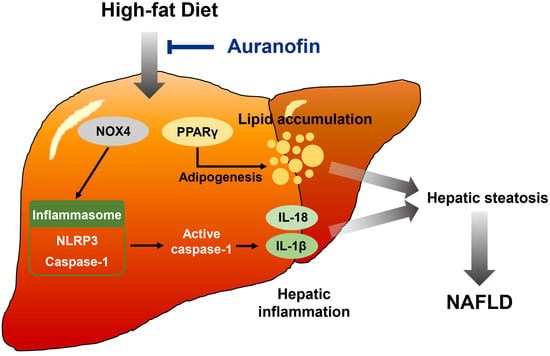
Auranofin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animal Models
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Cytokines Assays
2.7. Isolation of Hepatocytes
2.8. Chemical Treatment and Cell Viability Assay
2.9. Nitrite Production Measurement
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Auranofin Prevents Body Weight and Epididymal Fat Pad in HFD-Induced NAFLD Model
3.2. Auranofin Reduces Lipid Accumulation in Serum and Hepatic Steatosis in the HFD-Induced NAFLD Model
3.3. Auranofin Decreases HFD-Induced IL-1β and IL-18 Expression in the NAFLD Model
3.4. Auranofin Suppresses HFD-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome, NOX4 and PPARγ in the NAFLD Model
3.5. LPS and PA Stimulate Inflammatory Cytokines in Primary Hepatocytes
3.6. Auranofin Inhibits LPS and PA-Induced Inflammation in Primary Hepatocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brumbaugh, D.E.; Friedman, J.E. Developmental origins of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatric Res. 2014, 75, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, Y.; Ni, L.; Zhuge, F.; Fu, Z. The gut microbiota and its metabolites, novel targets for treating and preventing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase, D.M.; Gosav, E.M.; Costea, C.F.; Ciocoiu, M.; Lacatusu, C.M.; Maranduca, M.A.; Ouatu, A.; Floria, M. The intricate relationship between type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR) and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuman, M.G.; Cohen, L.B.; Nanau, R.M. Biomarkers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Adams, L.A.; Canbay, A.; Syn, W.K. Extrahepatic complications of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1174–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michelotti, G.A.; Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. NAFLD, NASH and liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baffy, G.; Brunt, E.M.; Caldwell, S.H. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging menace. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younes, R.; Bugianesi, E. A spotlight on pathogenesis, interactions and novel therapeutic options in NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertle, J.; Dechêne, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Penndorf, V.; Herzer, K.; Kaiser, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Gerken, G.; Syn, W.K.; Canbay, A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progresses to hepatocellular carcinoma in the absence of apparent cirrhosis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo, C.M.; Frühbeck, G.; Escalada, J. Impact of nutritional changes on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dajani, A.; AbuHammour, A. Treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Where do we stand? An overview. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, J.P.-Y.; Lovering, R.C.; Alnemri, E.S.; Bertin, J.; Boss, J.M.; Davis, B.K.; Flavell, R.A.; Girardin, S.E.; Godzik, A.; Harton, J.A. The NLR gene family: A standard nomenclature. Immunity 2008, 28, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baroja-Mazo, A.; Martín-Sánchez, F.; Gomez, A.I.; Martínez, C.M.; Amores-Iniesta, J.; Compan, V.; Barberà-Cremades, M.; Yagüe, J.; Ruiz-Ortiz, E.; Antón, J. The NLRP3 inflammasome is released as a particulate danger signal that amplifies the inflammatory response. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, E.-K.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, D.-M.; Sasakawa, C. Molecular mechanisms regulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Youm, Y.-H.; Ravussin, A.; Galgani, J.E.; Stadler, K.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M.; Dixit, V.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wree, A.; McGeough, M.D.; Peña, C.A.; Schlattjan, M.; Li, H.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Messer, K.; Canbay, A.; Hoffman, H.M.; Feldstein, A.E. NLRP3 inflammasome activation is required for fibrosis development in NAFLD. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 1069–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knorr, J.; Wree, A.; Tacke, F.; Feldstein, A.E. The NLRP3 inflammasome in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2020, 40, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H. A critical role for the NLRP3 inflammasome in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardier, C.; Ware, J.; Russell, I.J.; Larson, M.; Chalmers, A.; Read, J.L.; Arnold, W.; Bennett, R.; Caldwell, J.; Hench, P.K. Auranofin therapy and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results of a multicenter trial. Am. J. Med. 1986, 81, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; Sun, R.W.-Y.; Ott, I. Medicinal chemistry of gold anticancer metallodrugs. Met. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 199–217. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Haeberle, S.; Shytaj, I.L.; Gama-Brambila, R.A.; Theobald, J.; Ghafoory, S.; Wölker, J.; Basu, U.; Schmidt, C.; Timm, A. NHC-gold compounds mediate immune suppression through induction of AHR-TGFβ1 signalling in vitro and in scurfy mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Avorn, J.; Katz, J.N.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Setoguchi, S.; Levin, R.; Schneeweiss, S. Immunosuppressive medications and hospitalization for cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lee, S.J.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Lee, H.S.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Han, S.-H.; Ma, K.-H.; Jang, J.-K.; Lee, J.Y. Repurposing Auranofin, an Anti-Rheumatic Gold Compound, to Treat Acne Vulgaris by Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralph, S.J.; Nozuhur, S.; ALHulais, R.A.; Rodríguez-Enríquez, S.; Moreno-Sánchez, R. Repurposing drugs as pro-oxidant redox modifiers to eliminate cancer stem cells and improve the treatment of advanced stage cancers. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2397–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, J.M.; Schindler, S.M.; Klegeris, A. A new look at auranofin, dextromethorphan and rosiglitazone for reduction of glia-mediated inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Youn, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Saitoh, S.I.; Miyake, K.; Hwang, D.H. Auranofin, as an anti-rheumatic gold compound, suppresses LPS-induced homodimerization of TLR4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, K.-I.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Jue, D.-M. Thiol-reactive metal compounds inhibit NF-κB activation by blocking IκB kinase. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isakov, E.; Weisman-Shomer, P.; Benhar, M. Suppression of the pro-inflammatory NLRP3/interleukin-1β pathway in macrophages by the thioredoxin reductase inhibitor auranofin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locy, M.L.; Rogers, L.K.; Prigge, J.R.; Schmidt, E.E.; Arnér, E.S.; Tipple, T.E. Thioredoxin reductase inhibition elicits Nrf2-mediated responses in Clara cells: Implications for oxidant-induced lung injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staples, S.; Wall, S.B.; Li, R.; Tipple, T.E. Selenium-independent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of thioredoxin reductase inhibition in alveolar macrophages. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, S.B.; Wood, R.; Dunigan, K.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Rogers, L.K.; Tipple, T.E. Thioredoxin reductase-1 inhibition augments endogenous glutathione-dependent antioxidant responses in experimental bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.R.; Bae, S.J.; Kim, J.E.; Song, B.R.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, J.J.; Park, J.W.; Kang, M.J.; Choi, H.J.; Choi, Y.W. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress in high-fat-diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice: Efficacy of a novel extract from mulberry (Morus alba) leaves fermented with Cordyceps militaris. Lab. Anim. Res. 2018, 34, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwangbo, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Park, S.-H.; Hong, S.H.; Park, C.; Kim, G.-Y.; Leem, S.-H.; Hyun, J.W.; Cheong, J.; et al. Auranofin Enhances Sulforaphane-Mediated Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Hep3B Cells through Inactivation of the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.J.; Chay, K.O.; Yang, S.Y. Native low density lipoprotein increases the production of both nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in the human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, E.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Wilson, L.A.; Unalp, A.; Behling, C.E.; Lavine, J.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Network, N.C.R. Portal chronic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A histologic marker of advanced NAFLD—clinicopathologic correlations from the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research network. Hepatology 2009, 49, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caussy, C.; Hsu, C.; Lo, M.T.; Liu, A.; Bettencourt, R.; Ajmera, V.H.; Bassirian, S.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Richards, L.; et al. Link between gut-microbiome derived metabolite and shared gene-effects with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in NAFLD. Hepatology 2018, 68, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Herpen, N.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V. Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.-H.; Chen, X.-Y.; Hu, Q.-H.; Wang, M.-X.; Jin, R.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Kang, L.