Removal of Excess Alkali from Sodium Naphthenate Solution by Electrodialysis Using Bilayer Membranes for Subsequent Conversion to Naphthenic Acids
Abstract
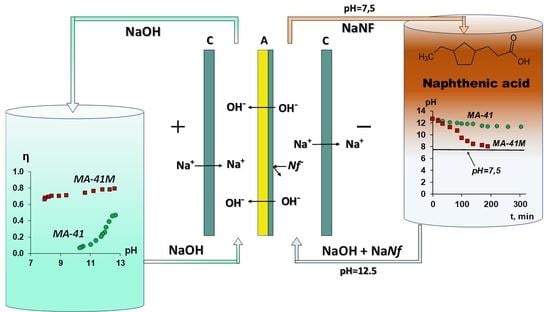
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objects of the Study
2.2. Electrodialysis Tests
2.3. Conductivity Measurement
2.4. Current–Voltage Curve Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Membrane Conductivity
3.2. Investigation of the Electromembrane Process of Removing Alkali from Sodium Naphthenate by Electrodialysis
3.2.1. Current–Voltage Characteristics of Membranes
3.2.2. Specific Selectivity of Anion-Exchange Membranes
3.2.3. Two-Chamber Electrodialyzer Tests
3.2.4. Stability of the Modified Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
List of Symbols and Abbreviations
| Parameter | Description | Dimension |
| PEEK | polyester ether ketone | |
| SPEEK | sulfonated polyester ether ketone | |
| DMFA | dimethylformamide | |
| diffusion boundary layer thickness | m | |
| electrical conductivity of membrane on alternating current | S/m | |
| Θj | molar fraction of ion j | |
| c0 | electrolyte concentration in the bulk of the solution | mol/L |
| Tj | transport number of ion j | |
| l | membrane thickness | m |
| P1.2 | membrane selective permeability coefficient | |
| F | Faraday’s constant | C/mol |
| h | solution compartment thickness | m |
| I | current | A/m2 |
| R | resistance of the membrane | Ohm |
| S | membrane area | m2 |
| V | volume of the solution | m3 |
| zi | charge of ion i |
References
- Adetunji, A.; Olaniran, A. Treatment of industrial oily wastewater by advanced technologies: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othmer, K. Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 2, p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Brient, J.A.; Wessner, P.J.; Doyle, M.N. Naphtenic Acid; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; Volume 91, p. 248. [Google Scholar]
- Pordes, O.; Bangert, N. Improvements in or Relating to Bituminous Polyepoxide Resin Compositions and Their Use. British Patent 1086390; Shell International Research, 20 July 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, J. Naphthenic Acids—Corrosion in Distillation Units. In Rules of Thumb for Petroleum Engineers; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2017; p. 481. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Gao, C. The energy-saving production of tartaric acid using ion exchange resin-filling bipolar membrane electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 341, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, E.; Nemestóthy, N.; Bélafi-Bakó, K. Utilisation of bipolar electrodialysis for recovery of galacturonic acid. Desalination 2010, 250, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärnamäe, R.; Mareev, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Melnikov, S.; Sheldeshov, N.; Zabolotskii, V.; Hamelers, H.V.; Tedesco, M. Bipolar membranes: A review on principles, latest developments, and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2020. 617, 118538. [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Ippersiel, D. Bipolar-membrane electrodialysis: Applications of electrodialysis in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; van Baak, W.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Monovalent-ion-selective membranes for reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 45, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Davis, J.R.; Nguyen, C.H.; Baygents, J.C.; Farrell, J. Electrochemical Ion-Exchange Regeneration and Fluidized Bed Crystallization for Zero-Liquid-Discharge Water Softening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5900–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, O.; Sengpiel, R.G.; Wessling, M. Closing the cycle: Phosphorus removal and recovery from diluted effluents using acid resistive. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achoh, A.; Zabolotsky, V.; Melnikov, S. Conversion of water-organic solution of sodium naphtenates into naphtenic acids and alkali by electrodialysis with bipolar membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroszek, H.; Dydo, P. Ion-exchange membranes in chemical synthesis—A review. Open Chem. 2016, 14, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petriev, I.; Pushankina, P.; Lutsenko, I.; Shostak, N.; Baryshev, M. Synthesis, Electrocatalytic and Gas Transport Characteristics of Pentagonally Structured Star-Shaped Nanocrystallites of Pd-Ag. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achoh, A.; Pribytkov, F.; But, A.; Zabolotsky, V. Exchange sorption and electrical conductivity of heterogeneous anion-exchange membranes in mixed sodium hydroxide/sodium naphthenate and sodium sulfate/sodium nitrate nlectrolyte solutions. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Innocent, C.; Pourcelly, G. Electrodialysis with ion exchange membranes in organic media. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 43, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabane, L.