Effects of a Multicomponent Exercise Program in Older Adults with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer during Adjuvant/Palliative Treatment: An Intervention Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting and Ethical Considerations
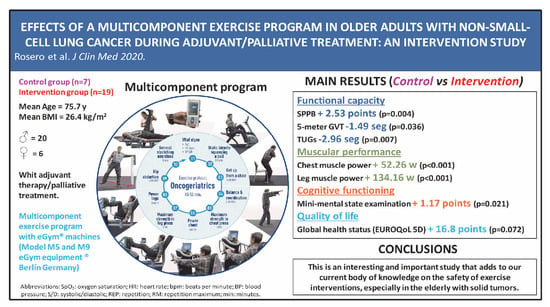
2.2. Patient Population
2.3. Outcome Assessment
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Intervention Effects
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions and Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blandin Knight, S.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hecht, S.S.; Szabo, E. Fifty Years of Tobacco Carcinogenesis Research: From Mechanisms to Early Detection and Prevention of Lung Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Brawley, O.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 212–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baile, W.F. Neuropsychiatric disorders in cancer patients. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 1996, 8, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsen, K.; Jensen, A.B.; Jacobsen, E.; Krasnik, M.; Johansen, C. Psychosocial aspects of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2005, 47, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollen, P.J.; Gralla, R.J.; Kris, M.G.; Potanovich, L.M. Quality of life assessment in individuals with lung cancer: Testing the Lung Cancer Symptom Scale (LCSS). Eur. J. Cancer 1993, 29, S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer NCCN Evidence BlocksTM Guidelines for patients Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (Version 1). Available online: www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp#nscl (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Sa, H.; Song, P.; Ma, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D. Perioperative Targeted Therapy or Immunotherapy In Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 8151–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michaels, C. The importance of exercise in lung cancer treatment. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peddle-McIntyre, C.J.; Singh, F.; Thomas, R.; Newton, R.U.; Galvao, D.A.; Cavalheri, V. Exercise training for advanced lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2, Cd012685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheri, V.; Burtin, C.; Formico, V.R.; Nonoyama, M.L.; Jenkins, S.; Spruit, M.A.; Hill, K. Exercise training undertaken by people within 12 months of lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 6, Cd009955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosero, I.D.; Ramirez-Velez, R.; Lucia, A.; Martinez-Velilla, N.; Santos-Lozano, A.; Valenzuela, P.L.; Morilla, I.; Izquierdo, M. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials on Preoperative Physical Exercise Interventions in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.H.; Yang, S.T. The new 8th TNM staging system of lung cancer and its potential imaging interpretation pitfalls and limitations with CT image demonstrations. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 25, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, B.C.; Gaus, W. Guidelines for reporting non-randomised studies. Forsch Komplementarmed Klass Naturheilkd 2004, 11, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: Association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Harhay, M.O.; Harhay, M.N. Physical function as a prognostic biomarker among cancer survivors. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, K.L.; Winters-Stone, K.M.; Wiskemann, J.; May, A.M.; Schwartz, A.L.; Courneya, K.S.; Zucker, D.S.; Matthews, C.E.; Ligibel, J.A.; Gerber, L.H.; et al. Exercise Guidelines for Cancer Survivors: Consensus Statement from International Multidisciplinary Roundtable. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, N.D.; Chiu, V.; Stewart, A.L. Mobility-related function in older adults: Assessment with a 6-min walk test. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1999, 80, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, A.; López-Roig, S.; Pérez, A.P.; Gómez, P.P.; Pastor, M.; Pomares, M.H. Validation Study of the Spanish Version of the Disability Assessment for Dementia Scale. Medicine 2015, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlinac, M.E.; Feng, M.C. Assessment of Activities of Daily Living, Self-Care, and Independence. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2016, 31, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez de Asteasu, M.L.; Martinez-Velilla, N.; Zambom-Ferraresi, F.; Casas-Herrero, A.; Cadore, E.L.; Galbete, A.; Izquierdo, M. Assessing the impact of physical exercise on cognitive function in older medical patients during acute hospitalization: Secondary analysis of a randomized trial. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinas-Regla, J.; Vilalta-Franch, J.; Lopez-Pousa, S.; Calvo-Perxas, L.; Torrents Rodas, D.; Garre-Olmo, J. The Trail Making Test. Assessment 2017, 24, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, A.S.; Wilke, C.T.; Lin, H.W.; Lloyd, A. Health utilities using the EQ-5D in studies of cancer. Pharmacoeconomics 2007, 25, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, B.; Aaronson, N.K.; Ahmedzai, S.; Kaasa, S.; Sullivan, M. The EORTC QLQ-LC13: A modular supplement to the EORTC Core Quality of Life Questionnaire (QLQ-C30) for use in lung cancer clinical trials. EORTC Study Group on Quality of Life. Eur. J. Cancer 1994, 30, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Barón, M.; Lacasta, M.A.; Ordóñez, A. Valoración Clínica en el Paciente con Cáncer, 1st ed.; Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2006; Volume 1, p. 208. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.M.; Schinka, J.A. Development and initial validation of a 15-item informant version of the Geriatric Depression Scale. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2005, 20, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlowicz, L.; Greenberg, S. The Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS). AJN Am. J. Nurs. 2007, 107, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhalter, N. Evaluación de la escala Borg de esfuerzo percibido aplicada a la rehabilitación cardiaca. Rev. Lat.-Am. Enfermagem 1996, 4, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izquierdo, M. Multicomponent physical exercise program: Vivifrail. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Simonsick, E.M.; Salive, M.E.; Wallace, R.B. Lower-extremity function in persons over the age of 70 years as a predictor of subsequent disability. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuart, M.; Benvenuti, F.; Macko, R.; Taviani, A.; Segenni, L.; Mayer, F.; Sorkin, J.D.; Stanhope, S.J.; Macellari, V.; Weinrich, M. Community-based adaptive physical activity program for chronic stroke: Feasibility, safety, and efficacy of the Empoli model. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, H.M.; Bell, M.L.