Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Nanocomposites for Dental Applications
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
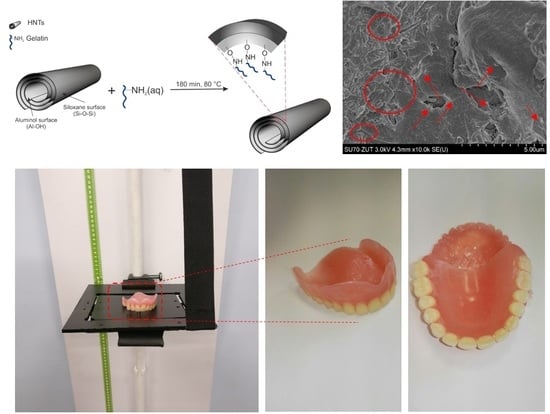
2.1. Preparation of Polymer Nanocomposites Containing Mineral Nanofillers
- 2.5% HNT + 2.5% ATH-sil and
- 2.5% HNT-g + 2.5% ATH-sil.
2.2. Characterization Methods
- —mass loss of the tested rubber sample, in mg;
- —determined value of mass loss of a rubber sample made of a reference composition, in mg;
- —the density of the tested rubber, in mg/mm2;
- —mass loss of a rubber sample made of a reference composition, in mg (212 mg).
- m1—mass of the sample after drying, before the absorbency test;
- m2—mass of the samples after absorbency test;
- m3—mass of the sample after absorbency test and after drying.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Nanofillers
3.2. Dispersion Characteristics
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. Study of Biofilm Formation on the Surface of Prosthetic Materials
- (−)—strain not forming the biofilm (corresponded to the lack of cells)
- (+)—strain weakly forming the biofilm (corresponded to 103–104 CFU/mL)
- (++)—strain strongly forming the biofilm (corresponded to 105–106 CFU/mL)
- (+++)—strain strongly forming the biofilm (corresponded to 107–108 CFU/mL)
3.4.1. Quality Method
3.4.2. Quantitative Method
4. Conclusions
- It is possible to modify the methyl methacrylate with the methyl methacrylate monomer (MM/mMM) by the addition of HNTs, in the proportion of 1—10 wt.%;
- It is possible to prepare the polymer hybrid nanocomposite based on MM/mMM containing 2.5% HNT + 2.5% ATH-sil;
- It is possible modify the same hybrid nanocomposites, except that the halloysite nanofiller was modified with natural polymer (gelatin);
- The incorporation of two mineral nanofillers into the polymer allows one to obtain nanocomposites with enhanced functional properties compared to the polymer matrix.
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashcroft, W.A. Industrial Polymer Applications: Essential Chemistry and Technology, 1st ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, E. A Review Article on Acrylic PMMA. J. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2016, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, U.; Karim, K.J.B.A.; Buang, N.A. A Review of the Properties and Applications of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA). Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puggal, S.; Dhall, N.; Singh, N.; Litt, M.S. A Review on Polymer Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Characterization and Mechanical Properties. Ind. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hojjati, M.; Okamoto, M.; Gorga, R.E. Review article: Polymer-matrix nanocomposites, processing, manufacturing and application: An overview. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Gao, X.; Xu, D. A review of the interfacial characteristics of polymer nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 28048–28085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeosun, S.O.; Lawal, G.I.; Balogun, S.A.; Akpan, E.I. Review of Green Polymer Nanocomposites. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2015, 11, 483–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, R.; He, Z.; Cheng, G.; Wang, H.; Yao, K. Synthesis and Characterization of PMMA/SiO2 Nanocomposites by In Situ Suspension Polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, G.M.; Ahmed, R.M. AC conductivity and dielectric properties of PMMA/fullerene composites. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 24, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motawie, A.M.; Madany, M.M.; El-dakrory, A.Z.; Osman, H.M. Physico-chemical characteristics of nano-organo bentonite prepared using different organo-modifiers. Egypt. J. Pet. 2014, 23, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, S.K.; Mandal, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Studies on Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(methyl methacrylate)-Bentonite Clay Composite by Emulsion Polymerization and Simultaneous In Situ Clay Incorporation. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Nikfarjami, N.; Sanjani, N.S.; Qazvini, N.T. Effect of silver nanoparticle on the properties of poly (methyl methacrylate) nanocomposite network made by in situ photoiniferter-mediated photopolymerization. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 1625–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logakis, E.; Pandis, C.; Pissis, P.; Pionteck, J.; Pötschke, P.; Logakis, E.; Pandis, C.; Pissis, P.; Pionteck, J.; Highly, P.P. Highly conducting poly (methyl methacrylate)/carbon nanotubes composites: Investigation on their thermal, dynamic-mechanical, electrical and dielectric properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 71, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, F.; Malekie, S.; Ziaie, F. Electrical Conductivity Simulation of PMMA-CNT Nano-Composite in Different Frequencies. Presented at the Conference National Conference on Nanostructure and Graphene, Tehran, Iran, 27–28 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, J.; Jacob, K.I.; Tannenbaum, R.; Sharaf, M.A.; Jasiuk, I. Experimental trends in polymer nanocomposites—A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 393, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.; Jang, L.W. Preparation and Characterization of PMMA-Clay Hybrid Composite by Emulsion Polymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 61, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Okamoto, M. Polymer/layered silicate nanocomposites: A review from preparation to processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1539–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, N.; Ayesha, K.; Ayesha, Y. A Review on Preparation, Properties and Applications of Polymeric Nanoparticle-Based Materials. