Clinical Usefulness of New R-R Interval Analysis Using the Wearable Heart Rate Sensor WHS-1 to Identify Obstructive Sleep Apnea: OSA and RRI Analysis Using a Wearable Heartbeat Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Methods
2.2. PSG Analysis
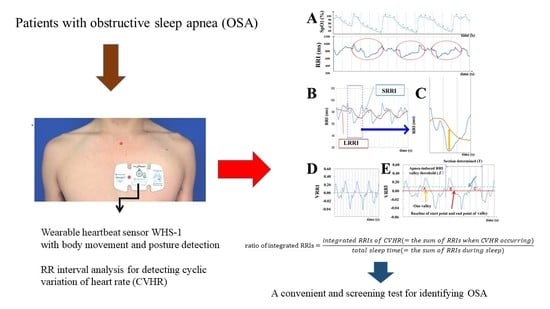
2.3. WHS-1 Analysis
2.4. Parameter Definition
2.5. Exclusion of RRI Outliers
2.6. RRI Filter
2.7. Exclusion of Body Movement
2.8. Exclusion of Postures Other than the Supine Position
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. AHI Value and Influence of Body Position
3.2. Correlation Matrix between Various Parameters and the Ratio of Integrated RRIs
3.3. Univariate and Multiple Regression Analysis of the Ratio of Integrated RRIs and AHI or 3% ODI
3.4. OSA Diagnosis Rate by WHS-1 Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OSA | obstructive sleep apnea |
| PSG | polysomnography |
| ECGs | electrocardiograms |
| RRI(s) | R-R interval(s) |
| CVHR | cyclic variation of heart rate |
| SpO2 | oxygen saturation |
| ODI | oxygen desaturation index |
| AHI | apnea-hypopnea index |
| HF | high-frequency components |
| LF | low-frequency components |
| VLF | very low frequency components |
| SRRI | short average of RRI |
| LRRI | long average of RRI |
| VRRI | valley of the RRI fluctuation |
| HRV | heart rate variability |
| PLMS | periodic leg movement during sleep |
| ACAT | auto-correlated wave detection with adaptive threshold |
References
- Malhotra, A.; White, D.P. Obstructive sleep apnoea. Lancet 2002, 360, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, C.F. Sleep apnea, alertness, and motor vehicle crashes. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care 2007, 176, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, J.M.; Somers, V.K. Obstructive sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.; Nagubadi, S.; Kryger, M.H.; Mokhlesi, B. Epidemiology of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Population-based Perspective. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2008, 2, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.A.; Yaggi, H.K.; Concato, J.; Mohsenin, V. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for coronary events or cardiovascular death. Sleep Breath. 2010, 14, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, H.; Henmi, T.; Minami, K.; Uchida, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nunohiro, T.; Maemura, K. Obstructive sleep apnoea increases the incidence of morning peak of onset in acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2013, 2, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marin, J.M.; Carrizo, S.J.; Vicente, E.; Agusti, A.G. Long-term cardiovascular outcomes in men with obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea with or without treatment with continuous positive airway pressure: An observational study. Lancet 2005, 365, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, T.L.; Lasserson, T.J.; Smith, B.H.; White, J.; Wright, J.; Cates, C.J. Continuous positive airways pressure for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhuo, S.Q.; Tian, X.T.; He, C.H.; Lu, X.L.; Gao, X.L. Continuous to Severe Obstructive Severe Sleep Apnea: A Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, B. Sleep apnea: Underdiagnosed and undertreated. Hosp. Pract. 1996, 31, 193–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R.; Ramar, K.; Harrod, C.G. Clinical practice guideline for diagnostic testing for adult obstructive sleep apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 480–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama-Ashida, Y.; Takegami, M.; Chin, K.; Sumi, K.; Nakamura, T.; Takahashi, K.; Wakamura, T.; Horita, S.; Oka, Y.; Minami, I.; et al. Sleep-disordered breathing in the usual lifestyle setting as detected with home monitoring in a population of working men in Japan. Sleep 2008, 31, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bearpark, H.; Elliott, L.; Grunstein, R.; Cullen, S.; Schneider, H.; Althaus, W.; Sullivan, C. Snoring and sleep apnea A population study in Australian men. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and GRADE Assessment. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppard, P.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased Prevalence of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcos, J.; Hornero, R.; Nabney, T.; Alvarez, D.; Campo, F. Analysis of Nocturnal Oxygen Saturation Recordings using Kernel Entropy to Assist in Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 1745–1748. [Google Scholar]