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V.; Bulvestre, G.; Auclair, B. The influence of absorbed methanol on the conductivity and on the microstructure of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 298, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, O.A.; Demin, A.V.; Zabolotskii, V.I.; Berezina, N.P. The effect of aprotic solvent on the selectivity of ion-exchange membranes. Rus. J. Electrochem. 2011, 47, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T.; Yang, W. Studies on cation-exchange membranes having permselectivity between cations in electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, S.; Bondarev, D.; Nosova, E.; Melnikova, E.; Zabolotskiy, V. Water splitting and transport of ions in electromembrane system with bilayer ion-exchange membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.M.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D.; Kaliaguine, S. Proton conducting composite membranes from polyether ether ketone and heteropolyacids for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 173, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berezina, N.P.; Kononenko, N.A.; Dyomina, O.A.; Gnusin, N.P. Characterization of ion-exchange membrane materials: Properties vs structure. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 139, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafan, M.; Zabolotsky, V. Study of electric mass transfer peculiarities in electromembrane systems by the rotating membrane disk method. Desalination 2014, 343, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, L.V.; Demina, O.A.; Dvorkina, G.A.; Parshikov, S.B.; Larchet, C.; Auclair, B.; Berezina, N.P. Comparative study of methods used for the determination of electroconductivity of ion-exchange membranes. Elektrokhimiya 2001, 37, 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Abdu, S.; Wessling, M. Selectivity of Ion Exchange Membranes: A Review. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonin, A.A.; Grossman, G. Ion transport through layered ion exchange membranes. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 3996–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achoh, A.R.; Zabolotsky, V.I.; Lebedev, K.A.; Sharafan, M.V.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Electrochemical Properties and Selectivity of Bilayer Ion-Exchange Membranes in Ternary Solutions of Strong Electrolytes. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2021, 3, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, E.R. Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radII of hydrated ions. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 109, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelkers, E. Calculation of diffusion coefficients for aqueous organic species at temperatures from 0 to 350 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1991, 55, 3515–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R. Electric field effects on proton transfer between ionizable groups and water in ion exchange membranes. Electrochim. Acta 1984, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J. Reformulating the permselectivity-conductivity tradeoff relation in ion-exchange membranes. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Membrane | MK-40 | MA-41 |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed groups | -SO3− | -N+(CH3)3 |
| Ion-exchange resin | KU-2-8 | AV-17-8 |
| Ion-exchange capacity, mmol/g-wet | 1.08 | 0.91 |
| Water uptake, % | 33 | 36 |
| Swollen membrane thickness, microns | 540 | 530 |
| Elementary Cell | Two-Chamber |
|---|---|
| Number of elementary cells | 5 pcs |
| Solutions flow mode | Parallel from bottom up |
| Membranes | |
| anion-exchange | MA-41, MA-41M |
| cation-exchange | MK-40 |
| Materials | |
| anode | Ruthenium oxide titanium anode |
| cathode | Stainless steel |
| spacers | polyethylene |
| Channel dimensions | |
| length | 200 mm |
| width | 50 mm |
| height | 0.9 m |
| Electrolyte Diffusion Coefficients, ×10−9 m2/s | Limiting Current Value, mA/cm2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 M NaOH solution | 2.13 [31] | 168 1 |
| 0.1 M NaNf solution | 0.11 [32] | 39 1 |
| MA-41 in the mixed solution | – | 135 ± 3 2 |
| MA-41M in the mixed solution | – | 72 ± 3 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Achoh, A.; Petriev, I.; Melnikov, S. Removal of Excess Alkali from Sodium Naphthenate Solution by Electrodialysis Using Bilayer Membranes for Subsequent Conversion to Naphthenic Acids. Membranes 2021, 11, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120980
Achoh A, Petriev I, Melnikov S. Removal of Excess Alkali from Sodium Naphthenate Solution by Electrodialysis Using Bilayer Membranes for Subsequent Conversion to Naphthenic Acids. Membranes. 2021; 11(12):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120980
Chicago/Turabian StyleAchoh, Aslan, Ilya Petriev, and Stanislav Melnikov. 2021. "Removal of Excess Alkali from Sodium Naphthenate Solution by Electrodialysis Using Bilayer Membranes for Subsequent Conversion to Naphthenic Acids" Membranes 11, no. 12: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120980
APA StyleAchoh, A., Petriev, I., & Melnikov, S. (2021). Removal of Excess Alkali from Sodium Naphthenate Solution by Electrodialysis Using Bilayer Membranes for Subsequent Conversion to Naphthenic Acids. Membranes, 11(12), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120980