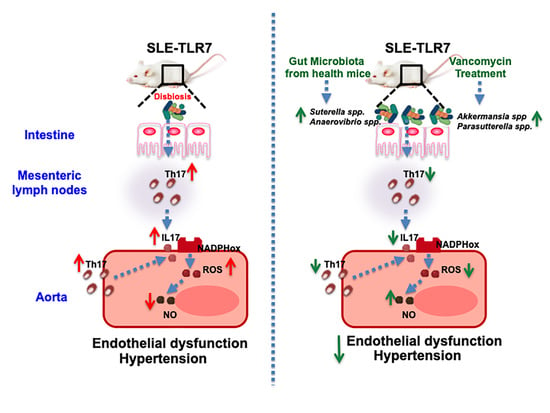
Gut Microbiota Has a Crucial Role in the Development of Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction in Toll-like Receptor 7-Driven Lupus Autoimmunity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Experimental Groups
2.2. Blood Pressure, Morphology, Organ Weight Indices, and Renal Injury
2.3. Plasma and Urine Parameters
2.4. Vascular Reactivity Studies
2.5. NADPH Oxidase Activity and eNOS Expression
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, Bioinformatics
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antibiotic Treatment Prevented the Raise of Blood Pressure, Renal Injury, and Disease Activity in TLR7-Dependent SLE
3.2. Antibiotic Treatment Changed Colonic Microbiota Composition
3.3. Antibiotic Treatments Attenuates T Cells Imbalance
3.4. The Antibiotics Prevented Endothelial Dysfunction, Vascular Oxidative Stress and Th17 Vascular Infiltration
3.5. Bacterial Communities from IMQ-Mice Were Transferable and Induced High Blood Pressure and Endothelial Dysfunction in Control Animals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frostegård, J. Systemic lupus erythematosus and cardiovascular disease. Lupus 2008, 17, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.M.; Buhr, K.A.; Goldberg, J.W.; Bell, C.L.; Visekruna, M.; Nekkanti, S.; Greenlee, R.T. Mortality and Cardiovascular Burden of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in a US Population-based Cohort. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Herz, A.; Ensworth, S.; Shojania, K.; Esdaile, J.M. Cardiovascular risk factor screening in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, V.L.; Ryan, M.J. Autoimmune Disease-Associated Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2019, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, E.B.; Ryan, M.J. Understanding mechanisms of hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 11, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Q.; Szodoray, P.; Zeher, M. Toll-Like Receptor Pathways in Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.-W.; Tang, W.; Zuo, J.-P. Toll-like receptors: Potential targets for lupus treatment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidenbusch, M.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Anders, H.-J. The innate immune system in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokogawa, M.; Takaishi, M.; Nakajima, K.; Kamijima, R.; Fujimoto, C.; Kataoka, S.; Terada, Y.; Sano, S. Epicutaneous Application of Toll-like Receptor 7 Agonists Leads to Systemic Autoimmunity in Wild-Type Mice: A New Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celhar, T.; Fairhurst, A.-M. Modelling clinical systemic lupus erythematosus: Similarities, differences and success stories. Rheumatology 2017, 56 (Suppl. 1), i88–i99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crow, M.K. Type I Interferon in the Pathogenesis of Lupus. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5459–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, F.J.; Meeker, T.; Chan, J.H.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R.L. Treatment of lupus-prone mice with a dual inhibitor of TLR7 and TLR9 leads to reduction of autoantibody production and amelioration of disease symptoms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; de la Visitación, N.; Toral, M.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; O’Valle, F.; Jimenez, R.; Duarte, J.; Romero, M. Toll-like receptor 7-driven lupus autoimmunity induces hypertension and vascular alterations in mice. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 1322–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, A.; Milani, C.; Lopez-Suarez, P.; Cuervo, A.; Arboleya, S.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; González, S.; Suarez-Diaz, A.M.; Gueimonde, M.; et al. Intestinal Dysbiosis Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. MBio 2014, 5, e01548-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- López, P.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A.; Suárez, A. Intestinal dysbiosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: Cause or consequence? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2016, 28, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.M.; Edwards, M.R.; Mu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Vieson, M.D.; Reilly, C.; Ahmed, S.A.; Bankole, A.A. Gut Microbiota in Human Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and a Mouse Model of Lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02288-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Liao, X.; Sparks, J.B.; Luo, X.M. Dynamics of Gut Microbiota in Autoimmune Lupus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7551–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Tavella, V.J.; Kirby, J.L.; Cecere, T.E.; Chung, M.; Lee, J.; Li, S.; Ahmed, S.A.; Eden, K.; Allen, I.C.; et al. Antibiotics ameliorate lupus-like symptoms in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liao, X.; Lin, K.; Liu, H.; Edwards, M.R.; Ahmed, S.A.; Yuan, R.; Li, L.; Cecere, T.E.; et al. Control of lupus nephritis by changes of gut microbiota. