Up-to-Date Applications of Microarrays and Their Way to Commercialization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. History and Scientific Base


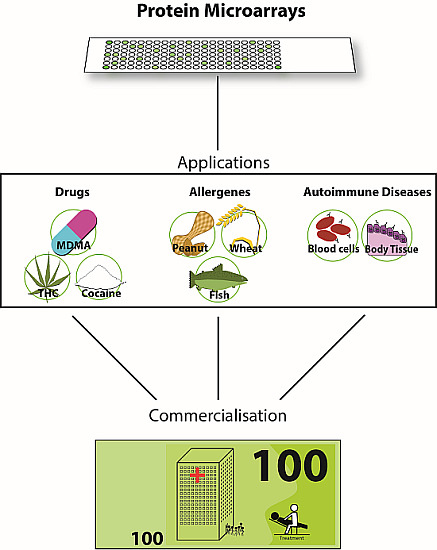
3. Applications
3.1. Application of PMAs for Small Molecules
Drug Abuse
3.2. Applications of PMAs—Allergen Arrays
3.2.1. MeDALL versus ImmunoCAP ISAC
3.2.2. Lateral Flow Assays (LFA)
3.2.3. Bead based Allergen Test
3.3. Applications of PMAs—Autoimmune Diseases
3.4. Issues of Clinical Trials
4. Conclusions
- ELISA is a well-established method in a widespread format, but mostly lacks the opportunity for multiplexing and needs a high reagent volume.
- LFA is an easy-to-perform and fast method, but is often characterized by a high detection limit and an unpredictable performance.
- Protein Microarrays have the advantage of low sample consumption, the possibility of multiplexing and are normally performed on conventional glass slides. But in most cases they are expensive in the production, especially because of the technical equipment needed for dispensing and handling of very low volumes.
- The Bead Based System is the most flexible tool of the presented applications. They are applicable in personalized medicine and have a longer storage time than PMAs.
| Application | Sample Volume | Processing Time | Sensitivity | Multiplexing Grade | Field Applicability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFA | low | <1 h | low | low | yes | [58,59] |
| ELISA | high | <5 h | middle | low | no | [31,42] |
| Beads | middle | <3 h | middle | middle | no | [60,61] |
| PMAs | low | <5 h | high | high | no | [16,27,31] |
5. Outlook
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Romanov, V.; Davidoff, S.N.; Miles, A.R.; Grainger, D.W.; Gale, B.K.; Brooks, B.D. A critical comparison of protein microarray fabrication technologies. Analyst 2014, 139, 1303–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrade, L.; Garcia, A.E.; Camarero, J.A. Protein microarrays: Novel developments and applications. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1480–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Hingamp, P.; Quackenbush, J.; Sherlock, G.; Spellman, P.; Stoeckert, C.; Aach, J.; Ansorge, W.; Ball, C.A.; Causton, H.C.; et al. Small molecule microarrays: The first decade and beyond. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5664–5670. [Google Scholar]
- Brazma, A. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)-toward standards for microarray data. Nat. Genet. 2001, 29, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owzar, K.; Barry, W.T.; Jung, S.H. Statistical considerations for analysis of microarray experiments. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2011, 4, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoheisel, J.D.; Alhamdani, M.S.S.; Schröder, C. Affinity-based microarrays for proteomic analysis of cancer tissues. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna Coronell, J.A.; Syed, P.; Sergelen, K.; Gyurján, I.; Weinhäusel, A. The current status of cancer biomarker research using tumour-associated antigens for minimal invasive and early cancer diagnostics. J. Proteomics 2012, 76, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, J.G.; Wheeler, A.W. Detection of auto-immune antibody and tissue antigens by the “microspot” technique. J. Clin. Pathol. 1963, 16, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berson, S.A.; Yalow, R.S.; Bauman, A.; Rothschild, M.A.; Newerly, K. Insulin-I131 metabolism in human subjects: Demonstration of insulin binding globulin in the circulation of insulin treated subjects. J. Clin. Invest. 1956, 35, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wide, L.; Bennich, H.; Johansson, S.G. Diagnosis of allergy by an in vitro test for allergen antibodies. Lancet 1967, 2, 1105–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, L.E.; Hales, C.N. Labelled antibodies and immunological assay systems. Nature 1968, 219, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, G.; Milstein, C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 1975, 256, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekins, R.P. Multi-analyte immunoassay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1989, 7, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekins, R.; Chu, F.; Biggart, E. Multispot, multianalyte, immunoassay. Ann. Biol. Clin. (Paris) 1990, 48, 655–666. [Google Scholar]
