A Motor-Driven and Computer Vision-Based Intelligent E-Trap for Monitoring Citrus Flies
Abstract
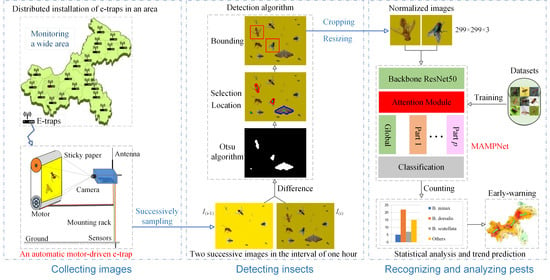
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Automatic Motor-Driven Citrus Fly E-Trap with Computer Vision
2.1.1. Overview
2.1.2. Processing of Yellow Sticky Trap
2.1.3. Electromechanical Designs of E-Trap
2.2. Image Analysis Based Autocontrol of E-Trap
| Algorithm 1 Autocontrol of trap. |
|
2.3. Citrus Fly Detection Based on Differences of Two Successive Samplings
2.4. MAMPNet for Recognition of Citrus Flies
2.4.1. Structures of MAMPNet
2.4.2. Learning and Reference
2.4.3. Training MAMPNet
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Experiment Settings
3.1.1. Dataset Settings
3.1.2. Parameter Settings
3.2. Experiments for Autocontrol of E-Trap
3.3. Experiments for Detection of Insects on Synthesized Yellow Paper Images
3.4. Experiments for Recognition of Citrus Flies
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion on Design Schemes of E-Trap
4.2. Discussion on Recognition of Citrus Flies
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolution Neural Networks |
| LBP | Local Binary Pattern |
| HSV | Hue Saturation Value |
| FGVC | Fine-Grained Visual Classification |
| RoI | Region of Interest |
| GAP | Global Average Pooling |
| FC | Full Connection |
| FAR | False Accept Rate |
| FRR | False Reject Rate |
| PDR | Positive Detection Rate |
Appendix A. Datasets
Appendix A.1. Dataset D 1 -Citrus Flies
References
- Cardim Ferreira Lima, M.; Damascena de Almeida Leandro, M.E.; Valero, C.; Pereira Coronel, L.C.; Gonçalves Bazzo, C.O. Automatic Detection and Monitoring of Insect Pests—A Review. Agriculture 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, A.C.; Hamacek, E.L.; Kopittke, R.A.; Peek, T.; Wyatt, P.M.; Neale, C.J.; Eelkema, M.; Gu, H. Area-wide management of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) in the Central Burnett district of Queensland, Australia. Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessup, A.J.; Dominiak, B.; Woods, B.; De Lima, C.P.F.; Tomkins, A.; Smallridge, C.J. Area-wide management of fruit flies in Australia. In Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests; Vreysen, M.J.B., Robinson, A.S., Hendrichs, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 685–697. [Google Scholar]
- Shaked, B.; Amore, A.; Ioannou, C.; Valdes, F.; Alorda, B.; Papanastasiou, S.; Goldshtein, E.; Shenderey, C.; Leza, M.; Pontikakos, C.; et al. Electronic traps for detection and population monitoring of adult fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 142, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doitsidis, L.; Fouskitakis, G.N.; Varikou, K.N.; Rigakis, I.I.; Chatzichristofis, S.A.; Papafilippaki, A.K.; Birouraki, A.E. Remote monitoring of the Bactrocera oleae (Gmelin) (Diptera: Tephritidae) population using an automated McPhail trap. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 137, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, E.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, G. Moth Detection from Pheromone Trap Images Using Deep Learning Object Detectors. Agriculture 2020, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, C.; Ji, L. Construction, implementation and testing of an image identification system using computer vision methods for fruit flies with economic importance (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2016, 73, 1511–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alorda, B.; Valdes, F.; Mas, B.; Leza, M.; Almenar, L.; Feliu, J.; Ruiz, M.; Miranda, M. Design of an energy efficient and low cost trap for Olive fly monitoring using a ZigBee based Wireless Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Precision Agriculture (ECPA), Rishon LeTsiyon, Israel, 12–16 July 2015; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Philimis, P.; Psimolophitis, E.; Hadjiyiannis, S.; Giusti, A.; Perello, J.; Serrat, A.; Avila, P. A centralised remote data collection system using automated traps for managing and controlling the population of the Mediterranean (Ceratitis capitata) and olive (Dacus oleae) fruit flies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSGY), Paphos, Coral Bay Cyprus, 5 August 2013; pp. 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- George, S.C. History and use of the McPhail trap. Florida Entomol. 1977, 60, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.G. An assessment of yellow sticky card traps as indicators of the abundance of adult Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) in citrus. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 10, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Niu, C.; Han, P.; Desneux, N. Field evaluation of attractive lures for the fruit fly Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae) and their potential use in spot sprays in Hubei Province (China). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.G. Field comparison of chemical attractants and traps for Caribbean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Florida citrus. J. Econ. Entomol. 2005, 98, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Yang, Q.; Fu, J.; Deng, X.; Feng, J.; Ye, Y.; Lu, Y. A multi-target trapping and tracking algorithm for Bactrocera Dorsalis based on cost model. Comput. Electron. Argic. 2016, 123, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Taylor, G. Automatic moth detection from trap images for pest management. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalamatianos, R.; Karydis, I.; Doukakis, D.; Avlonitis, M. DIRT: The Dacus Image Recognition Toolkit. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Yuan, M.; Ren, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Automatic in-trap pest detection using deep learning for pheromone-based Dendroctonus valens monitoring. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 176, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Duan, X.; Xu, S.; Song, Z.; Luo, M. An improved moving object detection algorithm based on frame difference and edge detection. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Image and Graphics (ICIG), Chengdu, China, 22–24 August 2007; pp. 519–523. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Krause, J.; Li, F. Fine-grained crowdsourcing for fine-grained recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.S.; Wu, J.; Cui, Q. Deep learning for fine-grained image analysis: A survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.03069. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, A.; Jayadevaprakash, N.; Yao, B.; Li, F.F. Novel dataset for fine-grained image categorization: Stanford dogs. In Proceedings of the CVPR Workshop on Fine-Grained Visual Categorization (FGVC), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, T.; Liu, J.; Woo Lee, S.; Alexander, M.L.; Jacobs, D.W.; Belhumeur, P.N. Large-scale fine-grained visual categorization of birds. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2011–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martineau, M.; Conte, D.; Raveaux, R.; Arnault, I.; Munier, D.; Venturinia, G. A survey on image-based insect classification. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 65, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonardo, M.M.; Avila, S.; Zucchi, R.A.; Faria, F.A. Mid-level image representation for fruit fly identification (diptera: Tephritidae). In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 13th International Conference on e-Science (e-Science), Auckland, New Zealand, 24–27 October 2017; pp. 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, F.A.; Perre, P.; Zucchi, R.A.; Jorge, L.R.; Lewinsohn, T.M.; Rocha, A.; Torres, R. Automatic identification of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Vis. Commun. 2014, 25, 1516–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Chang, K.; Hsieh, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, C. LIBLINEAR: A library for large linear classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 115, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardo, M.M.; Carvalho, T.; Rezende, E.; Zucchi, R.; Faria, F.A. Deep feature-based classifiers for fruit fly identification (diptera: Tephritidae). In Proceedings of the 31st SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images (SIBGRAPI), Parana, Brazil, 29 October–1 November 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Remboski, T.B.; Souza, W.D.; Aguiar, M.S.; Ferreira, P.R. Identification of fruit fly in intelligent traps using techniques of digital image processing, machine learning. In Proceedings of the 33rd ACM/SIGAPP Symposium On Applied Computing (ACM-SAC), Pau, France, 9–13 April 2018; pp. 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Chazot, P.L.; Celebi, M.E.; Crookes, D.; Jiang, R. Social Behavioral Phenotyping of Drosophila with a 2D–3D Hybrid CNN Framework. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 67972–67982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liao, M.; Huang, W.; Deng, H.; Ao, L.; Hua, J. Fruit fly classification via convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Xi’an, China, 30 November–2 December 2018; pp. 3395–3399. [Google Scholar]
- Murali, N.; Schneider, J.; Levine, J.; Taylor, G. Classification and re-identification of fruit fly individuals across days with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Hawaii, HI, USA, 8–10 January 2019; pp. 570–578. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Xu, Z.; Tao, D.; Zhang, Y. Part-stacked cnn for fine-grained visual categorization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.; Tian, Q.; Hong, R.; Yan, S.; Zhang, B. Hierarchical part matching for fine-grained visual categorization. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1641–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Yao, X.; Cheng, G.; Feng, X.; Xu, D. P-CNN: Part-based convolutional neural networks for fine-grained visual categorization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Yang, X.; Mo, X.; Lu, Y.; Davis, L.S.; Li, J.; Lim, S.N. Cross-X learning for fine-grained visual categorization. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8242–8251. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Fu, J.; Mei, T.; Luo, J. Learning multi-attention convolutional neural network for fine-grained image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 5209–5217. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, F.; Ding, E. Multi-attention multi-class constraint for fine-grained image recognition. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 805–821. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; So Kweon, I. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchi, A.; Sambado, P.; Royo, A.B.; Bagnoli, B.; Benelli, G. Lobesia botrana males mainly fly at dusk: Video camera-assisted pheromone traps and implications for mating disruption. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, M.; Verheggen, F.; Angeli, S. Insect pest monitoring with camera-equipped traps: Strengths and limitations. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S. Digital image smoothing and the sigma filter. Comput. Vision, Graph. Image Process. 1983, 24, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibe, B.; Schindler, K.; Cornelis, N.; Van Gool, L. Coupled object detection and tracking from static cameras and moving vehicles. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 1683–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moghaddam, R.F.; Cheriet, M. AdOtsu: An adaptive and parameterless generalization of Otsu’s method for document image binarization. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L. Morphological transformations of binary images with arbitrary structuring elements. Signal Process. 1991, 22, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y. Kalman filter for robot vision: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 4409–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Twenty-ninth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–10 December 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. Multi-attention multi-class constraint for fine-grained image recognition. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1806.05372. [Google Scholar]