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, A.B.; Gilman, J.W. An overview of flame retardance of polymeric materials: Application, technology, and future directions. Fire Mater. 2013, 37, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Costa, L. Performance and mechanisms of fire retardants in polymers—A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1988, 20, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samujlo, B.; Rudawska, A. Influence of modification of low-density polyethylene with aluminium trihydroxide on its surface free energy. Polimery 2010, 55, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiewicz, P.; Lutynski, M.; Soltys, J.; Pytlinski, A. Purification of halloysite by magnetic separation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2016, 52, 991–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Chinellato, A.C.; Vidotti, S.E.; Hu, G.H.; Pessan, L.A. Compatibilizing effect of acrylic acid modified polypropylene on the morphology and permeability properties of polypropylene/organoclay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, M.; Dubois, P. Polymer-layered silicate nanocmposites: Preparation, properties and uses of a class of materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2000, 28, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Pan, S.L.; Lehmann, B.; Friedrich, K. Analysis of the interfacial interactions in polypropylene/silica nanocomposites. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Noda, I.; Im, S.S. Effect of hydrogen bonding on the crystallization behavior of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)/silica hybrid composites. Polymer 2007, 48, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashantha, K.; Lacrampe, M.F.; Krawczak, P. Processing and characterization of halloysite nanotubes filled polypropylene nanocomposites based on a masterbatch route: Effect of halloysites treatment on structural and mechanical properties. Exp. Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.H.; Wen, W.; Xie, W.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, M.X.; Zhou, C.R. Modified Halloysite Nanotube/Biodegradable Polyester Composite Material and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent 102952385A, 6 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, B.H.; Wen, W.; Xie, W.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, M.X. Modified Halloysite Nanotube/Biodegradable Polyester Composite Material and Preparation Method Thereof. CN Patent 102952385B, 4 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, D.; Lvov, Y.M. Ceramic Nanotube Composites with Sustained Drug Release Capability for Implants, Bone Repair and Regeneration. U.S. Patent 9192912B1, 24 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kausch, C.; Verrocchi, A.; Pomeroy, J.E., III; Peterson, K.M.; Payne, P.F. Flame Resistant Polyolefin Compostions Containing Organically Modified Clay. U.S. Patent 6414070B1, 2 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Weil, E.D.; Levchik, S.V. Commercial flame retardancy of unsaturated polyester and vinyl resins: Review. J. Fire Sci. 2004, 22, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Paul, W.G. Flame Retardant Hydrotalcite Containing Polycarbonate Compositions. PCT Patent WO2003046067A1, 5 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sheist, I. Handbook of Adhesives, 3rd ed.; Chapman & Hall, International Thomson Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kango, S.; Kalia, S.; Celli, A.; Njuguna, J.; Habibi, Y.; Kumar, R. Surface modification of inorganic nanoparticles for development of organic–inorganic nanocomposites—A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1232–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Hill, C.A.S.; Xiao, Z.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Silane coupling agents used for natural fiber/polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, L.N.; Daitx, T.S.; Soares, G.V.; Crespo, J.S.; Mauler, R.S. The effects of silane coupling agents on the properties of PHBV/halloysite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 87, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunova, V.; Kristóf, J.; Kelnar, I.; Dybal, J. The effect of halloysite modification combined with in situ matrix modifications on the structure and properties of polypropylene/halloysite nanocomposites. Exp. Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Marshall, J.; Haroosh, H.J.; Mohammadzadehmoghadam, S.; Liu, D.; Qi, X.; Lau, K.T. Polylactic acid (PLA)/halloysite nanotube (HNT) composite mats: Influence of HNT content and modification. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 76, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos-Ramírez, S.; De Oca-Ramírez, G.M.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Pastor-Blas, M.M.; González-Montiel, A. Surface modification of natural halloysite clay nanotubes with aminosilanes. Application as catalyst supports in the atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 406, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Delvaux, B. Behavior of halloysite clay under formamide treatment. Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 35, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjuvants Help Vaccines Work Better. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vaccinesafety/concerns/adjuvants.html (accessed on 22 February 2019).
