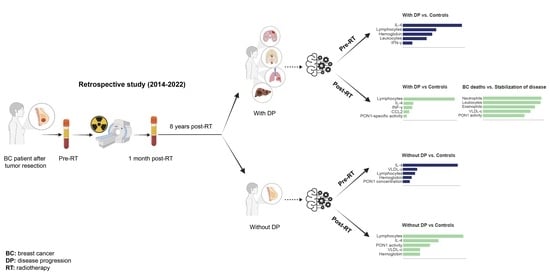
Gradient Boosting Machine Identified Predictive Variables for Breast Cancer Patients Pre- and Post-Radiotherapy: Preliminary Results of an 8-Year Follow-Up Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. Analytical Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. Density Plots, Venn Diagrams, Circular Packaging, and Volcano Plots
2.5. Two-Dimensional Linear Discriminant Analysis and Heatmap Representations
2.6. Machine Learning
3. Results
3.1. Follow-Up of BC Patients
3.2. Clinico-Pathological Features and Analytical Alterations in BC Patients with and without DP
3.3. IL-4 Was the Best Pre-RT Index Predicting the Presence of BC
3.4. Lymphocytes Were the Best Post-RT Index Predicting the Presence of BC
3.5. Relationships between Predictive Variables Pre- and Post-RT, and the Prognosis of Patients Who Developed DP Post-RT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zardavas, D.; Irrthum, A.; Swanton, C.; Piccart, M. Clinical management of breast cancer heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Roozendaal, L.M.; Smit, L.H.M.; Duijsens, G.H.N.M.; de Vries, B.; Siesling, S.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; de Boer, M.; de Wilt, J.H.W.; Smidt, M.L. Risk of regional recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer patients: A Dutch cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 156, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Han, B.K.; Kim, E.K.; Choi, W.J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H.H.; Moon, W.K. Breast Cancer Detected at Screening US: Survival Rates and Clinical-Pathologic and Imaging Factors Associated with Recurrence. Radiology 2017, 284, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, C.; Bauer-Nilsen, K.; McNulty, R.H.; Vicini, F. Novel radiation therapy approaches for breast cancer treatment. Semin. Oncol. 2020, 47, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.S.; Schnaper, L.A.; Bellon, J.R.; Cirrincione, C.T.; Berry, D.A.; McCormick, B.; Muss, H.B.; Smith, B.L.; Hudis, C.A.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Lumpectomy plus tamoxifen with or without irradiation in women age 70 years or older with early breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of CALGB 9343. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2382–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkler, I.H.; Williams, L.J.; Jack, W.J.L.; Cameron, D.A.; Dixon, J.M. Breast-conserving surgery with or without irradiation in women aged 65 years or older with early breast cancer (PRIME II): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Vanderplas, A.; Hughes, M.E.; Theriault, R.L.; Edge, S.B.; Wong, Y.N.; Blayney, D.W.; Niland, J.C.; Winer, E.P.; Weeks, J.C. Clinicopathologic features, patterns of recurrence, and survival among women with triple-negative breast cancer in the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Cancer 2012, 15, 5463–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britt, K.L.; Cuzick, J.; Phillips, K.A. Key steps for effective breast cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, J.; Castañé, H.; Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Arenas, M.; Iftimie, S.; Joven, J. On the role of paraoxonase-1 and chemokine ligand 2 (c-c motif) in metabolic alterations linked to inflammation and disease. A 2021 update. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arenas, M.; Rodríguez, E.; Sahebkar, A.; Sabater, S.; Rizo, D.; Pallisé, O.; Hernández, M.; Riu, F.; Camps, J.; Joven, J. Paraoxonase-1 activity in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 127, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, M.; García-Heredia, A.; Cabré, N.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Sabater, S.; Bonet, M.; Gascón, M.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Fort-Gallifa, I.; et al. Effect of radiotherapy on activity and concentration of serum paraoxonase-1 in breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Arguís, M.; Arenas, M.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Murcia, M.; Sabater, S.; Torres, L.; Baiges-Gayà, G.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; Camps, J.; et al. Alterations in plasma concentrations of energy-balance-related metabolites in patients with lung, or head & neck, cancers: Effects of radiotherapy. J. Proteom. 