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Turner, J.D.; Kabourakis, M.; Spencer, L.; Lewis, C.; Hui, R.; Blinman, P.; Clarke, S.J.; et al. Impact of physical activity on fatigue and quality of life in people with advanced lung cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, R.; Meyers, C.A.; Shin, D.M.; Garden, A.S.; Byrne, K.; Nickens, J.A.; Cox, J.D. Evaluation of cognitive function in patients with limited small cell lung cancer prior to and shortly following prophylactic cranial irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 33, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, M.; Root, J.C.; Vaquero, L.; Ripolles, P.; Jove, J.; Ahles, T.; Navarro, A.; Cardenal, F.; Bruna, J.; Rodriguez-Fornells, A. Cognitive and brain structural changes in a lung cancer population. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chodzko-Zajko, W.J.; Schuler, P.; Solomon, J.; Heinl, B.; Ellis, N.R. The influence of physical fitness on automatic and effortful memory changes in aging. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 1992, 35, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.D.; Storandt, M.; Malley, M. The impact of long-term exercise training on psychological function in older adults. J. Gerontol. 1993, 48, P12–P17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Sanchez, M.A.; Bustos-Cruz, R.H.; Velasco-Orjuela, G.P.; Quintero, A.P.; Tordecilla-Sanders, A.; Correa-Bautista, J.E.; Triana-Reina, H.R.; Garcia-Hermoso, A.; Gonzalez-Ruiz, K.; Pena-Guzman, C.A.; et al. Acute Effects of High Intensity, Resistance, or Combined Protocol on the Increase of Level of Neurotrophic Factors in Physically Inactive Overweight Adults: The BrainFit Study. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stubbs, B.; Vancampfort, D.; Hallgren, M.; Firth, J.; Veronese, N.; Solmi, M.; Brand, S.; Cordes, J.; Malchow, B.; Gerber, M.; et al. EPA guidance on physical activity as a treatment for severe mental illness: A meta-review of the evidence and Position Statement from the European Psychiatric Association (EPA), supported by the International Organization of Physical Therapists in Mental Health (IOPTMH). Eur. Psychiatry 2018, 54, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweegers, M.G.; Altenburg, T.M.; Chinapaw, M.J.; Kalter, J.; Verdonck-de Leeuw, I.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Newton, R.U.; Aaronson, N.K.; Jacobsen, P.B.; Brug, J.; et al. Which exercise prescriptions improve quality of life and physical function in patients with cancer during and following treatment? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buffart, L.M.; Kalter, J.; Sweegers, M.G.; Courneya, K.S.; Newton, R.U.; Aaronson, N.K.; Jacobsen, P.B.; May, A.M.; Galvao, D.A.; Chinapaw, M.J.; et al. Effects and moderators of exercise on quality of life and physical function in patients with cancer: An individual patient data meta-analysis of 34 RCTs. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 52, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.Q.; Courneya, K.S.; Carter, S.J.; Anton, P.M.; Verhulst, S.; Vicari, S.K.; Robbs, R.S.; McAuley, E. Effects of a multicomponent physical activity behavior change intervention on breast cancer survivor health status outcomes in a randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 159, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patsou, E.D.; Alexias, G.D.; Anagnostopoulos, F.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Effects of physical activity on depressive symptoms during breast cancer survivorship: A meta-analysis of randomised control trials. ESMO Open 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.M.; Tsai, C.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Lin, K.C.; Lin, C.C. Randomised controlled trial on the effectiveness of home-based walking exercise on anxiety, depression and cancer-related symptoms in patients with lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meneses-Echávez, J.F.; González-Jiménez, E.