The Necessity of Taking Culture and Context into Account When Studying the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Brain Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Historical Perspectives Linking Socioeconomic Status (SES) and Brain Development
1.2. The Importance of Studying the Association between SES and Brain Development
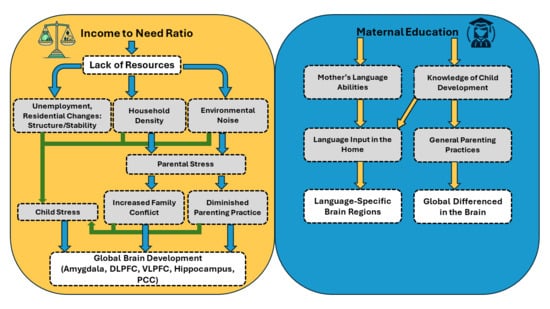
1.3. Pathway 1. Maternal Education, Language Experiences, and Brain Development
1.4. Pathway 2. Income, Stress Related Experiences, and Brain Development
2. Understanding the Role of Cultural Context When Examining SES-Related Differences in Brain and Cognitive Development
2.1. Consideration of Multigenerational Households
2.2. Consideration of Caregiver Practices and Belief Systems
2.3. Consideration of Underrepresented Cultures
2.4. Consideration of Bilingual Populations
2.5. Current Demographic Shifts: Household Density, Urbanization, Chaos, and Noise
2.6. Considerations for Texture and Style of Hair in Neuroimaging Techniques
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farah, M.J. The Neuroscience of Socioeconomic Status: Correlates, Causes, and Consequences. Neuron 2017, 96, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, G.J.; Magnuson, K. Socioeconomic Status and Cognitive Functioning: Moving from Correlation to Causation. WIREs Cogn. Sci. 2012, 3, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmony, T.; Alvarez, A.; Pascual, R.; Ramos, A.; Marosi, E.; Díaz De León, A.E.; Valdés, P.; Becker, J. EEG Maturation on Children with Different Economic and Psychosocial Characteristics. Int. J. Neurosci. 1988, 41, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, M.J.; Schneider, J.M. Socioeconomic Status Related Differences in Resting State EEG Activity Correspond to Differences in Vocabulary and Working Memory in Grade School. Brain Cogn. 2019, 137, 103619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, K.G.; Houston, S.M.; Kan, E.; Sowell, E.R. Neural Correlates of Socioeconomic Status in the Developing Human Brain. Dev. Sci. 2012, 15, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, K.G.; Houston, S.M.; Brito, N.H.; Bartsch, H.; Kan, E.; Kuperman, J.M.; Akshoomoff, N.; Amaral, D.G.; Bloss, C.S.; Libiger, O.; et al. Family Income, Parental Education and Brain Structure in Children and Adolescents. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, L.; Chen, B.; Fishman, I. Neural Correlates of Socioeconomic Status in Early Childhood: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Child Neuropsychol. 2021, 27, 390–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, G.A. Poverty, Cultural Disadvantage and Brain Development: A Study of Pre-School Children in Mexico. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 102, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, G.J.; Yeung, W.J.; Brooks-Gunn, J.; Smith, J.R. How Much Does Childhood Poverty Affect the Life Chances of Children? Am. Sociol. Rev. 1998, 63, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Chen, E.; Matthews, K.A. Childhood Socioeconomic Status and Adult Health. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1186, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.; Cassells, R.C. Childhood Poverty, Cumulative Risk Exposure, and Mental Health in Emerging Adults. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 2, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnack, H.G.; van Haren, N.E.M.; Brouwer, R.M.; Evans, A.; Durston, S.; Boomsma, D.I.; Kahn, R.S.; Hulshoff Pol, H.E. Changes in Thickness and Surface Area of the Human Cortex and Their Relationship with Intelligence. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowell, E.R.; Peterson, B.S.; Thompson, P.M.; Welcome, S.E.; Henkenius, A.L.; Toga, A.W. Mapping Cortical Change across the Human Life Span. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamnes, C.K.; Herting, M.M.; Goddings, A.-L.; Meuwese, R.; Blakemore, S.-J.; Dahl, R.E.; Güroğlu, B.; Raznahan, A.; Sowell, E.R.; Crone, E.A.; et al. Development of the Cerebral Cortex across Adolescence: A Multisample Study of Inter-Related Longitudinal Changes in Cortical Volume, Surface Area, and Thickness. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 3402–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, R.M.; Klein, M.; Grasby, K.L.; Schnack, H.G.; Jahanshad, N.; Teeuw, J.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Sprooten, E.; Franz, C.E.; Gogtay, N.; et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Longitudinal Changes in Brain Structure across the Lifespan. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bethlehem, R.A.I.; Seidlitz, J.; White, S.R.; Vogel, J.W.; Anderson, K.M.; Adamson, C.; Adler, S.; Alexopoulos, G.S.; Anagnostou, E.; Areces-Gonzalez, A.; et al. Brain Charts for the Human Lifespan. Nature 2022, 604, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, C. The Cognitive Neuroscience of Ageing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, B. Developmental Changes in Cognitive Control through Adolescence. In Advances in Child Development and Behavior; Bauer, P., Ed.; JAI: Greenwich, CT, USA, 2009; Volume 37, pp. 233–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hackman, D.A.; Farah, M.J. Socioeconomic Status and the Developing Brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2009, 13, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, A.P.; Finn, A.S.; Leonard, J.A.; Jacoby-Senghor, D.S.; West, M.R.; Gabrieli, C.F.O.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Neuroanatomical Correlates of the Income-Achievement Gap. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 26, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.L.; Hair, N.; Shen, D.G.; Shi, F.; Gilmore, J.H.; Wolfe, B.L.; Pollak, S.D. Family Poverty Affects the Rate of Human Infant Brain Growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jednoróg, K.; Altarelli, I.; Monzalvo, K.; Fluss, J.; Dubois, J.; Billard, C.; Dehaene-Lambertz, G.; Ramus, F. The Influence of Socioeconomic Status on Children’s Brain Structure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, G.M.; Duda, J.T.; Avants, B.B.; Wu, J.; Farah, M.J. Associations between Children’s Socioeconomic Status and Prefrontal Cortical Thickness. Dev. Sci. 2013, 16, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-J.; Davis, E.P.; Sandman, C.A.; Glynn, L.; Sporns, O.; O’Donnell, B.F.; Hetrick, W.P. Childhood Poverty and the Organization of Structural Brain Connectome. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriguchi, Y.; Shinohara, I. Socioeconomic Disparity in Prefrontal Development during Early Childhood. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakesh, D.; Whittle, S. Socioeconomic Status and the Developing Brain—A Systematic Review of Neuroimaging Findings in Youth. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 130, 379–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, M.A.; Sarsour, K.; Jutte, D.; D’Esposito, M.; Boyce, W.T. The Impact of Social Disparity on Prefrontal Function in Childhood. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Li, P.; Zhou, W.; Shu, H. Effects of Socioeconomic Status in Predicting Reading Outcomes for Children: The Mediation of Spoken Language Network. Brain Cogn. 2021, 147, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.R.; Leonard, J.A.; Robinson, S.T.; West, M.R.; Mackey, A.P.; Rowe, M.L.