Composite Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Organo-Modified Nanoclays: Investigation on Lithium-Ion Transport and Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
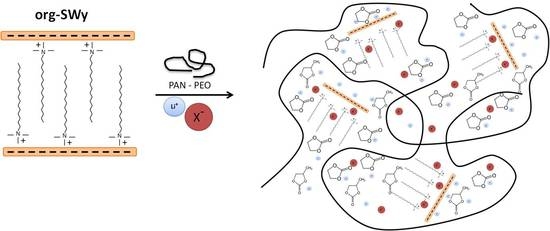
2.2. Synthesys of Organo-Modified Clay (Org-Swy)
2.3. GPE Membrane Preparation
2.4. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological, Thermal, and Mechanical Characterizzation of the GPEs
3.2. Transport Properties of Ions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrosati, B.; Neat, R.J. Applications of Electroactive Polymers; Scrosati, B., Ed.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1993; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Ngai, K.S.; Ramesh, S.; Ramesh, K.; Juan, J.C. A review of polymer electrolytes: Fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics 2016, 22, 1259–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossari, P.; Simari, C.; Cannavale, A.; Gigli, G.; Nicotera, I. Advanced processing and characterization of Nafion electrolyte films for solid-state electrochromic devices fabricated at room temperature on single substrate. Solid State Ion. 2018, 317, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujahadeen, B.A.; Thompson, J.W.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Hameed, M.A. A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. J. Sci.: Adv. Mater. Devices 2018, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wan, C.C. Review of gel-type polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 1999, 77, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, D.; Xie, X. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2015, 3, 19218–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Coppola, L.; Oliviero, C.; Ranieri, G.A. Properties and Impedance Spectroscopy of PMMA-PVdF Blend and PMMA Gel Polymer Electrolytes for Advanced Lithium Batteries. Ionics 2005, 11, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, H.; Hong, J.; Kim, H.; Seo, D.H.; Jeon, S.; Kang, K. Recent progress on flexible lithium rechargeable batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. A PEO-based gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 23494–23501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polu, A.R.; Rhee, H.W. Ionic liquid doped PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion polymer batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 7212–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Oliviero, C.; Ranieri, G.A.; Spadafora, A.; Castriota, M.; Cazzanelli, E. Temperature evolution of thermoreversible polymer gel electrolytes LiClO4/ethylene carbonate/polyacrylonitrile. J. Phys. Chem. 2002, 117, 7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuel Stephan, A.; Nahm, K.S. Review on composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Polymer 2006, 47, 5952–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.Y.; Qiu, X.P.; Li, J.; Tang, X.Z.; Zhu, W.T.; Chen, L.Q. PVDF-PEO blends based microporous polymer electrolyte: Effect of PEO on pore configurations and ionic conductivity. J. Power Sources 2006, 157, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Gao, M.H.; Yin, B.H.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.P.; Xu, G.W.; Bao, J.J. A promising TPU/PEO blend polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 257, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.J.; Costa, C.M.; Lanceros, M.S. Polymer composites and blends for battery separators: State of the art, challenges and future trends. J. Power Sources 2015, 281, 378–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Coppola, L.; Oliviero, C.; Castriota, M.; Cazzanelli, E. Investigation of ionic conduction and mechanical properties of PMMA–PVdF blend-based polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helan Flora, X.; Ulaganathan, M.; Shanker Babu, R.; Rajendran, R. Evaluation of lithium ion conduction in PAN/PMMA-based polymer blend electrolytes for Li-ion battery applications. Ionics 2012, 18, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Kim, Y.W.; Shin, H.K. Ionic conduction in PEO–PAN blend polymer electrolytes. Electrochimica Acta 2000, 45, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, F.L.; Leite, E.R. Hybrid polymer electrolytes for electrochemical devices. Polym. Electrolytes Fundam. Appl. 2010, 583–602. [Google Scholar]
- Wetjen, M.; Navarra, M.A.; Panero, S.; Passerini, S.; Scrosati, B.; Hassoun, J. Composite Poly(ethylene oxide) Electrolytes Plasticized by N-Alkyl-N-butylpyrrolidinium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide for Lithium Batteries. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, E.M.; Bellihi, E.A.A.; Bayoumy, W.A.; Mousa, M.A. Organic–inorganic composite polymer electrolyte based on PEO–LiClO4 and nano-Al2O3 filler for lithium polymer batteries: Dielectric and transport properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 575, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plylahan, N.; Letiche, M.; Barr, M.K.S.; Djenizian, T. All-solid-state lithium-ion batteries based on self-supported titania nanotubes. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 43, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.M.; Wang, Z.D.; Liu, D.P.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, Y.G.; Xia, Y.Y. Bonding polyether onto ZnO nanoparticles: An effective method for preparing polymer nanocomposites with tunable luminescence and stable conductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panero, S.; Scrosati, B.; Sumathipala, H.H.; Wieczorek, W. Dual-composite polymer electrolytes with enhanced transport properties. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, F.; Chen, Y.; Xiaoxiong, X. A promising PEO/LAGP hybrid electrolyte prepared by a simple method for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Solid State Ion. 2016, 295, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, M.; Galvin, M.E.; Trapa, P.E.; Sadoway, D.R.; Mayes, A.M. Single-ion conducting polymer–silicate nanocomposite electrolytes for lithium battery applications. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, H.C.; Lin, W.T.; Tsai, C.H. Effect of the addition of hydrophobic clay on the electrochemical property of polyacrylonitrile/LiClO4 polymer electrolytes for lithium battery. Polymer 2009, 50, 2856–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Enotiadis, A.; Angjeli, K.; Coppola, L.; Gournis, D. Evaluation of smectite clays as nanofillers for the synthesis of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 6236–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.E. Use of the stimulated echo in NMR diffusion studies. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 2523–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, J.; Cui, J.; Li, J.; Wu, X. A gel polymer electrolyte based on Polyacrylonitrile/organic montmorillonite membrane exhibiting dense structure for lithium ion battery. Solid State Ion. 2018, 315, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, Z. Polyacrylonitrile, an unusual linear homopolymer with two glass transition. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 1999, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Cao, Q.; Meng, Q.; Yang, L. Investigation on the structure and the conductivity of plasticized polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 1992, 53–56, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotera, I.; Coppola, L.; Oliviero, C.; Russo, A.; Ranieri, G.A. Some physicochemical properties of PAN-based electrolytes: Solution and gel microstructures. Solid State Ion. 2004, 167, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enotiadis, A.; Fernandes, N.J.; Becerra, N.A.; Zammarano, M.; Giannelis, E.P. Nanocomposite electrolytes for lithium batteries with reduced flammability. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Chiam, W.L. Rheological characterizations of ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolytes and fumed silica-based composite polymer electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 3411–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Mahendran, O.; Kannan, R. Characterisation of [(1−x)PMMA–xPVdF] polymer blend electrolyte with Li+ ion. Fuel 2002, 81, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Subadevi, R.; Rajendran, S.; Wu, N.L.; Lee, J.Y. Electrochemical studies on [(1−x)PVA–xPMMA] solid polymer blend electrolytes complexed with LiBF4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 97, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.H.S.; He, K.Q.; Liua, Y.; Zha, J.W.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Ma, R.L.W.; Dang, Z.M.; Li, R.K.Y.; Chung, C.Y. Electrochemical performance of all-solid-state lithium batteries using inorganic lithium garnets particulate reinforced PEO/LiClO4 electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 253, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castriota, M.; Cazzanelli, E.; Nicotera, I.; Coppola, L.; Oliviero, C.; Ranieri, G.A. Temperature dependence of lithium ion solvation in ethylene carbonate–LiClO4 solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewde, B.W.; Carbone, L.; Greenbaum, S.; Hassoun, J. A novel polymer electrolyte membrane for application in solid state lithium metal battery. Solid State Ion. 2018, 317, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L.; Xu, F.; Feng, W.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Armand, M.; Nie, J.; Zhou, Z. Lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide/poly(ethylene oxide) polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 133, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorecki, W.; Jeannin, M.; Belorizky, E.; Roux, C.; Armand, M. Physical properties of solid polymer electrolyte PEO(LiTFSI) complexes. Phys. Condens. Matter 1995, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumathipala, H.H.; Hassoun, J.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B. High performance PEO-based polymer electrolytes and their application in rechargeable lithium polymer batteries. Ionics 2007, 13, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| T (°C) | PAN | PAN-PEO + 10% SW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σEIS | σNMR | Ionicity | tLi+ | σEIS | σNMR | Ionicity | tLi+ | |
| 20 | 1.77 | 3.92 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 2.79 | 4.31 | 0.68 | 0.68 |
| 30 | 2.08 | 5.02 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 3.22 | 4.74 | 0.65 | 0.67 |
| 40 | 2.31 | 6.96 | 0.33 | 0.41 | 3.37 | 7.84 | 0.53 | 0.59 |
| 50 | 2.56 | 8.19 | 0.31 | 0.43 | 3.17 | 9.07 | 0.45 | 0.56 |
| 60 | 2.74 | 9.68 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 3.77 | 9.82 | 0.48 | 0.56 |
| 70 | 3.03 | 11.1 | 0.27 | 0.43 | 4.05 | 11.20 | 0.42 | 0.57 |
| 80 | 3.12 | 11.8 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 4.24 | 12.33 | 0.38 | 0.58 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simari, C.; Lufrano, E.; Coppola, L.; Nicotera, I. Composite Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Organo-Modified Nanoclays: Investigation on Lithium-Ion Transport and Mechanical Properties. Membranes 2018, 8, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030069
Simari C, Lufrano E, Coppola L, Nicotera I. Composite Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Organo-Modified Nanoclays: Investigation on Lithium-Ion Transport and Mechanical Properties. Membranes. 2018; 8(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimari, Cataldo, Ernestino Lufrano, Luigi Coppola, and Isabella Nicotera. 2018. "Composite Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Organo-Modified Nanoclays: Investigation on Lithium-Ion Transport and Mechanical Properties" Membranes 8, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030069
APA StyleSimari, C., Lufrano, E., Coppola, L., & Nicotera, I. (2018). Composite Gel Polymer Electrolytes Based on Organo-Modified Nanoclays: Investigation on Lithium-Ion Transport and Mechanical Properties. Membranes, 8(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030069