An Extensive Survey of Ciguatoxins on Grouper Variola louti from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Specimens
2.2. Reference Toxins and Reagents
2.3. Extraction and Sample Preparation of the Fish Flesh
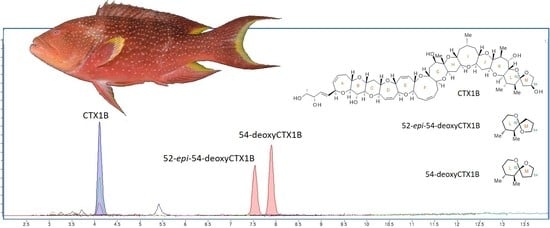
2.4. LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Toxicity Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO; WHO. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning. Rome, 19–23 November 2018; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; Volume 9, p. 156. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Darius, H.T.; Quod, J.P.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2020, 102, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearn, J. Neurology of ciguatera. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, Y. Marine Toxins and Other Bioactive Marine Metabolites; Japan Scientific Societies Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1979; p. 369. [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro, N.; Matsuo, T.; Sakugawa, S.; Yogi, K.; Matsuda, S.; Yasumoto, T.; Inafuku, Y. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning on Kakeroma Island, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. Trop. Med. Health 2011, 39, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.; Roué, M.; Darius, H.T. Ciguatera poisoning in French Polynesia: Insights into the novel trends of an ancient disease. New Microbes New Infect. 2019, 31, 100565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, F.; Bourrat, M.-B.; Pauillac, S. Prevalence, symptoms and chronicity of ciguatera in New Caledonia: Results from an adult population survey conducted in Noumea during 2005. Toxicon 2010, 56, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, C.M.I.; Chung, K.; Oehler, E.; Pierce, T.J.; Gribble, M.O.; Chinain, M. Screening for Predictors of Chronic Ciguatera Poisoning: An Exploratory Analysis among Hospitalized Cases from French Polynesia. Toxins 2021, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Nakajima, I.; Bagnis, R.; Adachi, R. Finding of a Dinoflagellate as a Likely Culprit of Ciguatera. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1977, 43, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasumoto, T. Chemistry, etiology, and food chain dynamics of marine toxins. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2005, 81, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.; Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Subba Rao, D. Ciguatera-causing dinoflagellates in the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa: Distribution, ecophysiology and toxicology. In Dinoflagellates: Classification, Evolution, Physiology and Ecological Significance; Durvasula, S.R.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 405–457. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T.; Satake, M. Chemistry, Etiology and Determination Methods of Ciguatera Toxins. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1996, 15, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehara, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Yasumoto, T. Biooxidation of Ciguatoxins Leads to Species-Specific Toxin Profiles. Toxins 2017, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing Distinct Regional and Species Characteristics in Fish and Causative Alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Matsuda, S.; Sakugawa, S.; Matsuo, T.; Yasumoto, T. Toxin Profiles in Fish Implicated in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in Amami and Kakeroma Islands, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi (Food Hyg. Saf. Sci.) 2013, 54, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yogi, K.; Sakugawa, S.; Oshiro, N.; Ikehara, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of Toxins Involved in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in the Pacific by LC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Yogi, K.; Asato, S.; Sasaki, T.; Tamanaha, K.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Inafuku, Y. Ciguatera incidence and fish toxicity in Okinawa, Japan. Toxicon 2010, 56, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, M.; Uneyama, C.; Toyofuku, H.; Morikawa, K. Trends of Food Poisonings Caused by Natural Toxins in Japan, 1989–2011. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi (Food Hyg. Saf. Sci.) 2012, 53, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banner, A.H.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sasaki, S.; Helfrich, P.; Alender, C.B. Observations on ciguatera-type toxin in fish. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1960, 90, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helfrich, P.; Banner, A.H. Experimental Induction of Ciguatera Toxicity in Fish through Diet. Nature 1963, 197, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Arakaki, K.; Teruya, N.; Koja, A.; Tamanaha, K. Kaisan Doku ni Yoru Shokuchudoku ni Kansuru Kikitori Chousa (Interview Survey on Food Poisoning Caused by Marine Biotoxins); Okinawa Prefectural Institute of Health and Environment: Ozato, Japan, 2004; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Yasumoto, T. Quantification of Representative Ciguatoxins in the Pacific Using Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1975, 191, 1–382. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, T.; Connolly, P.L. The selection of suitable indices for the measurement and analysis of fish condition. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 34, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, T.; Tachihara, K. Age, growth, and gonadal condition of the Giant mottled eel, Anguilla marmorata, in Okinawa-Jima Island, Japan. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2020, 103, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Tachihara, K. Age, growth, and reproductive biology of the five-lined snapper Lutjanus quinquelineatus around Okinawa-jima Island, southern Japan. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunishima, T.; Higuchi, S.; Kawabata, Y.; Furumitsu, K.; Nakamura, I.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tachihara, K.; Tokeshi, M.; Arakaki, S. Age, growth, and reproductive biology of the blackfin seabass Lateolabrax latus, a major predator in rocky coastal ecosystems of southwestern Japan. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 41, 101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Igarashi, T.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Chinain, M.; Fujita, T.; Naoki, H. Structural elucidation of ciguatoxin congeners by fast-atom bombardment tandem mass spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4988–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Structures of ciguatoxin and its congener. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8929–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Fukui, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the moray eel Gymnothorax javanicus and its likely precursor from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure of CTX3C, a ciguatoxin congener isolated from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and Structure of Ciguatoxin-4A, a New Ciguatoxin Precursor, from Cultures of Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and Parrotfish Scarus gibbus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satake, M.; Fukui, M.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structures of new ciguatoxin analogs, 2,3-dihydroxyCTX3C and 51-hydroxyCTX3C, accumulated in tropical reef fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 1197–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Nagasawa, H.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Asakura, H.; Yasumoto, T. Characteristic Distribution of Ciguatoxins in the Edible Parts of a Grouper, Variola louti. Toxins 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Tomikawa, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Ishikawa, A.; Toyofuku, H.; Kojima, T.; Asakura, H. LC–MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing the Regional and Species Distinction of Fish in the Tropical Western Pacific. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Tomikawa, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Kimura, K.; Kojima, T.; Yasumoto, T.; Asakura, H. Detection of ciguatoxins from the fish introduced to a wholesale market in Japan. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi (Food Hyg. Saf. Sci.) 2021, 62, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish–Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed.; Department of Health and Human Services, U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/seafood-guidance-documents-regulatory-information/fish-and-fishery-products-hazards-and-controls (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Oshiro, N. Shigatera Doku (Ciguatera Poison). In Shokuhin Eisei Kensa Shishin Rikagaku-Hen 2015 (Standard Methods of Analysis in Food Safety Regulation, Physical and Chemical Edition 2015); Japan Food Hygiene Association, Ed.; Japan Food Hygiene Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 842–847. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, Y.L.; Wai, T.-C.; Murphy, M.B.; Chan, W.H.; Wu, J.J.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S. Pacific Ciguatoxins in Food Web Components of Coral Reef Systems in the Republic of Kiribati. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14070–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Henao, A.; García-Álvarez, N.; Silva Sergent, F.; Estévez, P.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Martín, F.; Ramos-Sosa, M.; Fernández, A.; Diogène, J.; Real, F. Presence of CTXs in moray eels and dusky groupers in the marine environment of the Canary Islands. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 221, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaboriau, M.; Ponton, D.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera fish toxicity in French Polynesia: Size does not always matter. Toxicon 2014, 84, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Abraham, A.; Stopa, J.E.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Jester, E.L.E.; La Pinta, J.; Deeds, J.; Benner, R.A.; Adolf, J. Ciguatoxin in Hawai’i: Fisheries forecasting using geospatial and environmental analyses for the invasive Cephalopholis argus (Epinephelidae). Environ. Res. 2021, 112164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Sosa, M.J.; García-Álvarez, N.; Sanchez-Henao, A.; Silva Sergent, F.; Padilla, D.; Estévez, P.; Caballero, M.J.; Martín-Barrasa, J.L.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Diogène, J.; et al. Ciguatoxin Detection in Flesh and Liver of Relevant Fish Species from the Canary Islands. Toxins 2022, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, G.S.; Haslauer, K.; Sarowar, C.; Kretzschmar, A.L.; Boulter, M.; Harwood, D.T.; Laczka, O.; Murray, S.A. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of the presence of ciguatoxin, P-CTX-1B, in Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus commerson) from waters in New South Wales (Australia). Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, A.C.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Cooke, S.J. Linking ciguatera poisoning to spatial ecology of fish: A novel approach to examining the distribution of biotoxin levels in the great barracuda by combining non-lethal blood sampling and biotelemetry. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, R.J. Ciguatoxins are potent ichthyotoxins. Toxicon 1992, 30, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledreux, A.; Brand, H.; Chinain, M.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Ramsdell, J.S. Dynamics of ciguatoxins from Gambierdiscus polynesiensis in the benthic herbivore Mugil cephalus: Trophic transfer implications. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Henao, A.; García-Álvarez, N.; Padilla, D.; Ramos-Sosa, M.; Silva Sergent, F.; Fernández, A.; Estévez, P.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Diogène, J.; Real, F. Accumulation of C-CTX1 in Muscle Tissue of Goldfish (Carassius auratus) by Dietary Experience. Animals 2021, 11, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, I.D.P.; Sdiri, K.; Taylor, A.; Viallon, J.; Gharbia, H.B.; Mafra Júnior, L.L.; Swarzenski, P.; Oberhaensli, F.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; et al. Experimental Evidence of Ciguatoxin Accumulation and Depuration in Carnivorous Lionfish. Toxins 2021, 13, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, I.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Poole, S.; Graham, G.; Paulo, C.; Wickramasinghe, W.; Sadler, R.; Shaw, G.R. Establishing a public health analytical service based on chemical methods for detecting and quantifying Pacific ciguatoxin in fish samples. Toxicon 2010, 56, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, J.E. Survey of ciguatera at Enewetak and Bikini, Marshall Islands, with notes on the systematics and food habits of ciguatoxic fishes. Fish. Bull. 1980, 78, 201–249. [Google Scholar]
- Rongo, T.; van Woesik, R. Ciguatera poisoning in Rarotonga, southern Cook islands. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P. Status of ciguatera in Fiji. SPC Ciguatera Inf. Bull. 1992, 2, 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Glaizal, M.; Tichadou, L.; Drouet, G.; Hayek-Lanthois, M.; de Haro, L. Ciguatera contracted by French tourists in Mauritius recurs in Senegal. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamele, I.J.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. The Incidence of Marine Toxins and the Associated Seafood Poisoning Episodes in the African Countries of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. Toxins 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quod, J.P.; Turquet, J. Ciguatera in Réunion Island (SW Indian Ocean): Epidemiology and clinical patterns. Toxicon 1996, 34, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.A.; Wood, E.; Islam, F.; Najeeb, A. Current Status of the Reef Fisheries of Maldives and Recommendations of Management: Darwin Reef Fish Project; Marine Research Centre/Marine Conservation Society (UK): 2014. Available online: https://www.mrc.gov.mv/en/publications/show/current-status-of-the-reef-fisheries-of-maldives-and-recommendations-for-management (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Amorim, P.; Westmeyer, M. Snapper and grouper: SFP fisheries sustainability overview 2015. Sustain. Fish. Partnersh. Found. 