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Beyond the 30-Million-Word Gap: Children’s Conversational Exposure Is Associated with Language-Related Brain Function. Psychol. Sci. 2018, 29, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, L.S.; Camacho, M.C.; Montez, D.F.; Humphreys, K.L.; Gotlib, I.H. Naturalistic Language Input Is Associated with Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Infancy. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, C.L.; Seidlitz, J.; Nadig, A.; Liu, S.; Clasen, L.S.; Blumenthal, J.D.; Reardon, P.K.; Lalonde, F.; Greenstein, D.; Patel, R.; et al. Longitudinally Mapping Childhood Socioeconomic Status Associations with Cortical and Subcortical Morphology. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.D.; Raichle, M.E. Spontaneous Fluctuations in Brain Activity Observed with Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; De Stefano, N.; Matthews, P.M.; Smith, S.M. fMRI Resting State Networks Define Distinct Modes of Long-Distance Interactions in the Human Brain. NeuroImage 2006, 29, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damoiseaux, J.S.; Rombouts, S.A.R.B.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; Stam, C.J.; Smith, S.M.; Beckmann, C.F. Consistent Resting-State Networks across Healthy Subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13848–13853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantini, D.; Perrucci, M.G.; Del Gratta, C.; Romani, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Electrophysiological Signatures of Resting State Networks in the Human Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13170–13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, D.A.; Murayama, Y.; Logothetis, N.K. Very Slow Activity Fluctuations in Monkey Visual Cortex: Implications for Functional Brain Imaging. Cereb. Cortex 2003, 13, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bice, K.; Yamasaki, B.L.; Prat, C.S. Bilingual Language Experience Shapes Resting-State Brain Rhythms. Neurobiol. Lang. 2020, 1, 288–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.C.; Cooper, N.R. The Association between High Levels of Cumulative Life Stress and Aberrant Resting State EEG Dynamics in Old Age. Biol. Psychol. 2017, 127, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellci, K.; Marusak, H.A.; Peters, C.; Elrahal, F.; Iadipaolo, A.S.; Rabinak, C.A. Community and Household-Level Socioeconomic Disadvantage and Functional Organization of the Salience and Emotion Network in Children and Adolescents. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Alcauter, S.; Elton, A.; Hernandez-Castillo, C.R.; Smith, J.K.; Ramirez, J.; Lin, W. Functional Network Development During the First Year: Relative Sequence and Socioeconomic Correlations. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barch, D.; Pagliaccio, D.; Belden, A.; Harms, M.P.; Gaffrey, M.; Sylvester, C.M.; Tillman, R.; Luby, J. Effect of Hippocampal and Amygdala Connectivity on the Relationship between Preschool Poverty and School-Age Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooley, U.A.; Mackey, A.P.; Ciric, R.; Ruparel, K.; Moore, T.M.; Gur, R.C.; Gur, R.E.; Satterthwaite, T.D.; Bassett, D.S. Associations between Neighborhood SES and Functional Brain Network Development. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooley, U.A.; Bassett, D.S.; Mackey, A.P. Environmental Influences on the Pace of Brain Development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsáki, G. Rhythms of the Brain; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-19-986371-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dustman, R.E.; Shearer, D.E.; Emmerson, R.Y. Life-Span Changes in EEG Spectral Amplitude, Amplitude Variability and Mean Frequency. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüchinger, R.; Michels, L.; Martin, E.; Brandeis, D. Brain State Regulation during Normal Development: Intrinsic Activity Fluctuations in Simultaneous EEG–fMRI. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, J. Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Reveals Brain Activity on the Move. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2208729119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitford, T.J.; Rennie, C.J.; Grieve, S.M.; Clark, C.R.; Gordon, E.; Williams, L.M. Brain Maturation in Adolescence: Concurrent Changes in Neuroanatomy and Neurophysiology. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2007, 28, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüchinger, R.; Michels, L.; Martin, E.; Brandeis, D. EEG–BOLD Correlations during (Post-)Adolescent Brain Maturation. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benninger, C.; Matthis, P.; Scheffner, D. EEG Development of Healthy Boys and Girls. Results of a Longitudinal Study. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1984, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.R.; Barry, R.J.; McCarthy, R.; Selikowitz, M. Age and Sex Effects in the EEG: Development of the Normal Child. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, L.; Kovacevic, N.; McIntosh, A.R.; Poulsen, C.; Martinu, K.; Leonard, G.; Paus, T. Maturation of EEG Power Spectra in Early Adolescence: A Longitudinal Study. Dev. Sci. 2011, 14, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmony, T.; Marosi, E.; Díaz de León, A.E.; Becker, J.; Fernández, T. Effect of Sex, Psychosocial Disadvantages and Biological Risk Factors on EEG Maturation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1990, 75, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthis, P.; Scheffner, D.; Benninger, C.; Lipinski, C.; Stolzis, L. Changes in the Background Activity of the Electroencephalogram According to Age. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1980, 49, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsen, R.J.M.; van’t Klooster, B.J.; van der Molen, M.W.; van Leeuwen, H.M.P.; Licht, R. Growth Spurts in Brain Maturation during Middle Childhood as Indexed by EEG Power Spectra. Biol. Psychol. 1997, 44, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tröndle, M.; Popov, T.; Dziemian, S.; Langer, N. Decomposing the Role of Alpha Oscillations during Brain Maturation. eLife 2022, 11, e77571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.L.; Pierce, L.J.; Sideridis, G.; Wade, M.; Nelson, C.A. Associations between EEG Trajectories, Family Income, and Cognitive Abilities over the First Two Years of Life. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2023, 61, 101260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, G.A. Eeg Spectral Analysis in Children with Sociocultural Handicaps. Int. J. Neurosci. 