- Koley, B.; Dey, D. Real-Time Adaptive Apnea and Hypopnea Event Detection Methodology for Portable Sleep Apnea Monitoring Devices. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 3354–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilleminault, C.; Connolly, S.; Winkle, R.; Melvin, K.; Tilkian, A. Cyclical variation of the heart rate in sleep apnoea syndrome: Mechanisms, and usefulness of 24 h electrocardiography as a screening technique. Lancet 1984, 1, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayano, J.; Watanabe, E.; Saito, Y.; Sasaki, F.; Kawai, K.; Kodama, I.; Sakakibara, H. Diagnosis of sleep apnea by the analysis of heart rate variation: A mini review. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 7731–7734. [Google Scholar]
- Penzel, T.; McNames, J.; Murray, A.; de Chazal, P.; Moody, G.; Raymond, B. Systematic comparison of different algorithms for apnoea detection based on electrocardiogram recordings. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, F.; Celle, S.; Pichot, V.; Barthelemy, J.C.; Sforza, E. Analysis of the interbeat interval increment to detect obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.O.; Corthout, J.; Van Huffel, S.; Matteucci, M.; Penzel, T.; Khandoker, A.H.; Palaniswami, M.; Karmakar, C.K. Support vector machines for automated recognition of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome from ECG recordings. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Arikawa, T.; Toyoda, S.; Haruyama, A.; Amano, H.; Inami, S.; Otani, N.; Sakuma, M.; Taguchi, I.; Abe, S.; Node, K.; et al. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea on Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Heart Lung Circ. 2016, 25, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arikawa, T.; Masuyama, T.; Waku, R.; Hirose, S.; Suwa, H.; Haruyama, A.; Inami, S.; Sakuma, M.; Toyoda, S.; Abe, S.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for the onset and progression of aortic dissection. Vasc. Fail. 2019, 3, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine. International Classification of Sleep Disorders, 3rd ed.; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep-related breathing disorders in adults: Recommendations for syndrome definition and measurement technique in clinical research. The report of an American Academy of Sleep Medicine Task Force. Sleep 1999, 22, 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkiewicz, K.; van de Borne, P.J.; Pesek, C.A.; Dyken, M.E.; Montano, N.; Somers, V.K. Selective potentiation of peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity in obstructive sleep apnea. Circulation 1999, 99, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pomeranz, B.; Macaulay, R.J.; Caudill, M.A.; Kutz, I.; Adam, D.; Gordon, D.; Kilborn, K.M.; Barger, A.C.; Shannon, D.C.; Cohen, R.J.; et al. Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis. Am. J. Physiol. 1985, 248, H151–H153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, B.M. Analysis of heart rate variability. Ergonomics 1973, 16, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Akselrod, S.; Gordon, D.; Ubel, F.A.; Shannon, D.C.; Berger, A.C.; Cohen, R.J. Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuation: A quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control. Science 1981, 213, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, M.; Lombardi, F.; Guzzetti, S.; Rimoldi, O.; Furlan, R.; Pizzinelli, P.; Sandrone, G.; Malfatto, G.; Dell’Orto, S.; Piccaluga, E.; et al. Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog. Circ. Res. 1986, 59, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, C. Beitrage zur Kenntniss des Einflusses der Respirationsbewegungen auf den Blutlauf im Aortensysteme. Arch Anat. Physiol. Leipzig 1847, 13, 242–302. [Google Scholar]
