Atypical Electrophysiological Indices of Eyes-Open and Eyes-Closed Resting-State in Children and Adolescents with ADHD and Autism
Abstract
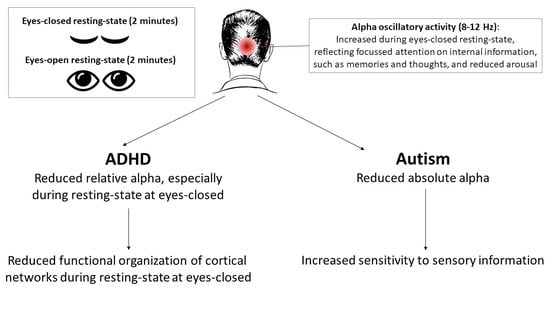
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Analysis Plan
3. Results
3.1. Absolute Alpha Power
3.2. Relative Alpha Power
3.3. Alpha Reactivity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Faraone, S.V.; Asherson, P.; Banaschewski, T.; Biederman, J.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Ramos-Quiroga, J.A.; Rohde, L.A.; Sonuga-Barke, E.J.S.; Tannock, R.; Franke, L. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geva, R.; Feldman, R. A neurobiological model for the effects of early brainstem functioning on the development of behavior and emotion regulation in infants: Implications for prenatal and perinatal risk. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmiloff-Smith, A. Nativism versus neuroconstructivism: Rethinking the study of developmental disorders. Dev. Psychol. 2009, 45, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanelli, D. Opinion: Is science really facing a reproducibility crisis, and do we need it to? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2628–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brokaw, K.; Tishler, W.; Manceor, S.; Hamilton, K.; Gaulden, A.; Parr, E.; Wamsley, E.J. Resting state EEG correlates of memory consolidation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2016, 130, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, J.; Schooler, J.W. The Science of Mind Wandering: Empirically Navigating the Stream of Consciousness. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2015, 66, 487–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, H. Über das Elektrenkephalogramm des Menschen. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1933, 98, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, M.; Yeung, N.; Kadosh, R.C. The many characters of visual alpha oscillations. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2017, 48, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Huang, H.; Schwab, N.; Tanner, J.; Rajan, A.; Lam, N.B.; Zaborszky, L.; Li, C.-S.R.; Price, C.C.; Ding, M. From eyes-closed to eyes-open: Role of cholinergic projections in EC-to-EO alpha reactivity revealed by combining EEG and MRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 40, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Ding, M. Coupling between visual alpha oscillations and default mode activity. NeuroImage 2012, 68, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, K.; Ro, T. Visual Modulation of Resting State α Oscillations. Eneuro 2020, 7, 0268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barry, R.J.; Rushby, J.; Wallace, M.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Johnstone, S.J.; Zlojutro, I. Caffeine effects on resting-state arousal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Johnstone, S.J.; Magee, C.; Rushby, J. EEG differences between eyes-closed and eyes-open resting conditions. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Johnstone, S.J.; Rushby, J. Timing of caffeine’s impact on autonomic and central nervous system measures: Clarification of arousal effects. Boil. Psychol. 2008, 77, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, R.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Johnstone, S.J.; Brown, C.R. EEG differences in children between eyes-closed and eyes-open resting conditions. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; De Blasio, F.M.; Fogarty, J.S.; Clarke, A.R. Natural alpha frequency components in resting EEG and their relation to arousal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 131, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, L.C.; Tedrus, G.M.; Bianchini, M.C.; Silva, T.F. Electroencephalographic Alpha Reactivity on Opening the Eyes in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2013, 44, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellato, A.; Arora, I.; Hollis, C.; Groom, M.J. Is autonomic nervous system function atypical in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? A systematic review of the evidence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 108, 182–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissler, J.M.; Romanos, M.; Hegerl, U.; Hensch, T. Hyperactivity and sensation seeking as autoregulatory attempts to stabilize brain arousal in ADHD and mania? ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2014, 6, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsi, J.; Klein, C. Intraindividual Variability in ADHD and Its Implications for Research of Causal Links. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 9, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeant, J. The cognitive-energetic model: An empirical approach to Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, C.M.; Steinhausen, H.-C. Comorbid mental disorders in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a large nationwide study. ADHD Atten. Deficit Hyperact. Disord. 