1994, 79, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, G.A.; Pliego-Rivero, F.B.; Fernández, T.; Ricardo, J. EEG Development in Children with Sociocultural Disadvantages: A Follow-up Study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantiani, C.; Piazza, C.; Mornati, G.; Molteni, M.; Riva, V. Oscillatory Gamma Activity Mediates the Pathway from Socioeconomic Status to Language Acquisition in Infancy. Infant Behav. Dev. 2019, 57, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalski, P.; Moore, D.G.; Ribeiro, H.; Axelsson, E.L.; Murphy, E.; Karmiloff-Smith, A.; Johnson, M.H.; Kushnerenko, E. Socioeconomic Status and Functional Brain Development—Associations in Early Infancy. Dev. Sci. 2013, 16, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troller-Renfree, S.V.; Brito, N.H.; Desai, P.M.; Leon-Santos, A.G.; Wiltshire, C.A.; Motton, S.N.; Meyer, J.S.; Isler, J.; Fifer, W.P.; Noble, K.G. Infants of Mothers with Higher Physiological Stress Show Alterations in Brain Function. Dev. Sci. 2020, 23, e12976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, R.J.; Clarke, A.R.; Hajos, M.; McCarthy, R.; Selikowitz, M.; Dupuy, F.E. Resting-State EEG Gamma Activity in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudi, M.H.; Castro, S.; Chalamalasetty, P.; Maguire, M.J. Development of Gamma Oscillation during Sentence Processing in Early Adolescence: Insights into the Maturation of Semantic Processing. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benasich, A.A.; Gou, Z.; Choudhury, N.; Harris, K.D. Early Cognitive and Language Skills Are Linked to Resting Frontal Gamma Power across the First 3 Years. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 195, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.J.; Perone, S. Developmental Change in the Resting State Electroencephalogram: Insights into Cognition and the Brain. Brain Cogn. 2018, 126, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, N.H.; Fifer, W.P.; Myers, M.M.; Elliott, A.J.; Noble, K.G. Associations among Family Socioeconomic Status, EEG Power at Birth, and Cognitive Skills during Infancy. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, P.J.; Fox, N.A.; Group, B.C. A Comparison of the Electroencephalogram between Institutionalized and Community Children in Romania. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhaas, P.J.; Singer, W. Abnormal Neural Oscillations and Synchrony in Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B.L.; Tottenham, N. The Stress Acceleration Hypothesis: Effects of Early-Life Adversity on Emotion Circuits and Behavior. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 7, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.A.; Romeo, R.R.; Park, A.T.; Takada, M.E.; Robinson, S.T.; Grotzinger, H.; Last, B.S.; Finn, A.S.; Gabrieli, J.D.E.; Mackey, A.P. Associations between Cortical Thickness and Reasoning Differ by Socioeconomic Status in Development. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2019, 36, 100641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, A.T.; Leonard, J.A.; Saxler, P.K.; Cyr, A.B.; Gabrieli, J.D.E.; Mackey, A.P. Amygdala–Medial Prefrontal Cortex Connectivity Relates to Stress and Mental Health in Early Childhood. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2018, 13, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Hermans, E.J.; van Marle, H.J.F.; Luo, J.; Fernández, G. Acute Psychological Stress Reduces Working Memory-Related Activity in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, K.G.; Norman, M.F.; Farah, M.J. Neurocognitive Correlates of Socioeconomic Status in Kindergarten Children. Dev. Sci. 2005, 8, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, M.J.; Shera, D.M.; Savage, J.H.; Betancourt, L.; Giannetta, J.M.; Brodsky, N.L.; Malmud, E.K.; Hurt, H. Childhood Poverty: Specific Associations with Neurocognitive Development. Brain Res. 2006, 1110, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, K.G.; McCandliss, B.D.; Farah, M.J. Socioeconomic Gradients Predict Individual Differences in Neurocognitive Abilities. Dev. Sci. 2007, 10, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics and U.S. Census Bureau (2023). HINC-01. Selected Characteristics of Households by Total Money Income. Current Population Survey (CPS) Annual Social and Economic (ASEC) Supplement. Available online: https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/income-poverty/cps-hinc/hinc-01.html (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Khanam, R.; Nghiem, S. Family Income and Child Cognitive and Noncognitive Development in Australia: Does Money Matter? Demography 2016, 53, 597–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, R.; Biesanz, J.; Taylor, L.; Burchinal, M.; Cox, M. Family income and its relation to preschool children’s adjustment for families in the NICHD Study of Early Child Care. Dev. Psychol. 2004, 40, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Harris, K.M. The mechanisms mediating the effects of poverty on children’s intellectual development. Demography 2000, 37, 431–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erola, J.; Jalonen, S.; Lehti, H. Parental education, class and income over early life course and children’s achievement. Res. Soc. Stratif. Mobil. 2016, 44, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, R.E.; Paul, R.A.; Smyser, C.D.; Rogers, C.E. Maternal intelligence quotient (IQ) predicts IQ and language in very preterm children at age 5 years. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.; Risley, T.R.; Kirby, J.R. Meaningful Differences in the Everyday Experience of Young American Children. Can. J. Educ. 1997, 22, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, R.H.; Whiteside, L.; Caldwell, B.M.; Casey, P.H.; Kelleher, K.; Pope, S.; Swanson, M.; Barrett, K.; Cross, D. Maternal IQ, the home environment, and child IQ in low birthweight, premature children. Int. J. Behav. Dev. 1993, 16, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronfani, L.; Vecchi Brumatti, L.; Mariuz, M.; Tognin, V.; Bin, M.; Ferluga, V.; Knowles, A.; Montico, M.; Barbone, F. The complex interaction between home environment, socioeconomic status, maternal IQ and early child neurocognitive development: A multivariate analysis of data collected in a newborn cohort study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, M.L. A Longitudinal Investigation of the Role of Quantity and Quality of Child-Directed Speech in Vocabulary Development. Child Dev. 2012, 83, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, J.; Vasilyeva, M.; Cymerman, E.; Levine, S. Language Input and Child Syntax. Cogn. Psychol. 2002, 45, 337–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, J.; Vasilyeva, M.; Waterfall, H.R.; Vevea, J.L.; Hedges, L.V. The Varieties of Speech to Young Children. Dev. Psychol. 2007, 43, 1062–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttenlocher, J.; Waterfall, H.; Vasilyeva, M.; Vevea, J.; Hedges, L.V. Sources of Variability in Children’s Language Growth. Cogn. Psychol. 2010, 61, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferjan Ramírez, N.; Lytle, S.R.; Kuhl, P.K. Parent Coaching Increases Conversational Turns and Advances Infant Language Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3484–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh-Pasek, K.; Adamson, L.B.; Bakeman, R.; Owen, M.T.; Golinkoff, R.M.; Pace, A.; Yust, P.K.S.; Suma, K. The Contribution of Early Communication Quality to Low-Income Children’s Language Success. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 26, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.L. Child-Directed Speech: Relation to Socioeconomic Status, Knowledge of Child Development and Child Vocabulary Skill. J. Child Lang. 2008, 35, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, J.F.; Lew-Williams, C. Language Learning, Socioeconomic Status, and Child-Directed Speech. WIREs Cogn. Sci. 2016, 7, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.R.; Segaran, J.; Leonard, J.A.; Robinson, S.T.; West, M.R.; Mackey, A.P.; Yendiki, A.; Rowe, M.L.