New Preparation Methods for Pore Formation on Polysulfone Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polymer Synthesis


2.3. Apparatus
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Nonaqueous Conductometric Titrations for Carboxylic Group Determination
3. Results and Discussions
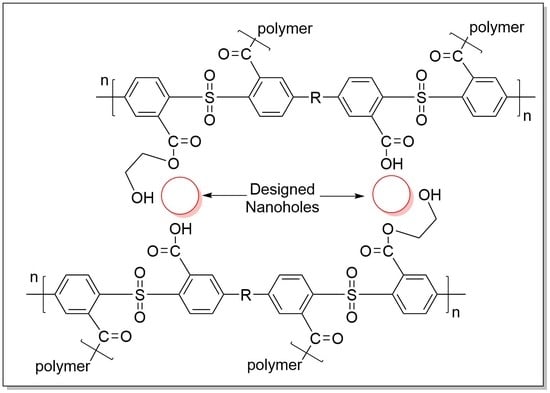
3.1. Nanoiron Acid Etching Method
3.2. Base Hydrolysis Method of the Crosslinked Polymer
3.3. Base Hydrolysis Method of a Component in Polymer Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loeb, S.; Sourirajan, S. Sea water demineralization by means of an osmotic membrane. Adv. Chem. Ser. 1963, 38, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Loeb, S.; Sourirajan, S. High Flow Porous Membranes for Separating Water from Saline Solutions. U.S. Patent 3,133,132, 12 May 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Sussex, UK, 2012; pp. 1–571. [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti, P.; Jimenez Solomon, M.F.; Szekely, G.; Livingston, A.G. Molecular separation with organic solvent nanofiltration: A critical review. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10735–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Witte, P.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Van den Berg, J.W.A.; Feijen, J. Phase separation processes in polymer solutions in relation to membrane formation. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.M.; Lai, J.Y. Recent advances in preparation and morphology control of polymeric membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holda, A.K.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nanofiltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Yan, Q. Rapid nanostructuration of polymer colloid surfaces by nonsolvent induced phase separation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2015, 441, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minbu, H.; Ochiai, A.; Kawase, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Lloyd, D.R.; Tanaka, T. Preparation of poly (L-lactic acid) microfiltration membranes by a nonsolvent-induced phase separation method with the aid of surfactants. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, T.; Song, L.; Chen, P.; Nie, W.; Zhou, Y. Nonsolvent/solvent-induced phase separation to multi-porous sulfonated polystyrene/chitosan/silver particles and their application in adsorbing chromium ion (III) and reduction of methylene blue. Colloid. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 481, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.H.; Tang, Y.H.; Matsuyama, H.; Wang, X.L. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation on the membrane formation of polymer-solvent system via nonsolvent induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockway, L.; Berryman, L.; Taylor, H. Nonsolvent-induced phase separation synthesis of superhydrophobic coatings composed of polyvinylidene difluoride microspheres with tunable size and roughness. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 119, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.H.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, J.F.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, Y.; Nam, S.E.; Park, Y.I.; Park, H. Tailoring the porous structure of hollow fiber membranes for osmotic power generation applications via thermally assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaan, R.C.; Chang, T.; Wang, D.M. Selection criteria for solvent and coagulation medium in view of macrovoid formation in the wet phase inversion process. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Kim, S.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. A novel green solvent alternative for polymeric membrane preparation via nonsolvent-induced phase separation (NIPS). J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuyama, H.; Teramoto, M.; Useka, T. Membrane formation and structure development by dry-cast process. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 135, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.C.; Macchione, M.; Drioli, E. High flux asymmetric gas separation membranes of modified poly (ether ether ketone) prepared by the dry phase inversion technique. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 225, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lee, W.; Choi, J.M.; Patel, R.; Min, B.R. Characterization of polyethersulfone/polyimide blend membranes prepared by a dry/wet phase inversion: Precipitation kinetics, morphology and gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.Z.; Umapathy, S.; Ramakrishnan, S. Functionalized and postfunctionalizable porous polymeric films through evaporation-induced phase separation using mixed solvents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2011, 3, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zong, C.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gai, H. Fabrication of Janus droplets by evaporation driven liquid-liquid phase separation. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5015–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriezekolk, E.J.; Nijmeijer, K.; de Vos, W.M. Dry-wet phase inversion block copolymer membranes with a minimum evaporation step from NMP/THF mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, S.; Fan, B.; Shi, X.; Cui, X.; et al. Solvothermal-assisted evaporation-induced self-assembly of ordered mesoporous alumina with improved performance. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 529, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plisko, T.V.; Penkova, A.V.; Burts, K.S.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Melnikova, G.B.; Atta, R.R.; Mazur, A.S.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Missyul, A.B. Effect of Pluronic F127 on porous and dense membrane structure formation via non-solvent induced and evaporation induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 580, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.A.S.; Jaroniec, M. Evaporation-induced self-assembly synthesis of nanostructured alumina-based mixed metal oxides with tailored porosity. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2019, 537, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.R.; Kinzer, K.E.; Tseng, H.S. Microporous membrane formation via thermally induced phase separation. I. Solid-liquid phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 52, 239–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, P.M.; Lloyd, D.R. Anisotropic flat sheet membrane formation via TIPS: Thermal effects. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 171, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, K.T.; Sanguineti, A.; Arcella, V.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Poly (vinylidene fluoride) membrane preparation with an environmental diluent via thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Cui, Z.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, D.W.; Sanguineti, A.; Arcella, V.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. PVDF hollow fiber membranes prepared from green diluent via thermally induced phase separation: Effect of PVDF molecular weight. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Woo, K.T.; Lee, J.M.; Sanguineti, A.; Arcella, V.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Tailoring novel fibrillar morphologies in poly (vinylidenefluoride) membranes using a low toxic triethylene glycol diacetate (TEGDA) diluent. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 473, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Cui, Z.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Sanguineti, A.; Arcella, V.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Microporous poly (vinylidene fluoride) hollow fiber membranes fabricated with polar clean as water-soluble green diluent and additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Thermally induced phase separation and electrospinning methods for emerging membrane applications: A review. AIChE J. 2016, 62, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervellere, M.R.; Tang, Y.; Qian, X.; Ford, D.M.; Millett, P.C. Mesoscopic simulations of thermally induced phase separation in PVDF/DPC solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 577, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cai, Y.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Drioli, E.; Cui, Z. ECTFE membrane fabrication via TIPS method using ATBC diluent for vacuum membrane distillation. Desalination 2019, 456, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, B.S.; Kochkodan, V.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. A review on membrane fabrication: Structure, properties and performance relationship. Desalination 2013, 326, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notario, B.; Pinto, J.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A. Nanoporous polymeric materials: A new class of materials with enhanced properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 78, 93–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stucki, M.; Loepfe, M.; Stark, W.J. Porous polymer membranes by hard templating—A review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.; Zhukova, O.; Vlbricht, M.; Ribitsch, V. Electrochemical and other transport properties of nanoporous track-etched membranes studied by the current switch-off technique. Langmuir 2005, 21, 6872–6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Singh, M.; He, J.; Vijay, T.J.; McPherson, G.L. Use of a self-assembling organogel as a reverse template in the preparation of imprinted porous polymer films. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9322–9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, G.; Dickey, M.; Willson, C.G. Preparation of porous polymer membranes using nan or micro-pillar arrays as templates. Polymer 2004, 45, 8469–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Range, S.; Epple, M. Nanoscopic NaCl crystals as water-soluble porogens for polymer membranes. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 6650–6654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Graham, C.L.; Wolff, J.; Iyer, R.G.; Kohli, P. Modulating molecular and nanoparticle transport in flexible polydimethylsiloxane membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kellenberger, C.R.; Pfleiderer, F.C.; Raso, R.A.; Burri, C.H.; Schumacher, C.M.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Limestone nanoparticles as nanopore templates in polymer membranes: Narrow pore size distribution and use as self-wetting dialysis membranes. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 61420–61426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, C.R.; Luechinger, N.A.; Lamprou, A.; Rossier, M.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Soluble nanoparticles as removable pore templates for the preparation of polymer ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 387, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, C.R.; Hess, S.C.; Schumacher, C.M.; Loepfe, M.; Nussbaumer, J.E.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Roll-to-roll preparation of mesoporous membranes by nanoparticle template removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9214–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, A.; Stark, W.J.; Grass, R.N. Rapid production of a porous cellulose acetate membrane for water filtration using readily available chemicals. J. Chem. Educ. 2017, 94, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozinski, J.S.; Seppala, H.J. Oil, Water and Sweat Repellent Microporous Membrane Materials. U.S. Patent 5260360, 9 November 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cavicchi, K.A.; Zalusky, A.S.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Lodge, T.P. An ordered nanoporous monolith from an elastomeric crosslinked block copolymer precursor. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, S.; Yoshida, A.; Nagai, K. Preparation of porous membranes by selective decomposition of adamantane unit in aba-type triblock copolymer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P. Block copolymer membranes for aqueous solution applications. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, T.; Muramatsu, A. Formation mechanism of monodispersed α-Fe2O3 particles in dilute FeCl3 solutions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 1996, 184, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastgar, M.; Bozorg, A.; Shakeri, A. novel dimensionally controlled nanopore forming template in forward osmosis membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2704–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, J.; Forester, R.; Kim, M.; Petersen, R.; Stocker, T. Nanofiltration membranes broaden the use of membrane separation technology. Desalination 1988, 70, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiver, M.D. Method of Manufacturing a Reverse Osmosis Membrane and the Membrane so Produced. U.S. Patent 4,894,159, 16 January 1990. [Google Scholar]











| Entry | Membrane Type | Pressure (Bar) | Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Rejection (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 a | Commercial polysulfone membrane | 34 | 6 | 25 |
| 2 | Polysulfone membrane by Method A | 10 | 30 | 22 |
| 3 b | Commercial polysulfone sulfonated membrane | 10 | 500 | 15 |
| 4 c | Patented polysulfone carboxylated membrane | 11 | 2100 | 20 |
| 5 | Polysulfone carboxylated membrane by Method B | 10 | 2200 | 20 |
| Entry | Membrane Type | Pressure (Bar) | Flux (L·m−2·h−1) | Rejection 0.2% CaCl2(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Polysulfone membrane by Method A | 10 | 30 | 43 |
| 2 | Polysulfone carboxylated membrane by Method B | 10 | 2200 | 20 |
| 3 | poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride) (12 h of hydrolysis) by Method C | 10 | 2680 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vainrot, N.; Li, M.; Isloor, A.M.; Eisen, M.S. New Preparation Methods for Pore Formation on Polysulfone Membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040292
Vainrot N, Li M, Isloor AM, Eisen MS. New Preparation Methods for Pore Formation on Polysulfone Membranes. Membranes. 2021; 11(4):292. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040292
Chicago/Turabian StyleVainrot, Natalia, Mingyuan Li, Arun M. Isloor, and Moris S. Eisen. 2021. "New Preparation Methods for Pore Formation on Polysulfone Membranes" Membranes 11, no. 4: 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040292
APA StyleVainrot, N., Li, M., Isloor, A. M., & Eisen, M. S. (2021). New Preparation Methods for Pore Formation on Polysulfone Membranes. Membranes, 11(4), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040292