- Shiomi, T.; Guilleminault, C.; Sasanabe, R.; Hirota, I.; Maekawa, M.; Kobayashi, T. Augmented very low frequency component of heart rate variability during obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 1996, 19, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Best, S.A.; Bivens, T.B.; Dean Palmer, M.; Boyd, K.N.; Melyn Galbreath, M.; Okada, Y.; Carrick-Ranson, G.; Fujimoto, N.; Shibata, S.; Hastings, J.L.; et al. Heart rate recovery after maximal exercise is blunted in hypertensive seniors. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maggio, A.C.V.; Bonomini, M.P.; Leber, E.L.; Arini, P.D. Quantification of Ventricular Repolarization Dispersion Using Digital Processing of the Surface ECG. In Advances in Electrocardiograms-Methods and Analysis; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mador, M.J.; Kufel, T.J.; Magalang, U.J.; Rajesh, S.K.; Watwe, V.; Grant, B.J.B. Prevalence of positional sleep apnea in patients undergoing polysomnography. Chest 2005, 128, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richard, W.; Kox, D.; Den Herder, C.; Laman, M.; Van Tinteren, H.; De Vries, N. The role of sleep position in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur. Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 263, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, R.D. Effect of sleep position on sleep apnea severity. Sleep 1984, 7, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillihps, B.A.; Okeson, J.; Pacsani, D.; Gilmore, R. Effect of sleep position on sleep apnea and parafunctional activity. Chest 1986, 90, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Itasaka, Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Ishikawa, K.; Togawa, K. The influence of sleep position and obesity on sleep apnea. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 54, 340–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, Y.; Kawakatsu, K.; Hattori, C.; Hattori, H.; Suzuki, K.; Nishimura, T. Posture of patients with sleep apnea during sleep. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 2003, 550, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.J.; Vila, X.A.; Rodríguez-Liñares, L.; Méndez, A.J.; Olivieri, D.N.; Félix, P. Detecting sleep apnea by heart rate variability analysis: Assessing the validity of databases and algorithms. J. Med. Syst. 2011, 35, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Estevez, D.; Moret-Bonillo, V. Spectral Heart Rate Variability analysis using the heart timing signal for the screening of the Sleep Apnea-Hypopnea Syndrome. Comput. Biol. Med. 2016, 71, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, C.; Fujiwara, K.; Sumi, Y.; Matsuo, M.; Kano, M.; Kadotani, H. Obstructive sleep apnea screening by heart rate variability-based apnea/normal respiration discriminant model. Physiol. Meas. 2019, 40, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gula, L.J.; Krahn, A.D.; Skanes, A.; Ferguson, K.A.; George, C.; Yee, R.; Klein, G.J. Heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea: A prospective study and frequency domain analysis. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2003, 8, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufoy, E.; Palma, J.A.; Lopez, J.; Alegre, M.; Urrestarazu, E.; Artieda, J.; Iriarte, J. Changes in the heart rate variability in patients with obstructive sleep apnea and its response to acute CPAP treatment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heneghan, C.; de Chazal, P.; Ryan, S.; Chua, C.P.; Doherty, L.; Boyle, P.; Nolan, P.; McNicholas, W.T. Electrocardiogram recording as a screening tool for sleep disordered breathing. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varon, C.; Caicedo, A.; Testelmans, D.; Buyse, B.; Van Huffel, S. A Novel Algorithm for the Automatic Detection of Sleep Apnea from Single-Lead ECG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.W.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, D.U.; Park, K.S. Apnea-Hypopnea Index Prediction Using Electrocardiogram Acquired During the Sleep-Onset Period. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggisberg, A.G.; Hess, C.W.; Mathis, J. The significance of the sympathetic nervous system in the pathophysiology of periodic leg movements in sleep. Sleep 2007, 30, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforza, E.; Pichot, V.; Barthelemy, J.C.; Haba-Rubio, J.; Roche, F. Cardiovascular variability during periodic leg movements: A spectral analysis approach. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Number | 30 |