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Language Exposure Relates to Structural Neural Connectivity in Childhood. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 7870–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, E.; Burridge, A.; Ribot, K.M.; Giguere, D. Language Specificity in the Relation of Maternal Education to Bilingual Children’s Vocabulary Growth. Dev. Psychol. 2018, 54, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff-Ginsberg, E. Mother-Child Conversation in Different Social Classes and Communicative Settings. Child Dev. 1991, 62, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, E.; Core, C.; Place, S.; Rumiche, R.; Señor, M.; Parra, M. Dual Language Exposure and Early Bilingual Development. J. Child Lang. 2012, 39, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.M.; McIlvain, G.; Johnson, C.L. Mechanical Properties of the Developing Brain Are Associated with Language Input and Vocabulary Outcome. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2022, 47, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizada, R.D.S.; Richards, T.L.; Meltzoff, A.; Kuhl, P.K. Socioeconomic Status Predicts Hemispheric Specialisation of the Left Inferior Frontal Gyrus in Young Children. NeuroImage 2008, 40, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, N.H.; Troller-Renfree, S.V.; Leon-Santos, A.; Isler, J.R.; Fifer, W.P.; Noble, K.G. Associations among the Home Language Environment and Neural Activity during Infancy. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2020, 43, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, L.J.; Reilly, E.; Nelson, C.A. Associations between Maternal Stress, Early Language Behaviors, and Infant Electroencephalography during the First Year of Life. J. Child Lang. 2021, 48, 737–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merz, E.C.; Wiltshire, C.A.; Noble, K.G. Socioeconomic Inequality and the Developing Brain: Spotlight on Language and Executive Function. Child Dev. Perspect. 2019, 13, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.L.; Sheridan, M.A.; Sambrook, K.A.; Meltzoff, A.N.; McLaughlin, K.A. Socioeconomic Disparities in Academic Achievement: A Multi-Modal Investigation of Neural Mechanisms in Children and Adolescents. NeuroImage 2018, 173, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, K.G.; Giebler, M.A. The Neuroscience of Socioeconomic Inequality. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2020, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIMH Data Archive—Data Dictionary: Data Structure. Available online: https://nda.nih.gov/data_structure.html?short_name=inr01 (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Merz, E.C.; Desai, P.M.; Maskus, E.A.; Melvin, S.A.; Rehman, R.; Torres, S.D.; Meyer, J.; He, X.; Noble, K.G. Socioeconomic Disparities in Chronic Physiologic Stress Are Associated with Brain Structure in Children. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 86, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troller-Renfree, S.V.; Costanzo, M.A.; Duncan, G.J.; Magnuson, K.; Gennetian, L.A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Halpern-Meekin, S.; Fox, N.A.; Noble, K.G. The Impact of a Poverty Reduction Intervention on Infant Brain Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115649119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks-Gunn, J.; Duncan, G.J. The Effects of Poverty on Children. Future Child. 1997, 7, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, C.R.; Weckman, A.M.; Wright, J.K.; Conroy, A.L.; Kain, K.C. Developmental Origins of Disease Highlight the Immediate Need for Expanded Access to Comprehensive Prenatal Care. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1021901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautarescu, A.; Craig, M.C.; Glover, V. Chapter Two—Prenatal Stress: Effects on Fetal and Child Brain Development. In International Review of Neurobiology; Clow, A., Smyth, N., Eds.; Stress and Brain Health: Across the Life Course; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 150, pp. 17–40. [Google Scholar]
- Conger, R.D.; Wallace, L.E.; Sun, Y.; Simons, R.L.; McLoyd, V.C.; Brody, G.H. Economic Pressure in African American Families: A Replication and Extension of the Family Stress Model. Dev. Psychol. 2002, 38, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conger, R.D.; Elder, G.H. Families in Troubled Times: Adapting to Change in Rural America. Social Institutions and Social Change; Aldine de Gruyter: Hawthorne, NY, USA, 1994; ISBN 0-202-30487-6/978-0-202-30488-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hobkirk, A.L.; Krebs, N.M.; Muscat, J.E. Income as a Moderator of Psychological Stress and Nicotine Dependence among Adult Smokers. Addict. Behav. 2018, 84, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, J.; Belden, A.; Botteron, K.; Marrus, N.; Harms, M.P.; Babb, C.; Nishino, T.; Barch, D. The Effects of Poverty on Childhood Brain Development: The Mediating Effect of Caregiving and Stressful Life Events. JAMA Pediatr. 2013, 167, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, A.J.; Israel, B.A.; Zenk, S.N.; Parker, E.A.; Lichtenstein, R.; Shellman-Weir, S.; Ab, L.K. Psychosocial Stress and Social Support as Mediators of Relationships between Income, Length of Residence and Depressive Symptoms among African American Women on Detroit’s Eastside. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, B.K.; Guerra, N.G.; Tolan, P.H. Neighborhood Disadvantage, Stressful Life Events and Adjustments in Urban Elementary-School Children. J. Clin. Child Psychol. 1994, 23, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, C.L. Crime and Unemployment among Youths in the United States, 1958–1990. Am. J. Econ. Sociol. 1994, 53, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W. The Environment of Childhood Poverty. Am. Psychol. 2004, 59, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, C.D.; Wadsworth, M.E.; Stump, J. Socioeconomic Status, Neighborhood Disadvantage, and Poverty-Related Stress: Prospective Effects on Psychological Syndromes among Diverse Low-Income Families. J. Econ. Psychol. 2011, 32, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.; Wells, N.M.; Moch, A. Housing and Mental Health: A Review of the Evidence and a Methodological and Conceptual Critique. J. Soc. Issues 2003, 59, 475–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Benefield, P. Systematic Reviews of Educational Research: Does the Medical Model Fit? Br. Educ. Res. J. 2001, 27, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, S.; Denicola-Prechtl, K.; Nelson, J.A.; Behboudi, M.H.; Benitez-Barrera, C.; Castro, S.; Maguire, M.J. Rethinking Household Size and Children’s Language Environment. Dev. Psychol. 2024, 60, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, A.D.; Kim, S.Y. Understanding Chinese American Adolescents’ Developmental Outcomes: Insights from the Family Stress Model. J. Res. Adolesc. 