Pepper-Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium and Tellurium Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Anticancer Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
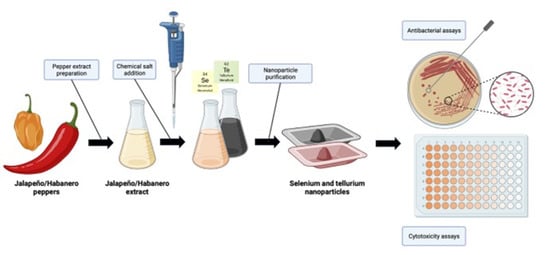
2.1. Se- and TeNPs Synthesis
2.2. Physical and Chemical Characterization of the NPs
2.2.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
2.2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.2.3. High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.2.5. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.2.6. Stability Analysis
2.3. Testing the NPs for Biomedical Applications
2.3.1. Preparation of the Bacterial Cultures and Testing Antimicrobial Efficacy
2.3.2. Testing the Effect of the Nanomaterials towards Human Cells
2.3.3. Cell Fixation and SEM Imaging (For Bacteria and Human Cells)
2.3.4. Mechanistic Analysis of the Se- and TeNP Interaction with Cells
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Se- and TeNP Synthesis and Purification
3.2. UV-Visible Spectroscopic Characterization of the Samples
3.3. FT-IR Spectroscopy Characterization of the Samples
3.4. TEM and SEM Characterization of the Samples
3.5. Testing the Antimicrobial Effect of the Nanoparticles
3.6. Testing the Effect of the Nanomaterials When Exposed to Human Cells
3.7. ROS Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Synthesis of Se and Te Nanoparticles

Appendix A.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)




Appendix A.3. EDX Measurements
- Spot 1: On top of a large spherical NP.
- Spot 2: Outside of the NPs in a darker zone.
- Spot 3: Outside of the NPs in a brighter area zone.

- Spot 1: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.


- Spot 1: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.
- Spot 2: Outside all nanoparticles.
- Spot 3: Outside all nanoparticles in a darker zone.

- Spot 1: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.


- Spot 1: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.
- Spot 2: On top of a nanoparticle cluster.
- Full area: corresponds to the beam scanning the full image.

- Spot 1: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.
- Spot 2: On top of another spherical nanoparticle.
- Selected Area: Area which includes a cluster of nanoparticles.


- Spot 1: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.
- Spot 2: Outside nanoparticles.

- Spot 1: On top of a cluster of spherical nanoparticles.
- Spot 2: On top of a spherical nanoparticle.


Appendix A.4. XRD Analyses

Appendix A.5. Stability Analyses
| Z-Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nanostructure | As-Synthesized | 60 days old |
| JP-SeNPs | −32 ± 3 | −30 ± 5 |
| HB-SeNPs | −45 ± 3 | −39 ± 3 |
| JP-TeNPs | −31 ± 3 | −28 ± 5 |
| HB-TeNPs | −43 ± 4 | −41 ± 2 |
Appendix A.6. Cell Fixation and SEM Imaging for Bacteria and Human Cells




