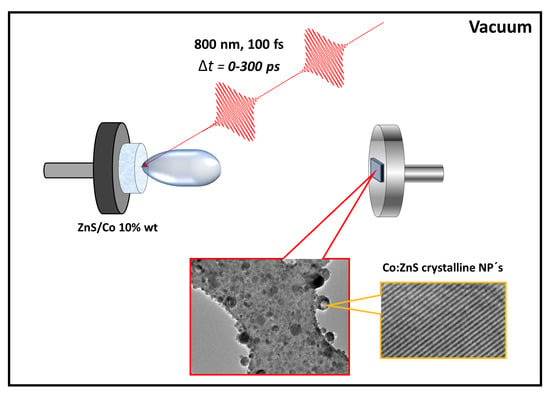
Femtosecond Double-Pulse Laser Ablation and Deposition of Co-Doped ZnS Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furdyna, J.K. Diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, R29–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T. Functional ferromagnets. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearton, S.J.; Heo, W.H.; Ivill, M.; Norton, D.P.; Steiner, T. Dilute magnetic semiconducting oxides. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2004, 19, R59–R74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittilstved, K.R.; Liu, W.K.; Gamelin, D.R. Electronic structure origins of polarity-dependent high-TC ferromagnetism in oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T. A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohno, H.; Shen, A.; Matsukura, F.; Oiwa, A.; Endo, A.; Katsumoto, S.; Iye, Y. (Ga,Mn)As: A new diluted magnetic semiconductor based on GaAs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhao, J.; Misuraca, J.; Xiong, P.; von Molnár, S. Enhancing the Curie Temperature of Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As to 200 K via Nanostructure Engineering. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietl, T.; Ohno, H.; Matsukura, F.; Cibert, J.; Ferrand, D. Zener Model Description of Ferromagnetism in Zinc-Blende Magnetic Semiconductors. Science 2000, 287, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietl, T. Ferromagnetic semiconductors. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2002, 17, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Murakami, M.; Koida, T.; Fan, X.J.; Hasegawa, T.; Fukumura, T.; Kawasaki, M.; Koshihara, S.Y.; Koinuma, H. Ferromagnetism in Co-Doped TiO2 Rutile Thin Films Grown by Laser Molecular Beam Epitaxy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, L1204–L1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, S.M. Spintronics: Future Technology for New Data Storage and Communication Devices. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 2557–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Zhang, X.J.; Wang, B.Q.; Zhang, X.Z.; Yu, D.P. Room Temperature Ferromagnetism and Optical Tunability in Cu Doped GaN Nanowires. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 3040–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, A.; Rao, C.N.R. Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of inorganic nanoparticles. Nano Today 2009, 4, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Shao, Y.C.; Hsieh, S.H.; Chang, Y.K.; Yeh, P.H.; Hsueh, H.C.; Chiou, J.W.; Wang, H.T.; Ray, S.C.; Tsai, H.M.; et al. Origin of magnetic properties in carbon implanted ZnO nanowires. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isshiki, M.; Wang, J. Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Wide-bandgap II-VI semiconductors: Growth and Properties; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-29185-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Cao, L.; Ouyang, H.; Yong, X. Morphology-controllable synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnS nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, L.J.; Mai, W.; Wang, Z.L. Tunable electric and magnetic properties of CoxZn1−xS nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 242503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivam, S.; Paul Joseph, D.; Lin, J.G.; Venkateswaran, C. Doping induced magnetism in Co–ZnS nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 2598–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, D.; Borah, J.P. Investigations of doping induced structural, optical and magnetic properties of Ni doped ZnS diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 8029–8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.S.; Alghamdi, Y.G.; Azad Malik, M.; Arif Khalil, R.M.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Structural, optical, magnetic and half-metallic studies of cobalt doped ZnS thin films deposited via chemical bath deposition. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 6755–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Verma, N.K. Room Temperature Magnetism in Cobalt-Doped ZnS Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2015, 28, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Pivin, J.C.; Chawla, A.K.; Chandra, R.; Kanjilal, D.; Kumar, L. Room temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1−xCoxS thin films with wurtzite structure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2734–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadraque, M.; Evtushenko, A.B.; Ávila-Brande, D.; López-Arias, M.; Loriot, V.; Shukhov, Y.G.; Kibis, L.S.; Bulgakov, A.V.; Martín, M. Co-Doped ZnS Clusters and Nanostructures Produced by Pulsed Laser Ablation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 5416–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivill, M.; Pearton, S.J.; Rawal, S.; Leu, L.; Sadik, P.; Das, R.; Hebard, A.F.; Chisholm, M.; Budai, J.D.; Norton, D.P. Structure and magnetism of cobalt-doped ZnO thin films. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 065002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, S.; Rawat, R.S.; Tan, T.L.; Lee, P.; Chen, R.; Sun, H.D.; Zhou, W. Ferromagnetism in ZnCoO thin films deposited by PLD. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 101, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Pivin, J.C.; Patel, M.K.; Won, J.; Chandra, R.; Kanjilal, D.; Kumar, L. Defects induced magnetic transition in Co doped ZnS thin films: Effects of swift heavy ion irradiations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2136–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Jin, C.; Kvit, A.; Kumar, D.; Muth, J.F.; Narayan, J. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of diluted magnetic semiconducting Zn1−xMnxO films. Solid State Commun. 2002, 121, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.; Sarma, D.D. Advances in Light-Emitting Doped Semiconductor Nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaqsara, S.M.T. Tunable visible emission of TM-doped ZnS quantum dots (TM: Mn2+, Co2+, Ag+). Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 59, 10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Bergqvist, L.; Kudrnovský, J.; Dederichs, P.H.; Eriksson, O.; Turek, I.; Sanyal, B.; Bouzerar, G.; Katayama-Yoshida, H.; Dinh, V.A.; et al. First-principles theory of dilute magnetic semiconductors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 1633–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacic, M.; Jakob, G.; Herbort, C.; Adrian, H.; Tietze, T.; Brück, S.; Goering, E. Magnetism of Co-doped ZnO thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 205206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, C.B.; Venkatesan, M.; Lunney, J.G.; Dorneles, L.S.; Coey, J.M.D. Cobalt-doped ZnO—A room temperature dilute magnetic semiconductor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 247, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Q. Intrinsic room temperature ferromagnetism in Zn0.92Co0.08O thin films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 3312–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Córdova, A.; Castañeda-Guzmán, R.; Sanchez-Aké, C. Zinc blende phase detection in ZnO thin films grown with low doping Mn concentration by double-beam pulsed laser deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 18971–18977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Z.; Song, W.D.; An, C.W.; Qiu, J.J.; Chong, J.F.; Lim, B.C.; Hong, M.H.; Liew, T.; Chong, T.C. Room temperature diluted magnetic semiconductor synthesized by dual beam laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A 2005, 80, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Fukumura, T.; Kawasaki, M.; Inaba, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Koinuma, H. Rutile-type oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductor: Mn-doped SnO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, F.; Sun, L.; Cheng, W.; Ma, X.; Shi, W. Doping concentration dependence of room-temperature ferromagnetism for Ni-doped ZnO thin films prepared by pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 062508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Pivin, J.C.; Maity, G.; Yadav, R.P.; Chandra, R.; Kanjilal, D.; Kumar, L. Microstructural and surface morphological studies on Co doped ZnS diluted magnetic semiconductor thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 13541–13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaurepaire, E.; Merle, J.C.; Daunois, A.; Bigot, J.Y. Ultrafast Spin Dynamics in Ferromagnetic Nickel. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 4250–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.S.; Silva, A.S.; Navas, D.; Miranda, M.; Silva, F.; Crespo, H.; Schmool, D.S. A Dual-Colour Architecture for Pump-Probe Spectroscopy of Ultrafast Magnetization Dynamics in the Sub-10-femtosecond Range. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gamaly, E.G.; Rode, A.V. Physics of ultra-short laser interaction with matter: From phonon excitation to ultimate transformations. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2013, 37, 215–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.K.; Mazur, E. Inducing and probing non-thermal transitions in semiconductors using femtosecond laser pulses. Nat. Mater. 2002, 1, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoruso, S.; Ausanio, G.; Bruzzese, R.; Vitiello, M.; Wang, X. Femtosecond laser pulse irradiation of solid targets as a general route to nanoparticle formation in a vacuum. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 33406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balling, P.; Schou, J. Femtosecond-laser ablation dynamics of dielectrics: Basics and applications for thin films. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2013, 76, 036502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrelie, F.; Bourquard, F.; Loir, A.S.; Donnet, C.; Colombier, J.P. [INVITED] Control of femtosecond pulsed laser ablation and deposition by temporal pulse shaping. Opt. Laser Technol. 2016, 78, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, S.I.; Samokhvalov, A.A.; Golubev, Y.D.; Ivanov, D.S.; Garcia, M.E.; Veiko, V.P.; Rethfeld, B.; Mikhailovskii, V.Y. Dynamic all-optical control in ultrashort double-pulse laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 537, 147940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñon, V.; Fotakis, C.; Nicolas, G.; Anglos, D. Double pulse laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with femtosecond laser pulses. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2008, 63, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulej, M.; Wiesendanger, R.; Riedo, A.; Knopp, G.; Wurz, P. Mass spectrometric analysis of the Mg plasma produced by double-pulse femtosecond laser irradiation. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildner, J.; Sarpe, C.; Götte, N.; Wollenhaupt, M.; Baumert, T. Emission signal enhancement of laser ablation of metals (aluminum and titanium) by time delayed femtosecond double pulses from femtoseconds to nanoseconds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 302, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, L.; Han, W.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Zhan, S.; Lu, Y. Manipulation of LIPSS orientation on silicon surfaces using orthogonally polarized femtosecond laser double-pulse trains. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 9782–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures on zinc oxide crystals upon two-colour femtosecond double-pulse irradiation. Phys. Scr. 2017, 92, 034003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourquard, F.; Tite, T.; Loir, A.S.; Donnet, C.; Garrelie, F. Control of the Graphite Femtosecond Ablation Plume Kinetics by Temporal Laser Pulse Shaping: Effects on Pulsed Laser Deposition of Diamond-Like Carbon. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 4377–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristoscu, C.; Socol, G.; Ghica, C.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Gray, D.; Klini, A.; Manousaki, A.; Anglos, D.; Fotakis, C. Femtosecond pulse shaping for phase and morphology control in PLD: Synthesis of cubic SiC. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 4857–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillermin, M.; Klini, A.; Colombier, J.P.; Garrelie, F.; Gray, D.; Liebig, C.; Audouard, E.; Fotakis, C.; Stoian, R. Tuning spectral properties of ultrafast laser ablation plasmas from brass using adaptive temporal pulse shaping. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 11159–11172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Yu, J.; Mo, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, B. Influence of double pulse ablation on the film topography in picosecond pulsed laser deposition of nickel. Appl. Phys. Express 2020, 13, 035505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegenyes, N.; Toth, Z.; Hopp, B.; Klebniczki, J.; Bor, Z.; Fotakis, C. Femtosecond pulsed laser deposition of diamond-like carbon films: The effect of double laser pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 4667–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Quintas, I.; Loriot, V.; Ávila, D.; Izquierdo, J.G.; Rebollar, E.; Bañares, L.; Castillejo, M.; de Nalda, R.; Martin, M. Ablation dynamics of Co/ZnS targets under double pulse femtosecond laser irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinten, M. A Practical Guide to Optical Metrology for Thin Films; Willey: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-527-41167-2. [Google Scholar]