2020, 213, 103605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Arenas, M.; Gómez, J.; Acosta, J.; Trilla, J.; López, Y.; Árquez, M.; Torres, L.; Araguas, P.; Hernández-Aguilera, A.; et al. Identification of potential metabolic biomarkers of rectal cancer and of the effect of neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps, J.; Marsillach, J.; Joven, J. The paraoxonases: Role in human diseases and methodological difficulties in measurement. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 46, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeeravalli, R.; Das, A. Molecular mediators of breast cancer metastasis. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell. Ther. 2021, 14, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gorp, H.; Lamkanfi, M. The emerging roles of inflammasome-dependent cytokines in cancer development. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e47575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Huertas, C.S.; Mitchell, A.; Plebanski, M. Tumor-induced inflammatory cytokines and the emerging diagnostic devices for cancer detection and prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.R. The interferon-gamma paradox in cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganggayah, M.D.; Taib, N.A.; Har, Y.C.; Lio, P.; Dhillon, S.K. Predicting factors for survival of breast cancer patients using machine learning techniques. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sammut, S.J.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Chin, S.F.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.A.; Ma, W.; Cope, W.; Dariush, A.; Dawson, S.J.; Abraham, J.E.; et al. Multi-omic machine learning predictor of breast cancer therapy response. Nature 2022, 601, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, C.M.; Abdollahi, B.; Fuqua, J.D.; de Carlo, A.R.; Bartholomai, J.A.; Balgemann, R.N.; van Berkel, V.H.; Frieboes, H.B. Prediction of lung cancer patient survival via supervised machine learning classification techniques. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2017, 108, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Canes, A.; Steinberg, D.; Lyashevska, O.; written on behalf of AME Big-Data Clinical Trial Collaborative Group. Predictive analytics with gradient boosting in clinical medicine. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibault, J.E.; Chang, D.T.; Xing, L. Development and validation of a model to predict survival in colorectal cancer using a gradient-boosted machine. Gut 2021, 70, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.W.; Jiao, C.Y.; Xu, Z.G.; Li, X.C.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.H. Development and validation of a gradient boosting machine to predict prognosis after liver resection for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, J.A.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Laurine, J.A.; Novotny, P.J.; Vargas-Chanes, D.; Krook, J.E.; O’Connell, M.J.; Kugler, J.W.; Tirona, M.T.; Kardinal, C.G.; et al. A simple stratification factor prognostic for survival in advanced cancer: The good/bad/uncertain index. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero, A.; Sanz, X.; Hernanz, R.; Cabrera, D.; Arenas, M.; Bayo, E.; Moreno, F.; Algara, M. Accelerated hypofractionated breast radiotherapy: FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) and facts. Breast 2014, 23, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prades, J.; Algara, M.; Espinàs, J.A.; Farrús, B.; Arenas, M.; Reyes, V.; García-Reglero, V.; Cambra, M.J.; Rubio, E.; Anglada, L.; et al. Understanding variations in the use of hypofractionated radiotherapy and its specific indications for breast cancer: A mixed-methods study. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, M.; Montero, Á.; de las Peñas, M.D.; Algara, M. The position and current status of radiation therapy after primary systemic therapy in breast cancer: A national survey-based expert consensus statement. Clin. Translat. Oncol. 2016, 18, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bots, W.T.C.; van den Bosch, S.; Zwijnenburg, E.M.; Dijkema, T.; van den Broek, G.B.; Weijs, W.L.J.; Verhoef, L.C.G.; Kaanders, J.H.A.M. Reirradiation of head and neck cancer: Long-term disease control and toxicity. Head Neck 2017, 39, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranda, N.; Viteri, F.E.; Montserrat, C.; Arija, V. Effects of C282Y, H63D, and S65C HFE gene mutations, diet, and life-style factors on iron status in a general Mediterranean population from Tarragona, Spain. Ann. Hematol. 