Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2. Feed Preparation
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.4. Filtration Configuration
2.5. Membrane Fouling Resistance Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Characterizations
3.1.1. Membrane Morphology
3.1.2. Membrane Pore Size and Distribution
3.1.3. Surface Contact Angle
3.1.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
3.1.5. Surface Chemical Composition
3.1.6. Clean Water Permeability
3.2. Effect of Exposure Time on Membrane Hydraulic Performance
3.2.1. Permeance Recovery Analysis
3.2.2. Rejection Performance
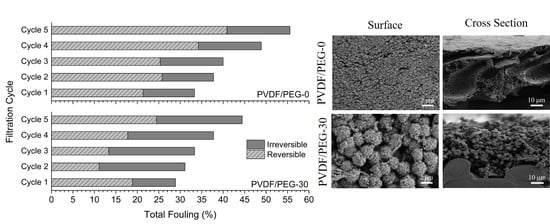
3.2.3. Fouling Resistance Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akdemir, E.O.; Ozer, A. Investigation of two ultrafiltration membranes for treatment of olive oil mill wastewater. Desalination 2009, 249, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoju, T.; Ahmad, A.; Ooi, B. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane for oil rejection from oily wastewater: A performance review. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 14, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, S. Effect of polymer surface modification on polymer–protein interaction via hydrophilic polymer grafting. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, N.; Masuelli, M.; Marchese, J. Effect of hydrophilicity on fouling of an emulsified oil wastewater with PVDF/PMMA membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Wang, H.H.; Di Nicolo, E.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Understanding the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) effect during the fabrication of microporous PVDF membranes via thermally induced phase separation (TIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuvers, A.; Van den Berg, J.; Smolders, C. Formation of membranes by means of immersion precipitation: Part I. A model to describe mass transfer during immersion precipitation. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 34, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, N.; Venault, A.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Bouyer, D.; Drioli, E.; Tavajohi Hassan Kiadeh, N. Investigating the potential of membranes formed by the vapor induced phase separation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 597, 17601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yushkin, A.A.; Bakhtin, D.; Efimov, M.; Karpacheva, G.; Volkov, A. Preparation of Polyacrylonitrile Membranes by Vapor Induced Phase Separation. In Key Engineering Materials; Nepal Government Census: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- AlMarzooqi, F.A.; Bilad, M.; Arafat, H.A. Development of PVDF membranes for membrane distillation via vapour induced crystallisation. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 77, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H. Effect of PEG additive on membrane formation by phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 138, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljoughi, E.; Amirilargani, M.; Mohammadi, T. Effect of PEG additive and coagulation bath temperature on the morphology, permeability and thermal/chemical stability of asymmetric CA membranes. Desalination 2010, 262, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part I: Production Techniques with Polysulfone and Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride). Polymers 2019, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yunos, M.Z.; Harun, Z.; Basri, H.; Ismail, A.F. Studies on fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) on polysulfone membranes: Effect of polyethylene glycol (PEG). Desalination 2014, 333, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, B.; Yoon, J.K.; Kim, B.; Rhee, H.-W. Effect of molecular weight of polymeric additives on formation, permeation properties and hypochlorite treatment of asymmetric polyacrylonitrile membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavukkandy, M.O.; Bilad, M.R.; Giwa, A.; Hasan, S.W.; Arafat, H.A. Leaching of PVP from PVDF/PVP blend membranes: Impacts on membrane structure and fouling in membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 51, 4328–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folgado, E.; Ladmiral, V.; Semsarilar, M. Towards permanent hydrophilic PVDF membranes. Amphiphilic PVDF-b-PEG-b-PVDF triblock copolymer as membrane additive. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 2020, 109708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbelia, L.; Bilad, M.R.; Vankelecom, I.F. Gradual PVP leaching from PVDF/PVP blend membranes and its effects on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y. Upgrading polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes by blending with amphiphilic block copolymers: Beyond surface segregation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, W.; Chu, Z. Structure and Performance of Poly (vinylidene chloride-co-vinyl chloride) Porous Membranes with Different Additives. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Fan, H.; Dong, Y.; Song, Y.; Han, H. Effects of exposure time on variations in the structure and hydrophobicity of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes prepared via vapor-induced phase separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7872–7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.K.; Bilad, M.; Nordin, N.; Faungnawakij, K.; Narkkun, T.; Wang, D.K.; Mahlia, T.; Jaafar, J. Effect of membrane properties on tilted panel performance of microalgae biomass filtration for biofuel feedstock. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2020, 120, 109666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Al Marzooqi, F.A.; Arafat, H.A. Shrinkage, defect and membrane distillation performance of composite PVDF membranes. Desalination 2015, 376, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Subramaniam, D.D.; Shamsuddin, N.; Khan, A.L.; Jaafar, J.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D. Low-pressure submerged membrane filtration for potential reuse of detergent and water from laundry wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, W.; Ding, A.; Morgenroth, E.; Derlon, N.; Desmond, P.; Burkhardt, M.; Wu, B.; Fane, A.G. Gravity-driven membrane filtration for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Water Res. 2019, 149, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Witte, P.; Dijkstra, P.; Van den Berg, J.; Feijen, J. Phase separation processes in polymer solutions in relation to membrane formation. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolders, C.; Reuvers, A.; Boom, R.; Wienk, I. Microstructures in phase-inversion membranes. Part 1. Formation of macrovoids. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boom, R.; Wienk, I.; Van den Boomgaard, T.; Smolders, C. Microstructures in phase inversion membranes. Part 2. The role of a polymeric additive. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venault, A.; Chang, Y.; Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Surface anti-biofouling control of PEGylated poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes via vapor-induced phase separation processing. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, T.; Russo, F.; Figoli, A. The formation of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes with tailored properties via vapour/non-solvent induced phase separation. Membranes 2018, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blundell, D.; Keller, A. Nature of self-seeding polyethylene crystal nuclei. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 1968, 2, 301–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, R.; Luo, F.; Faraj, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ju, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.-Y. Preparation of high strength poly (vinylidene fluoride) porous membranes with cellular structure via vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Wang, D.-M.; Deratani, A.; Quémener, D.; Bouyer, D.; Lai, J.-Y. Insight into the preparation of poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes by vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswaran, S.; Ngo, H.; Visvanathan, C.; Sundarvadivel, M. Wastewater recycle, reuse, and reclamation. Conv. Water Treat. Technol. 2009, 1, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, H.; Sourirajan, S. The origin of large pores on aromatic polyamide membrane surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 160, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Wright, C. Membrane Fabrication; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.F.; Xu, Z.L.; Yang, H.; Feng, C.P.; Shi, J.H. Hydrophilic microporous PES membranes prepared by PES/PEG/DMAc casting solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljoughi, E.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, T. Effect of preparation variables on morphology and pure water permeation flux through asymmetric cellulose acetate membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M. Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, R.; Goh, P.; Ismail, A.; Lau, W.; Ng, B.; Othman, N.; Noor, A.; Yusoff, M. Deacidification of crude palm oil using PVA-crosslinked PVDF membrane. J. Food Eng. 2015, 166, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, M.; Izati, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Zolkhiflee, N.; Nordin, N.A.H.; Lau, W.J.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Arahman, N.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Development of A Novel Corrugated Polyvinylidene difluoride Membrane via Improved Imprinting Technique for Membrane Distillation. Polymers 2019, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawi, N.I.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Mavukkandy, M.O.; Putra, Z.A.; Wirzal, M.D.H.; Jaafar, J.; Khan, A.L. Exploiting the Interplay between Liquid-Liquid Demixing and Crystallization of the PVDF Membrane for Membrane Distillation. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Xuan, H.; Qin, A.; Liu, D.; He, C. Improved antifouling property of PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with plasma treated PVDF powder. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 64526–64533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orooji, Y.; Faghih, M.; Razmjou, A.; Hou, J.; Moazzam, P.; Emami, N.; Aghababaie, M.; Nourisfa, F.; Chen, V.; Jin, W. Nanostructured mesoporous carbon polyethersulfone composite ultrafiltration membrane with significantly low protein adsorption and bacterial adhesion. Carbon 2017, 111, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Kong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Lei, J. Novel solid–solid phase change materials with biodegradable trihydroxy surfactants for thermal energy storage. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68881–68889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, M.; Bilad, M.R.