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz-Agranov, N.; Zandman-Goddard, G. The microbiome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.M.; Hiltensperger, M.; Kumar, V.; Zegarra-Ruiz, D.; Dehner, C.; Khan, N.; Costa, F.R.C.; Tiniakou, E.; Greiling, T.; Ruff, W.; et al. Translocation of a gut pathobiont drives autoimmunity in mice and humans. Science 2018, 359, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zegarra-Ruiz, D.F.; El Beidaq, A.; Iñiguez, A.J.; Lubrano Di Ricco, M.; Manfredo Vieira, S.; Ruff, W.E.; Mubiru, D.; Fine, R.L.; Sterpka, J.; Greiling, T.M.; et al. A Diet-Sensitive Commensal Lactobacillus Strain Mediates TLR7-Dependent Systemic Autoimmunity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 113–127.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, J.; Tian, G.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Wei, Q.; Niu, H. Gut microbiota promote the inflammatory response in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Visitación, N.; Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, M.; Moleón, J.; González-Correa, C.; Martín-Morales, N.; O’Valle, F.; Jiménez, R.; et al. Gut microbiota contributes to the development of hypertension in a genetic mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3708–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Visitación, N.; Robles-Vera, I.; Moleón-Moya, J.; Sánchez, M.; Jiménez, R.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; González-Correa, C.; Olivares, M.; Toral, M.; Romero, M.; et al. Probiotics Prevent Hypertension in a Murine Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Induced by Toll-Like Receptor 7 Activation. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbach, S.H.; Schönfelder, T.; Brandão, I.; Wilms, E.; Hörmann, N.; Jäckel, S.; Schüler, R.; Finger, S.; Knorr, M.; Lagrange, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota Promote Angiotensin II–Induced Arterial Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2016, 5, e003698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ascher, S.; Reinhardt, C. The gut microbiota: An emerging risk factor for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 48, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edwards, J.; Roy, S.; Tomcho, J.C.; Schreckenberger, Z.; Chakraborty, S.; Bearss, N.R.; Saha, P.; McCarthy, C.G.; Vijay-Kumar, M.; Joe, B.; et al. Microbiota are critical for vascular physiology: Germ-free status weakens contractility and induces sex-specific vascular remodeling in mice. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 125-126, 106633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Jama, H.A.; Tsyganov, K.; Gill, P.A.; Rhys-Jones, D.; Muralitharan, R.R.; Muir, J.; Holmes, A.; Mackay, C.R. Guidelines for Transparency on Gut Microbiome Studies in Essential and Experimental Hypertension. Hypertension 2019, 74, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. NC3Rs Reporting Guidelines Working Group. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): New requirements for publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souyris, M.; Mejia, J.E.; Chaumeil, J.; Guéry, J.-C. Female predisposition to TLR7-driven autoimmunity: Gene dosage and the escape from X chromosome inactivation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 41, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, M.; Vera, I.R.; de la Visitación, N.; Romero, M.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Yang, T.; Jiménez, R.; Algieri, F.; et al. Role of the immune system in vascular function and blood pressure control induced by faecal microbiota transplantation in rats. Acta Physiol. 2019, 227, e13285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Jimenez, R.; Romero, M.; Sánchez, M.; Zarzuelo, M.J.; Gómez-Morales, M.; O’Valle, F.; López-Farré, A.J.; Algieri, F.; Galvez, J.; et al. Chronic Hydroxychloroquine Improves Endothelial Dysfunction and Protects Kidney in a Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Hypertension 2014, 64, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toral, M.; Robles-Vera, I.; Romero, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; O’Valle, F.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Gálvez, J.; Duarte, J.; Jiménez, R. Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716: A novel alternative for the prevention of vascular disorders in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10005–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toral, M.; Romero, M.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Jiménez, R.; Robles-Vera, I.; Algieri, F.; Chueca-Porcuna, N.; Sánchez, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Olivares, M.; et al. Lactobacillus fermentum Improves Tacrolimus-Induced Hypertension by Restoring Vascular Redox State and Improving eNOS Coupling. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, M.; Toral, M.; Vera, I.R.; Sánchez, M.; Jimenez, R.; O’Valle, F.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Pérez-Vizcaino, F.; Galvez, J.; Duarte, J. Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator Activator Receptor β/δ Improves Endothelial Dysfunction and Protects Kidney in Murine Lupus. Hypertension 2017, 69, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 108 (Suppl. 1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.-W.; Li, D.; Tam, N.F.-Y.; Jiang, X.-T.; Zhang, H.; Sheng, H.-F.; Qin, J.; Liu, X.; Zou, F. BIPES, a cost-effective high-throughput method for assessing microbial diversity. ISME J. 2010, 5, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhan, Q.; Lai, W.; Zeng, Q.; Ren, H.; Xu, D. Moderate-Intensity Exercise Affects Gut Microbiome Composition and Influences Cardiac Function in Myocardial Infarction Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Flyvbjerg, H. Error filtering, pair assembly and error correction for next-generation sequencing reads. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, D.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Discrepant gut microbiota markers for the classification of obesity-related metabolic abnormalities. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, K.; Murphy, D. Application of ggplot2 to Pharmacometric Graphics. CPT: Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Edwards, M.R.; Swartwout, B.K.; Puig, X.C.; Mao, J.; Zhu, J.; Grieco, J.; Cecere, T.E.; Prakash, M.; Reilly, C.M.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Bacterial DNA Suppress Autoimmunity by Stimulating Regulatory B Cells in a Murine Model of Lupus. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 593353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaka, S.; Ussar, S.; Clish, C.; Devkota, S.; Dreyfuss, J.; Sakaguchi, M.; Soto, M.; Konishi, M.; Softic, S.; Altindis, E.; et al. Antibiotic effects on gut microbiota and metabolism are host dependent. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4430–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, V.E.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; Richey, J.J.; Zigler, M.C.; Cuevas, L.M.; Gonzalez, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Battson, M.L.; Smithson, A.T.; Gilley, A.D.; et al. Suppression of the gut microbiome ameliorates age-related arterial dysfunction and oxidative stress in mice. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2361–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; de la Visitación, N.; Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Romero, M.; Yang, T.; Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Jiménez, R.; Ruiz-Cabello, J.; et al. Probiotics Prevent Dysbiosis and the Rise in Blood Pressure in Genetic Hypertension: Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, e1900616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, R.; Mohamed, S.F.; Bassyouni, I.H.; Raouf, A.A. Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cytokine imbalance in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients: Correlation with disease activity. Cytokine 2015, 72, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, O.; Salaman, M.R.; Seifert, M.H.; Isenberg, D. B lymphocyte activation in systemic lupus erythematosus: Spontaneous production of IgG antibodies to DNA and environmental antigens in cultures of blood mononuclear cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1988, 73, 430–435. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, C.E.; Shaifta, Y.; Snetkov, V.V.; Francois, A.A.; Ward, J.; Knock, G.A. ROS-dependent activation of RhoA/Rho-kinase in pulmonary artery: Role of Src-family kinases and ARHGEF1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regen, T.; Isaac, S.; Amorim, A.; Núñez, N.G.; Hauptmann, J.; Shanmugavadivu, A.; Klein, M.; Sankowski, R.; Mufazalov, I.A.; Yogev, N.; et al. IL-17 controls central nervous system autoimmunity through the intestinal microbiome. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eaaz6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; Duarte, J. Microbiota and Hypertension: Role of the Sympathetic Nervous System and the Immune System. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 33, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomaeus, H.; Balogh, A.; Yakoub, M.; Homann, S.; Markó, L.; Höges, S.; Tsvetkov, D.; Krannich, A.; Wundersitz, S.; Avery, E.G.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Propionate Protects From Hypertensive Cardiovascular Damage. Circulation 2019, 139, 1407–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; De La Visitación, N.; Aguilera-Sánchez, N.; Redondo, J.M.; Duarte, J. Protective Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Angiotensin II. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ansaldo, E.; Slayden, L.C.; Ching, K.L.; Koch, M.A.; Wolf, N.K.; Plichta, D.R.; Brown, E.M.; Graham, D.B.; Xavier, R.J.; Moon, J.J.