2014, 7, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, I.; Bellato, A.; Ropar, D.; Hollis, C.; Groom, M. Is autonomic function during resting-state atypical in Autism: A systematic review of evidence. Psyarxiv 2020. in Preparation. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG Frequency Bands in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review of Resting State Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommelse, N.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Hartman, C.A. Structural brain imaging correlates of ASD and ADHD across the lifespan: A hypothesis-generating review on developmental ASD-ADHD subtypes. J. Neural Transm. 2016, 124, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shephard, E.; Tye, C.; Ashwood, K.L.; Azadi, B.; Asherson, P.; Bolton, P.; McLoughlin, G. Resting-State Neurophysiological Activity Patterns in Young People with ASD, ADHD, and ASD + ADHD. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groom, M.; Kochhar, P.; Hamilton, A.; Liddle, E.; Simeou, M.; Hollis, C. Atypical Processing of Gaze Cues and Faces Explains Comorbidity between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, M.A.; Ilmoniemi, R.J. Signal-space projection method for separating MEG or EEG into components. Med Boil. Eng. 1997, 35, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. JASP (Version 0.11.1) [Computer Software] 2019. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Rouder, J.N.; Morey, R.D.; Verhagen, J.; Swagman, A.R.; Wagenmakers, E.-J. Bayesian analysis of factorial designs. Psychol. Methods 2017, 22, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffreys, H. The Theory of Probability, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Bergh, D.V.D.; Van Doorn, J.; Marsman, M.; Draws, T.; Van Kesteren, E.-J.; Derks, K.; Dablander, F.; Gronau, Q.F.; Kucharský, Š.; Gupta, A.R.K.N.; et al. A Tutorial on Conducting and Interpreting a Bayesian ANOVA in JASP. L’Année Psychol. 2020, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, O.; Mazaheri, A. Shaping Functional Architecture by Oscillatory Alpha Activity: Gating by Inhibition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, I.; Bellato, A.; Ropar, D.; Hollis, C.; Groom, M.J. Heart rate variability as an index of autonomic arousal that differentiates ADHD and Autism: Findings from a passive oddball and an active response inhibition task. 2020; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Demographic and Clinical Variables Mean [SD] | Typically Developing Controls | ADHD-Only | Autism-Only | ADHD + Autism | Group Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (females) | 20 (3) | 9 (5) | 6 (0) | 8 (0) | - |
| Mean age (years) | 11.93 [1.78] | 12.09 [2.25] | 12.56 [2.24] | 13.12 [1.78] | None |
| Social Communication Questionnaire (total score) | 3.35 [3.74] | 13.75 [6.18] | 20.50 [9.09] | 26.25 [5.68] | ADHD + autism > ADHD-only; ADHD-only, ADHD + autism and autism-only > TD |
| Conners’ Rating Scales (total score) | 41.12 [16.35] | 80.78 [13.08] | 64.17 [12.51] | 78.75 [3.28] | ADHD-only, ADHD + autism and autism-only > TD |
| Full Scale IQ | 111.19 [9.62] | 93.00 [17.26] | 107.17 [8.89] | 89.86 [15.82] | ADHD-only < TD; ADHD + autism < TD |
| Condition | Group | Mean Relative Alpha Power | SD | 95 % Credible Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Eyes-open | No-ADHD | 0.258 | 0.152 | 0.197 | 0.319 |
| ADHD | 0.162 | 0.080 | 0.121 | 0.203 | |
| Eyes-closed | No-ADHD | 0.442 | 0.187 | 0.367 | 0.518 |
| ADHD | 0.261 | 0.154 | 0.181 | 0.340 | |
| Models | Bayes Factor | R² |
|---|---|---|
| a. IQ | 6.773 | 0.215 |
| b. ADHD | 0.601 | 0.105 |
| c. Autism | 0.125 | 0.006 |
| d. ADHD + autism | 0.226 | 0.105 |
| e. IQ + ADHD + autism | 0.626 | 0.222 |
| f. IQ + ADHD | 1.684 | 0.218 |
| g. IQ + autism | 1.676 | 0.218 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellato, A.; Arora, I.; Kochhar, P.; Hollis, C.; Groom, M.J. Atypical Electrophysiological Indices of Eyes-Open and Eyes-Closed Resting-State in Children and Adolescents with ADHD and Autism. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050272
Bellato A, Arora I, Kochhar P, Hollis C, Groom MJ. Atypical Electrophysiological Indices of Eyes-Open and Eyes-Closed Resting-State in Children and Adolescents with ADHD and Autism. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(5):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050272
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellato, Alessio, Iti Arora, Puja Kochhar, Chris Hollis, and Madeleine J. Groom. 2020. "Atypical Electrophysiological Indices of Eyes-Open and Eyes-Closed Resting-State in Children and Adolescents with ADHD and Autism" Brain Sciences 10, no. 5: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050272
APA StyleBellato, A., Arora, I., Kochhar, P., Hollis, C., & Groom, M. J. (2020). Atypical Electrophysiological Indices of Eyes-Open and Eyes-Closed Resting-State in Children and Adolescents with ADHD and Autism. Brain Sciences, 10(5), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10050272