2010, 89, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, S.T.; Wadleigh, D.J.; Grijalva, V.; Ng, C.; Hama, S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Shih, D.M.; Lusis, A.J.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M. Human paraoxonase-3 is an hdl-associated enzyme with biological activity similar to paraoxonase-1 protein but is not regulated by oxidized lipids. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.N.; Shao, Y.H.; Chen, W.J.; Wang, Z.; Deng, N.Y. Generalized two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis with regularization. Neural Netw. 2021, 142, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, J.T.; Bridgeford, E.W.; Tang, M.; Zheng, D.; Douville, C.; Burns, R.; Maggioni, M. Supervised dimensionality reduction for big data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Pedregosa, F.; Eickenberg, M.; Gervais, P.; Mueller, A.; Kossaifi, J.; Gramfort, A.; Thirion, B.; Varoquaux, G. Machine learning for neuroimaging with scikit-learn. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Maaren, M.C.; de Munck, L.; Strobbe, L.J.A.; Sonke, G.S.; Westenend, P.J.; Smidt, M.L.; Poortmans, P.M.P.; Siesling, S. Ten-year recurrence rates for breast cancer subtypes in the Netherlands: A large population-based study. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Leij, F.; Elkhuizen, P.H.M.; Bartelink, H.; van de Vijver, M.J. Predictive factors for local recurrence in breast cancer. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 22, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho-Huynh, A.; Tran, A.; Bray, G.; Abbot, S.; Elston, T.; Gunnarsson, R.; de Costa, A. Factors influencing breast cancer outcomes in Australia: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2019, 28, e13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; Marrelli, D.; Rossi, S.; De Stefano, A.; Mariani, F.; De Marco, G.; Caruso, S.; Corso, G.; Cioppa, T.; Pinto, E.; et al. Breast cancer local recurrence: Risk factors and prognostic relevance of early time to recurrence. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornetti, J.; Welm, A.L.; Stewart, S.A. Understanding the bone in cancer metastasis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tahara, R.K.; Brewer, T.M.; Theriault, R.L.; Ueno, N.T. Bone metastasis of breast cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1152, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, L.L.; Zheng, Y.; Stalgis-Bilinski, K.; Dunstan, C.R. The bone remodeling environment is a factor in breast cancer bone metastasis. Bone 2011, 48, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Azzouz, F.; Michel, B.; Lasla, H.; Gouraud, W.; François, A.F.; Girka, F.; Lecointre, T.; Guérin-Charbonnel, C.; Juin, P.P.; Campone, M.; et al. Development of an absolute assignment predictor for triple-negative breast cancer subtyping using machine learning approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 129, 104171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, S.; Bezas, K.; Exarchos, T.P. Decision Support System for Breast Cancer Detection Using Biomarker Indicators. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1338, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, Y.; Yin, P.; Liu, F.; Fang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. A machine learning model based on ultrasound image features to assess the risk of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients: Applications of scikit-learn and SHAP. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 944569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada-Torres, A.; van Maaren, M.C.; Hendriks, M.P.; Siesling, S.G. Explainable machine learning can outperform Cox regression predictions and provide insights in breast cancer survival. Sci. Rep. 2021, 26, 6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, R.; Wen, C.W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Pan, D.; Zheng, B.; Qin, G.; Chen, W. Predicting the molecular subtype of breast cancer and identifying interpretable imaging features using machine learning algorithms. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seruga, B.; Zhang, H.; Bernstein, L.J.; Tannock, I.F. Cytokines and their relationship to the symptoms and outcome of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carty, S.A.; Koretzky, G.A.; Jordan, M.S. Interleukin-4 regulates eomesodermin in cd8+ t cell development and differentiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francipane, M.G.; Perez Alea, M.; Lombardo, Y.; Todaro, M.; Medema, J.P.; Stassi, G. Crucial role of interleukin-4 in the survival of colon cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4022–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, S.; Shirota, H.; Kasahara, Y.; Saijo, K.; Ishioka, C. IL-4 blockade alters the tumor microenvironment and augments the response to cancer immunotherapy in a mouse model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, D.M.; Sánchez, A.C.; Rosas, D.A.; Rivero, E.; Paparoni, M.D.; Cruz, M.A.; Suárez, Y.P.; Galvis, N.F. Preliminary analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in IL-10, IL-4, and IL-4Rα genes and profile of circulating cytokines in patients with gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bednarz-Misa, I.; Diakowska, D.; Szczuka, I.; Fortuna, P.; Kubiak, A.; Rosińczuk, J.; Krzystek-Korpacka, M. Interleukins 4 and 13 and their receptors are differently expressed in gastrointestinal tract cancers, depending on the anatomical site and disease advancement, and improve colon cancer cell viability and motility. Cancers 2020, 12, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabeen, S.; Zucknick, M.; Nome, M.; Dannenfelser, R.; Fleischer, T.; Kumar, S.; Lüders, T.; von der Lippe Gythfeldt, H.; Troyanskaya, O.; Kyte, J.A.; et al. Serum cytokine levels in breast cancer patients during neoadjuvant treatment with bevacizumab. OncoImmunology 2018, 7, e1457598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papatestas, A.E.; Lesnick, G.J.; Genkins, G.; Aufses, A.H. The prognostic significance of peripheral lymphocyte counts in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 1976, 37, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gago-Dominguez, M.; Matabuena, M.; Redondo, C.M.; Patel, S.P.; Carracedo, A.; Ponte, S.M.; Martínez, M.E.; Castelao, J.E. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and breast cancer risk: Analysis by subtype and potential interactions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio is associated with the poor prognosis of breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Dong, L.; Cheng, L. Neutrophils in cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajioka, H.; Kagawa, S.; Ito, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Kikuchi, S.; Kuroda, S.; Yoshida, R.; Umeda, Y.; Noma, K.; et al. Targeting neutrophil extracellular traps with thrombomodulin prevents pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 497, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, J.; Iftimie, S.; García-Heredia, A.; Castro, A.; Joven, J. Paraoxonases and infectious diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Murcia, M.; Arenas, M.; Arguís, M.; Gil, M.; Amigó, N.; Correig, X.; Torres, L.; Sabater, S.; Baiges-Gayà, G.; et al. Serum paraoxonase-1-related variables and lipoprotein profile in patients with lung or head and neck cancer: Effect of radiotherapy. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jasinski, M.; Olszewska-Slonina, D. Serum paraoxonase-1 activity and the risk of prostate cancer recurrence in patients treated with radiotherapy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| With DP (n = 24) | Without DP (n = 213) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 46 (39–55) | 55 (47–65) | 0.005 |
| Alcohol habit (>20 g/day) | - | 10 (4.7) | 0.278 |
| Smoking habit | 5 (20.8) | 25 (11.7) | 0.203 |
| Hypertension | 6 (25) | 49 (23) | 0.826 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 2 (8.3) | 11 (5.2) | 0.518 |
| Dyslipidemia | 4 (16.7) | 51 (23.9) | 0.800 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | - | 7 (3.3) | 0.367 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 1 (4.2) | 6 (2.8) | 0.711 |
| Hypothyroidism | - | 20 (9.4) | 0.116 |
| Menopause status | |||
| Premenopausal | 9 (37.5) | 52 (24.4) | 0.164 |
| Peri-menopausal | 3 (12.5) | 22 (10.3) | 0.742 |