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Supervised exercise reduces cancer-related fatigue: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2015, 61, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vardy, J.L.; Bell, M.; Ploeg, H.V.D.; Turner, J.; Kabourakis, M.; Spencer, L.; Lewis, C.R.; Hui, R.; Blinman, P.L.; Clarke, S.J.; et al. The impact of physical activity on fatigue and quality of life in lung cancer patients: A randomised controlled trial (RCT). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldervoll, L.M.; Loge, J.H.; Lydersen, S.; Paltiel, H.; Asp, M.B.; Nygaard, U.V.; Oredalen, E.; Frantzen, T.L.; Lesteberg, I.; Amundsen, L.; et al. Physical exercise for cancer patients with advanced disease: A randomized controlled trial. Oncologist 2011, 16, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, C.L.; Yu, C.J.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C.; Wu, Y.T. Effects of exercise training on exercise capacity in patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving targeted therapy. Support Care Cancer 2012, 20, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhi, B.; Haenebalcke, C.; Perez-Bogerd, S.; Nguyen, M.D.; Ninane, V.; Malfait, T.L.; Vermaelen, K.Y.; Surmont, V.F.; Van Maele, G.; Colman, R.; et al. Rehabilitation in patients with radically treated respiratory cancer: A randomised controlled trial comparing two training modalities. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quist, M.; Rorth, M.; Langer, S.; Jones, L.W.; Laursen, J.H.; Pappot, H.; Christensen, K.B.; Adamsen, L. Safety and feasibility of a combined exercise intervention for inoperable lung cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: A pilot study. Lung Cancer 2012, 75, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n | Exercise | Frequency | Duration | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Endurance exercise: riding a bicycle | Twice a week | 3–5 min | 50–80% of HR max |
| 2. | Get up from a chair | Twice a week | 3 sets × 10 repetitions | − |
| 3. | Balance and coordination Walking on toes with flexion-extension shoulder Walking on heels of the feet with abduction-adduction shoulder Progression with obstacles along the way | Twice a week | 2 sets × 5 m | − |
| 4. | Maximum strength/power in chest press (eGym®) | Twice a week | 2 times (for control load) | 1RM |
| 5. | Maximum strength/power in leg press (eGym®) | Twice a week | 2 times (for control load) | 1RM |
| 6. | Power chest (Explosive program eGym®) | Twice a week | Week 1 3 sets/12 repetitions | 30% RM |
| Week 2–3 3 sets/12 repetitions | 40% RM | |||
| Week 4–7 3 sets/10 repetitions | 50% RM | |||
| Week 8–10 3 sets/8 repetitions | 60% RM | |||
| 7. | Power legs (Explosive program eGym®) | Twice a week | Week 1 3 sets/12 repetitions | 30% RM |
| Week 2–3 3 sets/12 repetitions | 40% RM | |||
| Week 4–7 3 sets/10 repetitions | 50% RM | |||
| Week 8–10 3 sets/8 repetitions | 60% RM | |||
| 8. | Hip abduction with elastic bands (TheraBand) | Twice a week | 3 sets/10 repetitions | 50–80% band elongation (red-black) |
| 9. | Squeezing a ball | Twice a week | 3 sets/3–5 min | − |
| 10. | General stretching exercises (6–10 exercises) | Twice a week | 5 min | − |
| Variables | Intervention Group (n = 19) | Control Group (n = 7) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 74.5 (3.6) | 79.0 (3.0) | 0.007 * |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.8 (4.5) | 25.5 (2.5) | 0.491 * |
| Underweight, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 1 (14.3) | 0.912 † |
