Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of Pulsed Electric Field Mode and Solution Flow Rate on Protein Fouling during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidificaiton of Caseinate Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Theoretical Section
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Formation of Deposit Layer
3.3. Boundary Conditions
- Membrane surface
- Bulk solution (x = δ)
3.4. Parameters of the Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Evolution of pH
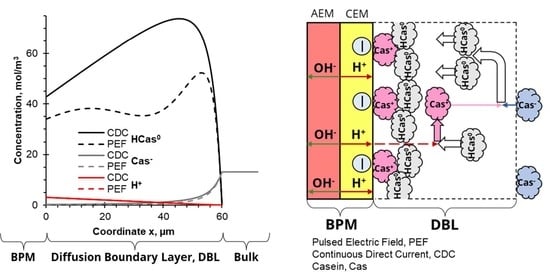
4.2. Evolution of Species Concentration
4.3. Quantification of Fouling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| BPM | Bipolar membrane |
| CC | Continuous current |
| CEM | Cation-exchange membrane |
| CP | Concentration polarization |
| DBL | Diffusion boundary layer |
| ED | Electrodialysis |
| EDBM | Electrodialysis with bipolar membranes |
| ICP-OES | Inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry |
| PEF | Pulsed electric field |
| SM | Supplementary material |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
References
- Castro-Muñoz, R.; García-Depraect, O.; León-Becerril, E.; Cassano, A.; Conidi, C.; Fíla, V. Recovery of protein-based compounds from meat by-products by membrane-assisted separations: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 3025–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.R.C.K.; Mason, B.; Doucette, A.A. Review of Membrane Separation Models and Technologies: Processing Complex Food-Based Biomolecular Fractions. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaningsih, E.; Reynard, R.; Khoiruddin, K.; Wenten, I.G.; Boopathy, R. Recent Advancements of UF-Based Separation for Selective Enrichment of Proteins and Bioactive Peptides—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.; Vavro, M.; Ondrušek, M.; Voropaeva, D.; Yaroslavtsev, A.; Dvořák, L.; Stulac, M.; Bauer, S.A.W. Lactose mother liquor stream valorisation using electrodialysis. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 121, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tao, Y.; He, Y.; Pan, J.; Yang, K.; Shen, J.; Gao, C. Preparation of Low-Lactose Milk Powder by Coupling Membrane Technology. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8543–8550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talebi, S.; Kee, E.; Chen, G.Q.; Bathurst, K.; Kentish, S.E. Utilisation of salty whey ultrafiltration permeate with electrodialysis. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 99, 104549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Electrodialysis with porous membrane for bioproduct separation: Technology, features, and progress. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronchuk, V.; Zmievskii, Y.; Dzyazko, Y.; Rozhdestveska, L.; Zakharov, V.; Bildyukevich, A. Electrodialytic whey demineralization involving polymer-inorganic membranes, anion exchange resin and graphene-containing composite. Acta Period. Technol. 2019, 50, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giesbrecht, P.K.; Freund, M.S. Recent Advances in Bipolar Membrane Design and Applications. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8060–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, S.; Serre, É.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Optimization of cranberry juice deacidification by electrodialysis with bipolar membrane: Impact of pulsed electric field conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Ippersiel, D.; Gendron, C.; René-Paradis, J.; Tétrault, C.; Beaudry, J.; Britten, M.; Mahdavi, B.; Amiot, J.; Lamarche, F. Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Demineralized Skim Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2812–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, A.; Ashrafi, A.M.; Ečer, J. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis assisted pH correction of milk whey. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.; Fernandes, C.; dos Santos, P.C.; de Pinho, M.N. Wine tartaric stabilization by electrodialysis and its assessment by the saturation temperature. J. Food Eng. 2003, 59, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülber-Beyer, É.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Low-waste fermentation-derived organic acid production by bipolar membrane electrodialysis—An overview. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 5223–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, H.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Xu, T. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis for cleaner production of N-methylated glycine derivative amino acids. AIChE J. 2020, 66, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Ippersiel, D.; Amiot, J. Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification to Produce Bovine Milk Casein Isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 5291–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, L.; Fouilloux, J.; Bdiri, M.; Larchet, C.; Renard, E.; Baklouti, L.; Sarapulova, V.; Kozmai, A.; Pismenskaya, N. A Review on Ion-Exchange Membrane Fouling during the Electrodialysis Process in the Food Industry, Part 1: Types, Effects, Characterization Methods, Fouling Mechanisms and Interactions. Membranes 2021, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Geoffroy, T.R. Electrodialytic Processes: Market Overview, Membrane Phenomena, Recent Developments and Sustainable Strategies. Membranes 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Moon, S.