References
- Seigneuric, R.; Markey, L.; S.A. Nuyten, D.; Dubernet, C.; T.A. Evelo, C.; Finot, E.; Garrido, C. From Nanotechnology to Nanomedicine: Applications to Cancer Research. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 640–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teli, M.K.; Mutalik, S.; Rajanikant, G.K. Nanotechnology and Nanomedicine: Going Small Means Aiming Big. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reverberi, A.P.; Kuznetsov, N.T.; Meshalkin, V.P.; Salerno, M.; Fabiano, B. Systematical analysis of chemical methods in metal nanoparticles synthesis. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2016, 50, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, D.; Banerjee, P. Green nanotechnology—A new hope for medical biology. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 36, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Sajadi, S.M.; Issaabadi, Z. Green Nanotechnology. In An Introduction to Green Nanotechnology; Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, M.S., Atarod, M., Sajjadi, M., Isaabadi, Z., Eds.; Elservier: London, UK; Oxford, UK; Cambridge, MA, USA; San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 145–198. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.; Ullah, N.; Khan, M.A.; ur Rehman Mashwani, Z.; Nadhman, A. Plant-based gold nanoparticles; a comprehensive review of the decade-long research on synthesis, mechanistic aspects and diverse applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 272, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Agarwal, P.; Kanawaria, S.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S.L. Plant-Based Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization. In Nanotechnology and Plant Sciences: Nanoparticles and Their Impact on Plants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 271–288. [Google Scholar]
- Venkat Kumar, S.; Rajeshkumar, S. Plant-Based Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Impact. In Nanomaterials in Plants, Algae, and Microorganisms; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 33–57. ISBN 9780128116463. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedy, A.K.; Upadhyay, N.; Asawa, S.; Kumar, M.; Prakash, B.; Dubey, N.K. Therapeutic Potential of Plant-Based Metal Nanoparticles: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Nanomater. Plants Algae Microorg. Concepts Controv. 2019, 2, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.K.; Singh, R.P.; Pandey, A.C. Black pepper assisted biomimetic synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 507, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Sushma, N.J.; Narasimha, G.; Manoj, L.; Raju, B.D.P. Phytochemical fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles by using Pepper leaf broth. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustine, R.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. A facile and rapid method for the black pepper leaf mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and the antimicrobial study. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendoza-Reséndez, R.; Núñez, N.O.; Barriga-Castro, E.D.; Luna, C. Synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles and silver organometallic nanodisks mediated by extracts of Capsicum annuum var. aviculare (piquin) fruits. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 20765–20771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinay, S.P.; Udayabhanu; Nagaraju, G.; Chandrappa, C.P.; Chandrasekhar, N. Rauvolfia tetraphylla (Devil Pepper)-Mediated Green Synthesis of Ag Nanoparticles: Applications to Anticancer, Antioxidant and Antimitotic. J. Clust. Sci. 2019, 30, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, D.M.; Menezes, D.B.; Andrade, L.R.; Lima, F.D.C.; Hollanda, L.; Zielinska, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P. Silver nanoparticles obtained from Brazilian pepper extracts with synergistic anti-microbial effect: Production, characterization, hydrogel formulation, cell viability, and in vitro efficacy. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Gomez-Zavaglia, A.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using polyphenol extracts from pepper waste (Capsicum annuum). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 350, 131541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaghani, S.; Ghanbari, D.; Khaghani, S. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide-Palladium Nanocomposites by Pepper extract and Its Application in Removing of Colored Pollutants from Water. J. Nanostruct. 2017, 7, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.G.; Huo, C.; Yu, S.; Gui, B. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum var. grossum pulp extract and its catalytic activity. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2017, 85, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandathil, V.; Dateer, R.B.; Sasidhar, B.S.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A. Green Synthesis of Palladium Nanoparticles: Applications in Aryl Halide Cyanation and Hiyama Cross-Coupling Reaction Under Ligand Free Conditions. Catal. Lett. 2018, 148, 1562–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, N.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K. Selenium nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and biomedical applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spallholz, J.E. On the nature of selenium toxicity and carcinostatic activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 17, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, L.B.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Mostafavi, E.; Rabiee, N. Selenium Nanomaterials to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Molecule 2021, 26, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, C.; Florindo, H.F.; Santos, H.A. Selenium Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: From Development and Characterization to Therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambonino, M.C.; Quizhpe, E.M.; Jaramillo, F.E.; Rahman, A.; Vispo, N.S.; Jeffryes, C.; Dahoumane, S.A. Green Synthesis of Selenium and Tellurium Nanoparticles: Current Trends, Biological Properties and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonaro, E.; Lampis, S.; Turner, R.J.; Qazi, S.J.S.; Vallini, G.; Junaid, S.; Vallini, G.; Qazi, S.J.S.; Vallini, G. Biogenic selenium and tellurium nanoparticles synthesized by environmental microbial isolates efficaciously inhibit bacterial planktonic cultures and biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, D.M.; Tien-Street, W.; Zhang, B.; Huang, X.; Crua, A.V.; Nieto-Argüello, A.; Cholula-Díaz, J.L.; Martínez, L.; Huttel, Y.; González, M.U.; et al. Citric juice-mediated synthesis of tellurium nanoparticles with antimicrobial and anticancer properties. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1982–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet Crua, A.; Medina, D.; Zhang, B.; González, M.U.; Huttel, Y.; García-Martín, J.M.; Cholula Díaz, J.L.; Webster, T.J. Comparison of cytocompatibility and anticancer properties of traditional and green chemistry-synthesized tellurium nanowires. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, Volume 14, 3155–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Cruz, D.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Mostafavi, E.; González, M.U.; Martínez, L.; Jones, A.A.D.; Kusper, M.; Sotelo, E.; Gao, M.; Geoffrion, L.D.; et al. Aloe vera-mediated te nanostructures: Highly potent antibacterial agents and moderated anticancer effects. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.D.; Medina Cruz, D.; Roy, A.K.; Webster, T.J. Synthesis and characterization of PVP-coated tellurium nanorods and their antibacterial and anticancer properties. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2018, 20, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidi, H.; Kobarfard, F.; Alizadeh, A.; Saravanan, M.; Barabadi, H. Green nanotechnology-based tellurium nanoparticles: Exploration of their antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic potentials against cancerous and normal cells compared to potassium tellurite. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 124, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ke, H.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, P.; Ling, D.; Chen, C.; et al. Bifunctional Tellurium Nanodots for Photo-Induced Synergistic Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10012–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina Cruz, D.; Mi, G.; Webster, T.J. Synthesis and characterization of biogenic selenium nanoparticles with antimicrobial properties made by Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancín-azpilicueta, C.; Esparza, I.; Jiménez-moreno, N. Biomolecules from Plant Residues. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L. V Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles—A review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagtepe, P.; Chikan, V. Quantized Ostwald Ripening of Colloidal Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16263–16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Green synthesis and structural characterization of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their antimicrobial property. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Holden, J.A.; Heath, D.E.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; O’Connor, A.J. Engineering highly effective antimicrobial selenium nanoparticles through control of particle size. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 14937–14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Rosales, D.A.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; Reyes-Maldonado, O.K.; López-Reyes, M.E.; Basulto-Padilla, G.C.; Lopez-Naranjo, E.J.; Zuñiga-Mayo, V.M.; Velázquez-Juárez, G. Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Capsicum chinense Plant. Molecules 2022, 27, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amruthraj, N.J.; Preetam Raj, J.P.; Lebel, A. Capsaicin-capped silver nanoparticles: Its kinetics, characterization and biocompatibility assay. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, N.; Ušjak, D.; Milenković, M.T.; Zheng, K.; Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Stevanović, M.M. Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Selenium Nanoparticles With Different Surface Chemistry and Structure. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, J.M.; Calderón, I.L.; Arenas, F.A.; Fuentes, D.E.; Pradenas, G.A.; Fuentes, E.L.; Sandoval, J.M.; Castro, M.E.; Elías, A.O.; Vásquez, C.C. Bacterial Toxicity of Potassium Tellurite: Unveiling an Ancient Enigma. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morena, A.G.; Bassegoda, A.; Hoyo, J.; Tzanov, T. Hybrid Tellurium-Lignin Nanoparticles with Enhanced Antibacterial Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 14885–14893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Shrudhi, S.D.; Agarwal, H.; Shanmugam, V.K. Efficacy of Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles from an Extract of Ginger towards Evaluation on Anti-Microbial and Anti-Oxidant Activities. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H.; Khatoon, N.; Raza, M.; Ghosh, P.C.; Sardar, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Nano Selenium Using Plant Biomolecules and Their Potential Applications. BioNanoScience 2018, 9, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, B.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Sepehrizadeh, Z.; Shakibaie, M.; Rezaie, S.; Shahverdi, A.R. Biosynthesis and recovery of rod-shaped tellurium nanoparticles and their bactericidal activities. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 3719–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forootanfar, H.; Adeli-Sardou, M.; Nikkhoo, M.; Mehrabani, M.; Amir-Heidari, B.; Shahverdi, A.R.; Shakibaie, M. Antioxidant and cytotoxic effect of biologically synthesized selenium nanoparticles in comparison to selenium dioxide. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Shanmugam, V.K. Cytotoxicity Analysis of Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles Towards A549 Lung Cancer Cell Line. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajideh, R.; Faghfuri, E.; Hosseini, M.; Yazdi, M.H.; Mirjani, R.; Sepehrizadeh, Z.; Shahverdi, A.R. The Cytotoxicity of Tellurium Nanoparticles on Different Cell lines and their in vivo Anticancer Effects in an Animal Model. Middle East J. Cancer 2022, 14, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Fan, C.; Chen, T. Positive surface charge enhances selective cellular uptake and anticancer efficacy of selenium nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 8956–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoffrion, L.D.; Hesabizadeh, T.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Kusper, M.; Taylor, P.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Chen, J.; Ajo, A.; Webster, T.J.; Guisbiers, G. Naked Selenium Nanoparticles for Antibacterial and Anticancer Treatments. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.S.; Zhang, J. Selenium nanoparticles are more efficient than sodium selenite in producing reactive oxygen species and hyper-accumulation of selenium nanoparticles in cancer cells generates potent therapeutic effects. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 126, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchman, J.T.; Hudson-Smith, N.V.; Landy, K.M.; Haynes, C.L. Understanding Nanoparticle Toxicity Mechanisms to Inform Redesign Strategies to Reduce Environmental Impact. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1632–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, J.J.; Cogswell, P.; Flavell, R.A.; Baldwin, A.S.; Davis, R.J. JNK potentiates TNF-stimulated necrosis by increasing the production of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2905–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cronholm, P.; Karlsson, H.L.; Hedberg, J.; Lowe, T.A.; Winnberg, L.; Elihn, K.; Wallinder, I.O.; Möller, L. Intracellular uptake and toxicity of Ag and CuO nanoparticles: A comparison between nanoparticles and their corresponding metal ions. Small 2013, 9, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Matteis, V.; Malvindi, M.A.; Galeone, A.; Brunetti, V.; De Luca, E.; Kote, S.; Kshirsagar, P.; Sabella, S.; Bardi, G.; Pompa, P.P. Negligible particle-specific toxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles: The role of Ag+ ion release in the cytosol. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjani, R.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Setayesh, N.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Shahverdi, A.R. Biosynthesis of tellurium nanoparticles by Lactobacillus plantarum and the effect of nanoparticle-enriched probiotics on the lipid profiles of mice. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadoo, S.; Stanley, D.; Hughes, R.J.; Moore, R.J.; Chapman, J. The synthesis and characterisation of highly stable and reproducible selenium nanoparticles. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 2017, 47, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Evidence for seed-mediated nucleation in the chemical reduction of gold salts to gold nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 2313–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherin, P.; Unger, P. The crystal structure of trigonal selenium. Inorg. Chem. 1967, 6, 1589–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenis, C.; Langer, V.; Lindqvist, O. Reinvestigation of the structure of tellurium. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Cryst. Struct. Commun. 1989, 45, 941–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Dash, S.K.; Mandal, D.; Ghosh, T.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Tripathy, S.; Das, S.; Dey, S.K.; Das, D.; Roy, S. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles destroy multidrug resistant bacteria via reactive oxygen species mediated membrane damage. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalandi, B.; Asadi, N.; Milani, M.; Davaran, S.; Abadi, A.J.N.; Abasi, E.; Akbarzadeh, A. A Review on Potential Role of Silver Nanoparticles and Possible Mechanisms of their Actions on Bacteria. Drug Res. 2017, 67, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Nanostructure | Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|
| JP-SeNPs | 79.2 ± 10.2 |
| JP-TeNPs | 82.1 ± 2.1 |
| HB-SeNPs | 90.6 ± 14.4 |
| HB-TeNPs | 74.3 ± 10.4 |
| MIC (µg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial Strain | JP-SeNPs | HB-SeNPs | JP-TeNPs | HB-TeNPs |
| MDR Escherichia coli | - | 72.2 | 0.9 | 1.2 |
| MRSA | - | 85.1 | 0.3 | 2.0 |
| Cell Type | HDF Cells | MEL Cells | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanosystems | 24 h | 72 h | 24 h | 72 h |
| JP-SeNPs | 74.4 | 52.9 | 28.2 | 49.1 |
| HB-SeNPs | 45.9 | 66.9 | 60.2 | 30.0 |
| JP-TeNPs | 58.6 | 34.1 | 80.8 | 51.0 |
| HB-TeNPs | 81.0 | 91.5 | 71.8 | 23.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, V.; Medina-Cruz, D.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Truong, L.B.; Sotelo, E.; Mostafavi, E.; González, M.U.; García-Martín, J.M.; Cholula-Díaz, J.L.; Webster, T.J. Pepper-Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium and Tellurium Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Anticancer Potential. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010024
Shah V, Medina-Cruz D, Vernet-Crua A, Truong LB, Sotelo E, Mostafavi E, González MU, García-Martín JM, Cholula-Díaz JL, Webster TJ. Pepper-Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium and Tellurium Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Anticancer Potential. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2023; 14(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Veer, David Medina-Cruz, Ada Vernet-Crua, Linh B. Truong, Eduardo Sotelo, Ebrahim Mostafavi, María Ujué González, José Miguel García-Martín, Jorge L. Cholula-Díaz, and Thomas J. Webster. 2023. "Pepper-Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium and Tellurium Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Anticancer Potential" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 14, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010024
APA StyleShah, V., Medina-Cruz, D., Vernet-Crua, A., Truong, L. B., Sotelo, E., Mostafavi, E., González, M. U., García-Martín, J. M., Cholula-Díaz, J. L., & Webster, T. J. (2023). Pepper-Mediated Green Synthesis of Selenium and Tellurium Nanoparticles with Antibacterial and Anticancer Potential. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 14(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14010024