A New Path Tracking Method Based on Multilayer Model Predictive Control
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivations
1.2. Related Works
1.3. Contributions
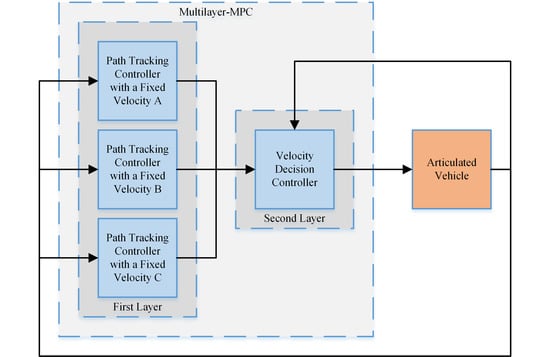
2. Controller Design
2.1. The Framework for Multilayer MPC
2.2. Path Tracking Controller with a Fixed Velocity
2.3. Velocity Decision Controller
3. Simulation
3.1. Comparison Between Controllers
3.2. Sequential Computation and Parallel Computation
3.3. Performance with Positioning Error
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheein, F.A. Intelligent sampling technique for path tracking controllers. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altafini, C. Path following with reduced off-tracking for multibody wheeled vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.P.; Hespanha, J.P. Trajectory-tracking and path-following of underactuated autonomous vehicles with parametric modeling uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 1362–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jia, L. On the layout of fixed urban traffic detectors: An application study. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. 2009, 1, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Liu, L.; Meng, Y.; Luo, W.; Gu, Q.; Ma, B. Path Tracking of Mining Vehicles Based on Nonlinear Model Predictive Control. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemami, A.; Polotski, V. Problem formulation for path tracking automation of low speed articulated vehicles. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Dearborn, MI, USA, 15 September–18 November 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotski, V.; Hemami, A. Control of articulated vehicle for mining applications: Modeling and laboratory experiments. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Conference on Control Applications, Hartford, CT, USA, 5–7 October 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemami, A.; Polotski, V. Path Tracking control problem formulation of an LHD loader. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1998, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, R.M. Modeling and path-tracking for a load-haul-dump mining vehicle. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1997, 119, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corke, P.; Ridley, P. Load haul dump vehicle kinematics and control. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2003, 125, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sasiadek, J.Z.; Lu, Y. Path tracking of an autonomous LHD articulated vehicle. IFAC Proc. 2005, 38, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Barfoot, T.; Larsson, J. Autonomous underground tramming for center-articulated vehicles. J. Field Robot. 2010, 25, 400–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, J. Feedback linearization control for path tracking of articulated dump truck. TELKOMNIKA (Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control) 2015, 13, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Yang, M.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Kinematics and path following control of an articulated drum roller. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, L.G.; Marshall, J.A.; Larsson, J. Experiments in feedback linearized iterative learning-based path following for center-articulated industrial vehicles. J. Field Robot. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, T.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Gustafsson, T. Path following for an articulated vehicle based on switching model predictive control under varying speeds and slip angles. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 17th International Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA 2012), Krakow, Poland, 17–21 September 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, T.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Gustafsson, T. Switching model predictive control for an articulated vehicle under varying slip angle. In Proceedings of the 2012 20th Mediterranean Conference on Control & Automation (MED), Barcelona, Spain, 3–6 July 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayl, T.; Nikolakopoulos, G.; Gustafsson, T. A full error dynamics switching modeling and control scheme for an articulated vehicle. Int. J. Control Autom. 2015, 13, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemami, A.; Mehrabi, M.G.; Cheng, R.M.H. Synthesis of an optimal control law for path tracking in mobile robots. Automatica 1992, 28, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divelbiss, A.W.; Wen, J.T. Trajectory tracking control of a car-trailer system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1997, 5, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suicmez, E.C.; Kutay, A.T. Optimal path tracking control of a quadrotor UAV. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Orlando, FL, USA, 27–30 May 2014; pp. 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Bai, G. LQR-GA Path Tracking Control of Articulated Vehicle Based on Predictive Information. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 375–384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Gan, X.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q. LQR-GA controller for articulated dump truck path tracking system. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 2019, 24, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, D.; Gambino, G.; Palmieri, G.; Glielmo, L. A comparison between LTV-MPC and LQR yaw rate-side slip controller. IFAC Proc. 2009, 42, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakub, F.; Mori, Y. Comparative study of autonomous path-following vehicle control via model predictive control and linear quadratic control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. D-J. Automob. 2015, 229, 1695–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klančar, G.; Škrjanc, I. Tracking-error model-based predictive control for mobile robots in real time. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2007, 55, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.W.; Xu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, K.; Guo, H.F.; Sun, Y.J. Multi-constrained model predictive control for autonomous ground vehicle trajectory tracking. J. Beijing. Inst. Technol. 2015, 24, 441–443. [Google Scholar]
- Plessen, M.M.G.; Bemporad, A. Reference trajectory planning under constraints and path tracking using linear time-varying model predictive control for agricultural machines. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 153, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.468 m | 2m/s2 | 1 | |||
| 3.439 m | 0.05s | ||||
| (−0.70 rad, 0.70 rad) | 30 | ||||
| (−0.14 rad/s, 0.14 rad/s) | 1 | 2 | |||
| (1 m/s, 5 m/s) | 100 | 1 |
| Nonlinear MPC | Switching MPC | Multilayer MPC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Displacement error | 0.7886m | divergent | 0.0558m |
| Heading error | 0.1510rad | divergent | 0.0347rad |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, G.; Meng, Y.; Liu, L.; Luo, W.; Gu, Q.; Li, K. A New Path Tracking Method Based on Multilayer Model Predictive Control. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132649
Bai G, Meng Y, Liu L, Luo W, Gu Q, Li K. A New Path Tracking Method Based on Multilayer Model Predictive Control. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(13):2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132649
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Guoxing, Yu Meng, Li Liu, Weidong Luo, Qing Gu, and Kailun Li. 2019. "A New Path Tracking Method Based on Multilayer Model Predictive Control" Applied Sciences 9, no. 13: 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132649
APA StyleBai, G., Meng, Y., Liu, L., Luo, W., Gu, Q., & Li, K. (2019). A New Path Tracking Method Based on Multilayer Model Predictive Control. Applied Sciences, 9(13), 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9132649