Conversion of Hemiarthroplasty to Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty with Humeral Stem Retention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
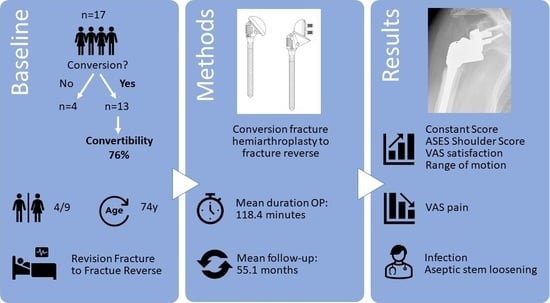
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Implant Characterstics
2.3. Operating Technique
2.4. Clinical Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Outcomes
3.2. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shukla, D.R.; McAnany, S.; Kim, J.; Overley, S.; Parsons, B.O. Hemiarthroplasty versus reverse shoulder arthroplasty for treatment of proximal humeral fractures: A meta-analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boileau, P.; Winter, M.; Cikes, A.; Han, Y.; Carles, M.; Walch, G.; Schwartz, D. Can surgeons predict what makes a good hemiarthroplasty for fracture? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2013, 22, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevang, B.T.L.; Lie, S.A.; Havelin, L.I.; Skredderstuen, A.; Furnes, O. Risk factors for revision after shoulder arthroplasty: 1825 shoulder arthroplasties from the Norwegian Arthroplasty register. Acta Orthop. 2009, 80, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiater, B.P.; Moravek, J.E.; Wiater, J.M. The evaluation of the failed shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wilde, L.M.M.; Van Petegem, P.; Verdonk, R. Revision of shoulder replacement with a reversed shoulder prosthesis (Delta III): Report of five cases. Acta Orthop. Belg. 2001, 67, 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Gohlke, F.; Rolf, O. Revision of failed fracture hemiarthroplasties to reverse total shoulder prosthesis through the transhumeral approach: Method incorporating a pectoralis-major-pedicled bone window. Oper. Orthop. Und Traumatol. 2007, 19, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.C.; Virani, N.; Pupello, D.; Frankle, M. Use of the reverse shoulder prosthesis for the treatment of failed hemiarthroplasty in patients with glenohumeral arthritis and rotator cuff deficiency. J. Bone Jt. Surgery. Br. Vol. 2007, 89, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.; Frankle, M.; Mighell, M.; Pupello, D. The use of the reverse shoulder prosthesis for the treatment of failed hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fracture. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2007, 89, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, B.M.; Chalmers, P.N.; Gupta, A.K.; Romeo, A.; Nicholson, G.P. Complication rates comparing primary with revision reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2014, 23, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, L.A.; Wright, T.W.; Yu, S.; Zuckerman, J.D. Conversion to reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with and without humeral stem retention: The role of a convertible-platform stem. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2017, 99, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsch, J.M.; Khan, M.; Thornley, P.; Gichuru, M.; Freehill, M.T.; Neviaser, A.; Moravek, J.; Miller, B.S.; Bedi, A. Platform shoulder arthroplasty: A systematic review. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2018, 27, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon, A.; Virani, N.; Shannon, R.; Levy, J.C.; Pupello, D.; Frankle, M. Revision Arthroplasty with Use of a Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis-Allograft Composite. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2009, 91, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilisio, M.F.; Miller, L.R.; Siegel, E.J.; Higgins, L.D. Conversion to Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: Humeral Stem Retention Versus Revision. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e773–e779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschner, H.; Vaske, B.; Albrecht, U.-V.; Meller, R.; Liodakis, E.; Wiebking, U.; Krettek, C.; Jagodzinski, M. Conversion of hemi into reverse shoulder arthroplasty: Implant design limitations. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2014, 134, 1683–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, K.; Borbas, P.; Ek, E.T.; Meyer, D.C.; Gerber, C. Conversion of stemmed hemi- or total to reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: Advantages of a modular stem design. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, B.C.; Dines, J.S.; Dines, D.M. Platform systems in shoulder arthroplasty. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2016, 9, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castagna, A.; Delcogliano, M.; De Caro, F.; Ziveri, G.; Borroni, M.; Gumina, S.; Postacchini, F.; De Biase, C.F. Conversion of shoulder arthroplasty to reverse implants: Clinical and radiological results using a modular system. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werner, B.S.; Boehm, D.; Gohlke, F. Revision to reverse shoulder arthroplasty with retention of the humeral component. Acta Orthop. 2013, 84, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lädermann, A.; Williams, M.D.; Melis, B.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Walch, G. Objective evaluation of lengthening in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2009, 18, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, B.; Bonnevialle, N.; Neyton, L.; Lévigne, C.; Favard, L.; Walch, G.; Boileau, P. Glenoid loosening and failure in anatomical total shoulder arthroplasty: Is revision with a reverse shoulder arthroplasty a reliable option? J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2012, 21, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.; Willis, M.P.; Brooks, J.P.; Pupello, D.; Mulieri, P.J.; Frankle, M.A. The use of the reverse shoulder arthroplasty for treatment of failed total shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2012, 21, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Sex (female/male) | 9/4 |
| Operated side (right/left) | 6/7 |
| Age at surgery (years) | 73.6 (64.9–89.6) |
| Time since implantation of hemiprosthesis (months) | 16.7 (3.9–61.7) |
| Follow-up period (months) | 55.1 (12.0–91.1) |
| Clinical Outcome | Preoperative (n = 13) | At 12 Months (n = 11) | p Value * | At Last Follow-up (n = 8) | p Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant score | 21.7 (4.0–52.0) | 50.1 (37.0–71.0) | 0.0001 | 57.9 (42.0–96.0) | 0.0001 |
| ASES Shoulder Score | 24.3 (6.7–46.8) | 63.8 (46.7–86.7) | <0.001 | 66.9 (46.7–98.3) | <0.001 |
| VAS for pain | 7.3 (5.0–9.0) | 2.3 (0.0–5.0) | <0.001 | 2.3 (0.0–5.0) | <0.001 |
| VAS for satisfaction | 2.0 (0.0–6.2) | 7.9 (5.0–10.0) | <0.001 | 8.0 (7.0–10.0) | <0.001 |
| Active ROM in abduction (°) | 38.8 (10.0–100.0) | 103.2 (50.0–180.0) | <0.001 | 111.9 (50.0–160.0) | 0.006 |
| Active ROM in forward flexion (°) | 46.2 (10.0–130.0) | 111.8 (60.0–160.0) | 0.0001 | 122.5 (60.0–180.0) | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reuther, F.; Irlenbusch, U.; Kääb, M.J.; Kohut, G. Conversion of Hemiarthroplasty to Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty with Humeral Stem Retention. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030834
Reuther F, Irlenbusch U, Kääb MJ, Kohut G. Conversion of Hemiarthroplasty to Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty with Humeral Stem Retention. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2022; 11(3):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030834
Chicago/Turabian StyleReuther, Falk, Ulrich Irlenbusch, Max J. Kääb, and Georges Kohut. 2022. "Conversion of Hemiarthroplasty to Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty with Humeral Stem Retention" Journal of Clinical Medicine 11, no. 3: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030834
APA StyleReuther, F., Irlenbusch, U., Kääb, M. J., & Kohut, G. (2022). Conversion of Hemiarthroplasty to Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty with Humeral Stem Retention. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 11(3), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11030834