Development and Validation of an Analytical Method for Carnosol, Carnosic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid in Food Matrices and Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Rosemary Extract as a Food Additive
Abstract
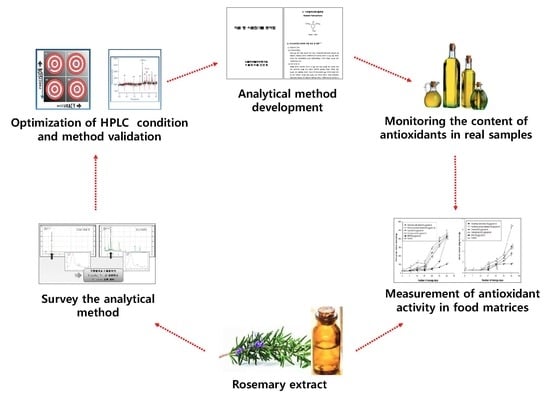
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Food Materials
2.3. Optimization of HPLC Conditions
2.4. Optimization of Extraction Method
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. HPLC Instrument Conditions
2.7. Method Validation
2.8. Function Evaluation as an Antioxidant
2.8.1. Experimental Condition
2.8.2. Measurement of Antioxidant Activity
2.8.3. Measurement of Residual Antioxidant Level
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of HPLC Conditions
3.2. Optimization of Extraction Method
3.3. Method Validation
3.3.1. Selectivity, Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
3.3.2. Trueness and Precision
3.4. Sample Collection and Monitoring of Residual Rosemary Extract Levels
3.5. Assessment of Functionality as Antioxidant
3.5.1. Antioxidant Activity
3.5.2. Oxidation Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Škrinjar, M.; Kolar, M.H.; Jelšek, N.; Hraš, A.R.; Bezjak, M.; Knez, Ž. Application of HPLC with electrochemical detection for the determination of low levels of antioxidants. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Lipid oxidation and improving the oxidative stability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandonienė, D.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Gruzdienė, D.; Murkovic, M. Antioxidative activity of sage (Salvia officinalis L.), savory (Satureja hortensis L.) and borage (Borago officinalis L.) extracts in rapeseed oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2002, 104, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acworth, I.N.; Bailey, B. The Handbook of Oxidative Metabolism; ESA Inc.: Chelmsford, MD, USA, 1997; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, H.; Ho, C.T. Effects of rosemary extracts and major constituents on lipid oxidation and soybean lipoxygenase activity. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1992, 69, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu, D.P.; Losada, P.P.; Maroto, J.; Cruz, J.M. Evaluation of the effectiveness of a new active packaging film containing natural antioxidants (from barley husks) that retard lipid damage in frozen Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.O.; Conceição, E.C.; Chaul, L.T.; Oliveira, E.M.; Martins, F.S.; Bara, M.T.F.; Rezende, K.R.; Alves, S.F.; Paula, J.R. Spray-dried rosemary extracts: Physicochemical and antioxidant properties. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorsen, M.A.; Hildebrandt, K.S. Quantitative determination of phenolic diterpenes in rosemary extracts: Aspects of accurate quantification. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 995, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesil-Celiktas, O.; Sevimli, C.; Bedir, E.; Vardar-Sukan, F. Inhibitory effects of rosemary extracts, carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid on the growth of various human cancer cell lines. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC). National Standard of The People’s Republic of China: National Food Safety Standard for Food Additive Use (GB2760-2014); National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014.
- EC. Commission regulation (EU) No 1129/2011 of 11 November 2011 amending Annex II to regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the european parliament and of the council by establishing a union list of food additives. Off. J. Eur. Union L 2011, 295, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Ramos, F.; Castilho, M.C.; Sanches-Silva, A. UHPLC-DAD Multi-Method for Determination of Phenolics in Aromatic Plants. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopia, A.I.; Huang, S.W.; Schwarz, K.; German, J.B.; Frankel, E.N. Effect of different lipid systems on antioxidant activity of rosemary constituents carnosol and carnosic acid with and without α-tocopherol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, E.N.; Huang, S.W.; Aeschbach, R.; Prior, E. Antioxidant activity of a rosemary extract and its constituents, carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmarinic acid, in bulk oil and oil-in-water emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Choi, S.H.; Shin, G.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.R.; Lee, K.Y.; Lim, H.S.; Kang, T.S.; Lee, O.H. Method validation and measurement uncertainty for the simultaneous determination of synthetic phenolic antioxidants in edible oils commonly consumed in Korea. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, H.J.; Choi, S.H. Assessment of Estimated Daily Intakes of Propyl Gallate, EDTA (ethylenediamine tetra acetate), and Erythorbic Acid in Korea. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 43, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH). International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guidline. Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology. Available online: https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2019).