| Postmenopausal | 12 (50) | 139 (65.3) | 0.140 |
| Use of oral contraceptives | 8 (33.3) | 73 (34.3) | 0.926 |
| Motherhood | 16 (66.7) | 162 (76.1) | 0.313 |
| Cancer characteristics | |||
| Tumor size (TNM system) | |||
| T0 | 2 (8.3) | 16 (7.5) | 0.885 |
| T1 | 6 (25) | 119 (55.9) | 0.004 |
| T2 | 9 (37.5) | 60 (28.2) | 0.340 |
| T3 | 3 (12.5) | 16 (7.5) | 0.393 |
| T4 | 4 (16.7) | 2 (0.9) | <0.001 |
| Nodes (TNM system) | |||
| N0 | 10 (41.7) | 146 (68.5) | 0.008 |
| N1 | 13 (37.5) | 49 (23) | 0.001 |
| N2 | 3 (12.5) | 14 (6.6) | 0.286 |
| N3 | 2 (8.3) | 4 (1.9) | 0.056 |
| Metastases (TNM system) | |||
| M0 | 24 (100) | (100) | - |
| M1 | - | - | - |
| Pathological anatomy of the tumor | |||
| Ductal carcinoma in situ | - | 14 (6.6) | 0.195 |
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 22 (91.7) | 176 (82.6) | 0.257 |
| Lobular carcinoma in situ | 1 (4.2) | - | 0.002 |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | - | 3 (1.4) | 0.558 |
| Papillary carcinoma | - | 13 (6.1) | 0.213 |
| Others | 1 (4.2) | 7 (3.3) | 0.820 |
| Histological grade | |||
| I | 3 (12.5) | 45 (21.1) | 0.318 |
| II | 11 (45.8) | 105 (49.3) | 0.747 |
| III | 10 (41.7) | 63 (29.6) | 0.223 |
| Positive Estrogen receptors | 15 (62.5) | 176 (82.6) | 0.018 |
| Positive Progesterone receptors | 11 (45.8) | 142 (66.7) | 0.043 |
| Positive HER2 in tumor biopsy | 7 (29.2) | 36 (16.9) | 0.139 |
| Ki67 antigen in tumor biopsy | |||
| Less than 15% | 4 (16.7) | 90 (42.3) | 0.015 |
| 15–50% | 10 (41.7) | 96 (45.1) | 0.750 |
| More than 50% | 10 (41.7) | 27 (12.7) | <0.001 |
| Tumor molecular classification | |||
| Luminal A | 2 (8.3) | 74 (34.7) | 0.008 |
| Luminal B | 8 (33.3) | 74 (34.7) | 0.890 |
| HER2 positive | 7 (29.2) | 37 (17.4) | 0.158 |
| Triple negative | 7 (29.2) | 28 (13.1) | 0.036 |
| Oncological Treatments | |||
| Surgical procedure | |||
| Lumpectomy | 11 (45.8) | 179 (84) | <0.001 |
| Mastectomy | 13 (54.2) | 34 (16) | <0.001 |
| Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy | 15 (62.5) | 61 (28.6) | <0.001 |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy | 6 (25) | 65 (30.5) | 0.576 |
| Adjuvant Hormone therapy | 14 (58.3) | 170 (79.8) | 0.016 |
| Adjuvant Radiotherapy | 24 (100) | 213 (100) | - |
| Secondary effects of Radiotherapy | |||
| Epithelitis | |||
| Grade I | 13 (54.2) | 113 (53.1) | 0.917 |
| Grade II | 8 (33.3) | 93 (43.7) | 0.332 |
| Grade III | 3 (12.5) | 7 (3.3) | 0.033 |
| Pneumonitis | - | 2 (0.9) | 0.633 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Tomàs, E.; Arenas, M.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Acosta, J.; Araguas, P.; Malave, B.; Castañé, H.; Jiménez-Franco, A.; Benavides-Villarreal, R.; Sabater, S.; et al. Gradient Boosting Machine Identified Predictive Variables for Breast Cancer Patients Pre- and Post-Radiotherapy: Preliminary Results of an 8-Year Follow-Up Study. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122394
Rodríguez-Tomàs E, Arenas M, Baiges-Gaya G, Acosta J, Araguas P, Malave B, Castañé H, Jiménez-Franco A, Benavides-Villarreal R, Sabater S, et al. Gradient Boosting Machine Identified Predictive Variables for Breast Cancer Patients Pre- and Post-Radiotherapy: Preliminary Results of an 8-Year Follow-Up Study. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(12):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122394
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Tomàs, Elisabet, Meritxell Arenas, Gerard Baiges-Gaya, Johana Acosta, Pablo Araguas, Bárbara Malave, Helena Castañé, Andrea Jiménez-Franco, Rocío Benavides-Villarreal, Sebastià Sabater, and et al. 2022. "Gradient Boosting Machine Identified Predictive Variables for Breast Cancer Patients Pre- and Post-Radiotherapy: Preliminary Results of an 8-Year Follow-Up Study" Antioxidants 11, no. 12: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122394
APA StyleRodríguez-Tomàs, E., Arenas, M., Baiges-Gaya, G., Acosta, J., Araguas, P., Malave, B., Castañé, H., Jiménez-Franco, A., Benavides-Villarreal, R., Sabater, S., Solà-Alberich, R., Camps, J., & Joven, J. (2022). Gradient Boosting Machine Identified Predictive Variables for Breast Cancer Patients Pre- and Post-Radiotherapy: Preliminary Results of an 8-Year Follow-Up Study. Antioxidants, 11(12), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11122394