- Ekins, R.P.; Chu, F.W. Multianalyte microspot immunoassay—Microanalytical “compact disk” of the future. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cretich, M.; Damin, F.; Chiari, M. Protein microarray technology: How far off is routine diagnostics? Analyst 2014, 139, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasilva, N.; Diez, P.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, M.; Matarraz, S.; Sayagues, J.M.; Orfao, A.; Fuentes, M. Protein microarrays: Technological aspects, applications and intellectual property. Recent Pat. Biotechnol. 2013, 7, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoevesandt, O.; Taussig, M.J.; He, M. Protein microarrays: High-throughput tools for proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2009, 6, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelinck, D.; Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Verweij, C.; Dillon, D.; Feng, Z.; Costa, J.; Haab, B.B. Optimized normalization for antibody microarrays and application to serum-protein profiling. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2005, 4, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Carbayo, M.; Socci, N.D.; Lozano, J.J.; Haab, B.B.; Cordon-Cardo, C. Profiling bladder cancer using targeted antibody arrays. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Snyder, M. Protein chip technology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, J.S.; Michaud, G.A.; Salcius, M.; Schweitzer, B.; Predki, P.F. Functional protein microarrays: Just how functional are they? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2005, 16, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, H.R.; Knoll, J.; van den Doel, L.R.; van Dedem, G.W.; Daran-Lapujade, P.A.; van Vliet, L.J.; Moerman, R.; Pronk, J.T.; Young, I.T. Nanoarrays: A method for performing enzymatic assays. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4112–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultschig, C.; Kreutzberger, J.; Seitz, H.; Konthur, Z.; Büssow, K.; Lehrach, H. Recent advances of protein microarrays. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutandy, F.X.; Qian, J.; Chen, C.S.; Zhu, H. Overview of protein microarrays. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellhausen, R.; Seitz, H. Facing current quantification challenges in Protein Microarrays. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 831347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, M.; Niessner, R. Automated analytical microarrays: A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1521–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hetlani, E. Forensic drug analysis and microfluidics. Electrophoresis 2012, 34, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, G.B. The effect of anabolic steroids on lean body mass: The dose response curve. Metabolism 1985, 34, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.D. Androgen abuse by athletes. Endocr. Rev. 1988, 9, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Cheng, J. Protein chips for high-throughput doping screening in athletes. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2006, 3, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Yang, W.; Xing, W.; Su, Y.; Cheng, J. Parallel detection and quantification using nine immunoassays in a protein microarray for drug from serum samples. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, D.; Haeberle, S.; Roth, G.; von Stetten, F.; Zengerle, R. Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip platforms: Requirements, characteristics and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1153–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, L.; Akash, M.S.H.; Rehman, K.; Liu, Z.; Shi, W.; Chen, S. Development and comparison of two competitive ELISAs for estimation of cotinine in human exposed to environmental tobacco smoke. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertol, E.; Vaiano, F.; Furlanetto, S.; Mari, F. Cross-reactivities and structure-reactivity relationships of six benzodiazepines to EMIT(®) immunoassay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 84, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Wu, M.; Yang, W.; Yuan, G.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Du, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; et al. Development of miniaturized competitive immunoassays on a protein chip as a screening tool for drugs. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.C.; Duverneuil, C.; Zouaoui, K.; Abe, E.; Charlier, P.; de la Grandmaison, G.L.; Grassin-Delyle, S. Evaluation of the first immunoassay for the semi-quantitative measurement of meprobamate in human whole blood or plasma using biochip array technology. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranova, N.; Byzova, N.; Zaiko, V.; Starovoitova, T.; Vengerov, Y.; Zherdev, A.; Dzantiev, B. Integration of lateral flow and microarray technologies for multiplex immunoassay: Application to the determination of drugs of abuse. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubou, H.; Namera, A.; Arima, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Torikoshi, A.; Moriya, F.; Nagao, M. Detection of abused drugs in human blood by using the on-site drug-screening device Oratect® III. Legal Med. 2014, 16, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burks, R.M.; Pacquette, S.E.; Guericke, M.A.; Wilson, M.V.; Symonsbergen, D.J.; Lucas, K.A.; Holmes, A.E. DETECHIP®: A Sensor for Drugs of Abuse*. J. Forensic Sci. 2010, 55, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batres, G.; Jones, T.; Johnke, H.; Wilson, M.; Holmes, A.E.; Sikich, S. Reactive arrays of colorimetric sensors for metabolite and steroid identification. J. Sens. Technol. 2014, 4, 43398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tort, N.; Salvador, J.P.; Marco, M.P. Multiplexed immunoassay to detect anabolic androgenic steroids in human serum. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwanegg, C.; Laffer, S.; Hiller, R.; Mueller, M.W.; Kraft, D.; Spitzauer, S.; Valenta, R. Microarrayed recombinant allergens for diagnosis of allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Product Characteristics ImmunoCAP ISAC sIgE112; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.: Uppsala, Sweden, 2012.
- Gadisseur, R.; Chapelle, J.; Cavalier, E. Performance of a new version of allergen microarray: preliminary results. Allergy 2012, 67, 533. [Google Scholar]
- Melioli, G.; Bonifazi, F.; Bonini, S.; Maggi, E.; Mussap, M.; Passalacqua, G.; Rossi, E.R.; Vacca, A.; Canonica, G.W. The ImmunoCAP ISAC molecular allergology approach in adult multi-sensitized Italian patients with respiratory symptoms. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.L.; Blázquez, A.B.; Garcia, B.E. Microarray of allergenic component-based diagnosis in food allergy. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 11, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, B.E.; Sandhu, N.; Tronstrøm, J.; Lydolph, M.; Trier, N.H.; Houen, G. Species cross-reactivity of rheumatoid factors and implications for immunoassays. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2015, 75, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.F.M.; van der Molen, R.G.; Bossuyt, X.; Damoiseaux, J. Antigen excess in modern immunoassays: To anticipate on the unexpected. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, A. When lab tests lie … heterophile antibodies. Aust. Fam. Phys. 2014, 43, 391–393. [Google Scholar]
- Tate, J.; Ward, G. Interferences in immunoassay. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2004, 25, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.A. Identifying and reducing potentially wrong immunoassay results even when plausible and “not-unreasonable”. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2014, 66, 241–294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melioli, G.; Compalati, E.; Bonini, S.; Canonica, G.W. The added value of allergen microarray technique to the management of poly-sensitized allergic patients. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigh-Conrad, K.A.; Conrad, D.F.; Preuss, D. A protein allergen microarray detects specific IgE to pollen surface, cytoplasmic, and commercial allergen extracts. PLoS One 2010, 5, e10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incorvaia, C.; Mauro, M.; Ridolo, E.; Makrì, E.; Montagni, M.; Ciprandi, G. A Pitfall to avoid when using an allergen microarray: The incidental detection of IgE to unexpected allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.; Bock, S.A. Skin testing and food challenges in allergy and immunology practice. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 1999, 17, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupinek, C.; Wollmann, E.; Baar, A.; Banerjee, S.; Breiteneder, H.; Broecker, B.M.; Bublin, M.; Curin, M.; Flicker, S.; Garmatiuk, T. Advances in allergen-microarray technology for diagnosis and monitoring of allergy: The MeDALL allergen-chip. Methods 2014, 66, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnasamy, T.; Segerink, L.I.; Nystrand, M.; Gantelius, J.; Svahn, H.A. A lateral flow paper microarray for rapid allergy point of care diagnostics. Analyst 2014, 139, 2348–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnasamy, T.; Segerink, L.I.; Nystrand, M.; Gantelius, J.; Andersson Svahn, H. Point-of-care vertical flow allergen microarray assay: Proof of concept. Clin. Chem. 2014, 60, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomponi, D.; Bernardi, M.L.; Liso, M.; Palazzo, P.; Tuppo, L.; Rafaiani, C.; Santoro, M.; Labrada, A.; Ciardiello, M.A.; Mari, A.; et al. Allergen micro-bead array for IgE detection: A feasibility study using allergenic molecules tested on a flexible multiplex flow cytometric immunoassay. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, E.; Pomponi, D.; Giani, M. Allergen microbead arrays: The future of allergy diagnostics? Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multiplexed Bead-Based in Vitro Pediatric Allergy Test; Food Safety Research Information Office: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2014.
