The Effect of Submaximal Exercise Followed by Short-Term Cold-Water Immersion on the Inflammatory State in Healthy Recreational Athletes: A Cross-Over Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Baseline Examination
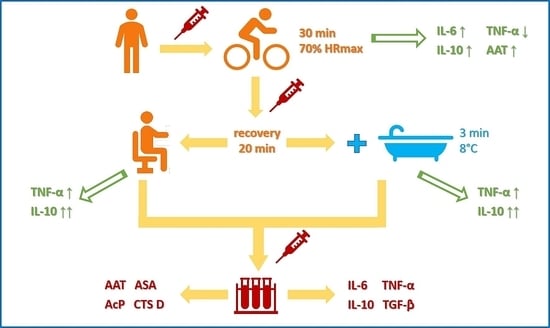
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Determination of the Activity of Protease Inhibitor and Lysosomal Enzymes
2.5. Determination of the Cytokine Concentrations
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of the Study Group
3.2. The Concentration of Cytokines
3.3. The Activity of Protease Inhibitor and Lysosomal Enzymes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dishman, R.K. Increasing and maintaining exercise and physical activity. Behav. Ther. 1991, 22, 345–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.G.; Oktedalen, O.; Opstad, P.K.; Lyberg, T. Plasma cytokine profiles in long-term strenuous exercise. J. Sports Med. 2016, 2016, 7186137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niemela, M.; Kangastupa, P.; Niemela, O.; Bloigu, R.; Juvonen, T. Acute changes in inflammatory biomarker levels in recreational runners participating in a marathon or half-marathon. Sports Med. Open 2016, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Powers, S.K.; Jackson, M.J. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 1243–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Powers, S.K.; Deminice, R.; Ozdemir, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Bomkamp, M.P.; Hyatt, H. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.A.; Carvalho, T.; Cruz, A.C.; Jesus, L.R.; Silva Neto, L.A.; Trajano, E.T.; Bezerra, F.S. Effect of time-dependent cryotherapy on redox balance of quadriceps injuries. Cryobiology 2016, 72, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Jurecka, A.; Woźniak, A.; Szpinda, M.; Augustyńska, B.; Woźniak, B. The effect of submaximal exercise preceded by single whole-body cryotherapy on the markers of oxidative stress and inflammation in blood of volleyball players. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 409567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woźniak, A.; Woźniak, B.; Drewa, G.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Rakowski, A. The effect of whole-body cryostimulation on lysosomal enzyme activity in kayakers during training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 100, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkowy, P.; Woźniak, A.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Jurecka, A. The activity of lysosomal enzymes in the health men’s blood after single Finnish sauna procedure—Preliminary study. Med. Biol. Sci. 2012, 26, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jonak, A.; Skrzek, A. Cryotherapy in athlete’s biological regeneration—Review. Acta Bio-Opt. Inform. Med. 2009, 15, 319–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bleakley, C.M.; Bieuzen, F.; Davison, G.W.; Costello, J.T. Whole-body cryotherapy: Empirical evidence and theoretical perspectives. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2014, 5, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutkowy, P.; Augustyńska, B.; Woźniak, A.; Rakowski, A. Physical exercise combined with whole-body cryotherapy in evaluating the level of lipid peroxidation products and other oxidant stress indicators in kayakers. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 402631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.; Willoughby, D.S. The effectiveness of whole body cryotherapy compared to cold water immersion: Implications for sport and exercise recovery. IJKSS 2016, 4, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bresnahan, R. Cold water immersion and anti-inflammatory response: A systematic review. ESN Rev. 2019, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- de Freitas, V.H.; Ramos, S.P.; Bara-Filho, M.G.; Freitas, D.G.S.; Coimbra, D.R.; Cecchini, R.; Guarnier, F.A.; Nakamura, F.Y. Effect of cold water immersion performed on successive days on physical performance, muscle damage, and inflammatory, hormonal, and oxidative stress markers in volleyball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/theipaq/questionnaire_links (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Ciechanowska, K.; Weber-Rajek, M.; Sikorska, J.; Bułatowicz, I.; Radzimińska, A.; Strojek, K.; Zukow, W. Biological recovery methods in sport. J. Health Sci. 2014, 4, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrand, T. Changes in the respiratory organs of workmen at an oresmelting works. Acta Med. Scand. 1974, 196, 687–699. [Google Scholar]
- Astrand, P.O.; Rodahl, K. Textbook of Work Physiology; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, E.; Borg, G.; Larsson, K.; Letzter, M.; Sundblad, B.M. An index for breathlessness and leg fatigue. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal hart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Błeszyński, W.; Działoszyński, L.M. Purification of soluble arylosulfatase from ox brain. Biochem. J. 1965, 97, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krawczyński, J. Diagnostyka Enzymologiczna w Medycynie Praktycznej. Metodyka Badań; Publikacje Wydawnictwa Lekarskiego PZWL: Warsaw, Poland, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Inkabi, S.E.; Pushpamithran, G.; Richter, P.; Attakora, K. Exercise immunology: Involved components and varieties in different types of physical exercise. Sci. J. Life Sci. 2017, 1, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaldivar, F.