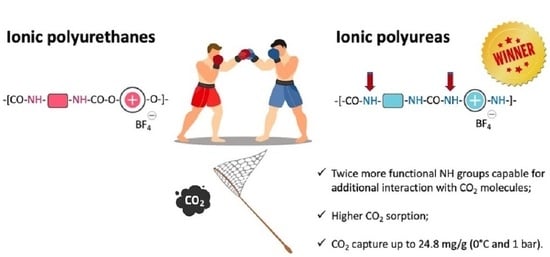
Ionic Polyureas—A Novel Subclass of Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for CO2 Capture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Ionic Diamine 3,3-Bis(4-Aminophenyl)-1-Ethylquinuclidin-1-Ium Iodide (4)
2.3. Synthesis of 3-Amino-1-(5-(3-Aminoquinuclidin-1-Ium-1-Yl)Pentyl)-Quinuclidin-1-Ium Bromide (5)
2.4. Polycondensation
2.5. Quaternization of PUR.4
2.6. Ion Exchange
2.7. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Ionic Diamines
3.2. Synthesis of Ionic Polyureas
3.3. Properties of Ionic Polyureas
3.3.1. Solubility and Molecular Weights
3.3.2. Thermal Properties
3.3.3. CO2 Sorption
3.3.4. Recycling Experiments
3.4. Future Outlook
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobson, M.Z. Review of solutions to global warming, air pollution, and energy security. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 148–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Moufouma-Okia, W.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A. Recent Progress and Emerging Topics on Weather and Climate Extremes Since the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2018, 43, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, I. Green House Gas Warming. In Climate Variability and Sunspot Activity; Springer Atmospheric Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 187–195. ISBN 978-3-319-77106-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zulfiqar, S.; Sarwar, M.I.; Mecerreyes, D. Polymeric ionic liquids for CO2 capture and separation: Potential, progress and challenges. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 6435–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.; Antonietti, M. Poly(ionic liquid)s: Polymers expanding classical property profiles. Polymer 2011, 52, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laschewsky, A. Recent trends in the synthesis of polyelectrolytes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Mecerreyes, D.; Antonietti, M. Poly(ionic liquid)s: An update. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1009–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecerreyes, D. Polymeric ionic liquids: Broadening the properties and applications of polyelectrolytes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1629–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obadia, M.M.; Drockenmuller, É. Poly(1,2,3-triazolium)s: A new class of functional polymer electrolytes. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2433–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Weber, J.; Yuan, J. Poly(ionic liquid)s: Platform for CO2 capture and catalysis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 16, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaplov, A.S.; Marcilla, R.; Mecerreyes, D. Recent Advances in Innovative Polymer Electrolytes based on Poly(ionic liquid)s. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 175, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kárászová, M.; Kačírková, M.; Friess, K.; Izak, P. Progress in separation of gases by permeation and liquids by pervaporation using ionic liquids: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasib-Ur-Rahman, M.; Siaj, M.; Larachi, F. Ionic liquids for CO2 capture—Development and progress. Chem. Eng. Process. Process. Intensif. 2010, 49, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, H.; Sun, W.; Plancher, H.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y.; Tang, J. Poly(ionic liquid)s: A new material with enhanced and fast CO2 absorption. Chem. Commun. 2005, 3325–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.L.; Duczinski, R.B.; Rojas, M.F.; Fialho, M.C.C.; Carreño, L.Á.; Chaban, V.V.; Vecchia, F.D.; Einloft, S. Cellulose based poly(ionic liquids): Tuning cation-anion interaction to improve carbon dioxide sorption. Fuel 2018, 211, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, S.M.; Shaplov, A.S.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Mecerreyes, D.; Sardon, H.; Zulfiqar, S.; Suárez-García, F.; Vygodskii, Y.S. Ionic Polyurethanes as a New Family of Poly(ionic liquid)s for Efficient CO2 Capture. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 2814–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Anderson, J.L. Selective extraction of CO2 from simulated flue gas using polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings in solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4517–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, R.S.; Kumbharkar, S.C.; Kharul, U.K. Polymeric ionic liquids (PILs): Effect of anion variation on their CO2 sorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privalova, E.I.; Karjalainen, E.; Nurmi, M.; Mäki-Arvela, P.; Eranen, K.; Tenhu, H.; Murzin, D.Y.; Mikkola, J.-P. Imidazolium-Based Poly(ionic liquid)s as New Alternatives for CO2 Capture. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, A.; Yuan, J.; Antonietti, M.; Weber, J. Enhanced Carbon Dioxide Adsorption by a Mesoporous Poly(ionic liquid). ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Li, Q.; Li, N.; Man, Z.; Pu, C.; Asumana, C.; Chen, X. Synthesis of new crosslinked porous ammonium-based poly(ionic liquid) and application in CO2 adsorption. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Huang, J. Benzimidazole-based hyper-cross-linked poly(ionic liquid)s for efficient CO2 capture and conversion. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Antonietti, M.; Yuan, J. Poly(Ionic Liquid)-Derived Carbon with Site-Specific N-Doping and Biphasic Heterojunction for Enhanced CO2 Capture and Sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7557–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Lin, H.; Grygiel, K.; Yuan, J. Main-chain poly(ionic liquid)-derived nitrogen-doped micro/mesoporous carbons for CO 2 capture and selective aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Wang, P.; Luo, J.; Fransaer, J.; De Vos, D.E.; Luo, Z.-H. Poly(ionic liquid)-Based Nanocomposites and Their Performance in CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Tang, H.L.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. Amine-functionalized poly(ionic liquid) brushes for carbon dioxide adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Qu, R.; Han, X.; Lin, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.J. The Counterion Effect of Imidazolium-Type Poly(ionic liquid) Brushes on Carbon Dioxide Adsorption. ChemPlusChem 2019, 84, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.-G.; Yao, B.-J.; Jiang, W.-L.; Li, J.-T.; Fu, Q.-J.; Li, Y.-A.; Liu, Z.-H.; Ma, J.-P.; Dong, Y.-B. Bifunctional Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid Decorated UiO-67 Type MOF for Selective CO2 Adsorption and Catalytic Property for CO2 Cycloaddition with Epoxides. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Jiang, H.-L. Incorporation of Imidazolium-Based Poly(ionic liquid)s into a Metal–Organic Framework for CO2 Capture and Conversion. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, H.; Vardhan, H.; Aguila, B.; Zhong, C.; Perman, J.A.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Nafady, A.; Ma, S. Facile Approach to Graft Ionic Liquid into MOF for Improving the Efficiency of CO2 Chemical Fixation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27124–27130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yu, J.; Peng, S.; Sheng, K.; Zhang, H. Poly(ionic liquid)-Modified Metal Organic Framework for Carbon Dioxide Adsorption. Polymers 2020, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Shan, W.; Wang, Q.; Ling, X.; Li, G.; Lyu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J. Ordered Porous Poly(ionic liquid) Crystallines: Spacing Confined Ionic Surface Enhancing Selective CO2 Capture and Fixation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6031–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Tang, H.; Sun, W.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y. Poly(ionic liquid)s as new materials for CO2 absorption. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 5477–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shen, Y.; Radosz, M.; Sun, W. Isothermal Carbon Dioxide Sorption in Poly(ionic liquid)s. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 9113–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, P.G.; Livoti, L.; Giannetto, M.; Gulino, A.; Schiavo, S.L.; Cardiano, P. Very fast CO2 response and hydrophobic properties of novel poly(ionic liquid)s. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 8861–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, P.G.; Livoti, L.; Schiavo, S.L.; Cardiano, P. Fast and reversible CO2 quartz crystal microbalance response of vinylimidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid)s. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, H.; Sun, W.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y. Low-pressure CO2 sorption in ammonium-based poly(ionic liquid)s. Polymer 2005, 46, 12460–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, T.O.; Aquino, A.S.; Vecchia, F.D.; Bernard, F.L.; Seferin, M.; Menezes, S.C.; Ligabue, R.; Einloft, S. Syntheses and characterization of new poly(ionic liquid)s designed for CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18164–18170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Wang, R.-M. Novel imidazolium-based poly(ionic liquid)s: Preparation, characterization, and absorption of CO2. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.L.; Polesso, B.B.; Cobalchini, F.W.; Donato, A.J.; Seferin, M.; Ligabue, R.; Chaban, V.V.; Nascimento, J.F.D.; Vecchia, F.D.; Einloft, S. CO2 capture: Tuning cation-anion interaction in urethane based poly(ionic liquids). Polymer 2016, 102, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiya, D.; Imanishi, M.; Saitow, K.-I. Solvation of Esters and Ketones in Supercritical CO2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-B.; Kang, Y.-H.; Shi, Y.-Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.-Q. Highly Selective Capture of the Greenhouse Gas CO2 in Polymers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3077–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vygodskii, Y.S.; Churochkina, N.A.; Panova, T.A.; Fedotov, Y.A. Novel condensation functional polymers having highly basic groups. React. Funct. Polym. 1996, 30, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuehui, S.; Yu-Kun, Y.; Fengcai, L. Novel polyimide ionene: Synthesis and characterization of polyimides containing aromatic bipyridinium salt. Polymer 1997, 38, 4737–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yang, Y.-K.; Lu, F. Synthesis and Properties of Ionic, Rigid-Rod, and Thermally Stable Polyimides Containing Bipyridinium Triflates. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 4291–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, Q.; Anderson, J.L.; Varanasi, S.; Coleman, M.R. Synthesis of copolyimides based on room temperature ionic liquid diamines. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 4036–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternbach, L.H.; Kaiser, S. Antispasmodics. I. Bicyclic Basic Alcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 2215–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, F. Spectragryph-Optical Spectroscopy Software, Version 1.2.9. 2019. Available online: http://www.effemm2.de/spectragryph/ (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Span, R.; Wagner, W. A New Equation of State for Carbon Dioxide Covering the Fluid Region from the Triple-Point Temperature to 1100 K at Pressures up to 800 MPa. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1996, 25, 1509–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrido, J.; Linares-Solano, A.; Martín-Martínez, J.M.; Molina-Sabio, M.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F.; Torregrosa, R. Use of nitrogen vs. carbon dioxide in the characterization of activated carbons. Langmuir 1987, 3, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wajert, J.C.; Anderson, J.L. Polymeric Ionic Liquids as CO2Selective Sorbent Coatings for Solid-Phase Microextraction. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.-W.; Moore, R.B.; Colby, R.H.; Long, T.E. Polyurethanes Containing an Imidazolium Diol-Based Ionic-Liquid Chain Extender for Incorporation of Ionic-Liquid Electrolytes. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, E.D.; Mayton, R.D.; Ntai, I.; Davis, J.H. CO(2) capture by a task-specific ionic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennecke, J.F.; Gurkan, B. Ionic Liquids for CO2 Capture and Emission Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.L.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Polesso, B.B.; Donato, A.J.; Seferin, M.; Chaban, V.V.; Vecchia, F.D.; Einloft, S. New cellulose based ionic compounds as low-cost sorbents for CO2 capture. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 149, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.M.; He, K.G.; Zhang, H.; Xin, F. Effect of Swelling on Carbon Dioxide Adsorption by Poly(Ionic Liquid)s. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2012, 30, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulfiqar, S.; Karadas, F.; Park, J.; Deniz, E.; Stucky, G.D.; Jung, Y.; Atilhan, M.; Yavuz, C.T. Amidoximes: Promising candidates for CO2 capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4528–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-F.; Huang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Tao, D.-J.; Jiang, D.; Dai, S. Multi-Molar Absorption of CO2 by the Activation of Carboxylate Groups in Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7166–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| No | Abbrev. | Poly(Ionic Liquid) | Mw, (g/mol) a | Mw/Mn a | Tg (°C) b | Tonset (°C) c | Tonset (°C) d | CO2 Uptake, (mg/g) e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ionic polyureas (PURs) | ||||||||
| 1 | PUR1.BF4 |  | 12,000 | 1.42 | 286 | 240 | 250 | 18.3 |
| 2 | PUR2.BF4 |  | 15,800 | 1.61 | 271 | 230 | 240 | 24.8 |
| 3 | PUR3.BF4 |  | 101,500 | 4.12 | 276 | 240 | 255 | 19.8 |
| 4 | PUR5.BF4 |  | 173,500 | 2.32 | 153 | 195 | 240 | 10.5 |
| 5 | PUR6.BF4 |  | 39,000 | 1.97 | 209 | 260 | 265 | 18.1 |
| ionic polyurethane (PU) | ||||||||
| 6 f | PU1.BF4 |  | 8500 | 1.51 | 195 | 265 | 265 | 13.1 |
| N | PIL | Structure | CO2 Sorption (mg/g) | Conditions (P, T) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CL-TBA |  | 44.0 | 0.1 MPa, 25 °C | [55] |
| 2 | [CelEt3N][PF6] |  | 38.0 | 0.1 MPa, 25 °C | [15] |
| 3 | PIL-8.1.BF4 |  | 24.8 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | [16] |
| 4 | PUR2.BF4 |  | 24.8 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | This work |
| 5 | Mesoporous PIL |  | 20.2 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | [20] |
| 6 | PUR3.BF4 |  | 19.8 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | This work |
| 7 | PIL-8.1.CH3COO |  | 18.3 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | [16] |
| 8 | PUR1.BF4 |  | 18.3 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | This work |
| 9 | PUR6.BF4 |  | 18.1 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | This work |
| 10 | Meso-SiO2- P[VBTMA][BF4] |  | 17.7 | 0.1 MPa, 30 °C | [25] |
| 11 | P[VBTMA][BF4] |  | 17.1 | 0.0078 MPa, 22 °C | [37] |
| 12 | Meso-SiO2- P[VBTMA][ PF6] |  | 16.7 | 0.1 MPa, 30 °C | [25] |
| 13 | PU-TABPU-TAB |  | 16.1 | 0.0082 MPa, 30 °C | [40] |
| 14 | P[VBTMA][ PF6] |  | 14.6 | 0.0078 MPa, 22 °C | [37] |
| 15 | P[MATMA][BF4] |  | 14.4 | 0.0078 MPa, 22 °C | [37] |
| 16 | P[(AMIM) BF4-AN] |  | 14.3 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | [56] |
| 17 | PU1.BF4 |  | 13.1 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | This work |
| 18 | PIL-8.1.NO3 |  | 13.1 | 0.1 MPa, 0 °C | [16] |
| 19 | P[BIEMA][CH3COO] |  | 12.5 | 0.1 MPa, 25 °C | [19] |
| 20 | P[VBTEA][ PF6] |  | 10.4 | 0.1 MPa, 25 °C | [21] |
| 21 | P[VBTEA][BF4] |  | 6.9 | 0.0078 MPa, 22 °C | [37] |
| 22 | P[VBMI][BF4] |  | 4.6 | 0.0078 MPa, 22 °C | [14] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morozova, S.M.; Lozinskaya, E.I.; Sardon, H.; Suárez-García, F.; Vlasov, P.S.; Vaudemont, R.; Vygodskii, Y.S.; Shaplov, A.S. Ionic Polyureas—A Novel Subclass of Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for CO2 Capture. Membranes 2020, 10, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090240
Morozova SM, Lozinskaya EI, Sardon H, Suárez-García F, Vlasov PS, Vaudemont R, Vygodskii YS, Shaplov AS. Ionic Polyureas—A Novel Subclass of Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for CO2 Capture. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090240
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorozova, Sofia M., Elena I. Lozinskaya, Haritz Sardon, Fabian Suárez-García, Petr S. Vlasov, Régis Vaudemont, Yakov S. Vygodskii, and Alexander S. Shaplov. 2020. "Ionic Polyureas—A Novel Subclass of Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for CO2 Capture" Membranes 10, no. 9: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090240
APA StyleMorozova, S. M., Lozinskaya, E. I., Sardon, H., Suárez-García, F., Vlasov, P. S., Vaudemont, R., Vygodskii, Y. S., & Shaplov, A. S. (2020). Ionic Polyureas—A Novel Subclass of Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for CO2 Capture. Membranes, 10(9), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090240