Nano- and Micro-Porous Chitosan Membranes for Human Epidermal Stratification and Differentiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2. Membrane Characterization
2.3. Cell Cultures
2.4. Cell Morphology
2.5. Cell Proliferation and Glucose Consumption
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
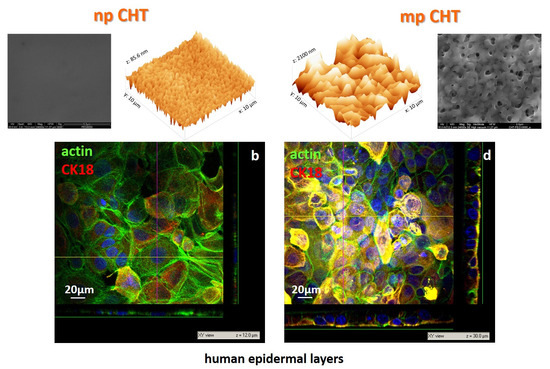
3.1. Membrane Properties
3.2. Epidermal Membrane Sytems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wickett, R.R.; Visscher, M.O. Structure and function of the epidermal barrier. Am. J. Infect. Control 2006, 34, S98–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.B.; Strickland, J.; Allen, D.; Casati, S.; Zuang, V.; Barroso, J.; Whelan, M.; Régimbald-Krnel, M.J.; Kojima, H.; Nishikawa, A.; et al. International regulatory requirements for skin sensitization testing. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 95, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemper, M.; de Paepe, K.; Rogiers, V. Practical Problems Encountered during the Cultivation of an Open-Source Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model on a Polycarbonate Membrane and Protein Quantification. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, L.F.; Troese, M.J.; Fuchs, H.W.; Engelking, O.; DeGeorge, G.L. The highly differentiated 3D epidermal skin model (epiCS®) to characterize skin sensitizers in mixtures. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Ueki, T.; Ogata, S.; Itagaki, H. Predicting the results of a 24-hr human patch test for surfactants: Utility of margin-setting in a reconstructed human epidermis model. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 44, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKim, J.M.; Keller, D.J.; Gorski, J.R. An in vitro method for detecting chemical sensitization using human reconstructed skin models and its applicability to cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and medical device safety testing. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alépée, N.; Tornier, C.; Robert, C.; Amsellem, C.; Roux, M.-H.; Doucet, O.; Pachot, J.; Méloni, M.; de Fraissinette, A. A catch-up validation study on reconstructed human epidermis (SkinEthicTM RHE) for full replacement of the Draize skin irritation test. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzlaff, F.; Lehr, C.-M.; Wertz, P.W.; Schaefer, U.F. The human epidermis models EpiSkin®, SkinEthic® and EpiDerm®: An evaluation of morphology and their suitability for testing phototoxicity, irritancy, corrosivity, and substance transport. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2005, 60, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, T.d.N.; Catarino, C.M.; Pennacchi, P.C.; de Assis, S.R.; Gimenes, F.; Consolaro, M.E.L.; de Barros, S.B.M.; Maria-Engler, S.S. A new reconstructed human epidermis for in vitro skin irritation testing. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 42, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathes, S.H.; Ruffner, H.; Graf-Hausner, U. The use of skin models in drug development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 69, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, S.; Morelli, S.; Giordano, F.; Gordano, A.; de Bartolo, L. Polymeric membranes modulate human keratinocyte differentiation in specific epidermal layers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, S.; Messina, A.; Giordano, F.; Bader, A.; Drioli, E.; de Bartolo, L. Dermal-epidermal membrane systems by using human keratinocytes and mesenchymal stem cells isolated from dermis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, S.; Morelli, S.; de Bartolo, L. Advanced membrane systems for tissue engineering. Curr. Org. Chem. 2017, 21, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, S.J.; Yang, D.H.; Chun, H.J. Chitosan for Tissue Engineering. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1077, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Vázquez, M.; Vega-Ruiz, B.; Ramos-Zúñiga, R.; Saldaña-Koppel, D.A.; Quiñones-Olvera, L.F. Chitosan and Its Potential Use as a Scaffold for Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 821279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miguel, S.P.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. Chitosan based-asymmetric membranes for wound healing: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, S.; Curcio, E.; Bader, A.; Giorno, L.; Drioli, E.; de Bartolo, L. Gas permeable membrane bioreactor for the co-culture of human skin derived mesenchymal stem cells with hepatocytes and endothelial cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 563, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, M.A.; El-Sonbati, A.Z.; Bader, D.M.D. Thermal stability and degradation of chitosan modified by benzophenone. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Fang, Z. Preparation of sub-micrometer porous membrane from chitosan/polyethylene glycol semi-IPN. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 245, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salerno, S.; Tasselli, F.; Drioli, E.; de Bartolo, L. Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Hollow Fiber Membranes for the Biofabrication of a Vascularized Human Liver Tissue. Membranes 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Salerno, S.; Remigy, J.-C.; Lahitte, J.-F.; Bacchin, P.; de Bartolo, L. Double porous poly (Ɛ-caprolactone)/chitosan membrane scaffolds as niches for human mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hendriks, F.M. Mechanical Behaviour of Human Skin In Vivo—A Literature Review; Koninklijke Philips Electronics, N.V.: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.S.; van Osdol, W.W.; Dauskardt, R.H. Mechanical properties of human stratum corneum: Effects of temperature, hydration, and chemical treatment. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Verma, R. Measuring microelastic properties of stratum corneum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 48, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geerligs, M.; van Breemen, L.; Peters, G.; Ackermans, P.; Baaijens, F.; Oomens, C. In vitro indentation to determine the mechanical properties of epidermis. J. Biomech. 2011, 44, 1176–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichton, M.L.; Donose, B.C.; Chen, X.; Raphael, A.P.; Huang, H.; Kendall, M.A.F. The viscoelastic, hyperelastic and scale dependent behaviour of freshly excised individual skin layers. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4670–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Casting Solution | CHT (wt/v) % | CHT/PEG Ratio | Mean Flow Pore Diameter (µm) | Largest Detected Pore Diameter (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3% CHT/PEG | 2 | 2/1 | 0.033 ± 0.008 | 0.419 ± 0.024 |
| 2.5% CHT/PEG | 1.5 | 1.5/1 | 0.054 ± 0.037 | 0.447 ± 0.094 |
| 2% CHT/PEG | 1 | 1/1 | 0.131 ± 0.072 | 0.849 ± 0.772 |
| 4% CHT/PEG | 2 | 1/1 | 0.042 ± 0.081 | 0.420 ± 0.091 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salerno, S.; De Santo, M.P.; Drioli, E.; De Bartolo, L. Nano- and Micro-Porous Chitosan Membranes for Human Epidermal Stratification and Differentiation. Membranes 2021, 11, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060394
Salerno S, De Santo MP, Drioli E, De Bartolo L. Nano- and Micro-Porous Chitosan Membranes for Human Epidermal Stratification and Differentiation. Membranes. 2021; 11(6):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060394
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalerno, Simona, Maria Penelope De Santo, Enrico Drioli, and Loredana De Bartolo. 2021. "Nano- and Micro-Porous Chitosan Membranes for Human Epidermal Stratification and Differentiation" Membranes 11, no. 6: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060394
APA StyleSalerno, S., De Santo, M. P., Drioli, E., & De Bartolo, L. (2021). Nano- and Micro-Porous Chitosan Membranes for Human Epidermal Stratification and Differentiation. Membranes, 11(6), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11060394