- Tyliszczak, B.; Drabczyk, A.; Drabczyk, A.; Kudłacik-kramarczyk, S. Acrylates in Dental Applications. In Acrylic Polymers in Healthcare; Reddy, B., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Song, G.; Zhong, L.; Tang, G. Study on Bulk Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate initiated by low intensity ultrasonic irridation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, A. Bulk polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate in the presence of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate). II. Effect of oxygen. J. Polym. Sci. 1974, 12, 2145–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, M. Effects of the wollastonite fiber modification on the sliding wear behavior of the UHMWPE composites. Wear 2003, 255, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.R.; Ryu, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Rhee, K.Y. Effect of clay surface modification and concentration on the tensile performance of clay/epoxy nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 448, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Li, Y.; Qi, T.; Li, X. Surface properties of superfine alumina trihydrate after surface modification with stearic acid Surface properties of superfine alumina trihydrate after surface modification with stearic acid. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2015, 22, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izabella, L.; Al-Zahari, M.; Ewa, W.; Osawaru, O. The method of obtaning the modyfier for polymers and polymer nanocomposites. PL Patent 213268, 16 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kavoosi, G.; Mahdi Dadfar, S.M.; ALi, D.S.M.; Niakousari, M. Investigation of gelatin/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite films as packaging materials. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.R.; Turner, R.J. A comparative study of techniques for the examination of biofilms by scanning electron microscopy. Water Res. 1984, 18, 676–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maczynska, B.; Neumann, K.; Junka, A.; Smutnicka, D.; Secewicz, A.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Wojkowska-Mach, J.; Sekowska, A.; Gospodarek, E.; Burdynowski, K. Analysis of properties related to selection and survival in hospital environment of Klebsiella strains isolated from nosocomial outbreaks. Forum Zakaz. 2013, 4, 77–97. [Google Scholar]
- Barrientos-Ramírez, S.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Pastor-Blas, M.M.; González-Montiel, A. Use of nanotubes of natural halloysite as catalyst support in the atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Microporous Microporous Mater. 2009, 120, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Green, M.E.R.; Hook, J.M.; Antill, S.J.; Kepert, C.J. Functionalization of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes by Grafting with γ-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15742–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W. A bio-surfactant for defect control: Multifunctional gelatin coated MWCNTs for conductive epoxy nanocomposites A bio-surfactant for defect control: Multifunctional gelatin coated MWCNTs for conductive epoxy nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 159, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Selvakumar, M.; Mahendran, A.; Anandhan, S. Structure-property relationship of halloysite nanotubes/ethylene-vinyl acetate-carbon monoxide terpolymer nanocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2017, 30, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhibar, S.; Das, C.K. Silver Nanoparticles Decorated Polyaniline/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Nanocomposite for High-Performance Supercapacitor Electrode. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3495–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombeshora, E.T.; Simoyi, R.; Nyamori, V.O.; Ndungu, P.G. Multiwalled carbon nanotube-titania nanocomposites: Understanding nano-structural parameters and functionality in dye-sensitized solar cells. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2015, 68, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol-gelatin hydrogel membranes for biomedical applications. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2007, 8, E1–E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoumi, B.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Jaymand, M. Electrically conductive nanocomposite adhesives based on epoxy or chloroprene containing polyaniline, and carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 6057–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, A.; Malek, A.; Fehrenbacher, U.; Brunklaus, G.; Wilhelm, M.; Hirth, T. Silane-functionalized Flame-retardant Aluminum Trihydroxide in Flexible Polyurethane Foam. J. Cell. Plast. 2010, 46, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, V.L.P.; Nascimento, R.S.V.; Menezes, V.J.; Batista, L. TG characterization of organically modified montmorillonite. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 75, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plueddemann, E.P. Silane Coupling Agents, 2nd ed.; Springer Science +Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Pu, S.; Lu, F.; Liu, K.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Li, J. Preparation of dispersed aluminum hydroxide nanoparticles via non-aqueous route and surface modification. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 135, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.M.; Abu-Ayana, Y.M. Preparation and characterization of ultrafine alumina via sol-gel polymeric route. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 111, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Z.; Jia, D.; Zhou, C. Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes-polymer nanocomposite. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1498–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Salas, B.; Beltrán-Partida, E.; Nedev, N. Controlled antifungal behavior on Ti6Al4V nanostructured by chemical nanopatterning. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 96, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilarrasa, J.; Delgado, L.M.; Galofré, M.; Àlvarez, G.; Violant, D.; Manero, J.M.; Blanc, V.; Gil, F.J.; Nart, J. In vitro evaluation of a multispecies oral biofilm over antibacterial coated titanium surfaces. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Lan, J.; Qi, Q. Effect of a denture base acrylic resin containing silver nanoparticles on Candida albicans adhesion and biofilm formation. Gerontology 2016, 33, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, H. Halloysite Nanotubes Supported Ag and Zno Nanoparticles with Synergistically Enhanced Antibacterial Activity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Enhanced antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles/halloysite nanotubes/graphene nanocomposites with Sandwich-lie structure. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervini-Silva, J.; Nieto-Camacho, A.; Palacios, E.; Montoya, J.A.; Gomez-Vidales, V.; Ramirez-Tapan, M.T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-bacterial activity, and cytotoxicity of halloysite surfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Sample | Et (GPa) | σB (MPa) | εB (%) | Ef (GPa) | σfM (MPa) | εfM (%) | H (Sh°D) | KC (kJ/m2) | ρ (g/cm3) | ∆Vrel (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 3.58 ± 0.34 | 39.29 ± 0.88 | 1.72 ± 0.15 | 2.23 ± 0.17 | 54.67 ± 5.93 | 2.81 ± 0.28 | 84 ± 1 | 12.4 ± 1.2 | 1.137 ± 0.004 | 214.98 ± 3.83 |
| 1% HNTs | 3.98 ± 0.32 | 24.93 ± 2.13 | 1.05 ± 0.09 | 2.48 ± 0.11 | 42.11 ± 4.54 | 1.76 ± 0.27 | 78 ± 4 | 4.9 ± 0.4 | 1.124 ± 0.001 | 233.11 ± 11.72 |
| 2.5% HNTs | 2.89 ± 0.11 | 21.93 ± 2.17 | 0.69 ± 0.07 | 2.23 ± 0.12 | 27.88 ± 1.92 | 1.25 ± 0.38 | 73 ± 6 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 1.175 ± 0.004 | 211.26 ± 7.09 |
| 5% HNTs | 2.63 ± 0.20 | 27.89 ± 1.55 | 1.54 ± 0.11 | 2.32 ± 0.17 | 44.71 ± 6.44 | 2.02 ± 0.27 | 85 ± 1 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 1.137 ± 0.017 | 207.92 ± 9.57 |