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila induces intestinal adaptive immune responses during homeostasis. Science 2019, 364, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berer, K.; Gerdes, L.A.; Cekanaviciute, E.; Jia, X.; Xiao, L.; Xia, Z.; Liu, C.; Klotz, L.; Stauffer, U.; Baranzini, S.; et al. Gut microbiota from multiple sclerosis patients enables spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10719–10724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Yoo, B.B.; Runia, T.F.; Debelius, J.W.; Singh, S.; Nelson, C.; Kanner, R.; Bencosme, Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Hauser, S.L.; et al. Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and exacerbate symptoms in mouse models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10713–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A purified membrane protein from Akkermansia muciniphila or the pasteurized bacterium improves metabolism in obese and diabetic mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katiraei, S.; de Vries, M.R.; Costain, A.H.; Thiem, K.; Hoving, L.R.; van Diepen, J.A.; Smits, H.; Bouter, K.E.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Quax, P.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphilaExerts Lipid-Lowering and Immunomodulatory Effects without Affecting Neointima Formation in Hyperlipidemic APOE*3-Leiden.CETP Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 64, e1900732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenink, M.H.; Santegoets, K.C.; Broen, J.C.; van Bon, L.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Popa, C.; Huijbens, R.; Remijn, T.; Lubberts, E.; van Riel, P.L.; et al. TLR2 promotes Th2/Th17 responses via TLR4 and TLR7/8 by abrogating the type I IFN amplification loop. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6960–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Che, L.; Lin, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Effects of dietary Clostridium butyricum supplementation on growth performance, intestinal development, and immune response of weaned piglets challenged with lipopolysaccharide. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De La Visitación, N.; Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; Duarte, J. Protective Effects of Probiotic Consumption in Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Seto, N.L.; Carmona-Rivera, C.; Kaplan, M.J. Accelerated model of lupus autoimmunity and vasculopathy driven by toll-like receptor 7/9 imbalance. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, V.R.; Wüthrich, R.P. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin. Nephrol. 1999, 19, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, M.J. An Update on Immune System Activation in the Pathogenesis of Hypertension. Hypertension 2013, 62, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.; Chiasson, V.L.; Chatterjee, P.; Kopriva, S.E.; Young, K.J.; Mitchell, B.M. Interleukin-17 causes Rho-kinase-mediated endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 97, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietrowski, E.; Bender, B.; Huppert, J.; White, R.; Luhmann, H.J.; Kuhlmann, C.R. Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Interleukin-17A on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Involve NAD(P)H- Oxidase Derived Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Vasc. Res. 2011, 48, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, A.L.; Kaye, D.M.; Marques, F.Z. The role of the gut microbiome in sex differences in arterial pressure. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de la Visitación, N.; Robles-Vera, I.; Moleón, J.; González-Correa, C.; Aguilera-Sánchez, N.; Toral, M.; Gómez-Guzmán, M.; Sánchez, M.; Jiménez, R.; Martin-Morales, N.; et al. Gut Microbiota Has a Crucial Role in the Development of Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction in Toll-like Receptor 7-Driven Lupus Autoimmunity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091426
de la Visitación N, Robles-Vera I, Moleón J, González-Correa C, Aguilera-Sánchez N, Toral M, Gómez-Guzmán M, Sánchez M, Jiménez R, Martin-Morales N, et al. Gut Microbiota Has a Crucial Role in the Development of Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction in Toll-like Receptor 7-Driven Lupus Autoimmunity. Antioxidants. 2021; 10(9):1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091426
Chicago/Turabian Stylede la Visitación, Néstor, Iñaki Robles-Vera, Javier Moleón, Cristina González-Correa, Nazaret Aguilera-Sánchez, Marta Toral, Manuel Gómez-Guzmán, Manuel Sánchez, Rosario Jiménez, Natividad Martin-Morales, and et al. 2021. "Gut Microbiota Has a Crucial Role in the Development of Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction in Toll-like Receptor 7-Driven Lupus Autoimmunity" Antioxidants 10, no. 9: 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091426
APA Stylede la Visitación, N., Robles-Vera, I., Moleón, J., González-Correa, C., Aguilera-Sánchez, N., Toral, M., Gómez-Guzmán, M., Sánchez, M., Jiménez, R., Martin-Morales, N., O’Valle, F., Romero, M., & Duarte, J. (2021). Gut Microbiota Has a Crucial Role in the Development of Hypertension and Vascular Dysfunction in Toll-like Receptor 7-Driven Lupus Autoimmunity. Antioxidants, 10(9), 1426. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091426