2016, 18. Available online: www.fishsource.com (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Yulianto, I.; Wiryawan, B.; Taurusman, A.A. Responsible grouper fisheries in Weh Island, Aceh Province, Indonesia. Galaxea J. Coral Reef Stud. 2013, 15, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadli, N.; Nor, S.A.M.; Othman, A.S.; Sofyan, H.; Muchlisin, Z.A. DNA barcoding of commercially important reef fishes in Weh Island, Aceh, Indonesia. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, P.; Ponwith, B.; Aitaoto, F.; Hamm, D. The commercial, subsistence, recreational fisheries of American Samoa. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1993, 55, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, M.K.; Quach, M.; Brousseau, K.R.; Tomita, A.S.; Matthews, T.E. Fishery Statistics of the Western Pacific; US Department of Commerce: Columbia, DC, USA, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.F. Guam’s small-boat-based fisheries. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1993, 55, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.; Richard, A.H. A multispecies fishery associated with coral reefs in the Tigak Islands, Papua New Guinea. Asian Mar. Biol. 1985, 2, 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Muallil, R.N.; Tambihasan, A.M.; Enojario, M.J.; Ong, Y.N.; Nañola, C.L. Inventory of commercially important coral reef fishes in Tawi-Tawi Islands, Southern Philippines: The Heart of the Coral Triangle. Fish. Res. 2020, 230, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, Y.; Ohta, I.; Ebisawa, A.; Uehara, M. Estimation of the fish catches of coastal species of the Yaeyama Islands. Fauna Ryukyuana 2016, 31, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, I.; Uehara, M.; Ebisawa, A. Evaluation of importance as fishery targets, ecological functions, and nursery of reef fishes, based on estimated species-specific catch data around the Okinawa Islands. Okinawaken Suisan Kaiyou Kenkyuu Senta Jigyou Houkokusho (Annu. Rep. Okinawa Prefect. Fish. Ocean. Res. Cent.) 2017, 77, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dalzell, P.; Adams, T.J.H.; Polunin, N.V.C. Coastal fisheries in the Pacific Islands. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1996, 34, 531. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa, H.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Tanigawa, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Asakura, H.; Oshiro, N. Analysis of Ciguatoxins in Variola louti Captured off the Ogasawara (Bonin) Islands. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi (Food Hyg. Saf. Sci.) 2021, 62, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Area | Total CTX Levels (µg/kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | <0.003 | 0.003–0.010 | 0.011–0.17 | ≥0.18 | |||||
| Amami | 8 | 0% | 2 | 25% | 6 | 75% | 0% | ||
| West-north, Okinawa | 35 | 16 | 46% | 8 | 23% | 11 | 31% | 0% | |
| West-south, Okinawa | 68 | 21 | 31% | 19 | 28% | 26 | 38% | 2 | 3% |
| East, Okinawa | 8 | 2 | 25% | 1 | 13% | 5 | 63% | 0% | |
| Miyako | 12 | 6 | 50% | 0% | 4 | 33% | 2 | 17% | |
| Yaeyama | 2 | 0% | 0% | 2 | 100% | 0% | |||
| Unknown | 21 | 10 | 48% | 6 | 29% | 5 | 24% | 0% | |
| Total | 154 | 55 | 36% | 36 | 23% | 59 | 38% | 4 | 3% |
| CTX Analogs | Average (%) | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| CTX1B | 35 | 7.7 |
| 52-epi-54-deoxyCTX1B | 27 | 8.1 |
| 54-deoxyCTX1B | 38 | 5.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oshiro, N.; Nagasawa, H.; Watanabe, M.; Nishimura, M.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Asakura, H.; Tachihara, K.; Yasumoto, T. An Extensive Survey of Ciguatoxins on Grouper Variola louti from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030423
Oshiro N, Nagasawa H, Watanabe M, Nishimura M, Kuniyoshi K, Kobayashi N, Sugita-Konishi Y, Asakura H, Tachihara K, Yasumoto T. An Extensive Survey of Ciguatoxins on Grouper Variola louti from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(3):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030423
Chicago/Turabian StyleOshiro, Naomasa, Hiroya Nagasawa, Miharu Watanabe, Mio Nishimura, Kyoko Kuniyoshi, Naoki Kobayashi, Yoshiko Sugita-Konishi, Hiroshi Asakura, Katsunori Tachihara, and Takeshi Yasumoto. 2022. "An Extensive Survey of Ciguatoxins on Grouper Variola louti from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 3: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030423
APA StyleOshiro, N., Nagasawa, H., Watanabe, M., Nishimura, M., Kuniyoshi, K., Kobayashi, N., Sugita-Konishi, Y., Asakura, H., Tachihara, K., & Yasumoto, T. (2022). An Extensive Survey of Ciguatoxins on Grouper Variola louti from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan, Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(3), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030423