- AOCS. Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society; AOCS: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Teruel, M.R.; Garrido, M.D.; Espinosa, M.C.; Linares, M.B. Effect of different format-solvent rosemary extracts (Rosmarinus officinalis) on frozen chicken nuggets quality. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puangsombat, K.; Smith, J.S. Inhibition of heterocyclic amine formation in beef patties by ethanolic extracts of rosemary. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Ameri, F.; Gadgil, P. Effect of marinades on the formation of heterocyclic amines in grilled beef steaks. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuppner, H.; Sturm, S.; Konwalinka, G. HPLC analysis of the main oxindole alkaloids from Uncaria tomentosa. Chromatographia 1992, 34, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; LoBrutto, R.; Kazakevich, Y.V.; Thompson, R. Influence of inorganic mobile phase additives on the retention, efficiency and peak symmetry of protonated basic compounds in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1049, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, J.W. Temperature selectivity in reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 965, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, B.; Sing, Y.Y.; Nawi, M.A.; Hashim, N.; Mohamed Ali, A.S.; Saleh, M.I.; Sulaiman, S.F.; Talib, K.M.; Ahmad, K. Determination of synthetic phenolic antioxidants in food items using reversed-phase HPLC. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marın, A.; Garcıa, E.; Garcıa, A.; Barbas, C. Validation of a HPLC quantification of acetaminophen, phenylephrine and chlorpheniramine in pharmaceutical formulations: Capsules and sachets. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 29, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Guidelines on Good Laboratory Practice in Residue Analysis, CAC/GL 40-1993. Available online: http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/codex-texts/guidelines/en/ (accessed on 10 March 2019).



| Matrix | Analytes | Range (μg/mL) | Slope | Intercept | Correlation Coefficient (R2) 1 | LOD (μg/mL) | LOQ (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | Rosmarinic acid | 1.56–100 | 34,243.3 | −27,953.9 | 0.9994 | 0.38 | 1.14 |
| Carnosol | 6.25–400 | 7926.7 | 8343.5 | 1.0000 | 0.78 | 2.38 | |
| Carnosic acid | 6.25–400 | 5585.2 | −13,120.1 | 0.9995 | 0.65 | 1.96 | |
| Processed meat products | Rosmarinic acid | 1.56–100 | 34,954.9 | −33,771.5 | 0.9995 | 0.38 | 1.15 |
| Carnosol | 6.25–400 | 8165.6 | −2906.3 | 1.0000 | 1.05 | 3.17 | |
| Carnosic acid | 6.25–400 | 5657.9 | −25,961.3 | 0.9987 | 1.50 | 4.55 | |
| Dressing | Rosmarinic acid | 1.56–100 | 33,781.5 | −45,267.7 | 0.9992 | 0.22 | 0.66 |
| Carnosol | 6.25–400 | 7941.4 | −17,908.1 | 0.9997 | 1.39 | 4.21 | |
| Carnosic acid | 6.25–400 | 5526.4 | −9656.3 | 0.9997 | 1.73 | 5.23 |
| Matrix | Analytes | Concentration (μg/mL) | Mean ± SD (μg/mL) | RSD 1 (%) | Recovery (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | Rosmarinic acid | Intra-day | 5.0 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 1.5 | 90.8 |
| 10.0 | 7.2 ± 0.1 | 1.8 | 72.2 | |||
| 20.0 | 14.1 ± 0.0 | 0.2 | 70.6 | |||
| Inter-day | 5.0 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 3.6 | 89.7 | ||
| 10.0 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 2.5 | 71.0 | |||
| 20.0 | 14.3 ± 0.4 | 2.4 | 71.3 | |||
| Carnosol | Intra-day | 25.0 | 21.4 ± 0.1 | 0.5 | 85.6 | |
| 50.0 | 42.4 ± 0.3 | 0.6 | 84.8 | |||
| 100.0 | 93.5 ± 0.2 | 0.2 | 93.5 | |||
| Inter-day | 25.0 | 20.6 ± 0.6 | 3.0 | 82.6 | ||
| 50.0 | 4.19 ± 1.6 | 3.8 | 83.8 | |||
| 100.0 | 93.8 ± 2.8 | 3.0 | 93.8 | |||
| Carnosic acid | Intra-day | 25.0 | 23.1 ± 0.1 | 0.6 | 92.5 | |
| 50.0 | 43.6 ± 0.1 | 0.3 | 87.1 | |||
