Exploring Perturbations in Peripheral B Cell Memory Subpopulations Early after Kidney Transplantation Using Unsupervised Machine Learning
Abstract
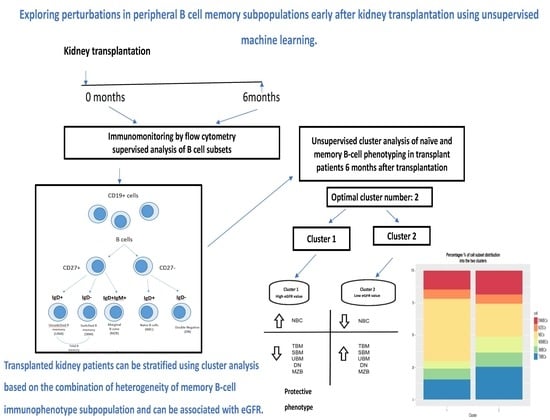
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Patients
- Inclusion criteria:
- Exclusion criteria:
2.2. Study Schedule
2.3. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
2.4. Immunosuppresion Regimen
2.5. Flow Cytometry-B Cell Phenotyping
- anti-CD19 PC5.5 clone J3-119, Beckman Coulter,
- anti -CD27 PE-Dylight 594 clone LT27, EXBIO, Praha SA
- anti-IgD FITC clone IA6-2, ThermoScientific LSG,
- anti-CD45-PC7 clone J33 Beckman, Coulter,
- anti-IgM PE clone SA-DA4 Beckman, Coulter.
| B Cell Subset Phenotypes | B Cell Population, References |
|---|---|
| CD19+ | total B lymphocytes, TBL, [18,19] |
| CD19+ CD27+ IgD−/+ | total memory B cells, TMBCs, [19,20,21] |
| CD19+ CD27+ IgM+ IgD+ | peripheral equivalent to marginal zone B cells, peripheral equivalent of MZBCs [22,23] |
| CD19+ CD27+ IgD− | class-switched memory B cells, SMBCs, [19] |
| CD19+ CD27+ IgD+ | class non-switched memory B cells, NSMBCs, [19,24] |
| CD19+ CD27− IgD− | double negative (with memory properties) DNMBCs, [25,26,27] |
| CD19+ CD27− IgD+ | naïve B cells, NBCs, gained from total memory B cells [17,18] |
2.6. Statistics and Cluster Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Transplantation on B Lymphocytes and Naïve and Memory B Cell Subpopulations
| B Cell Populations | Τ0 | Τ6 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Subpopulations (% Cells) | Ν = 47 Median (IQR) | Ν = 47 Median (IQR) | |
| CD19+, total B cells | 7.8 (5.9, 12.3) | 6.8 (5, 9.6) | 0.060 |
| Naïve B cells, NBCs | 76.4 (66.3, 84.9) | 71 (59, 77.6) | 0.032 |
| Total memory B cells, TMBCs | 24.6 (15.9, 37.1) | 27 (20.9, 38.7) | 0.280 |
| Class-switched memory B cells, SMBCs | 13.2 (9.7, 21) | 15 (9.8, 19.9) | 0.957 |
| Class non-Switched memory B cells, NSMBCs | 8.5 (3.8, 13) | 10 (49, 16.7) | 0.220 |
| Peripheral equivalent to marginal zone B cells, peripheral equivalent to MZBCs | 16.3 (4.7, 35.7) | 22.8 (11.8, 44.6) | 0.118 |
| Double negative with memory properties cells, DNMBCs | 12 (7.7, 18.8) | 11.1 (7.6, 16.7) | 0.875 |
3.2. Clustering Results
3.3. Proportion Model Cluster Distinction
3.4. Study Patients
3.4.1. eGFR Distribution of the Two Clusters 1 and 2
3.4.2. The Effect of Donor Type, Age of Recipient, Dialysis Duration on B Cells, Naïve and Memory B Cell Subpopulations
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newell, K.A.; Asare, A.; Kirk, A.D.; Gisler, T.D.; Bourcier, K.; Suthanthiran, M.; Burlingham, W.J.; Marks, W.H.; Sanz, I.; Lechler, R.I.; et al. Identification of a B cell signature associated with renal transplant tolerance in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1836–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Ming, Y.; Yang, C. Regulatory B cells: The cutting edge of immune tolerance in kidney transplantation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karahan, G.E.; Claas, F.H.J.; Heidt, S. B Cell immunity in Solid Organ Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, S.; Lúcia, M.; Bestard, O. Refinement of humoral immune monitoring in kidney transplantation: The role of “hidden” alloreactive memory B cells. Transpl. Int. 2017, 30, 955–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G.; Good, K.L. Human IgM + CD27 + B cells: Memory B cells or “memory” B cells? J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, K.L.; Avery, D.T.; Tangye, S.G. Resting human memory B cells are intrinsically programmed for enhanced survival and responsiveness to diverse stimuli compared to naive B cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, U.; Rajewsky, K.; Küppers, R.J. Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M + IgD + peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maecker, H.T.; McCoy, J.P.; Nussenblatt, R. Standardizing immunophenotyping for the human immunology project. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 3, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, K.; Camponeschi, A.; Cavallini, N.; Grimsholm, O.; Jacobsson, L.; Gjertsson, I.; Mårtensson, I.L. CD21(−/low) B cells in human blood are memory cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnell, J.L.; Kumar, V.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Voynova, E.; Ettinger, R. Role of CD11c+ T-bet+ B cells in human health and disease. Cell. Immunol. 2017, 321, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsov, A.V.; Swanson, C.L.; Troy, S.; Strauch, P.; Pelanda, R.; Torres, R.M. TLR agonists promote marginal zone B cell activation and facilitate T-dependent IgM responses. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 3882–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Segundo, D.; Rodrigo, E.; Fernández-Fresnedo, G.; Bonilla, G.; Arias, M.; López-Hoyos, M. Decrease in Marginal Zone B-cells (CD27+ IgD+ CD38–) as Surrogate Marker of Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Trends Transpl. 2013, 7, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Fa, R.; Nicosia, M.; Gorbacheva, V.; Fairchild, R.; Valujskikh, A. Marginal Zone B cells support cell reconstitution following ATG lymphoablation in heart allograft recipients. Am. J. Transpl. 2022, 22 (Suppl. S3), 458. [Google Scholar]
- Zorn, E. Effector B cells in cardiac allograft vasculopathy. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2019, 24, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Daccache, J.; Jain, D.; Ko, K.; Kinloch, A.; Veselits, M.; Wolfgeher, D.; Chang, A.; Josephson, M.; Cunningham, P.; et al. Innate-like self-reactive B cells infiltrate human renal allografts during transplant rejection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. CKD-EPI (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration). A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finak, G.; Langweiler, M.; Jaimes, M.; Malek, M.; Taghiyar, J.; Korin, Y.; Raddassi, K.; Devine, L.; Obermoser, G.; Pekalski, M.L.; et al. Standardizing Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping Analysis from the Human ImmunoPhenotyping Consortium. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 20686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, D.A.; Wei, C.; Qian, Y.; Rosenberg, A.F.; Sanz, I. Advances in human B cell phenotypic profiling. Front. Immunol. 2012, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, M.; Heidt, S.; Redondo, D.; Pascual, J. Monitoring B cell subsets and alloreactivity in kidney transplantation. Transpl. Rev. 2015, 29, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, I.; Wei, C.; Lee, F.E.; Anolik, J. Phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of human memory B cells. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agematsu, K.; Hokibara, S.; Nagumo, H.; Komiyama, A. CD27: A memory B-cell marker. Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capolunghi, F.; Rosado, M.M.; Sinibaldi, M.; Aranburu, A.; Carsetti, R. Why do we need IgM memory B cells? Immunol. Lett. 2013, 152, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnara, D.; Squillario, M.; Kipling, D.; Mora, T.; Walczak, A.M.; Silva, L.; Weller, S.; Walters, D.K.; Weil, J.C.; Reynaud, C.A. A Reassessment of IgM Memory Subsets in Humans. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3716–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.E.; Kaminski, D.; Jenks, S.A.; Maguire, C.; Ching, K.; Burbelo, P.D.; Iadarola, M.J.; Rosenberg, A.; Coca, A.; Anolik, J.; et al. Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Is Characterized by Distinct Phenotypic and Transcriptional Profiles of IgD+ Unswitched Memory B Cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 2558–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecteau, J.F.; Côté, G.; Néron, S. A new memory CD27− IgG+ B cell population in peripheral blood expressing VH genes with low frequency of somatic mutation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 3728–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Anolik, J.; Cappione, A.; Zheng, B.; Pugh-Bernard, A.; Brooks, J.; Lee, E.H.; Milner, E.C.; Sanz, I. A new population of cells lacking expression of CD27 represents a notable component of the B cell memory compartment in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6624–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, L.; Somers, V.; Fraussen, J. IgD−CD27− double negative (DN) B cells: Origins and functions in health and disease. Immunol. Lett. 2023, 255, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Fitch, Z.W.; Schroder, P.M.; Choi, A.Y.; Jackson, A.M.; Knechtle, S.J.; Kwun, J. B cells in transplant tolerance and rejection: Friends or foes? Transpl. Int. 2020, 1, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidt, S.; Hester, J.; Shankar, S.; Friend, P.J.; Wood, K.J. B cell repopulation after alemtuzumab induction-transient increase in transitional B cells and long-term dominance of naïve B cells. Am. J. Transpl. 2012, 7, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkhin, V.; Lovelace, P.A.; Li, L.; Hsieh, S.C.; Sarwal, M.M. Phenotypic evaluation of B-cell subsets after rituximab for treatment of acute renal allograft rejection in pediatric recipients. Transplantation 2011, 91, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Berg, P.J.E.J.; Hoevenaars, E.C.; Yong, S.-L.; van Donselaar, K.A.; Tellingen, A.; Florquin, S.; Lier, R.A.; Bemelman, F.J.; Berge, I.J. Circulating lymphocyte subsets in different clinical situations after renal transplantation. Immunology 2012, 136, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, R.; Legaz, I.; González-Martínez, G.; Jimenez-Coll, V.; Martínez-Banaclocha, H.; Coll, V.; Martinez, H.; Galian, J.A.; Botella, C.; Moral, J.; et al. Monitoring of B Cell in Kidney Transplantation: Development of a Novel Clusters Analysis and Role of Transitional B Cells in Transplant Outcome. Diagnostics 2021, 4, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.; Li, H.; Yu, M.; Peng, B.; Liu, S.; Luo, M.; Stefano, G.B.; Kream, R.M.; Ming, Y. Profiles of B-cell subsets in immunologically stable renal allograft recipients and end-stage renal disease patients. Transpl. Immunol. 2020, 58, 101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuller, M.; Pfeifer, V.; Kirsch, A.H.; Klötzer, K.A.; Mooslechner, A.A.; Rosenkranz, A.R.; Stiegler, P.; Schemmer, P.; Sourij, H.; Eller, P.; et al. B Cell composition is altered after kidney transplantation and transitional B cells correlate with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination response. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 818882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Rondaan, C.; de Joode, A.A.E.; Raveling-Eelsing, E.; Bos, N.A.; Westra, J. Changes in T and B cell subsets in end stage renal disease patients before and after kidney transplantation. Immun. Ageing 2021, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svachova, V.; Sekerkova, A.; Hruba, P.; Tycova, I.; Rodova, M.; Cecrdlova, E.; Slatinska, J.; Honsova, E.; Striz, I.; Viklicky, O. Dynamic changes of B-cell compartments in kidney transplantation: Lack of transitional B cells is associated with allograft rejection. Transpl. Int. 2016, 29, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betjes, M.G.H. Immune cell dysfunction and inflammation in end-stage renal disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, G.R.R.; da Luz Fernandes, M.; Agena, F.; Jaluul, O.; Silva, S.C.; Lemos, F.B.C.; Coelho, V.; Elias, D.N.; Galante, N.Z. Aging and End Stage Renal Disease Cause A Decrease in Absolute Circulating Lymphocyte Counts with A Shift to A Memory Profile and Diverge in Treg Population. Aging Dis. 2019, 10, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, A.; Désy, O.; Béland, S.; Bouchard-Boivin, F.; Marcoux, M.; De Serres, S.A. Proportion versus absolute counts of B cell populations in the assessment of immunological profiles of kidney transplant recipients. Transpl. Immunol. 2022, 70, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, A.; Chesneau, M.; Dubois, F.; Danger, R.; Bui, L.; Kerleau, C.; Guerif, P.; Brouard, S.; Dantal, J. Clinical and immunological follow-up of very long-term kidney transplant recipients treated with calcineurin inhibitors indicates dual phenotypes. Kidney Int. 2021, 6, 1418–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouel, A.; Segalen, I.; Jamin, C.; Doucet, L.; Caillard, S.; Renaudineau, Y.; Pers, J.O.; Le Meur, Y.; Hillion, S. B cells display an abnormal distribution and an impaired suppressive function in patients with chronic antibody-mediated rejection. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, I.; Almeida, M.; Martins, L.S.; Santos, J.; Dias, L.; Lobato, L.; Henriques, A.C.; Mendonca, D. First-year renal function predicts long-term renal allograft loss. Transpl. Proc. 2011, 43, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hariharan, S.; McBride, M.A.; Cherikh, W.S.; Tolleris, C.B.; Bresnahan, B.A.; Johnson, C.P. Post-transplant renal function in the first year predicts long-term kidney transplant survival. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischman, C.; Fribourg, M.; Fabrizio, G.; Cioni, M.; Comoli, P.; Nocera, A.; Cardillo, M.; Cantarelli, C.; Gallon, L.; Petrosyan, A.; et al. Circulating B Cells with memory and antibody-secreting phenotypes are detectable in pediatric kidney transplant recipients before the development of antibody-mediated rejection. Transpl. Direct 2019, 9, e481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Cell Subpopulation (% Cells) | Cluster 1, Ν = 37 Median (IQR) | Cluster 2, Ν = 10 Median (IQR) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total MBC | 23.8 (17.3, 9.6) | 49.9 (47.7, 55) | <0.001 |
| SMBC | 13 (9, 8) | 21.5 (16.8, 41.6) | 0.004 |
| NSMBC | 9 (4.7, 2.8) | 24 (16, 30.3) | <0.001 |
| DN MBC | 10.8 (7.2, 5) | 14.3 (10.8, 19.4) | 0.125 |
| NBC | 74.3 (69.2, 4) | 50 (38.7, 50.5) | <0.001 |
| MZBCs | 22.7 (9.9, 2) | 36.3 (17.5, 47.4) | 0.13 |
| Subpopulation and Model | Independent variables in the model | Estimate | p Value | CI 95% | Adjusted R-Squared (Adjusted R2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naïve B cells- NBCs model | age clusters | −0.16 −30.03 | 0.185 <0.001 | ( −0.42, 0.08) (−37.58, −22.50) | 0.59 |
| Total memory B cells- TMBCs model | age donor type clusters | 0.21 4.31 26.16 | 0.096 0.236 <0.001 | (−0.04, 0.46) (−2.91, 11.54) (18.82, 33.49) | 0.57 |
| Class-switched memory B cells- SMBCs model | age donor type clusters | 0.24 5.35 11.93 | 0.045 0.118 0.001 | (0.005, 0.47) (−1.42, 12.12) (5.06, 18.80) | 0.29 |
| Class non-switched memory B cells- NSMBCs model | clusters | 13.79 | <0.001 | (8.07, 19.51) | 0.33 |
