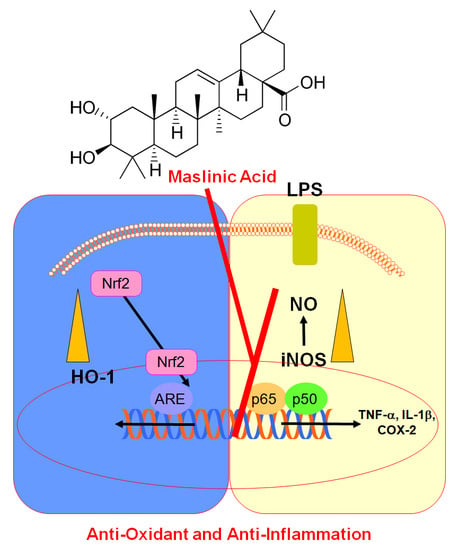
Maslinic Acid Ameliorates Inflammation via the Downregulation of NF-κB and STAT-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. Animal Care, LPS-Injected Lung Injury Model, and Analysis of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF)
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISA) for iNOS, PGE2, HO-1, STAT-1 (Both Total and Phosphorylated Forms), TNF-α, and IL-1β
2.4. Nitrite Determination
2.5. Subcellular Fractionation and Western Blotting
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.7. Plasmid Transfection
2.8. ARE Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.9. Histopathological Examination with Hematoxylin and Eosin H&E Staining
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of MA on Levels of iNOS and COX-2 in LPS-Treated HUVECs
3.2. Effect of MA on NF-κB Activity, STAT-1 Phosphorylation, and the Level of HO-1 Protein in LPS-Treated HUVECs
3.3. Effect of MA on Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2, ARE Reporter Activity, and Anti-Inflammatory Action
3.4. Effect of MA on TNF-α and iNOS Protein in an LPS-Induced Lung Injury Model
4. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chau, L.Y. Heme oxygenase-1: Emerging target of cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waza, A.A.; Hamid, Z.; Ali, S.; Bhat, S.A.; Bhat, M.A. A review on heme oxygenase-1 induction: Is it a necessary evil. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoyi, K.; Lee, T.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C. Heme-oxygenase-1 induction and carbon monoxide-releasing molecule inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced high-mobility group box 1 release in vitro and improve survival of mice in LPS- and cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis model in vivo. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Arfuso, F.; Bian, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Antioxidant response elements: Discovery, classes, regulation and potential applications. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Zurita, F.J.; Rufino-Palomares, E.E.; Lupianez, J.A.; Cascante, M. Maslinic acid, a natural triterpene from Olea europaea L., induces apoptosis in HT29 human colon-cancer cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Cancer Lett. 2009, 273, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Mena, G.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, M.; Juan, M.E.; Planas, J.M. Maslinic acid, a natural phytoalexin-type triterpene from olives--a promising nutraceutical? Molecules 2014, 19, 11538–11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moneriz, C.; Mestres, J.; Bautista, J.M.; Diez, A.; Puyet, A. Multi-targeted activity of maslinic acid as an antimalarial natural compound. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablos, L.M.; Gonzalez, G.; Rodrigues, R.; Garcia Granados, A.; Parra, A.; Osuna, A. Action of a pentacyclic triterpenoid, maslinic acid, against Toxoplasma gondii. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montilla, M.P.; Agil, A.; Navarro, M.C.; Jimenez, M.I.; Garcia-Granados, A.; Parra, A.; Cabo, M.M. Antioxidant activity of maslinic acid, a triterpene derivative obtained from Olea europaea. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Guan, T.; Qian, Y.; Huang, M.; Tang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. Anti-inflammatory effects of maslinic acid, a natural triterpene, in cultured cortical astrocytes via suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 672, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, W.; Yang, S.; Cho, S.H.; Baek, M.C.; Song, G.Y.; Bae, J.S. Suppressive effects of rare ginsenosides, Rk1 and Rg5, on HMGB1-mediated septic responses. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.C.; Bae, J.S. Pelargonidin Protects Against Renal Injury in a Mouse Model of Sepsis. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Lee, C.; Yang, S.; Ku, S.K.; Bae, J.S. Renal protective effects of zingerone in a mouse model of sepsis. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Jeong, M.H.; Kim, K.J.; Baek, S.H.; Hur, J.S.; Son, Y.J. The Extract of Ramalina litoralis Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2018, 23, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.H.; Kang, N.H.; Mukherjee, S.; Yun, J.W. Theobromine, a Methylxanthine in Cocoa Bean, Stimulates Thermogenesis by Inducing White Fat Browning and Activating Brown Adipocytes. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2018, 23, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, G.E.; Song, G.Y.; Bae, J.S. Pulmonary protective functions of rare ginsenoside Rg4 on particulate matter-induced inflammatory responses. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoyi, K.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, H.J.; Lee, S.S.; Ahn, S.K.; Yun-Choi, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Seo, H.G.; et al. HO-1 and JAK-2/STAT-1 signals are involved in preferential inhibition of iNOS over COX-2 gene expression by newly synthesized tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, CKD712, in cells activated with lipopolysacchride. Cell Signal. 2008, 20, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoyi, K.; Nizamutdinova, I.T.; Jang, H.J.; Mun, L.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C. Carbon monoxide from CORM-2 reduces HMGB1 release through regulation of IFN-beta/JAK2/STAT-1/INOS/NO signaling but not COX-2 in TLR-activated macrophages. Shock 2010, 34, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.H.; Hull, R.; Morton, D.; Pfister, R.; Rabemampianina, Y.; Smith, D.; Vidal, J.M.; van de Vorstenbosch, C. A good practice guide to the administration of substances and removal of blood, including routes and volumes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.; Lee, T.; Song, K.S.; Yang, E.J.; Bae, J.S. Isolation, Synthesis, and Antisepsis Effects of a C-Methylcoumarinochromone Isolated from Abronia nana Cell Culture. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Park, S.Y.; Yoo, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.W.; Seo, Y.K.; Park, E.K.; Kim, I.S.; Bae, J.S. Macrophagic Stabilin-1 Restored Disruption of Vascular Integrity Caused by Sepsis. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1776–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullaert, A.; Bonnet, M.C.; Pasparakis, M. NF-kappaB in the regulation of epithelial homeostasis and inflammation. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez Martin, A.; de la Puerta Vazquez, R.; Fernandez-Arche, A.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V. Supressive effect of maslinic acid from pomace olive oil on oxidative stress and cytokine production in stimulated murine macrophages. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Guan, T.; Tang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. Maslinic acid, a natural triterpenoid compound from Olea europaea, protects cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, W.H.; Lim, Y.M. Mechanistic Perspectives of Maslinic Acid in Targeting Inflammation. Biochem. Res Int. 2015, 2015, 279356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, W.; Kim, J.; Park, E.K.; Bae, J.-S. Maslinic Acid Ameliorates Inflammation via the Downregulation of NF-κB and STAT-1. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020106
Lee W, Kim J, Park EK, Bae J-S. Maslinic Acid Ameliorates Inflammation via the Downregulation of NF-κB and STAT-1. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Wonhwa, Jaehong Kim, Eui Kyun Park, and Jong-Sup Bae. 2020. "Maslinic Acid Ameliorates Inflammation via the Downregulation of NF-κB and STAT-1" Antioxidants 9, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020106
APA StyleLee, W., Kim, J., Park, E. K., & Bae, J. -S. (2020). Maslinic Acid Ameliorates Inflammation via the Downregulation of NF-κB and STAT-1. Antioxidants, 9(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020106