| 7.5% HNTs | 3.69 ± 0.31 | 26.51 ± 2.27 | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 2.58 ± 0.11 | 45.77 ± 3.11 | 1.78 ± 0.17 | 78 ± 3 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 1.125 ± 0.004 | 212.45 ± 11.86 |
| 10% HNTs | 3.17 ± 0.33 | 29.20 ± 1.99 | 1.37 ± 0.19 | 2.63 ± 0.04 | 38.54 ± 0.56 | 1.58 ± 0.31 | 84 ± 1 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 1.141 ± 0.001 | 211.02 ± 13.59 |
| Sample | Et (GPa) | σB (MPa) | εB (%) | Ef (GPa) | σfM (MPa) | εfM (%) | H (Sh°D) | KC (kJ/m2) | ρ (g/cm3) | ∆Vrel (mm3) | BSA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 3.58 ± 0.34 | 39.29 ± 0.88 | 1.72 ± 0.15 | 2.23 ± 0.17 | 54.67 ± 5.93 | 2.81 ± 0.28 | 84 ± 1 | 12.4 ± 1.2 | 1.137 ± 0.004 | 214.98 ± 3.83 | 2.75 ± 0.20 |
| 5% HNT | 2.63 ± 0.20 | 27.89 ± 1.55 | 1.54 ± 0.11 | 2.32 ± 0.17 | 44.71 ± 6.44 | 2.02 ± 0.27 | 85 ± 1 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 1.137 ± 0.017 | 207.92 ± 9.57 | 2.17 ± 0.07 |
| 5% HNT-g | 1.83 ± 0.06 | 42.22 ± 2.62 | 2.95 ± 0.13 | 2.69 ± 0.14 | 72.73 ± 6.75 | 3.28 ± 0.44 | 82 ± 1 | 6.6 ± 0.5 | 1.171 ± 0.001 | 194.49 ± 7.06 | 2.25 ± 0.13 |
| 5%ATH-sil | 2.47 ± 0.25 | 40.15 ± 1.95 | 2.00 ± 0.12 | 3.08 ± 0.17 | 64.56 ± 2.24 | 2.18 ± 0.12 | 88 ± 2 | 9.3 ± 0.7 | 1.204 ± 0.001 | 178.94 ± 63.04 | 1.76 ± 0.09 |
| 2.5%HNT-g + 2.5%ATH-sil | 3.35 ± 0.31 | 39.66 ± 2.03 | 1.83 ± 0.14 | 3.20 ± 0.08 | 50.95 ± 4.65 | 1.66 ± 0.18 | 86 ± 2 | 5.6 ± 0.6 | 1.196 ± 0.001 | 187.05 ± 4.85 | 2.07 ± 0.09 |
| 2.5%HNT + 2.5% ATH-sil | 2.59 ± 0.18 | 29.67 ± 2.27 | 1.27 ± 0.13 | 2.22 ± 0.22 | 40.37 ± 4.73 | 1.94 ± 0.12 | 88 ± 1 | 6.3 ± 0.9 | 1.153 ± 0.001 | 198.28 ± 7.98 | 1.92 ± 0.07 |
| Height [cm] Sample | 50 | 100 | 150 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Base + 5% HNT | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Base + 5% HNT-g | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Base + 5% ATH-sil | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Base + 2.5% HNT-g + 2.5% ATH-sil | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Base + 2.5% HNT + 2.5% ATH-sil | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Strain Used in Biofilm Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans | S. aureus | P. aeruginosa | E. faecalis | E. coli | ||
| Samples | Base | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| Base + 5% HNT | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | |
| Base + 5% HNT-g | +++ | ++ | ++ | + | + | |
| Base + 5% ATH-sil | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | |
| Base + 2.5% HNT-g + 2.5% ATH-sil | ++ | ++ | + | + | + | |
| Base + 2.5% HNT + 2.5% ATH-sil | + | ++ | + | + | + | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gawdzinska, K.; Paszkiewicz, S.; Piesowicz, E.; Bryll, K.; Irska, I.; Lapis, A.; Sobolewska, E.; Kochmanska, A.; Slaczka, W. Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Nanocomposites for Dental Applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9071381
Gawdzinska K, Paszkiewicz S, Piesowicz E, Bryll K, Irska I, Lapis A, Sobolewska E, Kochmanska A, Slaczka W. Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Nanocomposites for Dental Applications. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(7):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9071381
Chicago/Turabian StyleGawdzinska, Katarzyna, Sandra Paszkiewicz, Elzbieta Piesowicz, Katarzyna Bryll, Izabela Irska, Agnieszka Lapis, Ewa Sobolewska, Agnieszka Kochmanska, and Wojciech Slaczka. 2019. "Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Nanocomposites for Dental Applications" Applied Sciences 9, no. 7: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9071381
APA StyleGawdzinska, K., Paszkiewicz, S., Piesowicz, E., Bryll, K., Irska, I., Lapis, A., Sobolewska, E., Kochmanska, A., & Slaczka, W. (2019). Preparation and Characterization of Hybrid Nanocomposites for Dental Applications. Applied Sciences, 9(7), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9071381