| Normal weight, n (%) | 7 (36.8) | 4 (57.1) | |
| Overweight/obesity, n (%) | 7 (36.8) | 2 (28.6) | |
| Sex, n (%) Male Female | 15 (78.9) 4 (21.1) | 5 (71.4) 2 (28.6) | 0.700 + |
| TNM classification, n (%) I II IIIa-IIIb-IIIc IV | 1 (5.3) 0 (0.0) 4 (21.0) 14(73.7) | 0 (0.0) 1 (14.3) 3 (42.8) 3 (42.8) | 0.172 † |
| Clinically diagnosed comorbidities, n (%) | 0.496 + | ||
| COPD | 13 (68.4) | 2 (28.6) | |
| Hypertension | 9 (47.4) | 4 (57.1) | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (26.3) | 1 (14.3) | |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 8 (42.1) | 4 (57.1) | |
| Frailty status, n (%) G8 VES 13 G8 and VES13 No | 7 (36.8) 2 (10.5) 4 (21.1) 6 (31.6) | 3 (42.8) 0 (0.0) 3 (42.8) 1 (14.3) | 0.649 + |
| Alcohol status, n (%) Current Past No | 10 (52.6) 4 (21.1) 5 (26.3) | 2 (28.6) 3 (42.8) 2 (28.6) | 0.407 + |
| Smoking status, n (%) Current Past No | 5 (26.3) 11 (57.9) 3 (15.8) | 2 (28.6) 3 (42.8) 2 (28.6) | 0.763 + |
| Surgery, n (%) VATS Open Without surgery | 3 (17.6) 4 (23.5) 12 (58.8) | 0 (0.0) 1 (14.3) 6 (85.7) | 0.144 + |
| Adjuvant therapy/palliative treatment, n (%) Chemotherapy Immunotherapy Chemotherapy and radiotherapy Chemotherapy and immunotherapy Immunotherapy and radiotherapy Palliative treatment | 6 (31.6) 1 (5.3) 7 (36.8) 2 (10.5) 2 (10.5) 1 (5.3) | 2 (28.6) 1 (14.3) 4 (57.1) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) | 0.385 + |
| Intervention Group (n = 19) | Control Group (n = 7) | Group Difference ∆ (95% CI) p-Value Groups + | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | p-Value * | Before | After | p-Value * | ||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||||
| Functional capacity | |||||||
| Gait Speed Test 4-m (s) | 5.62 (1.57) | 4.89 (1.19) | 0.008 | 4.85 (0.83) | 5.71 (0.87) | 0.051 | −1.60 (−2.55 to -0.65); 0.002 |
| Static Balance (Score) | 3.84 (0.37) | 4.00 (0.00) | 0.083 † | 3.57 (1.13) | 3.57 (0.79) | 1.000 † | 0.34 (0.25 to 0.43); 0.024 |
| Chair Stand Test (s) | 12.23 (3.37) | 10.29 (2.39) | 0.009 | 10.66 (1.47) | 15.48 (7.83) | 0.132 | −6.75 (−10.80 to −2.70); 0.002 |
| SPPB Total (Score) | 9.84 (1.92) | 10.95 (1.03) | 0.004 | 10.86 (1.35) | 9.43 (1.27) | 0.118 | 2.53 (1.05 to 4.02); 0.002 |
| GVT 5-m (s) | 6.25 (1.63) | 5.62 (1.38) | 0.036 | 5.43 (1.09) | 6.30 (0.69) | 0.020 | −1.49 (−2.49 to −0.49); 0.005 |
| GVT Verbal (s) | 6.63 (1.71) | 6.47 (1.29) | 0.657 | 5.30 (1.10) | 7.22 (1.15) | 0.017 | −2.08 (−3.50 to −0.66); 0.006 |
| GVT Arithmetic (s) | 6.82 (1.88) | 6.35 (1.51) | 0.155 | 6.26 (1.24) | 7.45 (1.52) | 0.062 | −1.66 (−2.91 to −0.41); 0.012 |
| TUG (s) | 12.01 (2.80) | 11.03 (3.20) | 0.097 | 11.39 (1.67) | 13.37 (1.28) | 0.016 | −2.96 (−5.02 to −0.89); 0.007 |
| 6MWT (m) | 414.69 (120.79) | 420.11 (101.77) | 0.722 | 425.71 (71.52) | 398.50 (65.15) | 0.134 | 29.92 (−26.83 to 86.66); 0.286 |
| Barthel Index (Score) | 96.58 (5.79) | 98.16 (4.15) | 0.084 † | 100.00 (0.00) | 97.86 (3.93) | 0.180 † | 0.05 (0.01 to 0.09); 0.044 ‡ |
| Muscular performance | |||||||
| 1RM Chest Press (kg) | 43.89 (13.77) | 52.79 (17.16) | <0.001 | 34.71 (8.22) | 29.33 (5.89) | 0.049 | 12.89 (5.60 to 20.19); 0.001 |
| 1RM Leg Press (kg) | 100.74 (35.45) | 150.63 (47.06) | <0.001 | 76.43 (25.30) | 66.67 (14.46) | 0.338 | 52.73 (38.03 to 67.42); <0.001 |
| Chest Muscle Power (w) | 99.00 (48.30) | 136.26 (57.56) | <0.001 | 76.14 (34.58) | 52.50 (19.61) | 0.022 | 52.26 (25.67 to 78.86); <0.001 |
| Leg muscle Power (w) | 152.26 (86.13) | 262.42 (103.92) | <0.001 | 108.14 (57.21) | 72.83 (31.51) | 0.071 | 134.16 (89,91 to 178.40); <0.001 * |
| Hand Grip (kg) | 34.58 (8.35) | 34.16 (9.00) | 0.618 | 28.00 (8.71) | 28.29 (8.02) | 0.811 | −0.71 (-3.88 to 2.47); 0.650 |
