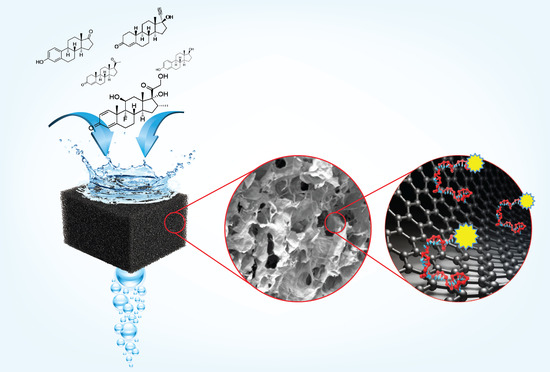
Graphene Oxide Membrane Immobilized Aptamer as a Highly Selective Hormone Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. ssDNA Aptamer
2.2. Graphene Oxide Synthesis
2.3. Functionalized rGO@polyethyleneimine Preparation
2.4. Apparatus and Characterizations
2.5. Developed Aptamer Specificity and Selectively Measurement
2.6. Adsorption Efficiency
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluorescence Intensity Dependency on Graphene Oxide Concentration
3.2. Characterization of rGO/PEI Membrane
3.3. Mechanism of DNA Adsorption on Reduced Graphene Oxide Foam
3.3.1. Binding Mechanism
3.3.2. Adsorption Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W.; Calizo, I.; Teweldebrhan, D.; Miao, F.; Lau, C.N. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.; Novoselov, K. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. High-efficiency loading and controlled release of doxorubicin hydrochloride on graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 17554–17558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisebois, P.; Siaj, M. Harvesting graphene oxide–years 1859 to 2019: A review of its structure, synthesis, properties and exfoliation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1517–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermoune, A.; Chari, T.; Popescu, F.; Sabri, S.S.; Guillemette, J.; Skulason, H.S.; Szkopek, T.; Siaj, M. Chemical vapor deposition synthesis of graphene on copper with methanol, ethanol, and propanol precursors. Carbon 2011, 49, 4204–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisebois, P.P.; Kuss, C.; Schougaard, S.B.; Izquierdo, R.; Siaj, M. New Insights into the Diels–Alder Reaction of Graphene Oxide. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 5849–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagier, L. Ecotoxicité comparative de l’oxyde de graphène et d’autres nanoparticules de carbone chez des organismes aquatiques modèles: D’une évaluation en conditions monospécifiques vers l’étude d’une chaîne trophique expérimentale. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier - Toulouse III, Toulouse, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bissessur, R.; Scully, S.F. Intercalation of solid polymer electrolytes into graphite oxide. Solid State Ion. 2007, 178, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, O.C.; Nguyen, S.T. Graphene oxide, highly reduced graphene oxide, and graphene: Versatile building blocks for carbon-based materials. Small 2010, 6, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Robinson, J.T.; Sun, X.; Dai, H. PEGylated nanographene oxide for delivery of water-insoluble cancer drugs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10876–10877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Y. Graphene and graphene oxide: Biofunctionalization and applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.H.; Yang, H.H.; Zhu, C.L.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.N. A graphene platform for sensing biomolecules. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4879–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangiovanni, D.G.; Gueorguiev, G.; Kakanakova-Georgieva, A. Ab initio molecular dynamics of atomic-scale surface reactions: Insights into metal organic chemical vapor deposition of AlN on graphene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 17751–17761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyenola, C.; Stafstrom, S.; Schmidt, S.; Hultman, L.; Gueorguiev, G.K. Carbon fluoride, CF x: Structural diversity as predicted by first principles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6514–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianco, A. Graphene: Safe or toxic? The two faces of the medal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4986–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoda, M.; Dudek, I.; Jarosz, A.; Szukiewicz, D. Graphene: One material, many possibilities—application difficulties in biological systems. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y. Molecular-level dispersion of graphene into poly (vinyl alcohol) and effective reinforcement of their nanocomposites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2297–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, K.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Nutt, S. Covalent polymer functionalization of graphene nanosheets and mechanical properties of composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7098–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, S.; Bekyarova, E.; Itkis, M.E.; McWilliams, J.L.; Hamon, M.A.; Haddon, R.C. Solution properties of graphite and graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7720–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehennaoui, S.; Poorahong, S.; Jimenez, G.C.; Siaj, M. Selection of high affinity aptamer-ligand for dexamethasone and its electrochemical biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized graphene oxide as an efficient gene delivery vector. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7736–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, J.