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Nemet, D.; Schwindt, C.; Galassetti, P.; Mills, P.J.; Wilson, L.D.; Cooper, D.M. Constitutive pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokine and growth factor response to exercise in leukocytes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.C.; Sierra, A.P.; Oliveira, R.; Caçula, K.G.; Momesso, C.M.; Sato, F.T.; Silva, M.B.; Oliveira, H.H.; Passos, M.E.; de Souza, D.R.; et al. Marathon race affects neutrophil surface molecules: Role of inflammatory mediators. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezil, Y.A.; Allison, D.; Kish, K.; Ditor, D.; Ward, W.E.; Tsiani, E.; Klentrou, P. Response of bone turnover markers and cytokines to high-intensity low-impact exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarish, V.; Chandrashekara, S.; Suresh, K.P. Moderate regular exercises reduce inflammatory response for physical stress. Indian J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 56, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Starkie, R.L.; Rolland, J.; Angus, D.J.; Anderson, M.J.; Febbraio, M.A. Circulating monocytes are not the source of elevations in plasma IL-6 and TNF-αlevels after prolonged running. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.P. Interleukin-6 in acute exercise and training: What is the biological relevance? Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 12, 6–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.A.; Nosaka, K.; Coombes, J.S.; Peake, J.M. Cold water immersion enhances recovery of submaximal muscle function after resistance exercise. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, G.E.; Rhind, S.G.; Wells, G.D. The effect of various cold-water immersion protocols on exercise-induced inflammatory response and functional recovery from high-intensity sprint exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 2353–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earp, J.E.; Hatfield, D.L.; Sherman, A.; Lee, E.C.; Kraemer, W.J. Cold-water immersion blunts and delays increases in circulating testosterone and cytokines post-resistance exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, V.; Silveira de Avelar, I.; Espíndola Mota Venâncio, P.; Pires-Oliveira, D.A.A.; de Almeida Silva, P.H.; Rodrigues Borges, A.; Fonseca, G.P.E.F.; Noll, M. Acute changes in interleukin-6 level during four days of long-distance walking. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 10, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Snick, J. Interleukin-6: An overview. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1990, 8, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.; Keller, P.; Giralt, M.; Hidalgo, J.; Pedersen, B.K. Exercise normalises verexpression of TNF-α in knockout mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 321, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov, T.; Hulteng, E.; Hong, S. Inflammation and exercise: Inhibition of monocytic TNF production by acute exercise via β2-adrenergic activation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 61, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovitch, D.; Tyrrell, R.M.; Thompson, D. The effect of prior exercise on ex vivo induction of heme oxygenase-1 in human lymphocytes. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, S.J.; Smith, L.L.; McKune, A.J.; Hoyos, J.; Mokgethwa, B.; San Juan, A.F.; Lucia, A.; Wadee, A.A. Serum concentrations of C reactive protein, a1 antitrypsin, and complement (C3, C4, C1 esterase inhibitor) before and during the Vuelta a Espańa. Br. J. Sports Med. 2006, 40, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schild, M.; Eichner, G.; Beiter, T.; Zügel, M.; Krumholz-Wagner, I.; Hudemann, J.; Pilat, C.; Krüger, K.; Niess, A.M.; Steinacker, J.M.; et al. Effects of acute endurance exercise on plasma protein profiles of endurance-trained and untrained individuals over time. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 4851935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eimonte, M.; Paulauskas, H.; Daniuseviciute, L.; Eimantas, N.; Vitkauskiene, A.; Dauksaite, G.; Solianik, R.; Brazaitis, M. Residual effects of short-term whole-body cold-water immersion on the cytokine profile, white blood cell count, and blood markers of stress. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eimontea, M.; Eimantasa, N.; Daniuseviciuteb, L.; Paulauskasa, H.; Vitkauskienec, A.; Dauksaitea, G.; Brazaitis, M. Recovering body temperature from acute cold stress is associated with delayed proinflammatory cytokine production in vivo. Cytokine 2021, 143, 155510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klich, S.; Krymski, I.; Michalik, K.; Kawczyński, A. Effect of short-term cold-water immersion on muscle pain sensitivity in elite track cyclists. Phys. Ther. Sport 2018, 32, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, J.M.; Roberts, L.A.; Figueiredo, V.C.; Egner, I.; Krog, S.; Aas, S.N.; Suzuki, K.; Markworth, J.F.; Coombes, J.S.; Cameron-Smith, D.; et al. The effects of cold water immersion and active recovery on inflammation and cell stress responses in human skeletal muscle after resistance exercise. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbickas, V.; Baranwskiene, N.; Eimantas, N.; Kamandulis, S.; Rutkauskas, S.; Satkunskiene, D.; Sadauskas, S.; Brazaitis, M.; Skurvydas, A. Effects of sprint cycling and stretch-shortering cycle exercises on the neuromuscular, immune and stress indicators in young men. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rhind, S.G.; Castellani, J.W.; Brenner, I.K.; Shephard, R.J.; Zamecnik, J.; Montain, S.J.; Young, A.J.; Shek, P.N. Intracellular monocyte and serum cytokine expression is modulted by exhausting exercise and col exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 281, R66–R75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belizário, J.E.; Fontes-Oliveira, C.C.; Borges, J.P.; Kashiabara, J.A.; Vannier, E. Skeletal muscle wasting and renewal: A pivotal role of myokine IL-6. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peake, J.M.; Neubauer, O.; Della Gatta, P.A.; Nosaka, K. Muscle damage and inflammation during recovery from exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhabhar, F.S.; Malarkey, W.B.; Neri, E.; McEwen, B.S. Stress-induced redistribution of immune cells—From barracks to boulevards to battlefields: A tale of three hormones—Curt Richter Award Winner. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2012, 37, 1345–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- White, G.E.; Wells, G.D. Cold-water immersion and other forms of cryotherapy: Physiological changes potentially affecting recovery from high-intensity exercise. Extrem. Physiol. Med. 2013, 2, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanagisawa, O.; Kudo, H.; Takahashi, N.; Yoshioka, H. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of cooling on blood flow and oedema in skeletal muscles after exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 91, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigmore, S.J.; Fearon, K.C.; Ross, J.A.; McNally, S.J.; Welch, W.J.; Garden, O.J. Febrile-range temperature but not heat shock augments the acute phase response to interleukin-6 in human hepatoma cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G903–G911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.R. Immune-modulating effects of alpha-1 antitrypsin. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, A.; Drewa, T.; Drewa, G.; Woźniak, B.; Malinowski, D.; Rakowski, A. Activity of arylosulphatase, cathepsin D and creatine kinase after submaximal and supermaximal exercise in untrained men and women. Biol. Sport 2002, 19, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Farges, M.C.; Balcerzak, D.; Fisher, B.D.; Attaix, D.; Béchet, D.; Ferrara, M.; Baracos, V.E. Increased muscle proteolysis after local trauma mainly reflects macrophage-associated lysosomal proteolysis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E326–E335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutkowy, P.; Woźniak, A.; Boraczyński, T.; Boraczyński, M.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C. The oxidant-antioxidant equilibrium, activities of selected lysosomal enzymes and activity of acute phase protein in peripheral blood of 18-year-old football players after aerobic cycle ergometer test combined with ice-water immersion or recovery at room temperature. Cryobiology 2017, 74, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Woźniak, A.; Szpinda, M.; Boraczyński, T.; Woźniak, B.; Rajewski, P.; Sutkowy, P. Effects of thermal stress on the activity of selected lysosomal enzymes in blood of experienced and novice winter swimmers. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2012, 72, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Inclusion Criteria |
|---|
|
| Exclusion Criteria |
|
| Parameter | Mean ± S.D. |
|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 25.0 ± 4.8 |
| BH (body height, cm) | 179.7 ± 5.0 |
| BM (body mass, kg) | 81.4 ± 9.6 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.3 ± 2.7 |
| BF (body fat, %) | 15.6 ± 4.3 |
| TBW (total body water, %) | 61.5 ± 3.3 |
| VO2 max (maximum oxygen consumption, mL/kg/min) 1 | 40.95 ± 6.6 |
| Borg CR10 (rating of perceived exertion scale) 1 | 4.06 ± 0.8 |
| VO2 max (maximum oxygen consumption, mL/kg/min) 2 | 40.67 ± 6.7 |
| Borg CR10 (rating of perceived exertion scale) 2 | 4.08 ± 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pawłowska, M.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Boraczyński, T.; Boraczyński, M.; Szewczyk-Golec, K.; Sutkowy, P.; Wesołowski, R.; Smoguła, M.; Woźniak, A. The Effect of Submaximal Exercise Followed by Short-Term Cold-Water Immersion on the Inflammatory State in Healthy Recreational Athletes: A Cross-Over Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184239
Pawłowska M, Mila-Kierzenkowska C, Boraczyński T, Boraczyński M, Szewczyk-Golec K, Sutkowy P, Wesołowski R, Smoguła M, Woźniak A. The Effect of Submaximal Exercise Followed by Short-Term Cold-Water Immersion on the Inflammatory State in Healthy Recreational Athletes: A Cross-Over Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2021; 10(18):4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184239
Chicago/Turabian StylePawłowska, Marta, Celestyna Mila-Kierzenkowska, Tomasz Boraczyński, Michał Boraczyński, Karolina Szewczyk-Golec, Paweł Sutkowy, Roland Wesołowski, Małgorzata Smoguła, and Alina Woźniak. 2021. "The Effect of Submaximal Exercise Followed by Short-Term Cold-Water Immersion on the Inflammatory State in Healthy Recreational Athletes: A Cross-Over Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 10, no. 18: 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184239
APA StylePawłowska, M., Mila-Kierzenkowska, C., Boraczyński, T., Boraczyński, M., Szewczyk-Golec, K., Sutkowy, P., Wesołowski, R., Smoguła, M., & Woźniak, A. (2021). The Effect of Submaximal Exercise Followed by Short-Term Cold-Water Immersion on the Inflammatory State in Healthy Recreational Athletes: A Cross-Over Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(18), 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10184239