| Knee Extension (kg) | 9.59 (1.76) | 11.63 (3.01) | 0.013 | 9.25 (1.76) | 8.78 (2.25) | 0.701 | 2.52 (−0.41 to 5.45); 0.089 |
| Flexion Hip (kg) | 9.31 (3.23) | 10.40 (3.03) | 0.044 | 9.03 (2.98) | 7.45 (1.26) | 0.244 | 2.67 (0.39 to 4.94); 0.024 |
| Abduction Hip (kg) | 8.05 (2.10) | 9.68 (1.86) | 0.001 | 6.55 (1.30) | 6.78 (1.83) | 0.769 | 1.39 (−0.24 to 3.02); 0.092 |
| Intervention Group (n = 19) | Control Group (n = 7) | Group Difference ∆ (95% CI) p-Value Groups + | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | p-Value * | Before | After | p-Value * | ||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||||
| MMSE (Score) | 28.16 (1.07) | 28.89 (0.81) | 0.005 | 27.57 (2.82) | 27.14 (1.95) | 0.407 | 1.17 (0.19 to 2.14); 0.021 |
| Verbal Fluency Test (Score) | 11.37 (5.84) | 12.11 (5.36) | 0.380 | 9.43 (5.47) | 7.57 (5.38) | 0.191 | 2.59 (−0.61 to 5.80); 0.108 |
| TMT-A (s) | 68.32 (38.96) | 65.92 (47.34) | 0.676 | 86.10 (62.19) | 78.35 (44.36) | 0.505 | 5.34 (−18.17 to 28.86); 0.643 |
| Intervention Group (n = 19) | Control Group (n = 7) | Group Difference ∆ (95% CI) p-Value Groups + | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | p-Value * | Before | After | p-Value * | ||
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||||
| EUROQoL 5D | |||||||
| EUROQoL 5D a | 6.42 (1.35) | 5.74 (1.19) | 0.038 | 5.14 (0.38) | 6.14 (1.21) | 0.038 | −1.68 (−2.83 to -0.53); 0.006 |
| EUROQoL 5D Health b | 69.05 (12.51) | 73.26 (17.53) | 0.340 | 72.29 (21.73) | 72.14 (17.76) | 0.974 | 4.35 (−11.28 to 19.99); 0.571 |
| EORTC QLQ-C30 (Functioning scale b) | |||||||
| Physical | 72.20 (26.70) | 83.30 (20.90) | 0.037 | 88.60 (15.70) | 82.90 (18.00) | 0.172 † | 16.83 (−0.31 to 33.96); 0.054 |
| Role | 88.90 (32.30) | 97.20 (11.80) | 0.276 † | 100.00 (0.00) | 100.00 (0.00) | 1.000 | 0.90 (0.84 to 0.96); 0.707 ‡ |
| Cognitive | 80.60 (25.10) | 86.10 (20.00) | 0.163 | 92.90 (18.90) | 95.20 (8.10) | 0.788 † | 3.17 (−13.42 to 19.77); 0.696 |
| Emotional | 80.10 (19.80) | 82.40 (18.10) | 0.686 | 85.70 (13.40) | 85.70 (19.70) | 1.000 † | 2.31 (−17.91 to 22.54); 0.815 |
| Social | 80.60 (25.70) | 86.10 (20.80) | 0.397 † | 100.00 (0.00) | 81.00 (27.90) | 0.109 | 0.05 (0.01 to 0.09); 0.062 ‡ |
| Global Health status/QoL b | 64.80 (21.30) | 76.90 (11.60) | 0.029 † | 77.40 (17.20) | 72.60 (14.20) | 0.436 † | 16.80 (−1.61 to 35.21); 0.072 |
| EORTC QLQ-C30 (Symptom scales and/or items c) | |||||||
| Fatigue | 35.80 (29.40) | 30.20 (21.80) | 0.464 | 14.30 (15.30) | 14.30 (15.30) | 1.000 † | −5.56 (−21.83 to 10.72); 0.485 |
| Nausea and Vomiting | 8.30 (24.40) | 3.70 (10.80) | 0.655 † | 0.00 (0.00) | 2.40 (6.30) | 0.317 | 0.56 (0.46 to 0.66); 0.362 ‡ |
| Pain | 32.40 (32.60) | 14.80 (21.30) | 0.030 | 14.30 (26.20) | 26.20 (30.20) | 0.454 † | −29.50 (−60.61 to 1.61); 0.062 |
| Dyspnea | 13.00 (20.30) | 3.70 (10.80) | 0.025 † | 14.30 (26.20) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.180 | 0.67 (0.58 to 0.76); 0.817 ‡ |
| Sleep Disturbance | 29.60 (36.00) | 22.20 (34.30) | 0.506 † | 14.30 (26.20) | 14.30 (26.20) | 1.000 | 0.88 (0.82 to 0.94); 0.818 ‡ |
| Appetite Loss | 25.90 (33.40) | 13.00 (28.30) | 0.083 † | 14.30 (26.20) | 19.00 (37.80) | 0.655 | 0.39 (0.29 to 0.49); 0.364 ‡ |
| Constipation | 22.20 (30.20) | 13.00 (23.30) | 0.248 † | 23.80 (31.70) | 33.30 (47.10) | 0.577 | 0.20 (0.12 to 0.28); 0.185 ‡ |
| Diarrhea | 13.00 (28.30) | 18.50 (28.50) | 0.603 † | 0.00 (0.00) | 9.50 (16.30) | 0.157 | 0.92 (0.87 to 0.97); 0.804 ‡ |
| Financial Impact | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 1.000 † | 4.80 (12.60) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.317 | 0.32 (0.23 to 0.41); 0.109 ‡ |