|---|---|
| Male: Female | 22:8 |
| Age, year | 63.6 ± 12.1 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.8 ± 4.8 |
| Risk factors, number | |
| Hypertension | 19 |
| Diabetes | 7 |
| Dyslipidemia | 13 |
| Smoking | 18 |
| Hyperuricemia | 3 |
| Hemodialysis | 1 |
| COPD | 1 |
| Cardiovascular disease, number | |
| CHF (HFpEF, HHD, OMI, Takotsubo) | 4 |
| pMVR | 1 |
| OMI | 2 |
| AAD | 1 |
| Drugs, number | |
| β-blockers | 6 |
| Ca-blockers | 16 |
| ACE-I/ARB | 10 |
| Diuretics | 6 |
| Statin | 10 |
| Oral diabetic drugs | 6 |
| Insulin | 3 |
| Parameters | Actual Data | r-Value (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 63.6 ±11.6 | −0.059 (0.725) |
| BMI | 26.3 ± 4.6 | 0.532 (<0.001) ** |
| Snoring rate (%) | 29.7 ± 20.5 | 0.104 (0.539) |
| 3% ODI | 38.7 ± 26.2 | 0.987 (<0.001) ** |
| Mean SpO2 | 95.7 ± 1.6 | −0.399 (0.013) * |
| Minimum SpO2 | 78.7 ± 13.1 | −0.652 (< 0.001) *** |
| Arousal Index | 41.0 ± 22.2 | 0.800 (<0.001) *** |
| PLMS Index | 9.4 ± 17.7 | 0.269 (0.121) |
| Parameters | r-Value (p-Value) |
|---|---|
| Age | −0.321 (0.060) |
| BMI | 0.358 (0.052) |
| Snoring rate (%) | 0.111 (0.567) |
| AHI | 0.416 (0.022) * |
| AHI (supine) | 0.392 (0.035) * |
| AI | 0.300 (0.108) |
| HI | 0.097 (0.609) |
| 3% ODI | 0.398 (0.030) * |
| Mean SpO2 | 0.089 (0.641) |
| Minimum SpO2 | −0.200 (0.298) |
| Arousal Index | 0.252 (0.179) |
| PLMS Index | 0.294 (0.122) |
| Dependent Variable: Log (Integrated RRIs) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |
| Independent variable. | β-value (p-value) | β-value (p-value) | β-value (p-value) | β-value (p-value) |
| AHI (log) | 0.382 (0.037) * | 0.392 (0.023) * | 0.464 (0.010) * | 0.663 (0.003) ** |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | |
| Independent variable. | β-value (p-value) | β-value (p-value) | β-value (p-value) | β-value (p-value) |
| 3% ODI | 0.381 (0.038) * | 0.379 (0.028) * | 0.464 (0.011) * | 0.637 (0.008) ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arikawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Yazawa, H.; Kaneda, H.; Haruyama, A.; Obi, S.; Amano, H.; Sakuma, M.; Toyoda, S.; Abe, S.; et al. Clinical Usefulness of New R-R Interval Analysis Using the Wearable Heart Rate Sensor WHS-1 to Identify Obstructive Sleep Apnea: OSA and RRI Analysis Using a Wearable Heartbeat Sensor. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103359
Arikawa T, Nakajima T, Yazawa H, Kaneda H, Haruyama A, Obi S, Amano H, Sakuma M, Toyoda S, Abe S, et al. Clinical Usefulness of New R-R Interval Analysis Using the Wearable Heart Rate Sensor WHS-1 to Identify Obstructive Sleep Apnea: OSA and RRI Analysis Using a Wearable Heartbeat Sensor. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(10):3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103359
Chicago/Turabian StyleArikawa, Takuo, Toshiaki Nakajima, Hiroko Yazawa, Hiroyuki Kaneda, Akiko Haruyama, Syotaro Obi, Hirohisa Amano, Masashi Sakuma, Shigeru Toyoda, Shichiro Abe, and et al. 2020. "Clinical Usefulness of New R-R Interval Analysis Using the Wearable Heart Rate Sensor WHS-1 to Identify Obstructive Sleep Apnea: OSA and RRI Analysis Using a Wearable Heartbeat Sensor" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 10: 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103359
APA StyleArikawa, T., Nakajima, T., Yazawa, H., Kaneda, H., Haruyama, A., Obi, S., Amano, H., Sakuma, M., Toyoda, S., Abe, S., Tsutsumi, T., Matsui, T., Nakata, A., Shinozaki, R., Miyamoto, M., & Inoue, T. (2020). Clinical Usefulness of New R-R Interval Analysis Using the Wearable Heart Rate Sensor WHS-1 to Identify Obstructive Sleep Apnea: OSA and RRI Analysis Using a Wearable Heartbeat Sensor. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(10), 3359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9103359