- Ketkar, N. Introduction to Pytorch. In Deep Learning with Python; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, G.V.; Aodha, O.M.; Song, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sun, C.; Shepard, A.; Adam, H.; Perona, P.; Belongie, S. The inaturalist species classification and detection dataset. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8769–8778. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Zhan, C.; Lai, Y.; Cheng, M.; Yang, J. IP102: A Large-Scale Benchmark Dataset for Insect Pest Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8787–8796. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Song, Y.; Sun, C.; Howard, A.; Belongie, S. Large scale fine-grained categorization and domain-specific transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4109–4118. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; RoyChowdhury, A.; Maji, S. Bilinear cnn models for fine-grained visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 Decemebre 2015; pp. 1449–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Liao, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, H.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y. FB-CNN: Feature Fusion-Based Bilinear CNN for Classification of Fruit Fly Image. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 3987–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Dang, L.M.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Moon, H. Crop pest recognition in natural scenes using convolutional neural networks. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, C.R.; Arko, P.S.; Ali, M.E.; Khan, M.A.I.; Apon, S.H.; Nowrin, F.; Wasif, A. Identification and recognition of rice diseases and pests using convolutional neural networks. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 194, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pattnaik, G.; Shrivastava, V.K.; Parvathi, K. Transfer Learning-Based Framework for Classification of Pest in Tomato Plants. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Dataset | Amount | Characteristics and Purposes |
|---|---|---|
| -Citrus flies | t = 5952, s = 15 | The dataset for validating the identification of citrus fly pests.
It contains the three species of citrus fly pests and the other 12 species of insects possibly captured by the yellow paper (See Appendix A.1). |
| -Fruit flies | t = , s = 25 | Flies similar to the citrus flies, namely with the similar
parts of wings, thoraxes and abdomens. They are additionally used to help to learn the attention module and improve the discrimination of part features. |
| -Wingedinsects | t = , s = 60 | Winged insects (Diptera and Hymenoptera) with
the similar ideotype and rich textures. They are collected to learn the common features of textures, micro-structures, and contours for citrus flies. |
| Case | Accuracy | Settings |
|---|---|---|
| A | Gray-level features, no blanking stamps; | |
| B | LBP features, no blanking stamps; | |
| C | LBP features, having blanking stamps; |
| Statistical Results | Detailed Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Stuck target insects, whose sizes are similar to citrus fly pests; | |
| Stuck non-target insects that are small or oversize, e.g., the mosquitos and butterflies; | |
| Correctly detected target insects; | |
| False target insects caused by non-target insects; | |
| What ratio of stuck non-target insects are incorrectly accepted as target insects; | |
| What ratio of stuck target insects are incorrectly rejected; | |
| What ratio of stuck target insects are correctly detected; |
| No. | Method | Accuracy | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MobileNet V2 [56] | Initialized by the pre-trained model from Pytorch; | |
| 2 | VGG16 [57] | Similar to No. 1; | |
| 3 | DenseNet121 [58] | Similar to No. 1; | |
| 4 | ResNet50 [48] | Baseline method, it will be used the backbone network as the following methods; | |
| 5 | Bilinear ResNet50 [59] | Backbone-ResNet50, Bilinear network architecture according to [59]; | |
| 6 | CBAM ResNet50 [38] | Backbone-ResNet50, Attention Blocks according to CBAM [38]; | |
| 7 | MAMPNet | Only utilize the classification loss to drive network training for feature learning; | |
| 8 | MAMPNet | Compared with No.7, the loss on attention matrices is combined with in feature learning; | |
| 9 | MAMPNet | Compared with No.7, the loss of across-category part constraints is combined with ; | |
| 10 | MAMPNet | All loss functions together. |
| Category | Synthesized Images | Source Images | All Images |
|---|---|---|---|
| B. minax | |||
| B. dorsalis | |||
| B. scutellata | |||
| Average |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, R.; Yao, T.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y. A Motor-Driven and Computer Vision-Based Intelligent E-Trap for Monitoring Citrus Flies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050460
Huang R, Yao T, Zhan C, Zhang G, Zheng Y. A Motor-Driven and Computer Vision-Based Intelligent E-Trap for Monitoring Citrus Flies. Agriculture. 2021; 11(5):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050460
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Renjie, Tingshan Yao, Cheng Zhan, Geng Zhang, and Yongqiang Zheng. 2021. "A Motor-Driven and Computer Vision-Based Intelligent E-Trap for Monitoring Citrus Flies" Agriculture 11, no. 5: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050460
APA StyleHuang, R., Yao, T., Zhan, C., Zhang, G., & Zheng, Y. (2021). A Motor-Driven and Computer Vision-Based Intelligent E-Trap for Monitoring Citrus Flies. Agriculture, 11(5), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11050460