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Marbelia, L.; Vankelecom, I. Membrane development for improved performance of a magnetically induced vibration system for anaerobic sludge filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, B.; Ghoshal, A.; Purkait, M. Effect of molecular weight of PEG on membrane morphology and transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 309, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.M.; Gekas, V.; Trägårdh, G. Study of membrane compaction and its influence on ultrafiltration water permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, K.; Fritsch, D.; Koll, J.; Tjahjawiguna, C. Influence of inorganic fillers on the compaction behaviour of porous polymer based membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 233, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Bokhary, A.; Maleki, E.; Liao, B. A review of membrane fouling and its control in algal-related membrane processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollom, M.N.; Rathilal, S. Fouling and Cleaning in Osmotically Driven Membranes. Osmotically Driven Membrane Processes: Approach, Development and Current Status; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 179–205. [Google Scholar]
- Shieh, J.-J.; Chung, T.-S.; Wang, R.; Srinivasan, M.; Paul, D.R. Gas separation performance of poly (4-vinylpyridine)/polyetherimide composite hollow fibers. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 182, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Jin, J.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2071–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chiang, C.-H.; Chang, H.-Y.; Hung, W.-S.; Chang, Y. Graphene oxide/PVDF VIPS membranes for switchable, versatile and gravity-driven separation of oil and water. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyuhara, T.; Hanamoto, Y.; Miyoshi, T.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Influence of membrane properties on physically reversible and irreversible fouling in membrane bioreactors. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Majid, M.; Ooi, B. Functionalized PSf/SiO2 nanocomposite membrane for oil-in-water emulsion separation. Desalination 2011, 268, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanangamudi, A.; Dumée, L.F.; Duke, M.C.; Yang, X. Nanofiber composite membrane with intrinsic janus surface for reversed-protein-fouling ultrafiltration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18328–18337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Yu, S.; Shi, W.; Wang, S.; Sun, N.; Jin, L.; Ma, C. Estimation of fouling stages in separation of oil/water emulsion using nano-particles Al2O3/TiO2 modified PVDF UF membranes. Desalination 2013, 319, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barambu, N.U.; Bilad, M.R.; Wibisono, Y.; Jaafar, J.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Khan, A.L. Membrane Surface Patterning as a Fouling Mitigation Strategy in Liquid Filtration: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliseus, A.; Bilad, M.R.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Putra, Z.A.; Wirzal, M.D.H. Tilted membrane panel: A new module concept to maximize the impact of air bubbles for membrane fouling control in microalgae harvesting. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, R.; Bilad, M.R.; Laziz, A.M.; Nordin, N.A.H.M.; Jusoh, N.; Putra, Z.A.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Jaafar, J. Finned spacer for efficient membrane fouling control in produced water filtration. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razak, N.N.A.N.; Rahmawati, R.; Bilad, M.R.; Pratiwi, A.E.; Elma, M.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Jaafar, J.; Lam, M.K. Finned spacer for enhancing the impact of air bubbles for membrane fouling control in Chlorella vulgaris filtration. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Nawi, M.; Izati, N.; Samsuri, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Shamsuddin, N.; Khan, A.L.; Jaafar, J.; Nordin, N.A.H. Patterned Membrane in an Energy-Efficient Tilted Panel Filtration System for Fouling Control in Activated Sludge Filtration. Polymers 2020, 12, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Membrane | Composition (at %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | F | O | |
| PVDF/PEG-0 | 50.79 | 46.98 | 2.22 |
| PVDF/PEG-5 | 51.37 | 45.38 | 3.25 |
| PVDF/PEG-15 | 52.31 | 43.72 | 3.97 |
| PVDF/PEG-30 | 57.78 | 37.25 | 4.97 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mat Nawi, N.I.; Chean, H.M.; Shamsuddin, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Khan, A.L. Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060121
Mat Nawi NI, Chean HM, Shamsuddin N, Bilad MR, Narkkun T, Faungnawakij K, Khan AL. Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment. Membranes. 2020; 10(6):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060121
Chicago/Turabian StyleMat Nawi, Normi Izati, Ho Min Chean, Norazanita Shamsuddin, Muhammad Roil Bilad, Thanitporn Narkkun, Kajornsak Faungnawakij, and Asim Laeeq Khan. 2020. "Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment" Membranes 10, no. 6: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060121
APA StyleMat Nawi, N. I., Chean, H. M., Shamsuddin, N., Bilad, M. R., Narkkun, T., Faungnawakij, K., & Khan, A. L. (2020). Development of Hydrophilic PVDF Membrane Using Vapour Induced Phase Separation Method for Produced Water Treatment. Membranes, 10(6), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060121