| 100.0 | 88.6 ± 0.3 | 0.4 | 88.9 | |||
| Inter-day | 25.0 | 22.4 ± 0.7 | 3.1 | 89.6 | ||
| 50.0 | 42.6 ± 1.3 | 3.1 | 85.1 | |||
| 100.0 | 88.1 ± 2.3 | 2.6 | 88.1 | |||
| Processed meat products | Rosmarinic acid | Intra-day | 5.0 | 5.4 ± 0.0 | 0.8 | 106.9 |
| 10.0 | 8.7 ± 0.0 | 0.8 | 86.7 | |||
| 20.0 | 14.7 ± 0.0 | 0.4 | 73.5 | |||
| Inter-day | 3.13 | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 1.5 | 102.1 | ||
| 12.5 | 8.4 ± 0.1 | 0.8 | 84.2 | |||
| 25.0 | 14.6 ± 0.2 | 1.2 | 72.8 | |||
| Carnosol | Intra-day | 25.0 | 27.0 ± 0.2 | 0.8 | 108.2 | |
| 50.0 | 53.4 ± 0.2 | 0.4 | 106.8 | |||
| 100.0 | 99.3 ± 0.6 | 0.6 | 99.3 | |||
| Inter-day | 25.0 | 25.4 ± 0.2 | 0.6 | 101.8 | ||
| 50.0 | 52.2 ± 0.5 | 1.0 | 104.4 | |||
| 100.0 | 99.1 ± 0.9 | 0.9 | 99.1 | |||
| Carnosic acid | Intra-day | 25.0 | 28.8 ± 0.2 | 0.6 | 115.2 | |
| 50.0 | 55.5 ± 0.3 | 0.6 | 111.0 | |||
| 100.0 | 101.4 ± 1.4 | 1.4 | 101.4 | |||
| Inter-day | 25.0 | 26.8 ± 0.2 | 0.8 | 107.2 | ||
| 50.0 | 54.5 ± 1.2 | 2.1 | 108.9 | |||
| 100.0 | 99.4 ± 1.5 | 1.5 | 99.4 | |||
| Dressing | Rosmarinic acid | Intra-day | 5.0 | 5.8 ± 0.0 | 0.5 | 116.3 |
| 10.0 | 9.5 ± 0.0 | 0.3 | 95.3 | |||
| 20.0 | 16.1 ± 0.1 | 0.4 | 80.5 | |||
| Inter-day | 5.0 | 5.5 ± 0.0 | 0.2 | 109.3 | ||
| 10.0 | 9.2 ± 0.1 | 0.7 | 92.0 | |||
| 20.0 | 16.1 ± 0.2 | 1.3 | 80.4 | |||
| Carnosol | Intra-day | 25.0 | 28.5 ± 0.1 | 0.4 | 114.0 | |
| 50.0 | 52.3 ± 0.2 | 0.4 | 104.5 | |||
| 100.0 | 101.5 ± 0.2 | 0.2 | 101.5 | |||
| Inter-day | 25.0 | 28.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 | 113.5 | ||
| 50.0 | 52.1 ± 0.2 | 0.3 | 104.1 | |||
| 100.0 | 102.8 ± 1.6 | 1.5 | 102.8 | |||
| Carnosic acid | Intra-day | 25.0 | 29.1 ± 0.1 | 0.2 | 116.5 | |
| 50.0 | 51.3 ± 0.2 | 0.4 | 102.5 | |||
| 100.0 | 99.2 ± 0.3 | 0.3 | 99.2 | |||
| Inter-day | 25.0 | 27.7 ± 0.3 | 1.1 | 110.8 | ||
| 50.0 | 51.0 ± 1.1 | 2.1 | 101.9 | |||
| 100.0 | 99.3 ± 0.9 | 0.9 | 99.3 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.-H.; Jang, G.-W.; Choi, S.-I.; Jung, T.-D.; Cho, B.-Y.; Sim, W.-S.; Han, X.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, D.-B.; et al. Development and Validation of an Analytical Method for Carnosol, Carnosic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid in Food Matrices and Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Rosemary Extract as a Food Additive. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030076
Choi S-H, Jang G-W, Choi S-I, Jung T-D, Cho B-Y, Sim W-S, Han X, Lee J-S, Kim D-Y, Kim D-B, et al. Development and Validation of an Analytical Method for Carnosol, Carnosic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid in Food Matrices and Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Rosemary Extract as a Food Additive. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(3):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seung-Hyun, Gill-Woong Jang, Sun-Il Choi, Tae-Dong Jung, Bong-Yeon Cho, Wan-Sup Sim, Xionggao Han, Jin-Sol Lee, Do-Yeon Kim, Dan-Bi Kim, and et al. 2019. "Development and Validation of an Analytical Method for Carnosol, Carnosic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid in Food Matrices and Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Rosemary Extract as a Food Additive" Antioxidants 8, no. 3: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030076
APA StyleChoi, S. -H., Jang, G. -W., Choi, S. -I., Jung, T. -D., Cho, B. -Y., Sim, W. -S., Han, X., Lee, J. -S., Kim, D. -Y., Kim, D. -B., & Lee, O. -H. (2019). Development and Validation of an Analytical Method for Carnosol, Carnosic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid in Food Matrices and Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Rosemary Extract as a Food Additive. Antioxidants, 8(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8030076