| EORTC QLQ- LC13 c | |||||||
| Coughing | 38.90 (23.60) | 24.10 (25.10) | 0.104 | 28.60 (12.60) | 23.80 (16.30) | 0.356 † | −10.05 (−30.42 to 10.32); 0.318 |
| Hemoptysis | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) | 1.000 † | 4.80 (12.60) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.317 | 0.32 (0.23 to 0.41); 0.109 ‡ |
| Dyspnoea | 14.20 (15.60) | 14.20 (14.70) | 1.000 | 12.70 (20.70) | 12.70 (16.30) | 1.000 † | 0.00 (−11.30 to 11.30); 1.000 |
| Sore Mouth | 9.30 (22.30) | 14.80 (28.50) | 0.546 † | 0.00 (0.00) | 4.80 (12.60) | 0.317 | 0.98 (0.95 to 1,00); 0.826 ‡ |
| Dysphagia | 9.30 (22.30) | 7.40 (18.30) | 0.705 † | 0.00 (0.00) | 4.80 (12.60) | 0.317 | 0.40 (0.30 to 0.50); 0.225 ‡ |
| Peripheral Neuropathy | 9.30 (19.20) | 13.00 (23.30) | 0.414 † | 9.50 (25.20) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.317 | 0.18 (0.11 to 0.26); 0.250 ‡ |
| Alopecia | 5.60 (17.10) | 11.10 (22.90) | 0.408 † | 0.00 (0.00) | 19.00 (37.80) | 0.180 | 0.45 (0.35 to 0.55); 0.540 ‡ |
| Pain in Chest | 13.00 (20.30) | 9.30 (15.40) | 0.317 † | 14.30 (17.80) | 4.80 (12.60) | 0.157 | 0.59 (0.49 to 0.69); 0.416 ‡ |
| Pain in Arms or Shoulder | 13.00 (30.50) | 7.40 (21.60) | 0.414 † | 4.80 (12.60) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.317 | 1.00 (0.97 to 1.00); 0.705 ‡ |
| Pain in Other Body Parts | 31.50 (35.20) | 9.30 (19.20) | 0.025 † | 14.30 (26.20) | 42.90 (46.00) | 0.059 | 0.00 (0.00 to 0.03); 0.007 ‡ |
| Categorical Pain Scale d | 1.89 (2.35) | 1.16 (2.34) | 0.317 † | 0.57 (1.51) | 1.14 (1.95) | 0.564 † | 0.25 (0.17 to 0.34); 0.216 ‡ |
| GDS e | 2.79 (1.72) | 2.74 (2.66) | 0.917 | 1.57 (1.51) | 2.71 (1.80) | 0.103 | −1.20 (−3.06 to 0.67); 0.197 |
| Borg Scale d | 3.67 (0.91) | 4.00 (1.33) | 0.210 | 3.14 (0.38) | 3.00 (1.67) | 1.000 | 0.33 (−0.88 to 1.55); 0.575 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosero, I.D.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Martínez-Velilla, N.; Cedeño-Veloz, B.A.; Morilla, I.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of a Multicomponent Exercise Program in Older Adults with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer during Adjuvant/Palliative Treatment: An Intervention Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030862
Rosero ID, Ramírez-Vélez R, Martínez-Velilla N, Cedeño-Veloz BA, Morilla I, Izquierdo M. Effects of a Multicomponent Exercise Program in Older Adults with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer during Adjuvant/Palliative Treatment: An Intervention Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2020; 9(3):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030862
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosero, Ilem D., Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Nicolas Martínez-Velilla, Bernardo Abel Cedeño-Veloz, Idoia Morilla, and Mikel Izquierdo. 2020. "Effects of a Multicomponent Exercise Program in Older Adults with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer during Adjuvant/Palliative Treatment: An Intervention Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 9, no. 3: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030862
APA StyleRosero, I. D., Ramírez-Vélez, R., Martínez-Velilla, N., Cedeño-Veloz, B. A., Morilla, I., & Izquierdo, M. (2020). Effects of a Multicomponent Exercise Program in Older Adults with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer during Adjuvant/Palliative Treatment: An Intervention Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(3), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030862