-L.; et al. Reactive oxygen species-induced TXNIP drives fructose-mediated hepatic inflammation and lipid accumulation through NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 848–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trauner, M.; Arrese, M.; Wagner, M. Fatty liver and lipotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedossa, P. Pathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.M.; Kim, Y.; Lee, E.S.; Huh, J.H.; Chung, C.H. Caffeic acid ameliorates hepatic steatosis and reduces ER stress in high fat diet–induced obese mice by regulating autophagy. Nutrition 2018, 55, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jeong, J.-M.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, W.; Kim, M.-H.; Choi, W.-M.; Yoo, W.; Lee, J.-H.; Shim, Y.-R.; Yi, H.-S. Pro-inflammatory hepatic macrophages generate ROS through NADPH oxidase 2 via endocytosis of monomeric TLR4–MD2 complex. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Kesarwala, A.H.; Eggert, T.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Kleiner, D.E.; Jin, P.; Stroncek, D.F.; Terabe, M.; Kapoor, V.; ElGindi, M.; et al. NAFLD causes selective CD4+ T lymphocyte loss and promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Nature 2016, 531, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mridha, A.R.; Wree, A.; Robertson, A.A.; Yeh, M.M.; Johnson, C.D.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Haczeyni, F.; Teoh, N.C.-H.; Savard, C.; Ioannou, G.N.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome blockade reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH in mice. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, D.; She, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, N.; Sun, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Wei, Q.; Aa, J.; et al. Silybin inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome assembly through the NAD+/SIRT2 pathway in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mankan, A.K.; Dau, T.; Jenne, D.; Hornung, V. The NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 axis regulates IL-1β processing in neutrophils. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhong, F. Nickel induces interleukin-1β secretion via the NLRP3–ASC–caspase-1 pathway. Inflammation 2014, 37, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-S.; Nakahira, K.; Chung, K.-P.; DeNicola, G.M.; Koo, M.J.; Pabón, M.A.; Rooney, K.T.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ryter, S.W.; Stout-Delgado, H.; et al. NOX4-dependent fatty acid oxidation promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Duan, F.; Hu, J.; Luo, B.; Huang, B.; Lou, X.; Sun, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Yin, S. NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Redox Biol. 2020, 101523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunigan, K.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Locy, M.L.; Wall, S.; Tipple, T.E. The thioredoxin reductase inhibitor auranofin induces heme oxygenase-1 in lung epithelial cells via Nrf2-dependent mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L545–L552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ament, Z.; Masoodi, M.; Griffin, J.L. Applications of metabolomics for understanding the action of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in diabetes, obesity and cancer. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, K.G.; Levorse, V.G.S.; Garcia, M.C.R.; de Souza Basso, B.; Costa, B.P.; Antunes, G.L.; Luft, C.; Haute, G.V.; Xavier, L.L.; Donadio, M.V.F. Octyl gallate induces hepatic steatosis in HepG2 cells through the regulation of SREBP-1c and PPAR-gamma gene expression. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwangbo, H.; Kim, M.Y.; Ji, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Park, C.; Keum, Y.-S.; Hong, S.H.; Cheong, J.; et al. Auranofin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation In Vivo and In Vitro. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111040
Hwangbo H, Kim MY, Ji SY, Kim SY, Lee H, Kim G-Y, Park C, Keum Y-S, Hong SH, Cheong J, et al. Auranofin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation In Vivo and In Vitro. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(11):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111040
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwangbo, Hyun, Min Yeong Kim, Seon Yeong Ji, So Young Kim, Hyesook Lee, Gi-Young Kim, Cheol Park, Young-Sam Keum, Su Hyun Hong, Jaehun Cheong, and et al. 2020. "Auranofin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation In Vivo and In Vitro" Antioxidants 9, no. 11: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111040
APA StyleHwangbo, H., Kim, M. Y., Ji, S. Y., Kim, S. Y., Lee, H., Kim, G.-Y., Park, C., Keum, Y.-S., Hong, S. H., Cheong, J., & Choi, Y. H. (2020). Auranofin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation In Vivo and In Vitro. Antioxidants, 9(11), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9111040