The Influence of Different Operation Conditions on the Treatment of Mariculture Wastewater by the Combined System of Anoxic Filter and Membrane Bioreactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
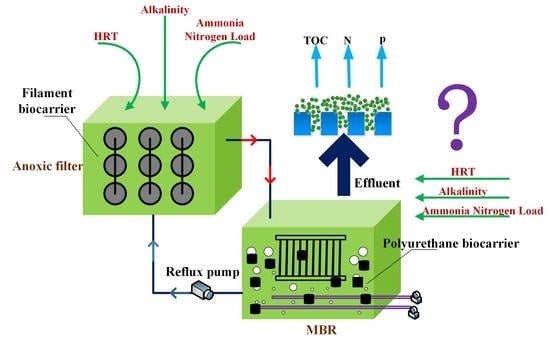
2.1. The AF-MBR System
2.2. Operation of AF-MBR
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different HRTs on AF-MBR Treatment Performance
3.1.1. Influence of Different HRTs on TOC Removal Efficiency
3.1.2. Influence of Different HRTs on Phosphate Removal Efficiency
3.1.3. Influence of Different HRTs on Nitrogen Removal Efficiency
3.2. Effect of Different Influent Alkalinity Values on AF-MBR Treatment Performance
3.2.1. Influence of Different Influent Alkalinity Values on TOC Removal Efficiency
3.2.2. Influence of Different Influent Alkalinity Values on Phosphate Removal Efficiency
3.2.3. Influence of Different Influent Alkalinity Values on Nitrogen Removal Efficiency
3.3. Effect of Different Ammonia Nitrogen Loads on AF-MBR Treatment Performance
3.3.1. Influence of Different Ammonia Nitrogen Loads on TOC Removal Efficiency
3.3.2. Influence of Different Ammonia Nitrogen Loads on Phosphate Removal Efficiency
3.3.3. Influence of Different Ammonia Nitrogen Loads on Total Nitrogen Removal Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, J.; Yin, W. Exploring stakeholder engagement in mariculture development: Challenges and prospects for China. Mar. Policy 2019, 103, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Chang, Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; She, Z.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, C.; Gao, F. Performance and microbial community of a sequencing batch biofilm reactor treating synthetic mariculture wastewater under long-term exposure to norfloxacin. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cuthbertson, A.; Gualtieri, C.; Shao, D. A Review on Mariculture Effluent: Characterization and Management Tools. Water 2020, 12, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal, L.C.C.; Sanz-Martín, J.L.; Barragán-Huerta, B.E. Biodegradation of organic pollutants in saline wastewater by halophilic microorganisms: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 9578–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Zeng, G. Influence of salinity on microorganisms in activated sludge processes: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 119, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Xie, K. Recent development of scale marine aquaculture wastewater treatment. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen, China, 20–21 December 2015; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 496–499. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D.; Hwang, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, W. Effects of salinity on the characteristics of biomass and membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panswad, T.; Anan, C. Specific oxygen, ammonia, and nitrate uptake rates of a biological nutrient removal process treating elevated salinity wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.; Sumanasekera, D.; Ibrahim, S.; Lubberding, H.; Hooijmans, C.; Gijzen, H.; van Loosdrecht, M. Long term effects of salt on activity, population structure and floc characteristics in enriched bacterial cultures of nitrifiers. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Membrane module assembly enhances the performance of A/O-MBBR in treating mariculture wastewater. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 514, 052048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Xia, S.; Wu, Y. Biofouling and control approaches in membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, G.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Performance of a MBR pilot plant treating high strength wastewater subject to salinity increase: Analysis of biomass activity and fouling behaviour. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 147, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, B.K.; Ozgun, H.; Ersahin, M.E.; Kaya, R.; Eliduzgun, S.; Altınbaş, M.; Kinaci, C.; Koyuncu, I. Impact of salinity on the population dynamics of microorganisms in a membrane bioreactor treating produced water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 646, 1080–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Leiknes, T.; Weitzenböck, J.; Thorstensen, B. Salinity effect on a biofilm-MBR process for shipboard wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, A.-M. Salinity stresses make a difference in the start-up of membrane bioreactor: Performance, microbial community and membrane fouling. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 42, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ahn, W.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Comparison of the filtration characteristics between attached and suspended growth microorganisms in submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, H.Y. Fouling control mechanism by suspended biofilm carriers addition in submerged ceramic membrane bioreactors. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, G.; Gori, R.; Mori, G.; Lubello, C. Powdered activated carbon and membrane bioreactors (MBRPAC) for tannery wastewater treatment: Long term effect on biological and filtration process performances. Desalination 2007, 207, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, M.; Potier, V.; Temmink, H.; Rulkens, W. Why low powdered activated carbon addition reduces membrane fouling in MBRs. Water Res. 2009, 44, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Jiang, W.; Song, Y.; Xia, S.; Hermanowicz, S.W. The characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances and soluble microbial products in moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Bi, X.; Ng, H.Y. Effects of bio-carriers on membrane fouling mitigation in moving bed membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 499, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-J.; Wu, M.; Sun, M.-X.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Dai, J. The effects of different carriers on removal performance and membrane fouling by HMBR in treating sewage with low carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, T.; Mogi, T.; Kimura, K. Influence of different biofilm carriers on the operation and membrane fouling of submerged membrane bioreactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 169, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, L.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, R. New functional biocarriers for enhancing the performance of a hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor system. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 208, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Li, J.; Listowski, A. Effects of Sludge Concentrations and Different Sponge Con-figurations on the Performance of a Sponge-Submerged Membrane Bioreactor. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Díaz, J.; Calderón, K.; Rodríguez, F.; González-López, J.; Hontoria, E.; Poyatos, J.M. Comparative kinetic study between moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor and membrane bioreactor systems and their influence on organic matter and nutrients removal. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 77, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassin, J.P.; Dezotti, M.; Sant’Anna, G.L., Jr. Nitrification of industrial and domestic saline wastewaters in moving bed biofilm reactor and sequencing batch reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Yu, C.; Bin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, X.; Huang, S.; Fu, F.; Ding, J.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; et al. Essential factors of an integrated moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor: Adhesion characteristics and microbial community of the biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y.; Liu, F.; You, H.; Qi, P.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Jin, C. Performance of a novel hybrid membrane bioreactor for treating saline wastewater from mariculture: Assessment of pollutants removal and membrane filtration performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johir, M.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J. Performance of submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR) with and without the addition of the different particle sizes of GAC as suspended medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viero, A.; Santannajr, G.; Nobrega, R. The use of polyetherimide hollow fibres in a submerged membrane bioreactor operating with air backwashing. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 302, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.-C.; Lee, L.-L.; Chang, C.-N.; Chao, A.C. Control of carbon and ammonium ratio for simultaneous nitrification and denitrification in a sequencing batch bioreactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, X.; Wei, H.; Jiang, L.-M.; Lv, Y. Effects of alkalinity on membrane bioreactors for reject water treatment: Performance improvement, fouling mitigation and microbial structures. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CEPB. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; Chinese Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.-W.; Tao, Y.; An, R. Digested sewage treatment using membrane-based process at different hydraulic retention times. Desalination 2012, 286, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montañés, R.; Pérez, M.; Solera, R. Mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and a lixiviation of sugar beet pulp: Optimisation of the semi-continuous process. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Current state and challenges of full-scale membrane bioreactor applications: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 271, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeev, A.G.; Nikolaev, Y.A.; Mardanov, A.V.; Pimenov, N.V. Role of Phosphate-Accumulating Bacteria in Biological Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2020, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Sleutels, T.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Hydrogen oxidizing bacteria are capable of removing orthophosphate to ultra-low concentrations in a fed batch reactor configuration. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wu, D.; Hu, Z. Impact of hydraulic retention time on organic and nutrient removal in a membrane coupled sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 2014, 55, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhou, F.; Xue, Y. Control of COD/N ratio for nutrient removal in a modified membrane bioreactor (MBR) treating high strength wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raper, E.; Fisher, R.; Anderson, D.R.; Stephenson, T.; Soares, A. Alkalinity and external carbon requirements for denitrification-nitrification of coke wastewater. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; He, P.; Gu, W.; Wang, G.; Shao, L. Recovery of phosphorus as struvite from sewage sludge ash. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1533–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xiang, L.; Song, Y.; Qian, F.; Meng, X. The effects and mechanism of alkalinity on the phosphate recovery from anaerobic digester effluent using dolomite lime. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 5067–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Irvin, S. The roles of nitrogen dissimilation and assimilation in biological nitrogen removal treating low, mid, and high strength wastewater. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2007, 6, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Ekama, G.A.; Capodici, M.; Cosenza, A.; Di Trapani, D.; Ødegaard, H. Moving bed membrane bioreactors for carbon and nutrient removal: The effect of C/N variation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 125, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liang, J.; Lin, X.; Xu, H.; Tadda, M.A.; Lan, L.; Liu, D. Fast start-up strategies of MBBR for mariculture wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergero, D.; Boccignone, M.; Di Natale, F.; Forneris, G.; Palmegiano, G.B.; Roagna, L.; Sicuro, B. Ammonia removal capacity of European natural zeolite tuffs: Application to aquaculture waste water. Aquac. Fish. Manag. 1994, 25, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradihamedani, P.; Abdullah, A.H. Preparation and characterization of polysulfone/zeolite mixed matrix mem-branes for removal of low-concentration ammonia from aquaculture wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarno, S.; Winter, J.; Gallert, C. Effect of varying salinity, temperature, ammonia and nitrous acid concentrations on nitrification of saline wastewater in fixed-bed reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5665–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.; Zeng, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Performance and microbial community of completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (CANON) process in two membrane bioreactors (MBR) fed with different substrate levels. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Guo, Z.; Ma, B.; Wang, F.; You, H.; Mei, J.; Hou, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, Z.; Jin, C. The Influence of Different Operation Conditions on the Treatment of Mariculture Wastewater by the Combined System of Anoxic Filter and Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes 2021, 11, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100729
Ding Y, Guo Z, Ma B, Wang F, You H, Mei J, Hou X, Liang Z, Li Z, Jin C. The Influence of Different Operation Conditions on the Treatment of Mariculture Wastewater by the Combined System of Anoxic Filter and Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes. 2021; 11(10):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100729
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yi, Zhansheng Guo, Binyu Ma, Fang Wang, Hong You, Junxue Mei, Xuguang Hou, Zhenlin Liang, Zhipeng Li, and Chao Jin. 2021. "The Influence of Different Operation Conditions on the Treatment of Mariculture Wastewater by the Combined System of Anoxic Filter and Membrane Bioreactor" Membranes 11, no. 10: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100729
APA StyleDing, Y., Guo, Z., Ma, B., Wang, F., You, H., Mei, J., Hou, X., Liang, Z., Li, Z., & Jin, C. (2021). The Influence of Different Operation Conditions on the Treatment of Mariculture Wastewater by the Combined System of Anoxic Filter and Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes, 11(10), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11100729