2010, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linver, M.R.; Brooks-Gunn, J.; Kohen, D.E. Family Processes as Pathways from Income to Young Children’s Development. Dev. Psychol. 2002, 38, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neppl, T.K.; Senia, J.M.; Donnellan, M.B. The Effects of Economic Hardship: Testing the Family Stress Model over Time. J. Fam. Psychol. 2016, 30, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupien, S.J.; Maheu, F.; Tu, M.; Fiocco, A.; Schramek, T.E. The Effects of Stress and Stress Hormones on Human Cognition: Implications for the Field of Brain and Cognition. Brain Cogn. 2007, 65, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shonkoff, J.P.; Garner, A.S.; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, Committee on Early Childhood, Adoption, and Dependent Care, and Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; Siegel, B.S.; Dobbins, M.I.; Earls, M.F.; Garner, A.S.; McGuinn, L.; Pascoe, J.; Wood, D.L. The Lifelong Effects of Early Childhood Adversity and Toxic Stress. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e232–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Evans, G.W.; Angstadt, M.; Ho, S.S.; Sripada, C.S.; Swain, J.E.; Liberzon, I.; Phan, K.L. Effects of Childhood Poverty and Chronic Stress on Emotion Regulatory Brain Function in Adulthood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18442–18447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S. Stress, Sex, and Neural Adaptation to a Changing Environment: Mechanisms of Neuronal Remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1204, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wager, T.D.; Sylvester, C.-Y.C.; Lacey, S.C.; Nee, D.E.; Franklin, M.; Jonides, J. Common and Unique Components of Response Inhibition Revealed by fMRI. NeuroImage 2005, 27, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, J.L.; Chandra, A.; Wolfe, B.L.; Pollak, S.D. Association between Income and the Hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegler, R.; McGregor, A.; Krebs, J.R.; Healy, S.D. A Larger Hippocampus Is Associated with Longer-Lasting Spatial Memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6941–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianaros, P.J.; Jennings, J.R.; Sheu, L.K.; Greer, P.J.; Kuller, L.H.; Matthews, K.A. Prospective Reports of Chronic Life Stress Predict Decreased Grey Matter Volume in the Hippocampus. NeuroImage 2007, 35, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, L.R.; Noble, K.G.; Pediatric Imaging, Neurocognition, and Genetics Study. Perceived Stress Is Associated with Smaller Hippocampal Volume in Adolescence. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S. Effects of Adverse Experiences for Brain Structure and Function. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 48, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagni, S.A.; Benetti, S.; Arulanantham, S.; McCrory, E.; McGuire, P.; Mechelli, A. Effects of Stressful Life Events on Human Brain Structure: A Longitudinal Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Stress 2011, 14, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radley, J.J.; Morrison, J.H. Repeated Stress and Structural Plasticity in the Brain. Ageing Res. Rev. 2005, 4, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisler, J.M.; James, G.A.; Tripathi, S.; Mletzko, T.; Heim, C.; Hu, X.P.; Mayberg, H.S.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Kilts, C.D. Differential Functional Connectivity within an Emotion Regulation Neural Network among Individuals Resilient and Susceptible to the Depressogenic Effects of Early Life Stress. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.S.; Valentine, T.R.; Sweet, L.H.; Tyrka, A.R.; Price, L.H.; Carpenter, L.L. Early Life Stress Impacts Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Functional Connectivity in Healthy Adults: Informing Future Studies of Antidepressant Treatments. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 52, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corning, W.C.; Steffy, R.A.; Anderson, E.; Bowers, P. EEG “Maturational Lag” Profiles: Follow-up Analyses. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 1986, 14, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmony, T.; Hinojosa, G.; Marosi, E.; Becker, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Reyes, A.; Rocha, C. Correlation between Eeg Spectral Parameters and an Educational Evaluation. Int. J. Neurosci. 1990, 54, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, K.A.; Fox, N.A.; Zeanah, C.H.; Sheridan, M.A.; Marshall, P.; Nelson, C.A. Delayed Maturation in Brain Electrical Activity Partially Explains the Association between Early Environmental Deprivation and Symptoms of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, L.J.; Thompson, B.L.; Gharib, A.; Schlueter, L.; Reilly, E.; Valdes, V.; Roberts, S.; Conroy, K.; Levitt, P.; Nelson, C.A. Association of Perceived Maternal Stress during the Perinatal Period with Electroencephalography Patterns in 2-Month-Old Infants. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartl, H.; Fezer, E.; Buettner, R. Two-Level Classification of Chronic Stress Using Machine Learning on Resting-State EEG Recordings. In Proceedings of the 25th Americas Conference on Information Systems, Cancún, Mexico, 12–16 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.M.U.; Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M.; Bhatti, A.M. Psychological Stress Measurement Using Low Cost Single Channel EEG Headset. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–10 December 2015; pp. 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- Vanhollebeke, G.; Kappen, M.; De Raedt, R.; Baeken, C.; van Mierlo, P.; Vanderhasselt, M.-A. Effects of Acute Psychosocial Stress on Source Level EEG Power and Functional Connectivity Measures. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Tang, A.; Debnath, R.; Humphreys, K.L.; Zeanah, C.H.; Nelson, C.A.; Fox, N.A. Resting Brain Activity in Early Childhood Predicts IQ at 18 Years. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2023, 63, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwood-Lowe, M.E.; Sacchet, M.D.; Gotlib, I.H. The Application of Neuroimaging to Social Inequity and Language Disparity: A Cautionary Examination. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2016, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, S.; Malan-Van Rooyen, M. Emotional Development, Effects of Parenting and Family Structure On. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Wright, J.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 438–444. ISBN 978-0-08-097087-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggles, S.; Heggeness, M. Intergenerational Coresidence in Developing Countries. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2008, 34, 253–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, D.; Horowitz, J.M.; Minkin, R.; Fry, R.; Hurst, K. The Demographics of Multigenerational Households. Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. 2022. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/social-trends/2022/03/24/the-demographics-of-multigenerational-households/ (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Sperry, D.E.; Sperry, L.L.; Miller, P.J. Reexamining the Verbal Environments of Children from Different Socioeconomic Backgrounds. Child Dev. 2019, 90, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, S.; Bergelson, E. Language Input to Infants of Different Socioeconomic Statuses: A Quantitative Meta-Analysis. Dev. Sci. 2022, 25, e13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkerson, J.; Richards, J.A.; Warren, S.F.; Montgomery, J.K.; Greenwood, C.R.; Kimbrough, O.D.; Hansen, J.H.L.; Paul, T.D. Mapping the Early Language Environment Using All-Day Recordings and Automated Analysis. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2017, 26, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, J.R.; Batson, C.D. Under One Roof: A Review of Research on Intergenerational Coresidence and Multigenerational Households in the United States. Sociol. Compass 2010, 4, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, R.R.; Leonard, J.A.; Grotzinger, H.M.; Robinson, S.T.; Takada, M.E.; Mackey, A.P.; Scherer, E.; Rowe, M.L.; West, M.R.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Neuroplasticity Associated with Changes in Conversational Turn-Taking Following a Family-Based Intervention. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2021, 49, 100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.L.; Denmark, N.; Harden, B.J.; Stapleton, L.M. The Role of Parent Education and Parenting Knowledge in Children’s Language and Literacy Skills among White, Black, and Latino Families. Infant Child Dev. 2016, 25, 198–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.E.; Acosta, S.; Davis, H.; Pollard-Durodola, S.; Saenz, L.; Soares, D.; Resendez, N.; Zhu, L. Latino Maternal Literacy Beliefs and Practices Mediating Socioeconomic Status and Maternal Education Effects in Predicting Child Receptive Vocabulary. Early Educ. Dev. 2017, 28, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskind, D.L.; Leung, C.Y.Y.; Webber, R.J.; Hundertmark, A.C.; Leffel, K.R.; Fuenmayor Rivas, I.E.; Grobman, W.A. Educating Parents about Infant Language Development: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Pediatr. 2018, 57, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, C.S.; Weiss, A.L. African American Mothers’ Views of Their Infants’ Language Development and Language-Learning Environment. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2000, 9, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Song, L.; Villacis, C.; Santiago-Bonilla, G. Parental Beliefs and Knowledge, Children’s Home Language Experiences, and School Readiness: The Dual Language Perspective. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 661208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, C.E.; Barnett, L.M.; Cook, C.J.; Cuartas, J.A.; Howard, S.J.; McCoy, D.C.; Merkley, R.; Molano, A.; Maldonado-Carreño, C.; Obradović, J.; et al. Publishing Child Development Research from around the World: An Unfair Playing Field Resulting in Most of the World’s Child Population under-Represented in Research. Infant Child Dev. 2023, 32, e2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.; Haun, D.; Kärtner, J.; Legare, C.H. The Persistent Sampling Bias in Developmental Psychology: A Call to Action. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2017, 162, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, M.I.; Kiernan, K.; McLanahan, S. Maternal education, changing family circumstances, and children’s skill development in the United States and UK. ANN. Am. Acad. Polit. Soc. Sci. 2017, 674, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, R.; Subramanian, S.V. How consistent are associations between maternal and paternal education and child growth and development outcomes across 39 low-income and middle-income countries? J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2018, 72, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Wu, Y. Family’s social economic status and child educational outcomes in China: The mediating effects of parenting practices and children’s learning attitudes. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 118, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.L.; Weisleder, A. Language Development in Context. Annu. Rev. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 2, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillas, M.; Brown, P.; Levinson, S.C. Early Language Experience in a Tseltal Mayan Village. Child Dev. 2020, 91, 1819–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristia, A. A Systematic Review Suggests Marked Differences in the Prevalence of Infant-Directed Vocalization across Groups of Populations. Dev. Sci. 2023, 26, e13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristia, A.; Dupoux, E.; Gurven, M.; Stieglitz, J. Child-Directed Speech Is Infrequent in a Forager-Farmer Population: A Time Allocation Study. Child Dev. 2019, 90, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneidman, L.A.; Goldin-Meadow, S. Language Input and Acquisition in a Mayan Village: How Important Is Directed Speech? Dev. Sci. 2012, 15, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers-Heinlein, K.; Esposito, A.G.; Winsler, A.; Marian, V.; Castro, D.C.; Luk, G. The Case for Measuring and Reporting Bilingualism in Developmental Research. Collabra Psychol. 2019, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, G.R. A Global Perspective on Bilingualism and Bilingual Education. In Georgetown University Round Table on Languages and Linguistics 1999; Georgetown University Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Surrain, S.; Luk, G. Describing Bilinguals: A Systematic Review of Labels and Descriptions Used in the Literature between 2005–2015. Biling. Lang. Cogn. 2019, 22, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KIDS COUNT Data Center. Children Who Speak a Language Other than English at Home. Available online: https://datacenter.aecf.org/data/tables/81-children-who-speak-a-language-other-than-english-at-home (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Katsiaficas, M.P.; O’Toole, A. Caitlin Dual Language Learners: A National Demographic and Policy Profile. Available online: https://www.migrationpolicy.org/research/dual-language-learners-national-demographic-and-policy-profile (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Espinosa, L.M.; LaForett, D.R.; Burchinal, M.; Winsler, A.; Tien, H.-C.; Peisner-Feinberg, E.S.; Castro, D.C. Child Care Experiences among Dual Language Learners in the United States: Analyses of the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study–Birth Cohort. AERA Open 2017, 3, 2332858417699380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, R.; Iglesias, A.; Bunta, F.; Goldstein, B.; Goldenberg, C.; Reese, L. Interlocutor Differential Effects on the Expressive Language Skills of Spanish-Speaking English Learners. Int. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2016, 18, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, T.S.; Paradis, J. Home Language Environment and Children’s Second Language Acquisition: The Special Status of Input from Older Siblings. J. Child Lang. 2020, 47, 982–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdon, S.; McLeod, S.; Winsler, A. Language Maintenance and Loss in a Population Study of Young Australian Children. Early Child. Res. Q. 2014, 29, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, V.; Rothman, J.; Bialystok, E.; Pliatsikas, C. Duration and Extent of Bilingual Experience Modulate Neurocognitive Outcomes. NeuroImage 2020, 204, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Abutalebi, J.; Zou, L.; Yan, X.; Liu, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, R.; Guo, T.; Ding, G. Bilingualism Alters Brain Functional Connectivity between “Control” Regions and “Language” Regions: Evidence from Bimodal Bilinguals. Neuropsychologia 2015, 71, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliatsikas, C.; DeLuca, V.; Voits, T. The Many Shades of Bilingualism: Language Experiences Modulate Adaptations in Brain Structure. Lang. Learn. 2020, 70, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, T.; Berroir, P.; Joanette, Y.; Ansaldo, A.I. Alerting, Orienting, and Executive Control: The Effect of Bilingualism and Age on the Subcomponents of Attention. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 483266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berken, J.A.; Chai, X.; Chen, J.-K.; Gracco, V.L.; Klein, D. Effects of Early and Late Bilingualism on Resting-State Functional Connectivity. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, C.L.; Luk, G.; Craik, F.I.M.; Bialystok, E. Brain Network Activity in Monolingual and Bilingual Older Adults. Neuropsychologia 2015, 66, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullifer, J.W.; Chai, X.J.; Whitford, V.; Pivneva, I.; Baum, S.; Klein, D.; Titone, D. Bilingual Experience and Resting-State Brain Connectivity: Impacts of L2 Age of Acquisition and Social Diversity of Language Use on Control Networks. Neuropsychologia 2018, 117, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, L.; Ding, G.; Wang, R.; Li, P. Effects of Language Proficiency on Cognitive Control: Evidence from Resting-State Functional Connectivity. Neuropsychologia 2019, 129, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, B.L.; Stocco, A.; Liu, A.S.; Prat, C.S. Effects of Bilingual Language Experience on Basal Ganglia Computations: A Dynamic Causal Modeling Test of the Conditional Routing Model. Brain Lang. 2019, 197, 104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialystok, E.; Craik, F.I.M.; Luk, G. Bilingualism: Consequences for Mind and Brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berken, J.A.; Gracco, V.L.; Chen, J.-K.; Watkins, K.E.; Baum, S.; Callahan, M.; Klein, D. Neural Activation in Speech Production and Reading Aloud in Native and Non-Native Languages. NeuroImage 2015, 112, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasinska, K.K.; Petitto, L.A. How Age of Bilingual Exposure Can Change the Neural Systems for Language in the Developing Brain: A Functional near Infrared Spectroscopy Investigation of Syntactic Processing in Monolingual and Bilingual Children. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauharatanahirun, N.; Maciejewski, D.; Holmes, C.; Deater-Deckard, K.; Kim-Spoon, J.; King-Casas, B. Neural Correlates of Risk Processing among Adolescents: Influences of Parental Monitoring and Household Chaos. Child Dev. 2018, 89, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.L.; Ahmed, S.P.; Blakemore, S.-J. Navigating the Social Environment in Adolescence: The Role of Social Brain Development. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwinski, S.; Donovan, S.M.; Fiese, B.; Bost, K. The Impact of Household Chaos and Dietary Intake on Executive Function in Young Children. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razza, R.A.; Martin, A.; Brooks-Gunn, J. The Implications of Early Attentional Regulation for School Success among Low-Income Children. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2012, 33, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, C.; Raver, C.C. Poverty, Stress, and Brain Development: New Directions for Prevention and Intervention. Acad. Pediatr. 2016, 16, S30–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecheile, B.M.; Spinrad, T.L.; Xu, X.; Lopez, J.; Eisenberg, N. Longitudinal Relations among Household Chaos, SES, and Effortful Control in the Prediction of Language Skills in Early Childhood. Dev. Psychol. 2020, 56, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernon-Feagans, L.; Willoughby, M.; Garrett-Peters, P. Predictors of Behavioral Regulation in Kindergarten: Household Chaos, Parenting, and Early Executive Functions. Dev. Psychol. 2016, 52, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, R.L.; Lynch, A.D.; Kull, M. Early Exposure to Environmental Chaos and Children’s Physical and Mental Health. Early Child. Res. Q. 2015, 32, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deater-Deckard, K.; Sewell, M.D.; Petrill, S.A.; Thompson, L.A. Maternal Working Memory and Reactive Negativity in Parenting. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Goldblatt, R.; Qin, W.; Liu, F.; Chu, C.; Luo, Q.; Ing, A.; Guo, L.; et al. Global Urbanicity Is Associated with Brain and Behaviour in Young People. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2022, 6, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G.W.; Gonnella, C.; Marcynyszyn, L.A.; Gentile, L.; Salpekar, N. The Role of Chaos in Poverty and Children’s Socioemotional Adjustment. Psychol. Sci. 2005, 16, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essen, J.; Fogelman, K.; Head, J. Children’s Housing and Their Health and Physical Development. Child Care Health Dev. 1978, 4, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.; Maxwell, L.E.; Hart, B. Parental Language and Verbal Responsiveness to Children in Crowded Homes. Dev. Psychol. 1999, 35, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.W.; Saegert, S.; Harris, R. Residential Density and Psychological Health among Children in Low-Income Families. Environ. Behav. 2001, 33, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havron, N.; Lovcevic, I.; Kee, M.Z.L.; Chen, H.; Chong, Y.S.; Daniel, M.; Broekman, B.F.P.; Tsuji, S. The Effect of Older Sibling, Postnatal Maternal Stress, and Household Factors on Language Development in Two- to Four-Year-Old Children. Dev. Psychol. 2022, 58, 2096–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatte, M.; Bergstroem, K.; Lachmann, T. Does Noise Affect Learning? A Short Review on Noise Effects on Cognitive Performance in Children. Front. Psychol. 2013, 4, 55965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kujala, T.; Brattico, E. Detrimental Noise Effects on Brain’s Speech Functions. Biol. Psychol. 2009, 81, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, L.E.; Evans, G.W. The effects of noise on pre-school children’s pre-reading skills. J. Environ. Psychol. 2000, 20, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foraster, M.; Esnaola, M.; López-Vicente, M.; Rivas, I.; Álvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Persavento, C.; Sebastian-Galles, N.; Pujol, J.; Dadvand, P.; Sunyer, J. Exposure to Road Traffic Noise and Cognitive Development in Schoolchildren in Barcelona, Spain: A Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1004001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werchan, D.M.; Brandes-Aitken, A.; Brito, N.H. Signal in the Noise: Dimensions of Predictability in the Home Auditory Environment Are Associated with Neurobehavioral Measures of Early Infant Sustained Attention. Dev. Psychobiol. 