-H.; Tsai, S.-P. Effects of pulsed electric fields on membrane fouling in electrodialysis of NaCl solution containing humate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 27, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Li, Z.; Lei, C.; Fu, R.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z. Application of Pulsed Electric Field in Antifouling Treatment of Sodium Gluconate Mother Liquor by Electrodialysis. Materials 2020, 13, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Fernandez, P.A.; Post, J.W.; Ramdlan, M.S.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M. Improving the performance of polymer-flooding produced water electrodialysis through the application of pulsed electric field. Desalination 2020, 484, 114424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchuk, N.A.; Koopal, L.K.; Gonzalez-Caballero, F. Intensification of electrodialysis by applying a non-stationary electric field. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 176, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, P.; Ortiz, J.M.; Richards, B.S.; Schäfer, A.I. Electrodialytic removal of NaCl from water: Impacts of using pulsed electric potential on ion transport and water dissociation phenomena. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 435, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dufton, G.; Mikhaylin, S.; Gaaloul, S.; Bazinet, L. Positive Impact of Pulsed Electric Field on Lactic Acid Removal, Demineralization and Membrane Scaling during Acid Whey Electrodialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwari, B.K.; Walsh, D.; Griffin, T.P.; Islam, N.; Lyng, J.G.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K. Impact of pulsed electric field pre-treatment on nutritional and polyphenolic contents and bioactivities of light and dark brewer’s spent grains. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemay, N.; Mikhaylin, S.; Mareev, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V.; Bazinet, L. How demineralization duration by electrodialysis under high frequency pulsed electric field can be the same as in continuous current condition and that for better performances? J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 117878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Sion, A.-V. Improvement of a sustainable hybrid technology for caseins isoelectric precipitation (electrodialysis with bipolar membrane/ultrafiltration) by mitigation of scaling on cation-exchange membrane. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balster, J.; Punt, I.G.; Stamatialis, D.; Wessling, M. Multi-layer spacer geometries with improved mass transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 282, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.; Sonin, A.A. Experimental study of the effects of hydrodynamics and membrane fouling in electrodialysis. Desalination 1972, 10, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.; Sonin, A.A. Membrane fouling in electrodialysis: A model and experiments. Desalination 1973, 12, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Bouvier, L.; Tonda, A.; Delaplace, G. A mathematical model for the prediction of the whey protein fouling mass in a pilot scale plate heat exchanger. Food Control 2019, 106, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Daigle, G.; Kadel, S.; Perreault, V.; Pellerin, G.; Thibodeau, J.; Bazinet, L. Predictive models for determination of peptide fouling based on the physicochemical characteristics of filtration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Moresoli, C.; Marcos, B. Fouling behavior of electroacidified soy protein extracts during cross-flow ultrafiltration using dynamic reversible–irreversible fouling resistances and CFD modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nic, S.S.S.; Buist, K.A.; Verdurmen, R.E.M.; Kuipers, J.A.M. Dynamic model to predict heat-induced protein denaturation and fouling in a Direct Contact Steam Condensation process. Chem. Eng. Sci. X 2020, 8, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jaegher, B.; Larumbe, E.; de Schepper, W.; Verliefde, A.; Nopens, I. Colloidal fouling in electrodialysis: A neural differential equations model. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 249, 116939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jaegher, B.; de Schepper, W.; Verliefde, A.; Nopens, I. Enhancing mechanistic models with neural differential equations to predict electrodialysis fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichka, V.S.