- Charpin, C.; Arnoux, F.; Martin, M.; Toussirot, E.; Lambert, N.; Balandraud, N.; Wendling, D.; Diot, E.; Roudier, J.; Auger, I. New autoantibodies in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.E.; Sokolove, J.; Hipp, B.G.; Lindstrom, T.M.; Elder, J.T.; Reveille, J.D.; Eberl, H.; Klause, U.; Robinson, W.H. Novel multiplex technology for diagnostic characterization of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peene, I.; Meheus, L.; Veys, E.M.; De Keyser, F. Detection and identification of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in a large and consecutive cohort of serum samples referred for ANA testing. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, M. Development of anti-TNF therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueber, W.; Tomooka, B.H.; Batliwalla, F.; Li, W.; Monach, P.A.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Lampa, J.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Blood autoantibody and cytokine profiles predict response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R76–R76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudon, A.L.; Vergnaud, P.; Valverde, C.c.; Mayr, A.; Klause, U.; Garnero, P. New automated multiplex assay for bone turnover markers in osteoporosis. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Liu, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Y.; Han, Y.; Zeng, H.; Huang, W.; Li, F.; Chen, P. Novel autoimmune hepatitis-specific autoantigens identified using protein microarray technology. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontela, P.S.; Pant Pai, N.; Schiller, I.; Dendukuri, N.; Ramsay, A.; Pai, M. Quality and reporting of diagnostic accuracy studies in TB, HIV and malaria: Evaluation using QUADAS and STARD standards. PLoS One 2009, 4, e7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Kleijnen, J. The development of QUADAS: A tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2003, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiting, P.; Weswood, M.; Rutjes, A.; Reitsma, J.; Bossuyt, P.; Kleijnen, J. Evaluation of QUADAS, a tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2006, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczynski, N.L. Quality of reporting of diagnostic accuracy studies: No change since STARD statement publication—Before-and-after study. Radiology 2008, 248, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, D. Emerging Applications of Biochips (Technical Insights); Frost and Sullivan: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rangesa, M. Top Technologies in Health and Wellness; Frost and Sullivan: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schumacher, S.; Muekusch, S.; Seitz, H. Up-to-Date Applications of Microarrays and Their Way to Commercialization. Microarrays 2015, 4, 196-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays4020196
Schumacher S, Muekusch S, Seitz H. Up-to-Date Applications of Microarrays and Their Way to Commercialization. Microarrays. 2015; 4(2):196-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays4020196
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchumacher, Sarah, Sandra Muekusch, and Harald Seitz. 2015. "Up-to-Date Applications of Microarrays and Their Way to Commercialization" Microarrays 4, no. 2: 196-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays4020196
APA StyleSchumacher, S., Muekusch, S., & Seitz, H. (2015). Up-to-Date Applications of Microarrays and Their Way to Commercialization. Microarrays, 4(2), 196-213. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays4020196