- Fairbrother, A.; Izquierdo-Roca, V.; Fontané, X.; Ibáñez, M.; Cabot, A.; Saucedo, E.; Pérez-Rodríguez, A. ZnS grain size effects on near-resonant Raman scattering: Optical non-destructive grain size estimation. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4120–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotillo, B.; Fernández, P.; Piqueras, J. Cathodoluminescence of in doped ZnS nanostructures grown by vapor–solid method. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 563, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Sudhiranjan, T.; Boothroyd, C.; Loh, K.P. Influence of Au catalyst on the growth of ZnS nanowires. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 400, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeltzer, D.; Beserman, R.; Slamovits, D. Zone-edge phonons in mixed zinc-sulfide-zinc-selenide crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1980, 22, 4038–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Chen, G.; Acord, J.D.; Liu, X.; Zengel, J.J.; Gutierrez, H.R.; Redwing, J.M.; Lew Yan Voon, L.C.; Lassen, B.; Eklund, P.C. Optical Properties of Rectangular Cross-sectional ZnS Nanowires. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Rho, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.G. Raman spectroscopy of ZnS nanostructures. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, W.G. Raman Spectrum of Cubic ZnS. Phys. Rev. 1969, 182, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Karthikeyan, B. A Raman spectral probe on polar w-ZnS nanostructures and surface optical phonon modes in nanowires. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4948–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Lynn, K.G.; Jacobsohn, L.G.; McCloy, J.S. Luminescence of undoped commercial ZnS crystals: A critical review and new evidence on the role of impurities using photoluminescence and electrical transient spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 075702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, X. Growth mechanism and blue shift of Mn2+luminescence for wurtzite ZnS: Mn2+nanowires. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 075403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.W. Spectroscopy of lattice defects in tetrahedral II-VI compounds. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1995, 10, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, J.E.; Davies, J.J.; Cavenett, B.C.; James, J.R.; Dunstan, D.J. Spin-dependent donor-acceptor pair recombination in ZnS crystals showing the self-activated emission. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1979, 12, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, M.; Li, C. Visible emission characteristics from different defects of ZnS nanocrystals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4715–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Song, D.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Park, I.Y.; Choi, Y.D. Effects of synthesis temperature on particle size/shape and photoluminescence characteristics of ZnS: Cu nanocrystals. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Fang, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, L. Origin of the green photoluminescence from zinc sulfide nanobelts. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3035–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.T.; Yu, S.H.; Pan, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J. Flexible Wurtzite-Type ZnS Nanobelts with Quantum-Size Effects: A Diethylenetriamine-Assisted Solvothermal Approach. Small 2005, 1, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Zhu, K.; Peterson, G.; Zhang, Z.; Jian, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, D. Phase controlled synthesis and cathodoluminescence properties of ZnS nanobelts synthesized by PVD. Solid State Commun. 2018, 269, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhu, S.; Vijayan, C. Observation of red emission in wurtzite ZnS nanoparticles and the investigation of phonon modes by Raman spectroscopy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Δt (ps) | Thickness (nm) |
|---|---|
| 10 | 66 ± 8 |
| 100 | 57 ± 7 |
| 300 | 43 ± 9 |
| SP | 8 ± 2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopez-Quintas, I.; Rebollar, E.; Ávila-Brande, D.; Izquierdo, J.G.; Bañares, L.; Díaz-Guerra, C.; Urbieta, A.; Castillejo, M.; Nalda, R.d.; Martín, M. Femtosecond Double-Pulse Laser Ablation and Deposition of Co-Doped ZnS Thin Films. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112229
Lopez-Quintas I, Rebollar E, Ávila-Brande D, Izquierdo JG, Bañares L, Díaz-Guerra C, Urbieta A, Castillejo M, Nalda Rd, Martín M. Femtosecond Double-Pulse Laser Ablation and Deposition of Co-Doped ZnS Thin Films. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopez-Quintas, Ignacio, Esther Rebollar, David Ávila-Brande, Jesús G. Izquierdo, Luis Bañares, Carlos Díaz-Guerra, Ana Urbieta, Marta Castillejo, Rebeca de Nalda, and Margarita Martín. 2020. "Femtosecond Double-Pulse Laser Ablation and Deposition of Co-Doped ZnS Thin Films" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112229
APA StyleLopez-Quintas, I., Rebollar, E., Ávila-Brande, D., Izquierdo, J. G., Bañares, L., Díaz-Guerra, C., Urbieta, A., Castillejo, M., Nalda, R. d., & Martín, M. (2020). Femtosecond Double-Pulse Laser Ablation and Deposition of Co-Doped ZnS Thin Films. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112229