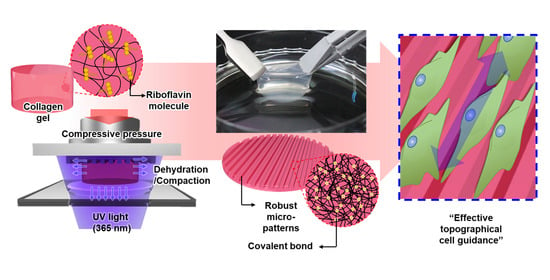
Robust Topographical Micro-Patterning of Nanofibrillar Collagen Gel by In Situ Photochemical Crosslinking-Assisted Collagen Embossing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Micro-Patterned PDMS Master Mold
2.2. Description of the IPC-CE Process
2.3. Parametric Effects of the IPC-CE Process
2.4. Nanofibrillar Architecture of the IPC-CE Construct
2.5. Structural Robustness and Topographical Effect of Micro-Patterns in an in Vitro Cell Culture
3. Results
3.1. Fabrication of the IPC-CE Construct
3.2. Effects of the Processing Parameters in the IPC-CE Process
3.3. Nanofibrillar Architecture of the IPC-CE Construct
3.4. Structural Robustness and Topographical Effect of the IPC-CE Construct in an in Vitro Cell Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, G.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, M.; Jin, G.; Lu, T.J.; Genin, G.M.; Xu, F. Functional and Biomimetic Materials for Engineering of the Three-Dimensional Cell Microenvironment. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12764–12850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Elkhooly, T.A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Shen, Z.; Feng, Q. Effects of hierarchical micro/nano-topographies on the morphology, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 145, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, J.A.; Purslow, P.P. Functional morphology of the endomysium in series fibered muscles. J. Morphol. 1992, 212, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieve, K.; Ghoubay, D.; Georgeon, C.; Thouvenin, O.; Bouheraoua, N.; Paques, M.; Borderie, V.M. Three-dimensional structure of the mammalian limbal stem cell niche. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 140, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cun, X.; Hosta-Rigau, L. Topography: A Biophysical Approach to Direct the Fate of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Tissue Engineering Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Sathe, S.R.; Yim, E.K. From nano to micro: Topographical scale and its impact on cell adhesion, morphology and contact guidance. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2016, 28, 183001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, M.; Wybieralska, E.; Miekus, K.; Drukala, J.; Madeja, Z. Topographical control of prostate cancer cell migration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2009, 2, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Leow, W.R.; Amini, S.; Nai, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Cai, P.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.L.; Miserez, A.; et al. Orientational Coupling Locally Orchestrates a Cell Migration Pattern for Re-Epithelialization. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, M.P.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Cleymand, F.; Mano, J.F. Surface Micro- and Nanoengineering: Applications of Layer-by-Layer Technology as a Versatile Tool to Control Cellular Behavior. Small 2019, 15, 1901228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, R.B.; Gooden, M.D.; Lara, S.L.; Wight, T.N. Microgrooved fibrillar collagen membranes as scaffolds for cell support and alignment. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3131–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijdener, H.; Konrad, J.; Hoffmann, B.; Gerardo-Nava, J.; Rutten, S.; Merkel, R.; Vazquez-Jimenez, J.; Brook, G.A.; Jockenhoevel, S.; Mela, P. A bench-top molding method for the production of cell-laden fibrin micro-fibers with longitudinal topography. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2020, 108, 1198–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, E.; Choi, Y.Y.; Chae, S.K.; Moon, J.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Microfluidic spinning of flat alginate fibers with grooves for cell-aligning scaffolds. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4271–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Chen, W.S.; Wang, Y.K.; Yeh, J.A.; Cheng, C.M. Probing neural cell behaviors through micro-/nano-patterned chitosan substrates. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copes, F.; Pien, N.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Boccafoschi, F.; Mantovani, D. Collagen-Based Tissue Engineering Strategies for Vascular Medicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clement, A.L.; Moutinho, T.J., Jr.; Pins, G.D. Micropatterned dermal-epidermal regeneration matrices create functional niches that enhance epidermal morphogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9474–9484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janakiraman, V.; Kienitz, B.L.; Baskaran, H. Lithography Technique for Topographical Micropatterning of Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Membranes for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Med. Device 2007, 1, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alekseeva, T.; Hadjipanayi, E.; Abou Neel, E.A.; Brown, R.A. Engineering stable topography in dense bio-mimetic 3D collagen scaffolds. Eur. Cell. Mater 2012, 23, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, G. Skeletal myotube formation enhanced through fibrillated collagen nanofibers coated on a 3D-printed polycaprolactone surface. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 181, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.S.; Alekseeva, T.; Brown, R.A. Roofed grooves: Rapid layer engineering of perfusion channels in collagen tissue models. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 29, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levis, H.J.; Massie, I.; Dziasko, M.A.; Kaasi, A.; Daniels, J.T. Rapid tissue engineering of biomimetic human corneal limbal crypts with 3D niche architecture. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8860–8868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, L.T.; Holbrook, K.A.; Byers, P.H. Structure of the dermal matrix during development and in the adult. J. Investig Dermatol. 1982, 79, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, S.; Osawa, T.; Tohyama, K. Comparative observations on corneas, with special reference to Bowman′s layer and Descemet′s membrane in mammals and amphibians. J. Morphol. 2002, 254, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Park, S.J.; Han, S.J.; Lim, J.; Kim, D.S. Aquatic flower-inspired cell culture platform with simplified medium exchange process for facilitating cell-surface interaction studies. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, M.; Lee, J.G.; Park, S.J. Numerical and experimental investigation of plastic injection molding of micro-engineered surfaces. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatemadi, A.; Daraee, H.; Zarghami, N.; Melat Yar, H.; Akbarzadeh, A. Nanofiber: Synthesis and biomedical applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, Y.; Heim, T.; Douillard, R. AC electric field-assisted assembly and alignment of cellulose nanocrystals. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bai, S.M.; Ding, Z.Z.; Guo, H.; Shao, Z.Z.; Zhu, H.S.; Kaplan, D.L. Hydrogel Assembly with Hierarchical Alignment by Balancing Electrostatic Forces. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1500687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalymov, A.A.; Van der Meeren, L.; Van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K.; Skirtach, A.G.; Parakhonskiy, B.V. Meshes-to-Fibrils Transition of Gellan Gum Hydrogel Architecture by Thermal Annealing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, M.S.; Jiao, A.; Kim, D.H.; Suh, K.Y. Patterning methods for polymers in cell and tissue engineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 1339–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.A.; Wiseman, M.; Chuo, C.B.; Cheema, U.; Nazhat, S.N. Ultrarapid engineering of biomimetic materials and tissues: Fabrication of nano- and microstructures by plastic compression. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Kim, J.; Cho, H.; Park, S.M.; Jeon, M.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, D.S. Ultra-stiff compressed collagen for corneal perforation patch graft realized by in situ photochemical crosslinking. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 045030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Han, K.; Gupta, K.; Kwon, K.W.; Suh, K.Y.; Levchenko, A. Mechanosensitivity of fibroblast cell shape and movement to anisotropic substratum topography gradients. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, C.; Xie, A.W.; Yamato, M.; Okano, T.; Wong, J.Y. Stacking of aligned cell sheets for layer-by-layer control of complex tissue structure. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5625–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, E.; Orkwis, J.A.; Weaver, R.; Conlin, L.; Madigan, N.N.; Harris, G.M. Micropatterning Decellularized ECM as a Bioactive Surface to Guide Cell Alignment, Proliferation, and Migration. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Gu, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Hierarchical Micro/Nanofibrous Bioscaffolds for Structural Tissue Regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Hong, H.; Park, S.M.; Kim, D.S. Metal-Electrolyte Solution Dual-Mode Electrospinning Process for In Situ Fabrication of Electrospun Bilayer Membrane. Adv. Mater Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Choi, A.; Kim, H.W.; Yoon, H.; Park, S.M.; Tsai, C.D.; Kaneko, M.; Kim, D.S. Constrained Adherable Area of Nanotopographic Surfaces Promotes Cell Migration through the Regulation of Focal Adhesion via Focal Adhesion Kinase/Rac1 Activation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14331–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventre, M.; Natale, C.F.; Rianna, C.; Netti, P.A. Topographic cell instructive patterns to control cell adhesion, polarization and migration. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, H.; Kim, D.S. Robust Topographical Micro-Patterning of Nanofibrillar Collagen Gel by In Situ Photochemical Crosslinking-Assisted Collagen Embossing. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122574
Hong H, Kim DS. Robust Topographical Micro-Patterning of Nanofibrillar Collagen Gel by In Situ Photochemical Crosslinking-Assisted Collagen Embossing. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122574
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Hyeonjun, and Dong Sung Kim. 2020. "Robust Topographical Micro-Patterning of Nanofibrillar Collagen Gel by In Situ Photochemical Crosslinking-Assisted Collagen Embossing" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122574
APA StyleHong, H., & Kim, D. S. (2020). Robust Topographical Micro-Patterning of Nanofibrillar Collagen Gel by In Situ Photochemical Crosslinking-Assisted Collagen Embossing. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122574