| Double negative with memory properties- DNMBCs model | clusters | 7.35 | 0.033 | (0.61, 14.09) | 0.08 |
| Peripheral equivalent to marginal zone B cells- MZBCs model | clusters | 8.68 | 0.282 | (−7.39, 24.76) | 0.01 |
| Study Sample N = 47 | Cluster 1 N = 37 | Cluster 2 N = 10 | p Value Cluster1 vs Cluster2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex Female, n (%) Male n (%) | 14 (30) 33 (70) | 11 (29) 26 (71) | 3 (30) 7 (70) | 1 |
| Age in years, mean (SD) | 51(12) | 49.6 (11) | 52.5 (16) | 0.52 |
| Type of donor, n (%) Deceased Living | 35 (74) 12 (26) | 29 (78) 8 (22) | 6 (60) 4 (40) | 0.251 |
| Duration of dialysis(months), mean (SD) | 89 (47) | 94.8 (44) | 82 (49) | 0.442 |
| Type of dialysis n (%) HD CAPD CAPD + HD | 41 (87) 2 (4) 4 (9) | 33 (89%) 1 (3%) 3 (8%) | 8 (80%) 1 (10%) 1 (10%) | 1 |
| Delayed graft function | Yes: 12 (32%) No: 25 (68%) | Yes: 3 (30%) No: 7 (70%) | 1 | |
| Cold ischaemia time (hours)), mean (SD) | 19.2(4.6) | 15.9(4.7) | 0.053 | |
| Hypertension, n (%) Yes No | 25 (67) 12 (33) | 6 (60) 4 (40) | 0.716 | |
| Diabetes, n (%) Yes No | 4 (11) 33 (89) | 1 (10) 9 (90) | 1 | |
| Distribution of underlying kidney disease | ||||
| Polycystic kidney disease% | 21% | |||
| Primary glomerulopathies% | 21.5% | |||
| Reflux nephropathy% | 13% | |||
| Diabetes mellitus% | 4% | |||
| Nephrosclerosis/hypertension% | 4% | |||
| Urinary tract infections/stones% | 3% | |||
| Other% | 18% | |||
| Unknown% | 15.5% | |||
| Induction therapy: | ||||
| Basiliximab, n (%) | 40 (85) | 30/37patients | 7/10patients | |
| ATG, n (%) | 7 (15) | 7/37patients | 3/10patients | |
| Maintenance immune suppression: | ||||
| tacrolimus/mycophenolate/prednisone% | 100.0% | |||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), median (IQR) | 53 (39–75) | 64 (38, 75) | 50.5 (46.25, 54.5) | 0.405 |
| Cell subpopulations, median (IQR) | ||||
| B cells—absolute | 81 (49.2, 142.4) | 78 (54.6, 123.7) | 0.636 | |
| B cells% | 7.5 (4.9, 10) | 6.55 (5.85, 6.8) | 0.475 | |
| TMBCs—absolute NBCs—absolute | 17.8 (10.5, 33.8) 62.3 (33.9, 128.4) | 39.2 (26.8, 59.7) 27.8 (19.2, 41.6) | 0.07 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fouza, A.; Tagkouta, A.; Daoudaki, M.; Stangou, M.; Fylaktou, A.; Bougioukas, K.; Xochelli, A.; Vagiotas, L.; Kasimatis, E.; Nikolaidou, V.; et al. Exploring Perturbations in Peripheral B Cell Memory Subpopulations Early after Kidney Transplantation Using Unsupervised Machine Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196331
Fouza A, Tagkouta A, Daoudaki M, Stangou M, Fylaktou A, Bougioukas K, Xochelli A, Vagiotas L, Kasimatis E, Nikolaidou V, et al. Exploring Perturbations in Peripheral B Cell Memory Subpopulations Early after Kidney Transplantation Using Unsupervised Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196331
Chicago/Turabian StyleFouza, Ariadni, Anneta Tagkouta, Maria Daoudaki, Maria Stangou, Asimina Fylaktou, Konstantinos Bougioukas, Aliki Xochelli, Lampros Vagiotas, Efstratios Kasimatis, Vasiliki Nikolaidou, and et al. 2023. "Exploring Perturbations in Peripheral B Cell Memory Subpopulations Early after Kidney Transplantation Using Unsupervised Machine Learning" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196331
APA StyleFouza, A., Tagkouta, A., Daoudaki, M., Stangou, M., Fylaktou, A., Bougioukas, K., Xochelli, A., Vagiotas, L., Kasimatis, E., Nikolaidou, V., Skoura, L., Papagianni, A., Antoniadis, N., & Tsoulfas, G. (2023). Exploring Perturbations in Peripheral B Cell Memory Subpopulations Early after Kidney Transplantation Using Unsupervised Machine Learning. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196331