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced chemotherapy efficacy by sequential delivery of siRNA and anticancer drugs using PEI-grafted graphene oxide. Small 2011, 7, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, D.; Lin, C.-T.; Li, J.; Lin, Y. Aptamer/graphene oxide nanocomplex for in situ molecular probing in living cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9274–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chu, X.; Chen, T.; Ge, J.; Yu, R. Graphene oxide–peptide conjugate as an intracellular protease sensor for caspase-3 activation imaging in live cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7065–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Shi, W.; Li, X.; Ma, H. A graphene oxide–peptide fluorescence sensor tailor-made for simple and sensitive detection of matrix metalloproteinase 2. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10680–10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Gao, W.; Yan, F.; Ji, H.; Ju, H. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer between quantum dots and graphene oxide for sensing biomolecules. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5511–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Graphene-based membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5016–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Lin, Y.Y.; Mattevi, C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.A.; Chen, I.S.; Chen, C.W.; Chhowalla, M. Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, T.; Godet, C.; Bouree, J.; Drevillon, B.; Conde, J. Radiative and nonradiative recombination in polymerlike a− C: H films. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Basko, D.M. Raman spectroscopy as a versatile tool for studying the properties of graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.K.; Tang, Y.; Crespi, V.H.; Eklund, P.C. Nondispersive Raman D band activated by well-ordered interlayer interactions in rotationally stacked bilayer graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 241406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, R.; Kong, W.; Sun, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Lv, M.; Song, S.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Hao, R. Highly stable graphene-based nanocomposite (GO–PEI–Ag) with broad-spectrum, long-term antimicrobial activity and antibiofilm effects. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17617–17629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Zou, L.; Ye, B. Nonenzymatic H2O2 Electrochemical Sensor Based on SnO2-NPs Coated Polyethylenimine Functionalized Graphene. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Song, B.; Li, D.; Zhu, C.; Qi, W.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Fang, H.; Fan, C. A graphene nanoprobe for rapid, sensitive, and multicolor fluorescent DNA analysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilibana, M.P.; Citartan, M.; Yeoh, T.S.; Rozhdestvensky, T.S.; Tang, T.-H. Aptamers as the Agent in Decontamination Assays (Apta-Decontamination Assays): From the Environment to the Potential Application In Vivo. J. Nucleic Acids 2017, 2017, 3712070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegyi, G.; Kardos, J.; Kovács, M.; Málnási-Csizmadia, A.; Nyitray, L.; Pál, G.; Radnai, L.; Reményi, A.; Venekei, I. Introduction to Practical Biochemistry; Eötvös Loránd University: Budapest, Hungary, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, J.P.; Arulanandam, B.P.; Matta, L.L.; Weis, A.; Valdes, J.J. Biosensor Recognition Elements; Texas Univ at San Antonio Dept of Biology: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, N.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Albolkany, M.K.; Liu, B. Graphite phase carbon nitride based membrane for selective permeation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akpotu, S.O.; Lawal, I.A.; Moodley, B.; Ofomaja, A.E. Covalently linked graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide-methoxylether polyethylene glycol functionalised silica for scavenging of estrogen: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakulski, D.; Czepa, W.; Witomska, S.; Aliprandi, A.; Pawluć, P.; Patroniak, V.; Ciesielski, A.; Samorì, P. Graphene oxide-branched polyethylenimine foams for efficient removal of toxic cations from water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9384–9390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chergui, S.; Rhili, K.; Poorahong, S.; Siaj, M. Graphene Oxide Membrane Immobilized Aptamer as a Highly Selective Hormone Removal. Membranes 2020, 10, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090229
Chergui S, Rhili K, Poorahong S, Siaj M. Graphene Oxide Membrane Immobilized Aptamer as a Highly Selective Hormone Removal. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090229
Chicago/Turabian StyleChergui, Siham, Khaled Rhili, Sujittra Poorahong, and Mohamed Siaj. 2020. "Graphene Oxide Membrane Immobilized Aptamer as a Highly Selective Hormone Removal" Membranes 10, no. 9: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090229
APA StyleChergui, S., Rhili, K., Poorahong, S., & Siaj, M. (2020). Graphene Oxide Membrane Immobilized Aptamer as a Highly Selective Hormone Removal. Membranes, 10(9), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090229