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Bazinet, L. Fouling Mitigation by Optimizing Flow Rate and Pulsed Electric Field during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidification of Caseinate Solution. Membranes 2021, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, B.; Sistat, P.; Huguet, P.; Pourcelly, G.; Arayafarias, M.; Bazinet, L. Application of relaxation periods during electrodialysis of a casein solution: Impact on anion-exchange membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Bazinet, L. Fouling prevention of peptides from a tryptic whey hydrolysate during electromembrane processes by use of monovalent ion permselective membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Diab, M.; Thibodeau, J.; Deracinois, B.; Flahaut, C.; Fliss, I.; Dhulster, P.; Nedjar, N.; Bazinet, L. Bovine Hemoglobin Enzymatic Hydrolysis by a New Ecoefficient Process—Part I: Feasibility of Electrodialysis with Bipolar Membrane and Production of Neokyotophin (α137-141). Membranes 2020, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, M.; Mikhaylin, S.; Doyen, A.; Firdaous, L.; Hammami, R.; Chevalier, M.; Flahaut, C.; Dhulster, P.; Bazinet, L. Formation of peptide layers and adsorption mechanisms on a negatively charged cation-exchange membrane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Post, A.E.; Arnold, B.; Weiss, J.; Hinrichs, J. Effect of temperature and pH on the solubility of caseins: Environmental influences on the dissociation of αS- and β-casein. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Zabolotskii, V.I. Mass-transfer in a planar crevice channel with a separator. Elektrokhimiya 1992, 28, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Persico, M.; Mikhaylin, S.; Doyen, A.; Firdaous, L.; Hammami, R.; Bazinet, L. How peptide physicochemical and structural characteristics affect anion-exchange membranes fouling by a tryptic whey protein hydrolysate. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, J.-F.; Amiot, J.; Bazinet, L. Improved peptide fractionation by electrodialysis with ultrafiltration membrane: Influence of ultrafiltration membrane stacking and electrical field strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Ippersiel, D.; Gendron, C.; Mahdavi, B.; Amiot, J. Comparison of Electrochemical and Chemical Acidification of Skim Milk. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.A.; Stokes, R.H. Electrolyte Solutions: Second Revised Edition; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 9780486138787. [Google Scholar]
- Bazinet, L.; Ippersiel, D.; Gendron, C.; Beaudry, J.; Mahdavi, B.; Amiot, J.; Lamarche, F. Cationic balance in skim milk during bipolar membrane electroacidification. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 173, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Startsev, M.A.; Inglis, D.W.; Baker, M.S.; Goldys, E.M. Nanochannel pH Gradient Electrofocusing of Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7133–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivovarov, A.S.; Calahorro, F.; Walker, R.J. Na+/K+-pump and neurotransmitter membrane receptors. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Symbol | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 60, 40, 30 µm 1 | DBL thicknesses | |
| 5 mA/cm2 | Average current density | |
| 1.33 × 10−9 m2/cm | Ion (molecule) diffusion coefficients in the solution | |
| 9.3 × 10−9 m2/cm | ||
| 5.27 × 10−9 m2/cm | ||
| 1.98 × 10−9 m2/cm | ||
| 2.03 × 10−9 m2/cm | ||
| 6.6 × 10−11 m2/cm | ||
| 1 × 10−12 m2/cm | ||
| 1.58 1/s | Forward rate constant of the reaction (1) | |
| 1 × 107 m3/s mol | Backward rate constant of the reaction (1) | |
| 0.016 mol/m3 | Equilibrium acid dissociation constant of the reaction (1) | |
| 1 1/s | Dissolution rate coefficient of the fouling layer | |
| 5 × 10−4 m/s | Formation rate coefficient of the fouling layer | |
| pH0 | 6.5 | The initial pH value of the solution |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nichka, V.; Mareev, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V.; Bazinet, L. Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of Pulsed Electric Field Mode and Solution Flow Rate on Protein Fouling during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidificaiton of Caseinate Solution. Membranes 2022, 12, 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020193
Nichka V, Mareev S, Pismenskaya N, Nikonenko V, Bazinet L. Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of Pulsed Electric Field Mode and Solution Flow Rate on Protein Fouling during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidificaiton of Caseinate Solution. Membranes. 2022; 12(2):193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020193
Chicago/Turabian StyleNichka, Vladlen, Semyon Mareev, Natalia Pismenskaya, Victor Nikonenko, and Laurent Bazinet. 2022. "Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of Pulsed Electric Field Mode and Solution Flow Rate on Protein Fouling during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidificaiton of Caseinate Solution" Membranes 12, no. 2: 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020193
APA StyleNichka, V., Mareev, S., Pismenskaya, N., Nikonenko, V., & Bazinet, L. (2022). Mathematical Modeling of the Effect of Pulsed Electric Field Mode and Solution Flow Rate on Protein Fouling during Bipolar Membrane Electroacidificaiton of Caseinate Solution. Membranes, 12(2), 193. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020193