2022, 64, e22325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, K.R.; Merz, E.C.; He, X.; Noble, K.G. Environmental Noise, Brain Structure, and Language Development in Children. Brain Lang. 2022, 229, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Vilavella, G.; Pujol, J.; Blanco-Hinojo, L.; Deus, J.; Rivas, I.; Persavento, C.; Sunyer, J.; Foraster, M. The Effects of Exposure to Road Traffic Noise at School on Central Auditory Pathway Functional Connectivity. Environ. Res. 2023, 226, 115574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Krantz, D.S.; Evans, G.W.; Stokols, D.; Kelly, S. Aircraft Noise and Children: Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Evidence on Adaptation to Noise and the Effectiveness of Noise Abatement. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1981, 40, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.C.; Pendergast, L.L.; Schaefer, B.A.; Rasheed, M.; Svensen, E.; Scharf, R.; Shrestha, R.; Maphula, A.; Roshan, R.; Rasmussen, Z.; et al. Measuring Home Environments across Cultures: Invariance of the HOME Scale across Eight International Sites from the MAL-ED Study. J. Sch. Psychol. 2017, 64, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcini, L.M.; Arredondo, M.M.; Berry, O.; Church, J.A.; Fryberg, S.; Thomason, M.E.; McLaughlin, K.A. Increasing Diversity in Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience: A Roadmap for Increasing Representation in Pediatric Neuroimaging Research. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2022, 58, 101167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polemiti, E.; Hese, S.; Schepanski, K.; Yuan, J.; Schumann, G.; environMENTAL Consortium. How Does the Macroenvironment Influence Brain and Behaviour—A Review of Current Status and Future Perspectives. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, T.; Baker, E.; Stavropoulos, K. Systemic Racism in EEG Research: Considerations and Potential Solutions. Affect. Sci. 2022, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricard, J.A.; Parker, T.C.; Dhamala, E.; Kwasa, J.; Allsop, A.; Holmes, A.J. Confronting Racially Exclusionary Practices in the Acquisition and Analyses of Neuroimaging Data. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, C.C.; Webster, C.T.; Gloe, L.M.; Moser, J.S. Hair Me out: Highlighting Systematic Exclusion in Psychophysiological Methods and Recommendations to Increase Inclusion. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1058953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatzke-Kopp, L.M. Diversity and Representation: Key Issues for Psychophysiological Science. Psychophysiology 2016, 53, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.O.; Bareket-Shavit, C.; Dollins, F.A.; Goldie, P.D.; Mortenson, E. Racial Inequality in Psychological Research: Trends of the Past and Recommendations for the Future. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2020, 15, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulvio, J.M.; Akinnola, I.; Postle, B.R. Gender (Im)Balance in Citation Practices in Cognitive Neuroscience. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2021, 33, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.M.; Pritschet, L.; Jacobs, E.G. The Scientific Body of Knowledge—Whose Body Does It Serve? A Spotlight on Oral Contraceptives and Women’s Health Factors in Neuroimaging. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 60, 100874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfarb, M.G.; Brown, D.R. Diversifying Participation: The Rarity of Reporting Racial Demographics in Neuroimaging Research. NeuroImage 2022, 254, 119122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.A.; Kalbaugh, C.A. Challenging Assumptions About Minority Participation in US Clinical Research. Am. J. Public Health 2011, 101, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, D.; Kington, R.; Madans, J.; Wye, G.V.; Christ-Schmidt, H.; Pratt, L.A.; Brawley, O.W.; Gross, C.P.; Emanuel, E. Are Racial and Ethnic Minorities Less Willing to Participate in Health Research? PLoS Med. 2005, 3, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.K.; Etter, J.A.; Kwasa, J.A. Addressing Racial and Phenotypic Bias in Human Neuroscience Methods. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long Shadows: The Black-White Gap in Multigenerational Poverty. Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/articles/long-shadows-the-black-white-gap-in-multigenerational-poverty/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Heard-Garris, N.; Boyd, R.; Kan, K.; Perez-Cardona, L.; Heard, N.J.; Johnson, T.J. Structuring Poverty: How Racism Shapes Child Poverty and Child and Adolescent Health. Acad. Pediatr. 2021, 21, S108–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.; Taylor, E.K.; Abdurokhmonova, G.; Romeo, R.R. Developing Best Practices for Inclusion in Pediatric fNIRS Research: Equity for Participants with Afro-Textured Hair; Flux: Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience Society: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.; Rollock, D.; Foti, D. Conducting Electroencephalography with Black Individuals: Barriers, Recommendations, and Impact on Generalizability. Policy Insights Behav. Brain Sci. 2023, 10, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, D.M.; Goff, P.A. Clearing the Air: The Effect of Experimenter Race on Target’s Test Performance and Subjective Experience. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2005, 44, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorson, K.R.; Mendes, W.B.; West, T.V. Controlling the Uncontrolled: Are There Incidental Experimenter Effects on Physiologic Responding? Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, D.E.; DeFalco, A.; Perkins, E.R.; Carbajal, I.; Kwasa, J.; Goodman, F.R.; Jackson, F.; Richardson, L.N.S.; Woodley, N.; Neuberger, L.; et al. Whose Signals Are Being Amplified? Toward a More Equitable Clinical Psychophysiology. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2024, 12, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schneider, J.M.; Behboudi, M.H.; Maguire, M.J. The Necessity of Taking Culture and Context into Account When Studying the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Brain Development. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14040392
Schneider JM, Behboudi MH, Maguire MJ. The Necessity of Taking Culture and Context into Account When Studying the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Brain Development. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(4):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14040392
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchneider, Julie M., Mohammad Hossein Behboudi, and Mandy J. Maguire. 2024. "The Necessity of Taking Culture and Context into Account When Studying the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Brain Development" Brain Sciences 14, no. 4: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14040392
APA StyleSchneider, J. M., Behboudi, M. H., & Maguire, M. J. (2024). The Necessity of Taking Culture and Context into Account When Studying the Relationship between Socioeconomic Status and Brain Development. Brain Sciences, 14(4), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14040392