active Torsional Vibration Control of an HEV. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Biqing, Bin Deng, and Han Zhao. 2019. "Simulation Model and Method for Active Torsional Vibration Control of an HEV" Applied Sciences 9, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010034
APA StyleZhong, B., Deng, B., & Zhao, H. (2019). Simulation Model and Method for Active Torsional Vibration Control of an HEV. Applied Sciences, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9010034